Lecture 13-19: Viruses
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Double stranded DNA genome
1.Papovaviridae
2.Adenoviridae
3.Herpesviridae
4.Poxviridae
Papovaviridae
-Icosahedral capsid
-45-55nm
-No envelope
Cause:
-Tumours in rodents - polyomavirus +simian virus
-Human and animal warts-Papillomavirus
-Cervical carcinoma -Papillomavirus

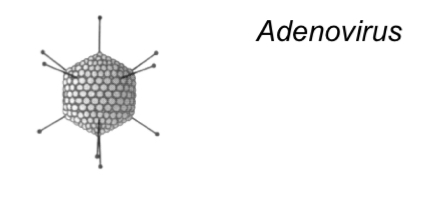
Adenoviridae
-Icosahedral capsid
-80nm
-No envelope
Cause:
-Acute respiratory disease
Herpesviridae
-Icosahedral capsid
-120nm
-Envelope
Cause:
-Cold sores (type 1 HSV)
-Genital herpes (type 2 HSV)
-Chicken pox and shingles (VZV)
-Glandular fever + burkitt lymphoma (EBV)
-Cytomegalic inclusion disease in neonates (HCMV)
-Kaposi’s sarcome (Human herpes 8)
-Lymphoma in chickens (Mareks disease virus)
-Aujesky’s disease of pigs (pseudorabies virus)
-Abortion (Equine herpes virus)

HSV epidemiology
Ubiquitous. Two types: HSV1 (oral) and HSV2 (genital). Establishes lifelong latency in sensory neurons.
HSV clinical
Oral/Genital blisters/ulcers, encephalitis (rare but severe), neonatal infection.
HSV transmission + prevention and control
Direct contact with lesions or mucosal surfaces.
Antivirals (Acyclovir) for outbreaks, barrier protection, no vaccine.
Chicken pox epidemiology
VZV (Varicella-Zoster Virus)
Ubiquitous. Establishes lifelong latency in sensory ganglia
Chicken pox clinical
Primary Infection (Chickenpox): Fever, itchy vesicular rash. Reactivation (Shingles/Zoster): Painful, unilateral rash following a dermatome.
Chicken pox transmission+ prevention and control
Airborne (respiratory droplets) and direct contact with blister fluid.
Vaccination (Varicella and Zoster vaccines), antivirals (Acyclovir).
EBV epidemiology
Ubiquitous; over 90% of adults are infected. Establishes latency in B cells.
EBV clinical
Primary Infection: Usually asymptomatic or Infectious Mononucleosis (fever, fatigue, sore throat, lymphadenopathy). Associated with Burkitt's lymphoma and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.
EBV transmission + prevention and control
Saliva ("kissing disease").
No vaccine, hygiene, management of symptoms.
CMV epidemiology
Highly ubiquitous; most infections are asymptomatic. Establishes latency.
CMV clinical
Immunocompetent: Asymptomatic or mild mono-like illness. Immunocompromised/Congenital: Severe end-organ disease (retinitis, pneumonitis, brain damage).
CMV transmission+ prevention and control
Direct contact with body fluids (saliva, urine, blood, breast milk, sexual contact).
Antivirals (Ganciclovir), screening of blood and organ donors.
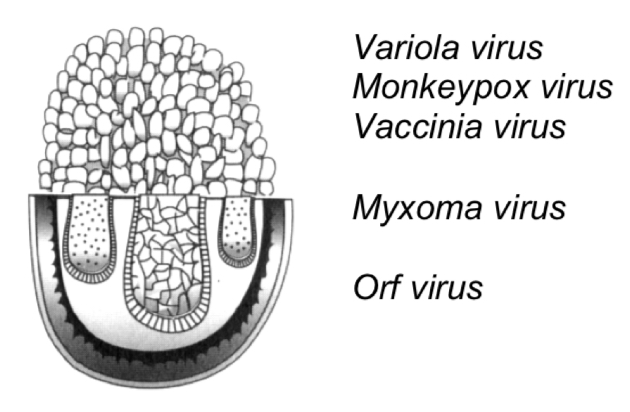
Poxviridae
-Complex capsid
-200×350nm
-Envelope
-Virion transcriptase
-Small pox (variola virus)
-Monkey pox (monkeypox)
-Vaccine against small pox (vaccinia virus)
-Myxomatosis in rabbits (myxoma virus)
-Contagious pustular dermatitis in sheep and goats (Orf virus)
Single stranded DNA genome
1.Parvovirus
Parvovirus
-Icosahedral virion
-20nm
-No envelope
Cause:
-Cat fever, enteritis (feline panleucopenia virus)

Human parvovirus epidemiology
Global, highly contagious respiratory transmission.
Human parvovirus clinical
"Fifth Disease" (Erythema Infectiosum): Mild flu-like illness followed by a characteristic "slapped cheek" rash. Can cause severe anemia in fetuses and immunocompromised patients.
Human parvovirus transmission + treatment and control
Respiratory droplets.
Hygiene, symptomatic care.
Double stranded RNA genome
1.Reoviridae
Reoviridae
-Icosahedral virion
-60-80nm
-No envelope
-10-11 RNA segments
-Virion transcriptase
-Catarrhal fever of sheep (blue tongue virus)
-Acute infantile gastroenteritis (human and animal rotavirus)

Rotavirus epidemiology
Global, major cause of severe, dehydrating diarrhea in infants and young children.
Rotavirus clinical
Severe watery diarrhea, vomiting, fever, often leading to life-threatening dehydration in infants.
Rotavirus transmission+ prevention and control
Fecal-oral route.
Vaccination (oral vaccine), sanitation, fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy.
Positive single stranded RNA genome
1.Picornaviridae
2.Caliciviridae
3.Togaviridae + flaviviridae
4.Coronoviridae
Picornaviridae
-Icosahedral
-20-30nm
-No envelope
Cause:
-Poliomyelitis (poliovirus)
-Acute hepatitis (hepatitis A virus)
-Common cold (rhinovirus)
-Foot and mouth disease (FMDV)

Polio epidemiology
Historically global, now near-eradicated due to vaccination efforts (endemic only in a few countries).
Polio transmission + prevention and control
Fecal-oral route.
Vaccination IPV - inactivated; OPV - oral, sanitation
Polio clinical features
95% asymptomatic.
4-5% minor illness.
<1% develop paralytic poliomyelitis (flaccid paralysis).
FMD epidemiology
Affects cloven-hoofed animals (cattle, pigs, sheep). Highly contagious. Major economic impact globally.
FMD clinical
High fever, painful blisters (vesicles) on tongue, lips, mouth, and feet. Causes lameness and weight loss.
FMD transmission + prevention and control
Aerosols, direct contact, contaminated objects/vehicles, and human clothing.
Vaccination (in endemic areas), quarantine, culling of infected herds (in non-endemic areas).
Hepatitis A epidemiology
Global, endemic in areas with poor sanitation. Fecal-oral transmission.
Hepatitis A clinical
Acute, self-limiting hepatitis: fever, fatigue, jaundice, loss of appetite. Does not cause chronic disease.
Hepaititis A transmission+ prevention and control
Fecal-oral route (contaminated food/water or person-to-person).
Vaccination, sanitation, hand hygiene.
Caliciviridae
-Icosahedral capsid
-30-40nm
-No envelope
Cause:
-Winter vomiting disease (norovirus)
-Respiratory disease (feline calicivirus)

Togaviridae + flaviviridae
-Icosahedral capsid
-40-80nm
-Envelope
Cause:
-Congenital abnormality (rubella virus)
-Acute and chronic hepatitis (hepatitis C virus)
-Yellow fever (yellow fever)
-Dengue hemorrhagic fever (dengue virus)
-Microcephaly (Zika virus)

Measles epidemiology
Highly contagious, vaccine-preventable. Major cause of child mortality globally where vaccination coverage is low.
Measles cllinical
High fever, cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis, Koplik spots (inside mouth), maculopapular rash. Can cause Pneumonia or SSPE (rare late complication).
Measles transmission+ prevention and control
Airborne/Respiratory droplets.
Vaccination (MMR) isolation.
Hepatitis C epidemiology
Global, major cause of chronic liver disease. Often asymptomatic for decades.
Hepatitis C clinical
Acute: Usually asymptomatic. Chronic: Progressive liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and HCC.
Hepatitis C transmission + prevention and control
Bloodborne: Contaminated needles (IV drug use), blood transfusions (historically).
Blood screening, harm reduction (clean needles), Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAAs) for cure, no vaccine.
Coronoviridae
-Helical nucleocaspid
-120-160nm
-Envelope
Cause:
-Avian bronchitis (infectious bronchitis virus)
-Severe acute respiratory syndrome + COVID-19 (SARS-coronavirus-2)

COVID-19 epidemiology
Global pandemic (2019 onward). Highly transmissible respiratory virus.
COVID-19 clinical
Cough, fever, fatigue, loss of taste/smell, respiratory distress, multi-organ failure.
COVID-19 transmission+ prevention and control
Respiratory droplets (aerosols), close contact.
Vaccination, social distancing, masks, antivirals (Paxlovid).
Negative single stranded RNA genome
1.Orthomyxoviridae
2.Paramyxoviridae
3.Rhabdoviridae
4.Filoviridae
Orthomyxoviridae
-Helical capsid and envelope
-~100nm
-Genome has 8 fragments
-Virion transcriptase
Influenza A virus causes:
-Influenza epidemics and pandemics in man
-Avian influenza
-Equine influenza

Influenza epidemiology
Global, seasonal epidemics; occasional pandemics (e.g., H1N1). High mutation rate (antigenic drift/shift).
Influenza clinical
Fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, headache. Can cause severe pneumonia, especially in the elderly/young.
Influenza transmission + prevention and control
Respiratory droplets (aerosols), direct contact.
Vaccination (seasonal), antiviral drugs (oseltamivir (tamiflu) - NA inhibitor), good hygiene.
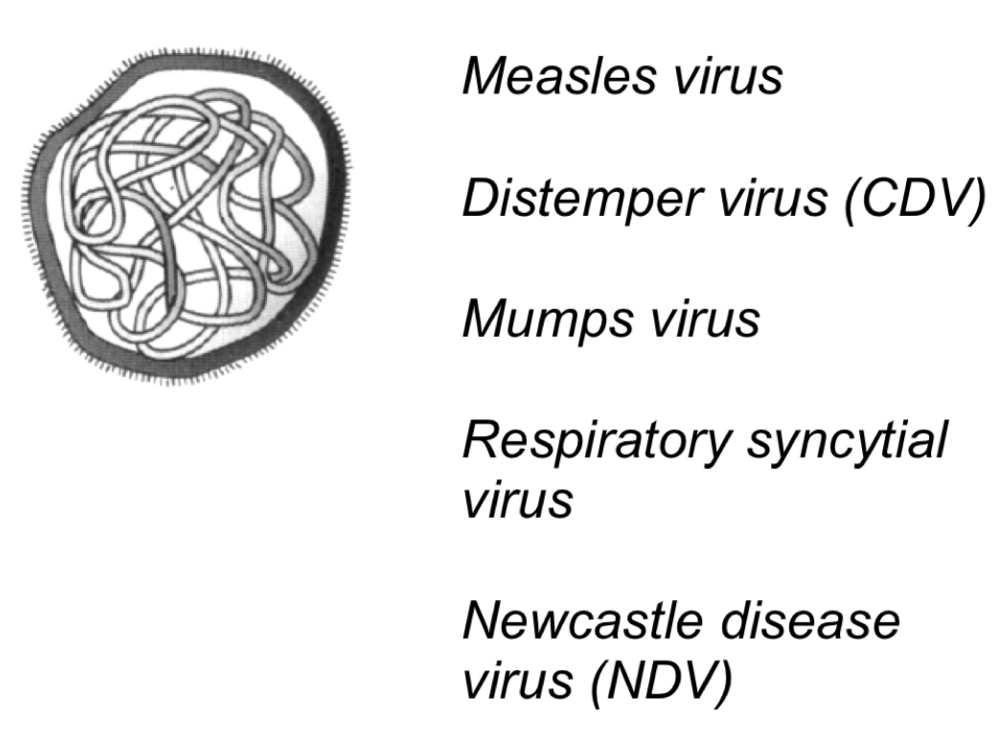
Paramyxoviridae
-Helical capsid
-Plemorphic 150nm
-Envelope
-Virion transcriptase
Cause:
-Measles (measles virus)
-Canine distemper (distemper virus-CDV)
-Mumps (Mumps virus)
-Bronchitis (respiratory syncytial virus)
-Fowl pest (newcastle disease virus)
Rhabdoviridae
-Helical capsid
-200×80nm
-Envelope
-Bullet shape
-Virion transcriptase
Cause:
-vesicular stomatitis in cattle + horses (Vesicular stomatitis virus)
-Rabies (rabies virus)

rabies epidemiology
Worldwide, primarily in animals (dogs, bats, raccoons, skunks).
Rabies clinical
Initially flu-like. Progresses to encephalitis, hydrophobia, paralysis, and near-100% fatality once symptoms appear.
Rabies transmission + prevention and control
Bite of an infected animal (virus in saliva).
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), animal vaccination (domestic/wildlife), pre-exposure prophylaxis for high-risk workers.
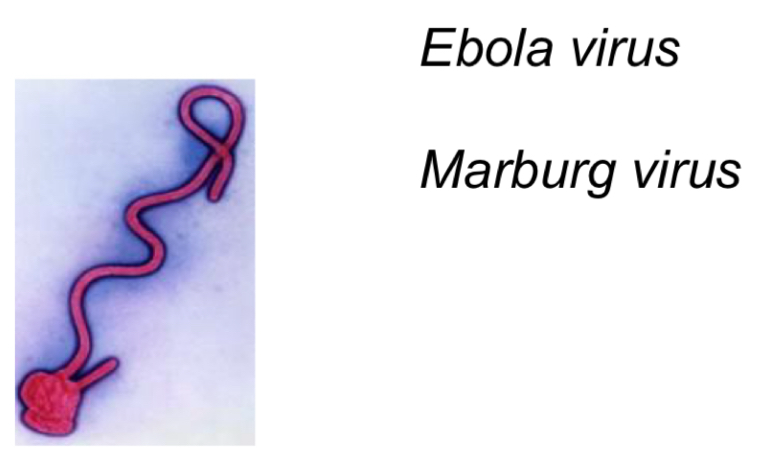
Filoviridae
-Helical capsid
-Envelope
-Filamentous
-Up to 1000nm length
-Virion transcriptase
Cause:
-Ebola hemorrhagic fever (ebola virus)
Ebola epidemiology
Ebola is a zoonotic disease that is believed to have originated from fruit bats. The first outbreaks in humans occurred in 1976 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (then Zaire) and Sudan.
Current evidence strongly implicates several species of African fruit bats as the source of origin for EBV as bats can carry the virus without becoming ill which allows the virus to persist within their populations.
The virus is introduced into the human population through a "spillover event," which involves close contact with the blood, secretions, organs, or other bodily fluids of an infected animal.
Ebola structure
-filamentous long,thin and flexible structure with a highly variable length
It’s genome is a single molecule of linear negative sense ssRNA
It also has a nucleocapsid where the genomic RNA is tightly wrapped around the central core structure and is composed of several structural proteins like:
-Nucleoprotein (NP): The major protein that encapsulates the RNA, forming the helical structure.
-L Protein (RNA Polymerase): The critical viral enzyme that drives replication and transcription.
-VP35 and VP30: Proteins that function as cofactors for the polymerase and help regulate transcription.
Matrix that surrounds the nucleocapsid to provide structural integrity and links core to outer envelope. Primary protein is VP40 which is essential for driving the assembly and budding of new viral particles from the host cell membrane.
Envelope which is a lipid bilayer that it acquires from the host cell's plasma membrane during budding and has glycoprotein spikes in this envelope which are trimeric structures critical for infection via mediating fusion and entry.
Ebola replication
1. The virus attaches to the host cell, primarily macrophages, dendritic cells, and endothelial cells, via its Glycoprotein (GP).The GP binds to various receptors as it is a non-specific receptor that targets the glycans on receptors for virus to enter early endosome then most notably the intracellular receptor Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) found in lysosome and endosomes after endocytosis binds to the altered glycoprotein having been processed from macropinocytosis and the viral envelope fuses with the endosomal membrane to release the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm.
2. The negative-sense single-stranded genomic RNA (gRNA) is never released from its protective nucleocapsid core. The viral enzyme, RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (L protein), is packaged within the virion, and immediately begins transcribing the genomic RNA into individual positive-sense messenger RNAs (mRNAs). These mRNAs are then translated by the host cell's ribosomes to produce the initial batch of viral proteins (structural proteins, enzymes, and regulatory proteins).
3. Replication Switch (Template Synthesis): Once enough viral proteins are produced, particularly the L protein and the nucleoprotein (NP), the L protein switches its function: to ignore the gene start and stop signals and synthesizes a full-length, positive-sense antigenome from the negative-sense gRNA template.
4. The positive-sense antigenome then serves as the template for synthesizing hundreds of copies of the new negative-sense genomic RNA (gRNA) and this is a tightly regulated process and results in a rapid exponential increase in the viral genome.
5. The newly synthesized genomic RNA is immediately packaged by the newly synthesized nucleoprotein (NP), along with the VP30 and VP35 proteins, to form new nucleocapsids.
6. The new nucleocapsids migrate toward the cell membrane and other viral matrix proteins like VP20 line the inner surface of the plasma membrane, driving the final assembly process.The viral envelope glycoprotein GP is inserted into the host cell's plasma membrane, marking the site for the virion to exit.
7. The newly assembled nucleocapsid is guided to the membrane patch containing the GP. The viral VP40 protein mediates the final step, driving the membrane to curve outward and buds off from the host cell.
Ebola transmission
-Fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family are natural hosts of the Orthoebolavirus
-close contact with blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected animals such as fruit bats, chimpanzees, gorillas, monkeys, forest antelope or porcupines found ill or dead or in the rainforest.
-Direct contact with infected individuals via broken skin/mucous membranes or contaminated objects/surfaces with bodily fluids of infected individual
-Disease not transmitted unless symptoms are expressed and remain infectious as long as blood contains virus.
-Burial ceremonies that involve direct contact with the body of a person who has died.
Ebola clinical features
-Initially fever,fatigue,malaise,muscle pain,headache + sore throat
-Then vomiting,diarrhoea,abdominal pain rash,impaired kidney and liver functions
-Internal or external bleeding is less frequent and occurs later in the disease:blood in vomit and faeces, bleeding from the nose, gums and vagina, at sites where needles have punctured skin.
-Impacts CNS: confusion,irritability and aggression.
Ebola prevention and control
-Raising awareness of risk factors and how virus is transmitted
-Reduce contact between humans and infected wildlife or infected humans via isolation
-Safe and dignified burial of deceased + maintain good hygiene
-Early intensive supportive care with rehydration and the treatment of symptoms improves survival.
-Treatment with monoclonal antibodies mAb114 (ansuvimab) or REGN-EB3 (Inmazeb).
Positive single stranded RNA genome with DNA intermediate
1.Retroviridae
Retroviridae
-Capsid
-100nm
-Envelope
-Virion transcriptase
Cause:
-Scarcomas in fowl (RSV)
-Leukaemia in cats (feline leukaemia virus)
-Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV)

HIV epidemiology
Global pandemic. Highly prevalent in certain risk groups and geographic regions.
HIV clinical
Initially flu-like illness. Progresses to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) characterized by opportunistic infections and cancers.
HIV transmission+ prevention and control
Bloodborne: Sexual contact, contaminated needles, vertical transmission.
Antiretroviral Therapy (ART), PrEP/PEP, safe sex, blood screening.
Double stranded DNA genome with RNA intermediate
1.Hepadnaviridae
Hepadnaviridae
-Icosahedral capsid
-Envelope
-42nm
Hepatitis B virus causes:
-Acute and chronic hepatitis
-Liver cancer

Hepatitis B epidemiology
Global burden; highly endemic in Asia and Africa. Chronic infection is a major cause of liver cancer.
Hepatitis B clinical
Acute: Mild or asymptomatic.
Chronic: Liver inflammation, cirrhosis, Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC).
Hepatitis B transmission+ prevention and control
Bloodborne: Sexual contact, vertical transmission (mother-to-child), contaminated needles.
Vaccination (highly effective), blood screening, safe sex practices, antiviral drugs.