Organic Chemsitry Exam 1
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
2 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs
Linear
2 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
180
3 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs
Trigonal Planar
3 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
120
3 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs
Bent
3 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
<120
4 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs
Tetrahedral
4 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
109.5
4 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs
Trigonal Pyramid
4 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
<109.5 (~107)
4 Electron Groups 2 Lone Pairs
Bent
4 Electron Groups 2 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
<109.5 (~105)
5 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs
Trigonal bipyramidal
5 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
90, 120
5 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs
See-saw
5 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
<90, <120
5 Electron Groups 2 Lone Pairs
T-structure
5 Electron Groups 2 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
<90
5 Electron Groups 3 Lone Pairs
Linear
5 Electron Groups 3 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
180
6 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs
Octahedral
6 Electron Groups 0 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
90
6 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs
Square pyramidal
6 Electron Groups 1 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
90, <90
6 Electron Groups 2 Lone Pairs
Square planar
6 Electron Groups 2 Lone Pairs Bond Angle
90
Ionic Bonding
One Metal + Non-Metal
One would be an electron donor, while the other would be an electron acceptor
Covalent Bonding
Non-Metal + Non-Metal
Mutual sharing of an electron
Formal Charge Equation
# of Valence Electrons - # of non-bonded electrons - (# of bonded electrons/2)
Sigma
Head to head overlap
Pi
Lateral Overlap
Hybridization
Mixing of atomic orbitals
Hydrocarbons
Compounds containing C and H
Alkanes
Simplest hydrocarbon
Saturated Hydrocarbons
All single bonds and contains the max nuumber of hydrogens possible
Name: CH4
Methane
Name: C2H6
Ethane
Name: C3H8
Propane
Name: C4H10
Butane
Name: C5H12
Pentane
Name: C6H14
Hexane
Name: C7H16
Heptane
Name: C8H18
Octane
Name: C9H20
Nonane
Name: C10H22
Decane
Isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formula, but there is something different about them
Constitutional Isomer
Molecular Formula is the same, but different bonding pattern
Stereoisomer
Molecular Formula and bonding pattern same, arrangements of atoms in space is different
Name the 2 Stereoisomers
Cis-Trans and Optical
Naming Conventions of IUPAC Nomenclature
Number where substituent is attached - Identity of Substituent - Parent Carbon chain
Isopropyl Group
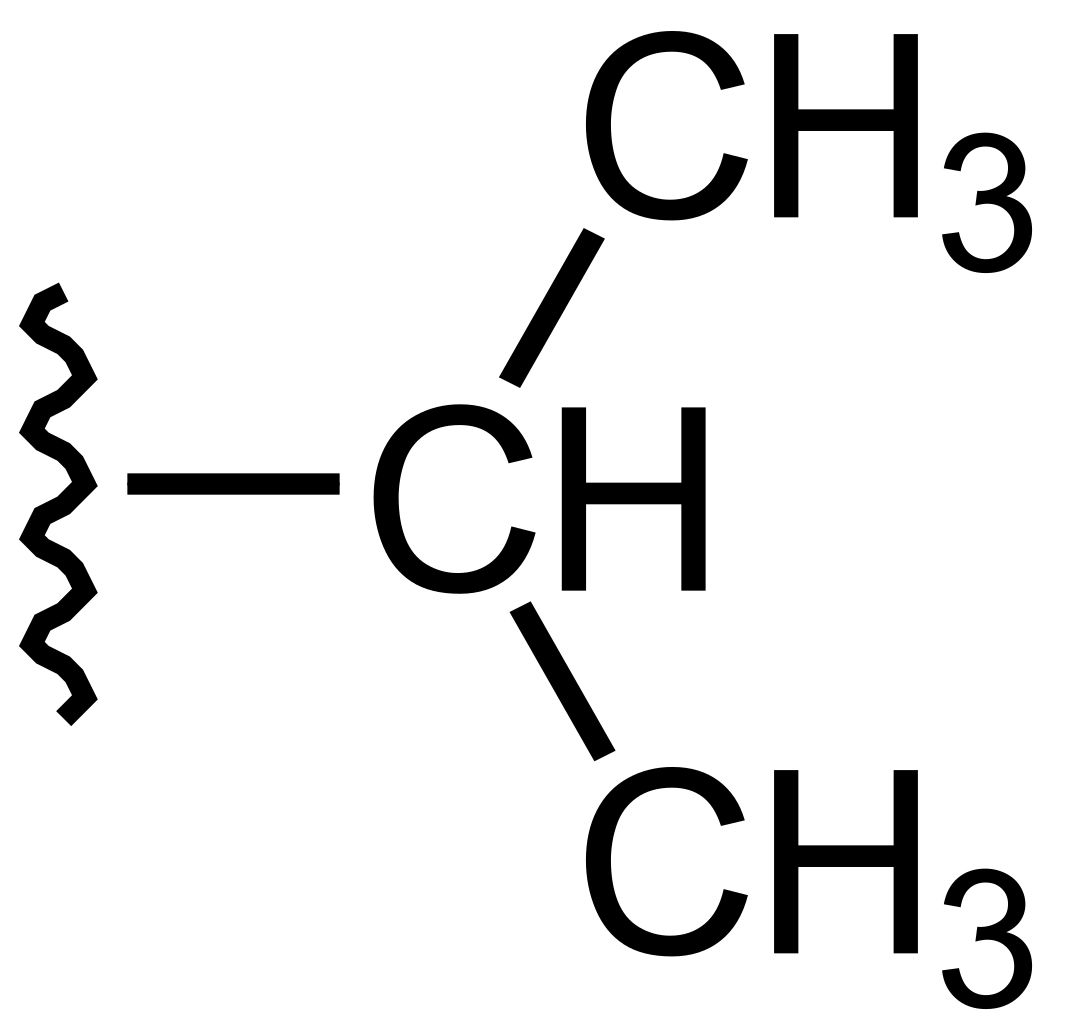
Secbutyl Group
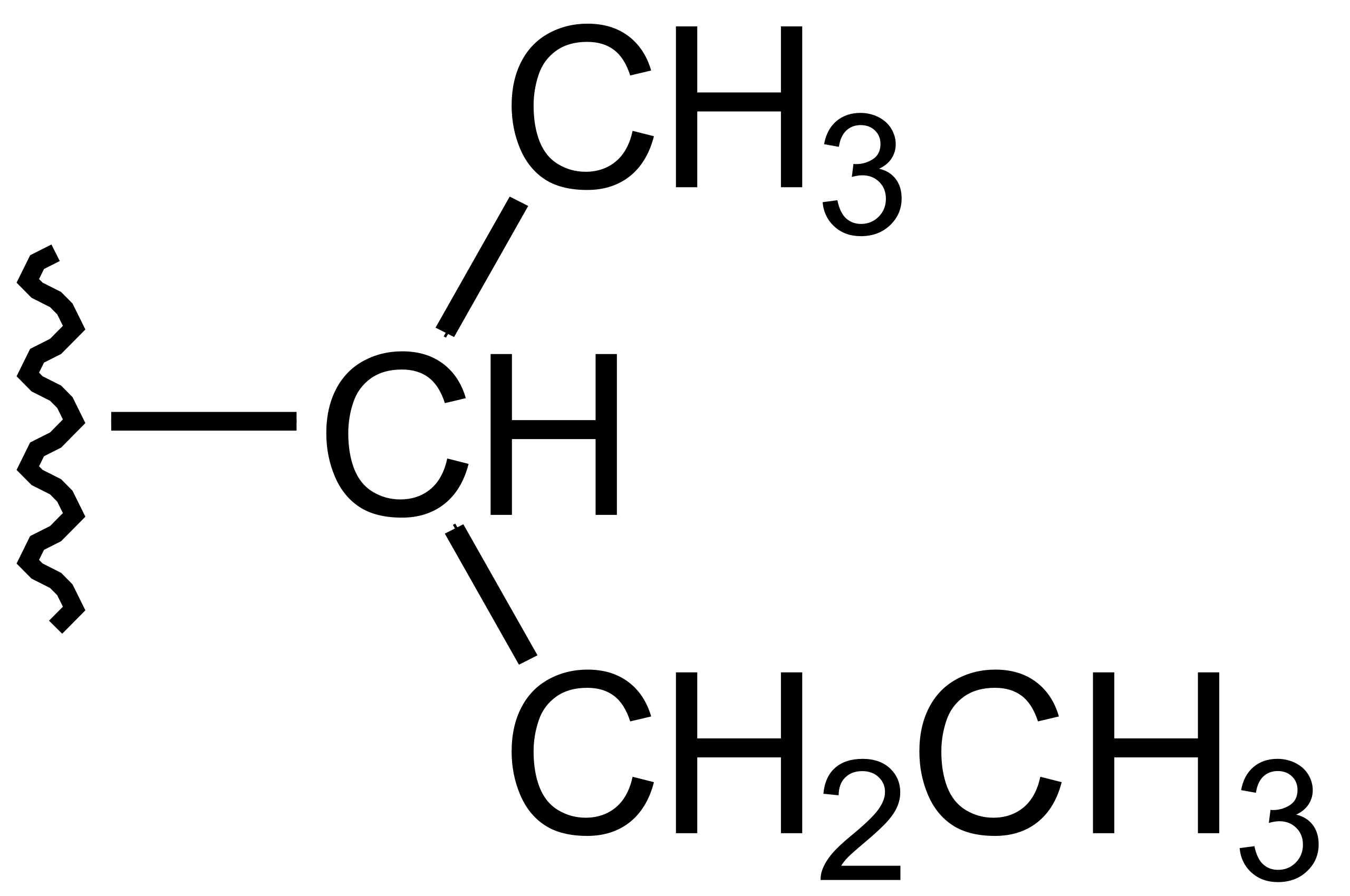
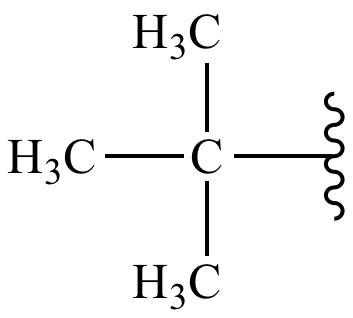
Tertbutyl Group
IHD Formula
((2C+2)-H+N/P-x)/2
Intermolecular Forces (Strongest to Weakest)
Ion-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Dispersion
Alkenes
Organic compounds with one or more C=C double bonds
Alkynes
Organic compounds that have one or more triple bonds
Alcohol Functional Group
R-OH
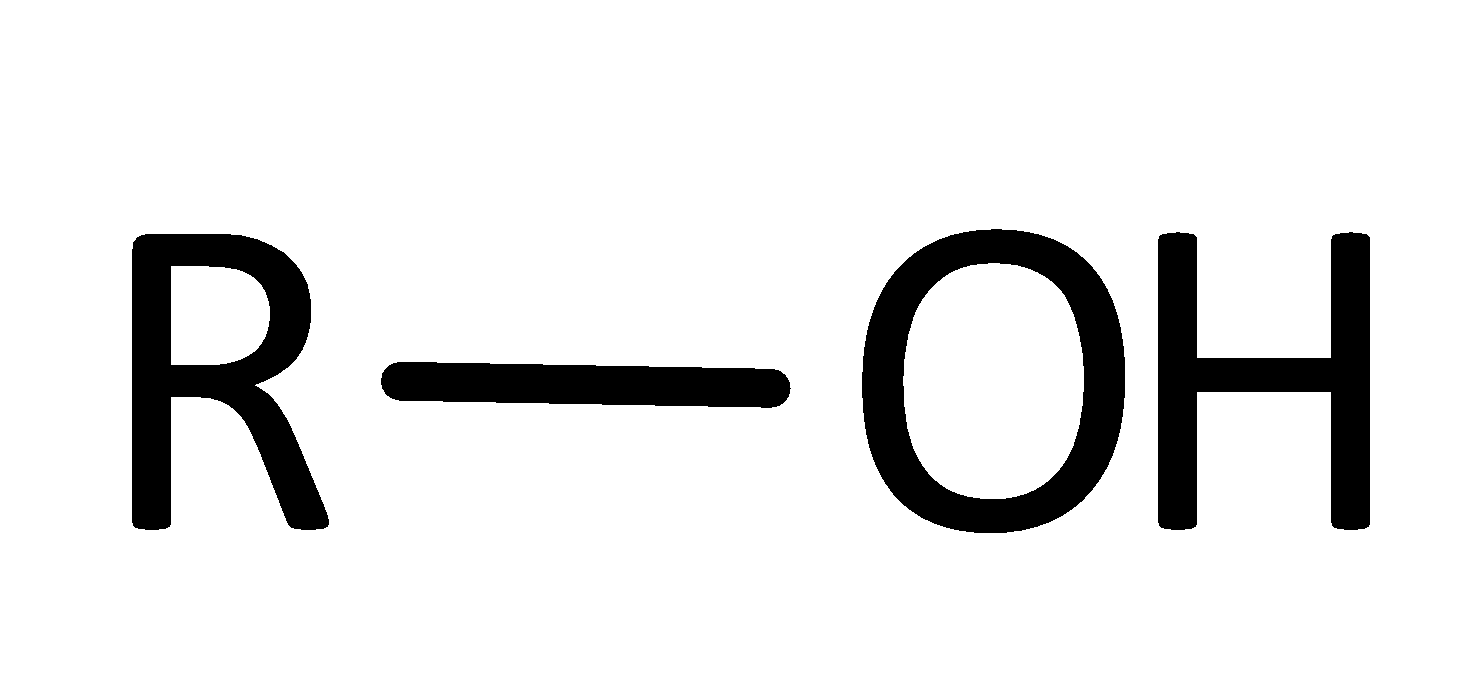
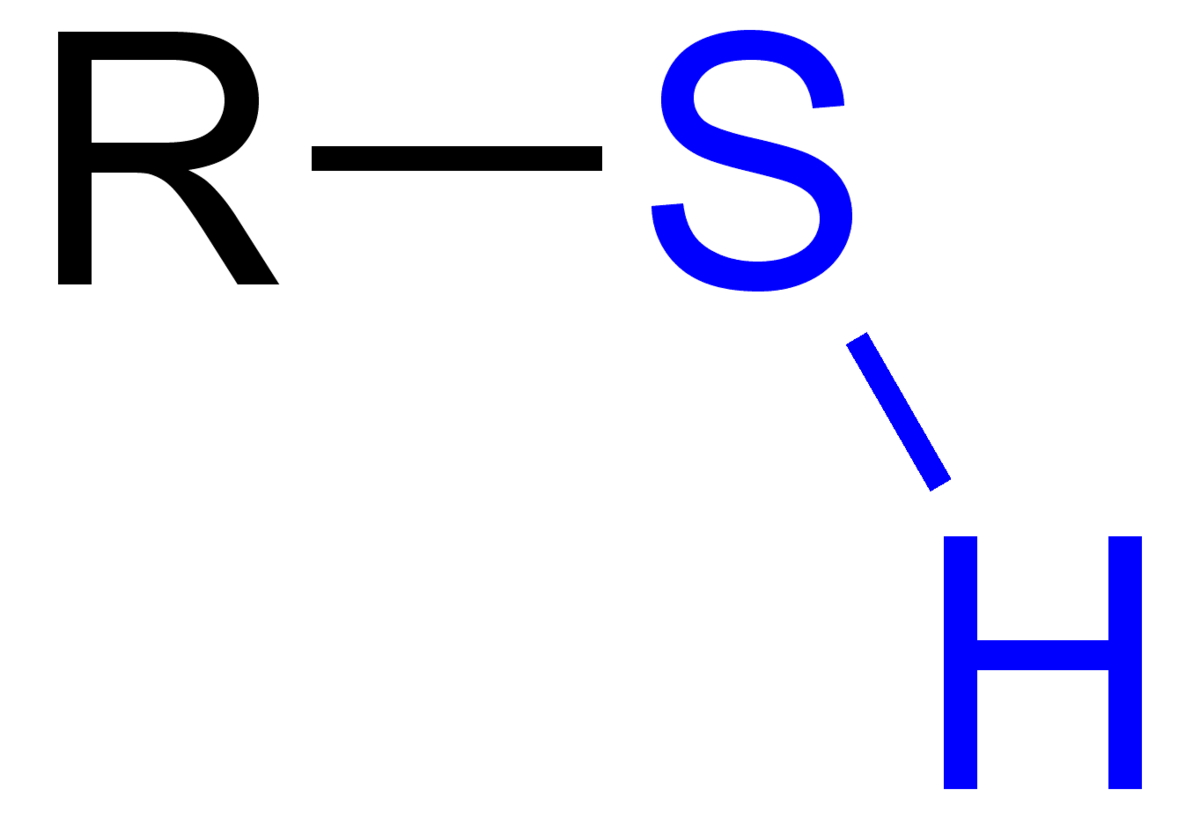
Thiol Functional Group
R-SH
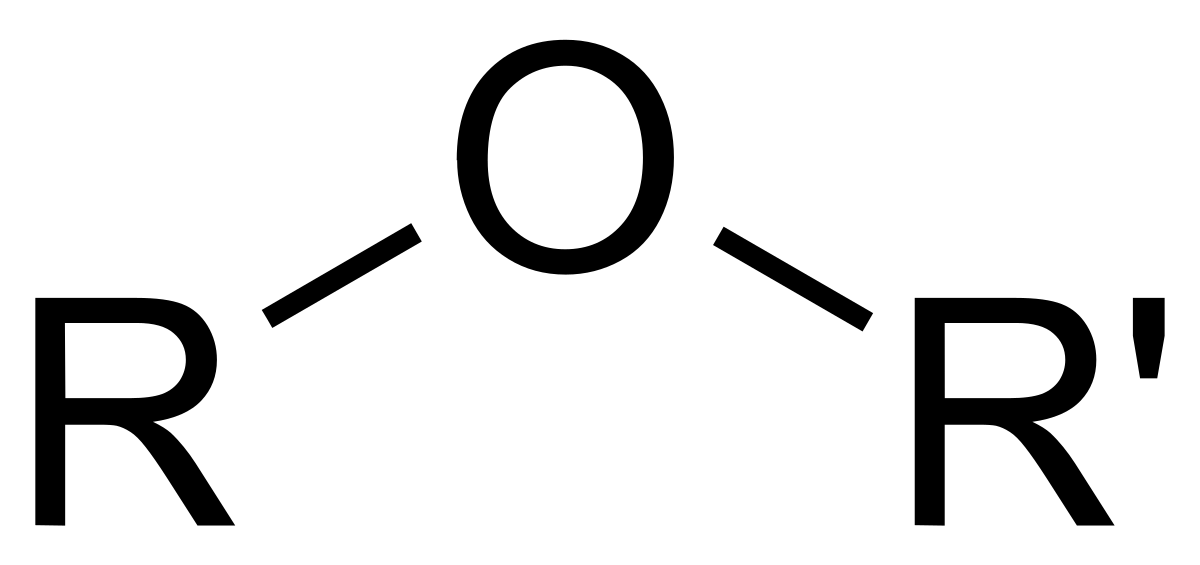
Ethers Functional Group
ROR’
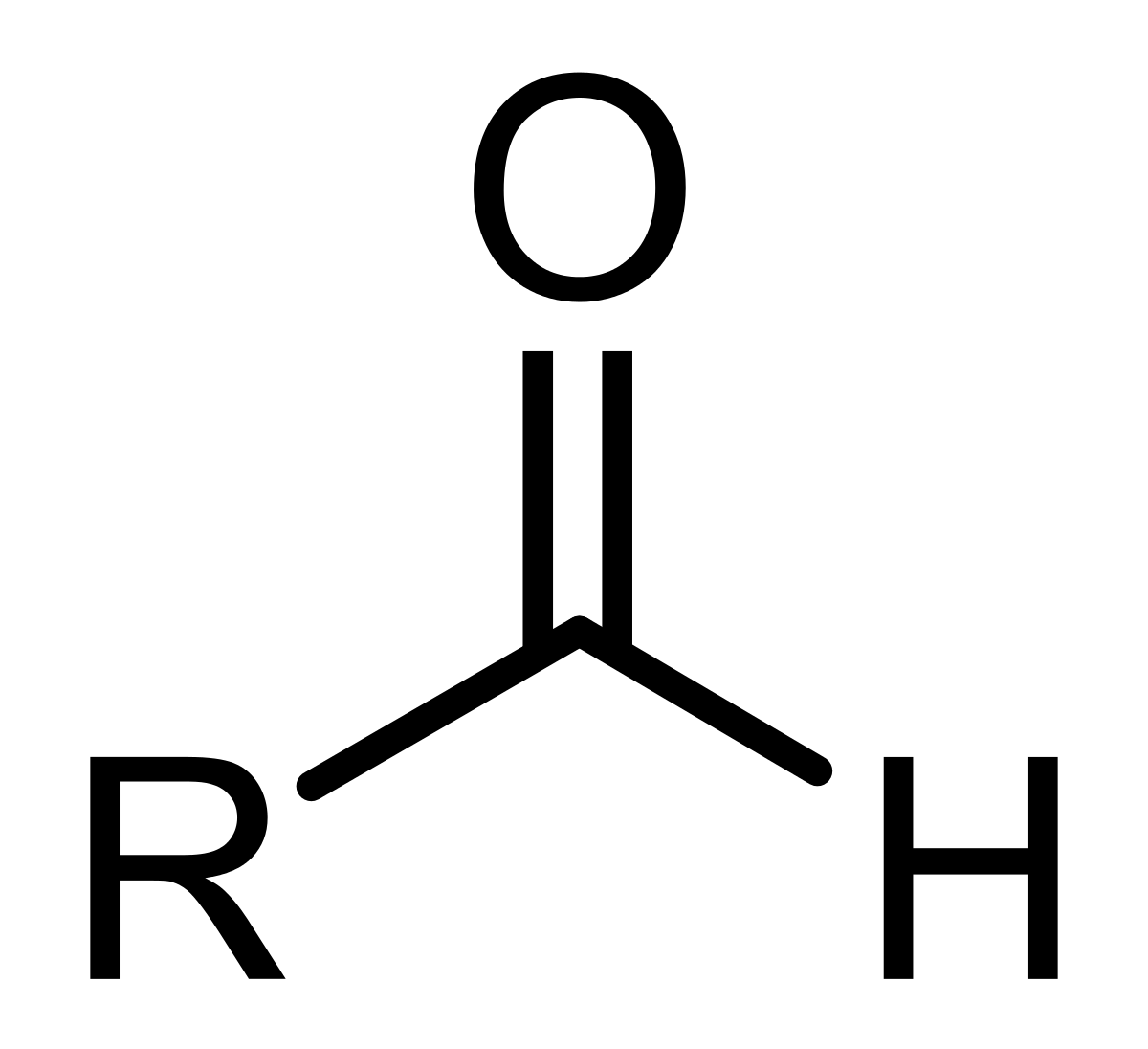
Aldehyde
RCHO; Carbonyl Functional Group
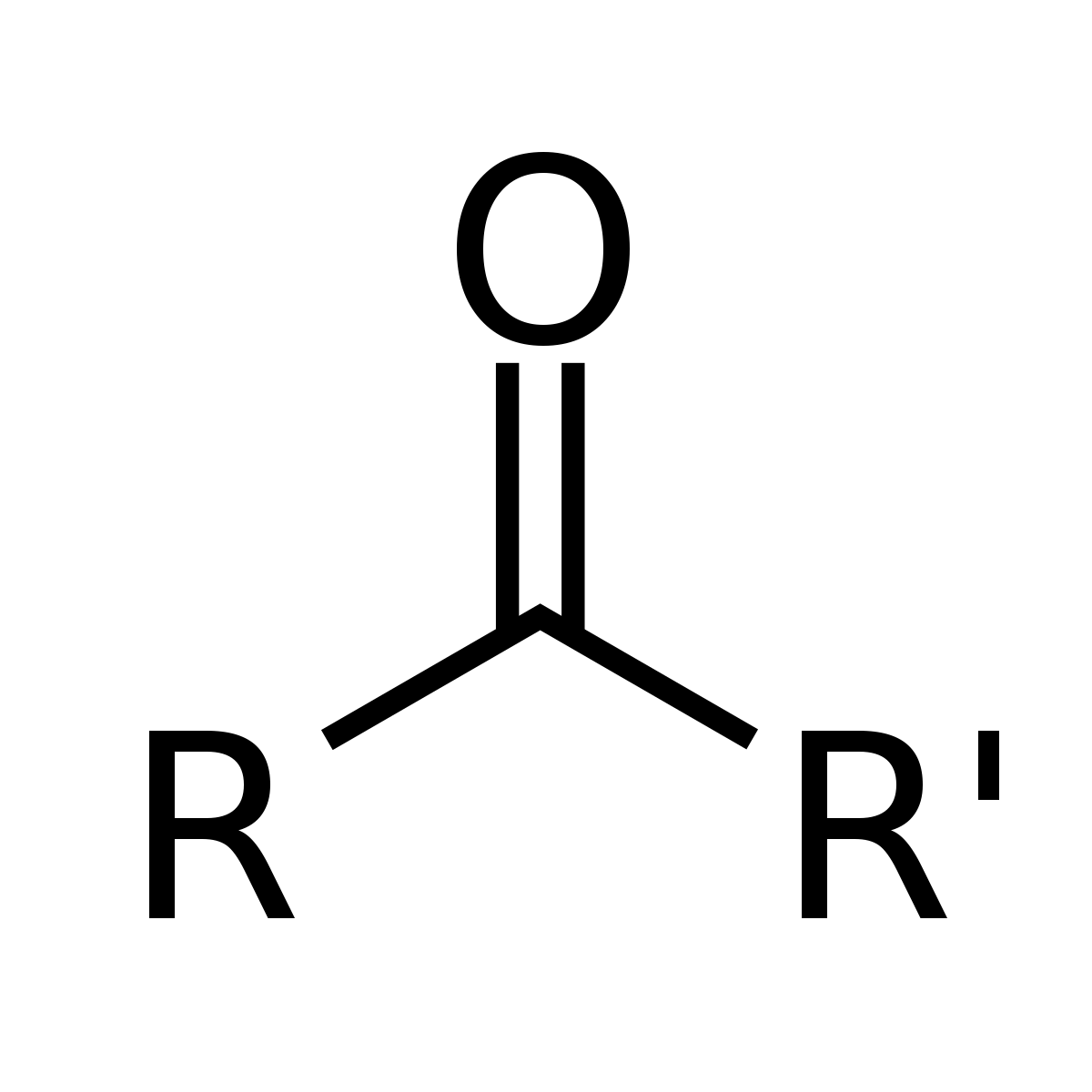
Ketones
R’COR; Carbonyl Functional Group
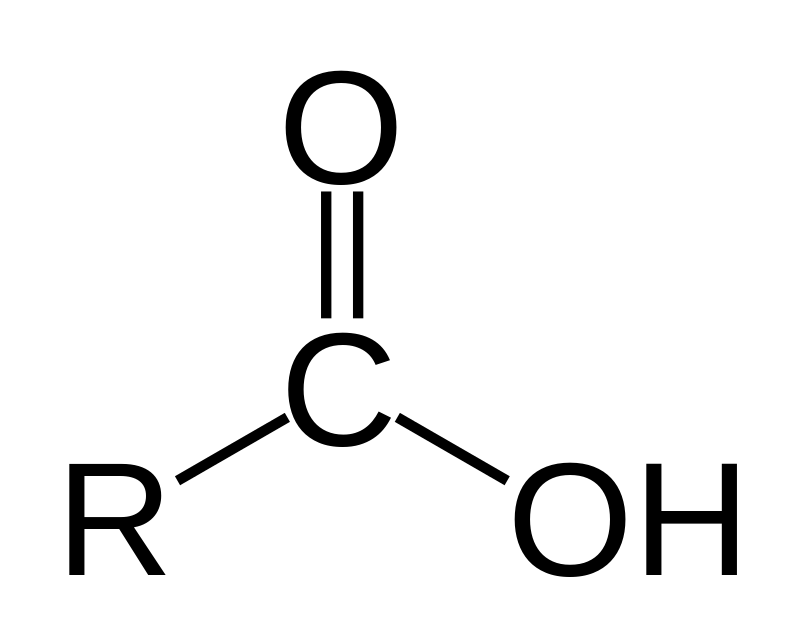
Carboxylic Acid
RCOOH; Carbonyl Functional Group
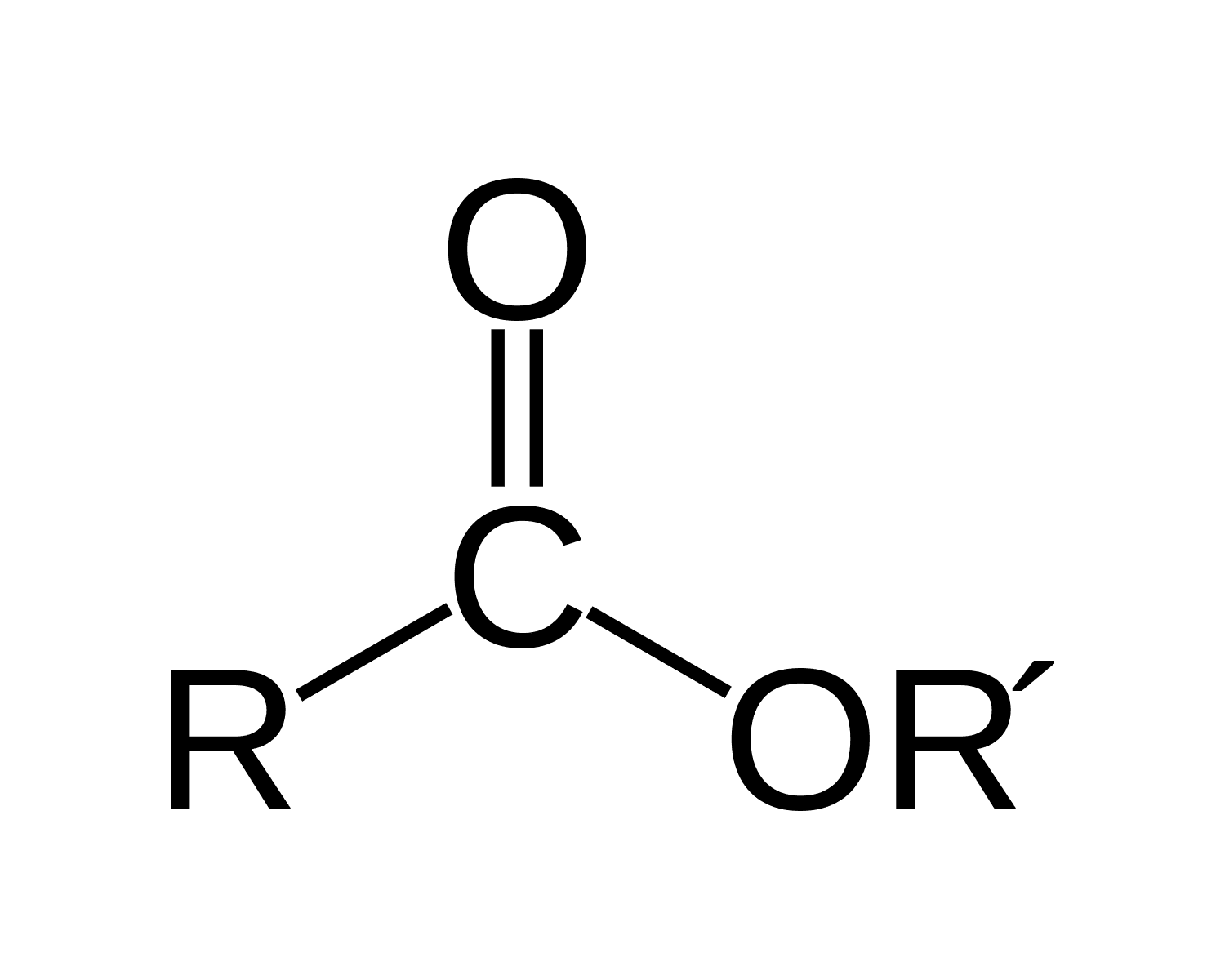
Esters
RCOOR’; Carbonyl Functional Group
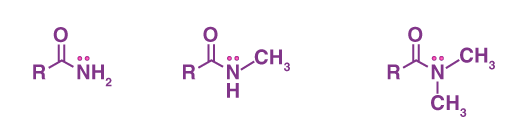
Amides
RONH2; Carbonyl Functional Group
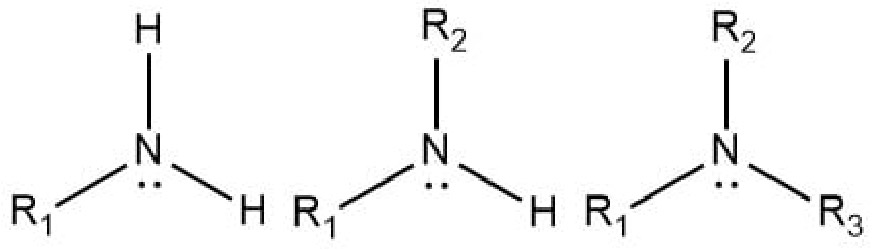
Amines Functional Group
Nitro Functional Group
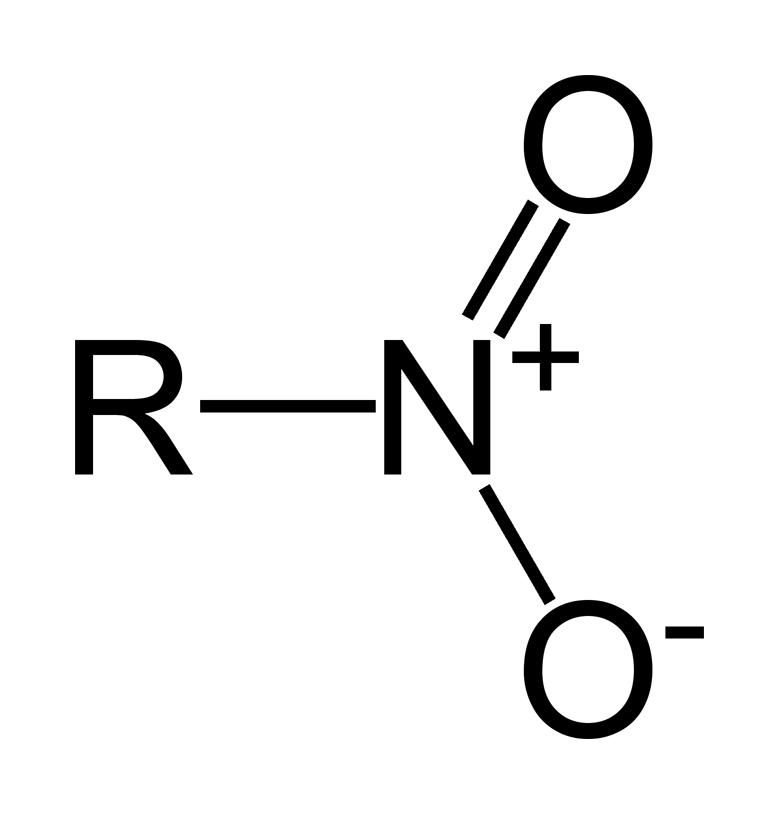
R-NO2
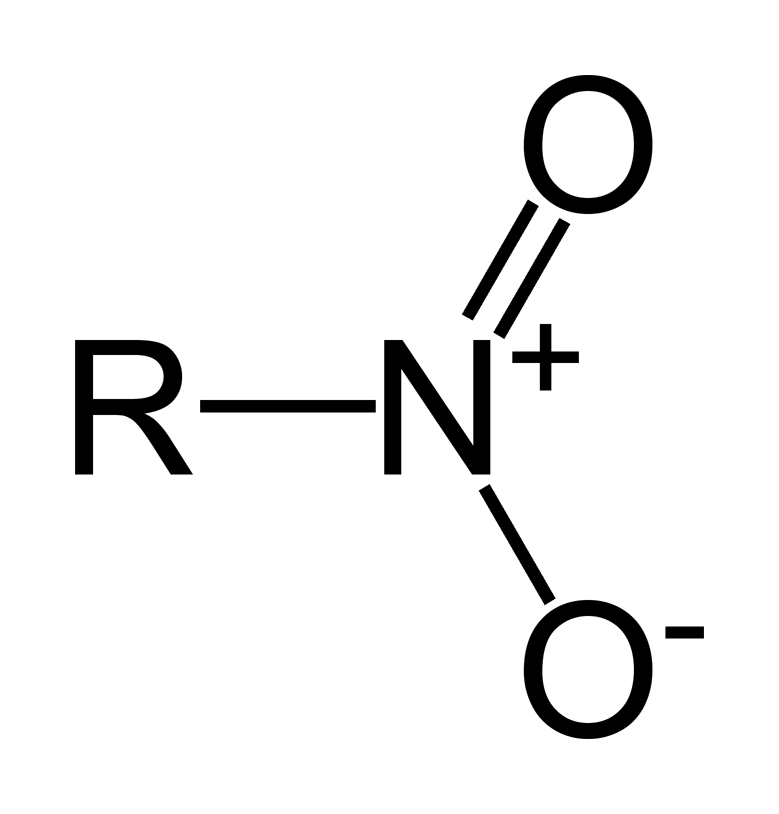
Nitride Functional Group
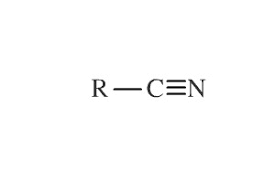
What is/are the R(s) in the Nitro Functional Group?
C-Containing Group
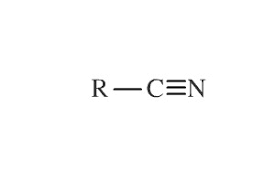
What is/are the R(s) in the Nitride Functional Group?
C-Containing Group
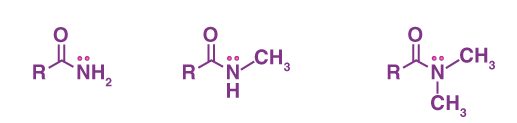
What is/are the R(s) in the Amides Functional Group?
R → H or a C-Containing Group
R’ and R” → C-Containing Group
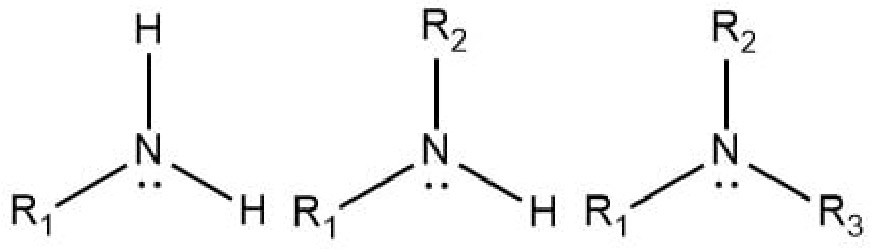
What is/are the R(s) in the Amines Functional Group?
R → Some C-Containing Group
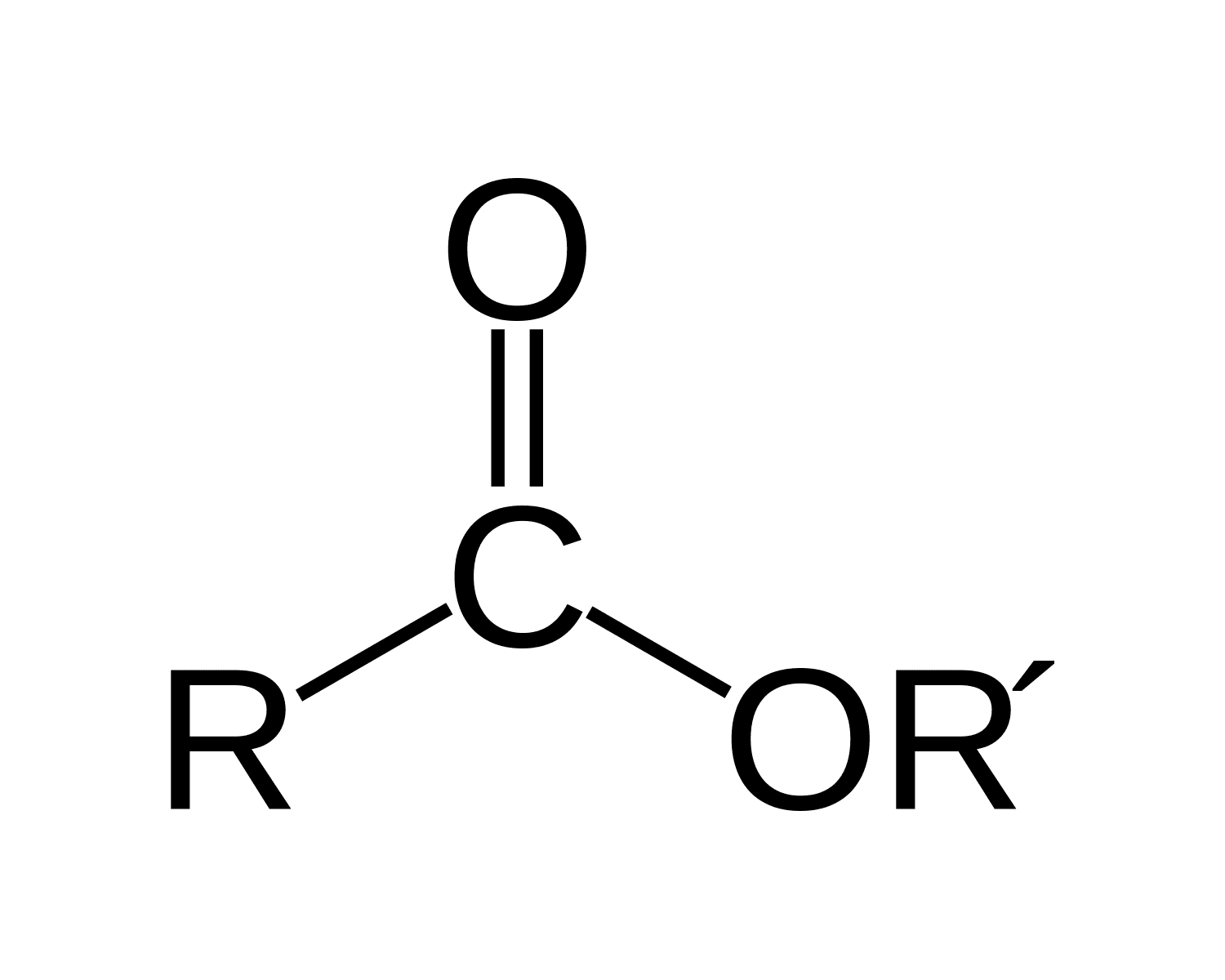
What is/are the R(s) in the Esters Functional Group?
R → H or C-Containing Group
R’ → C-Containing group same or different than R
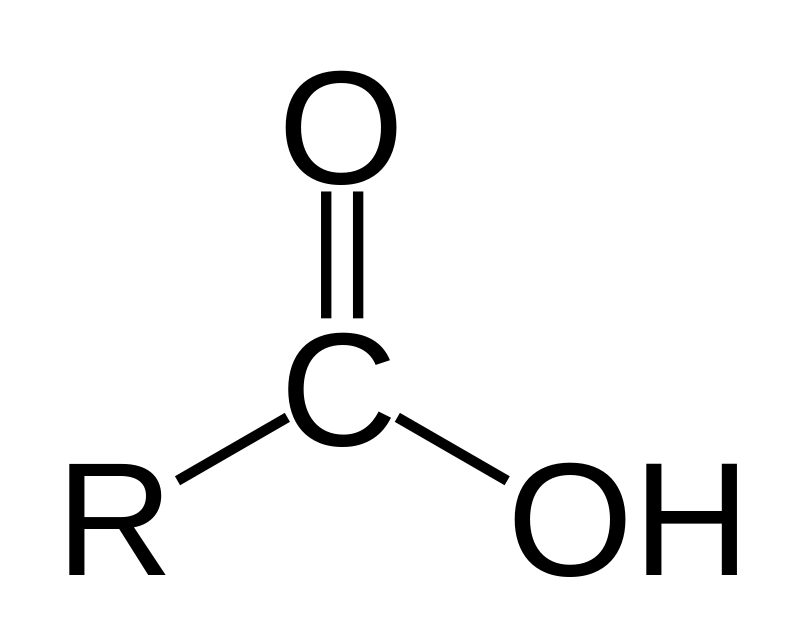
What is/are the R(s) in the Carboxylic Acid Functional Group?
R → Either H or a C-Containing Group
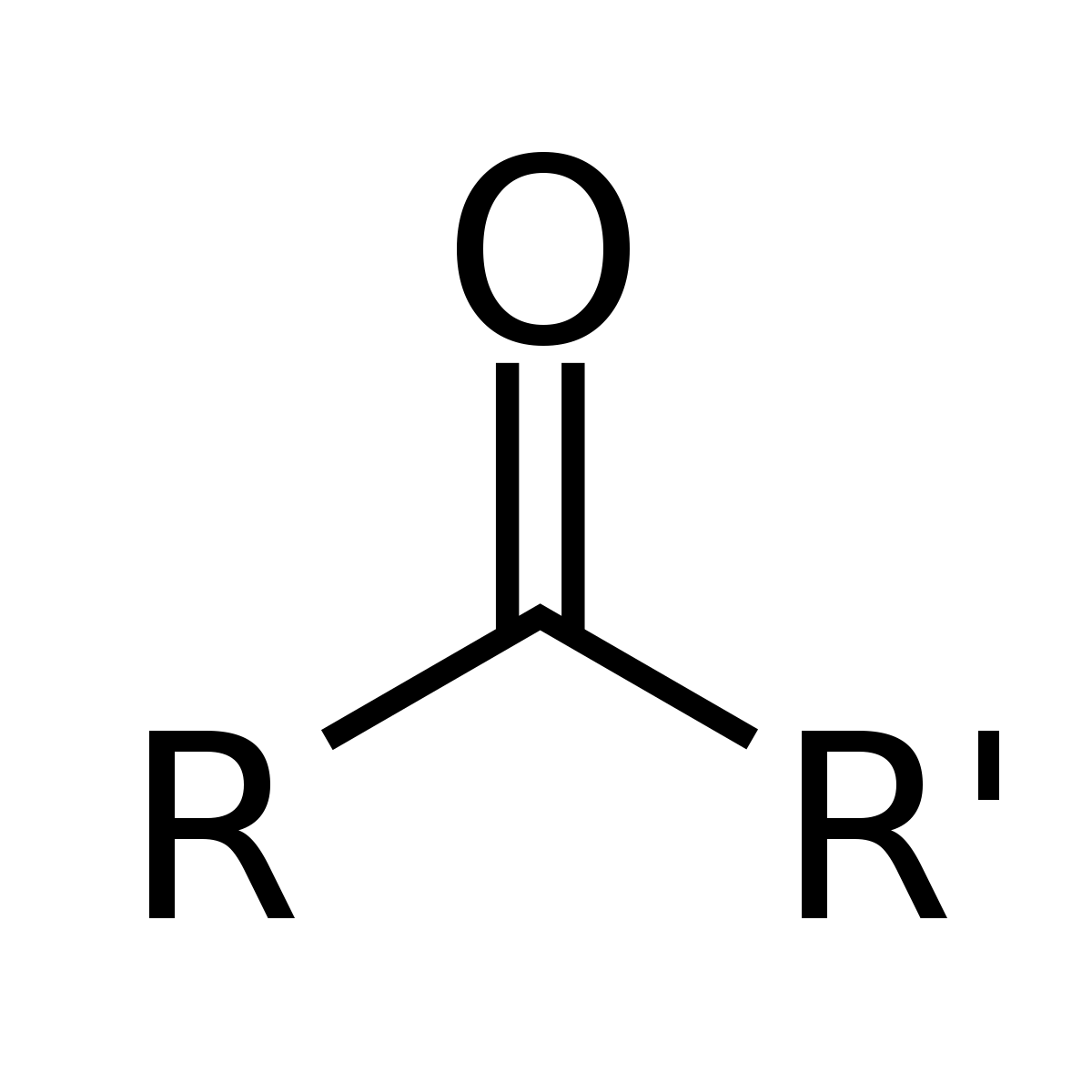
What is/are the R(s) in the Ketones Functional Group?
R and R’ → Both are carbon containing groups; same or different
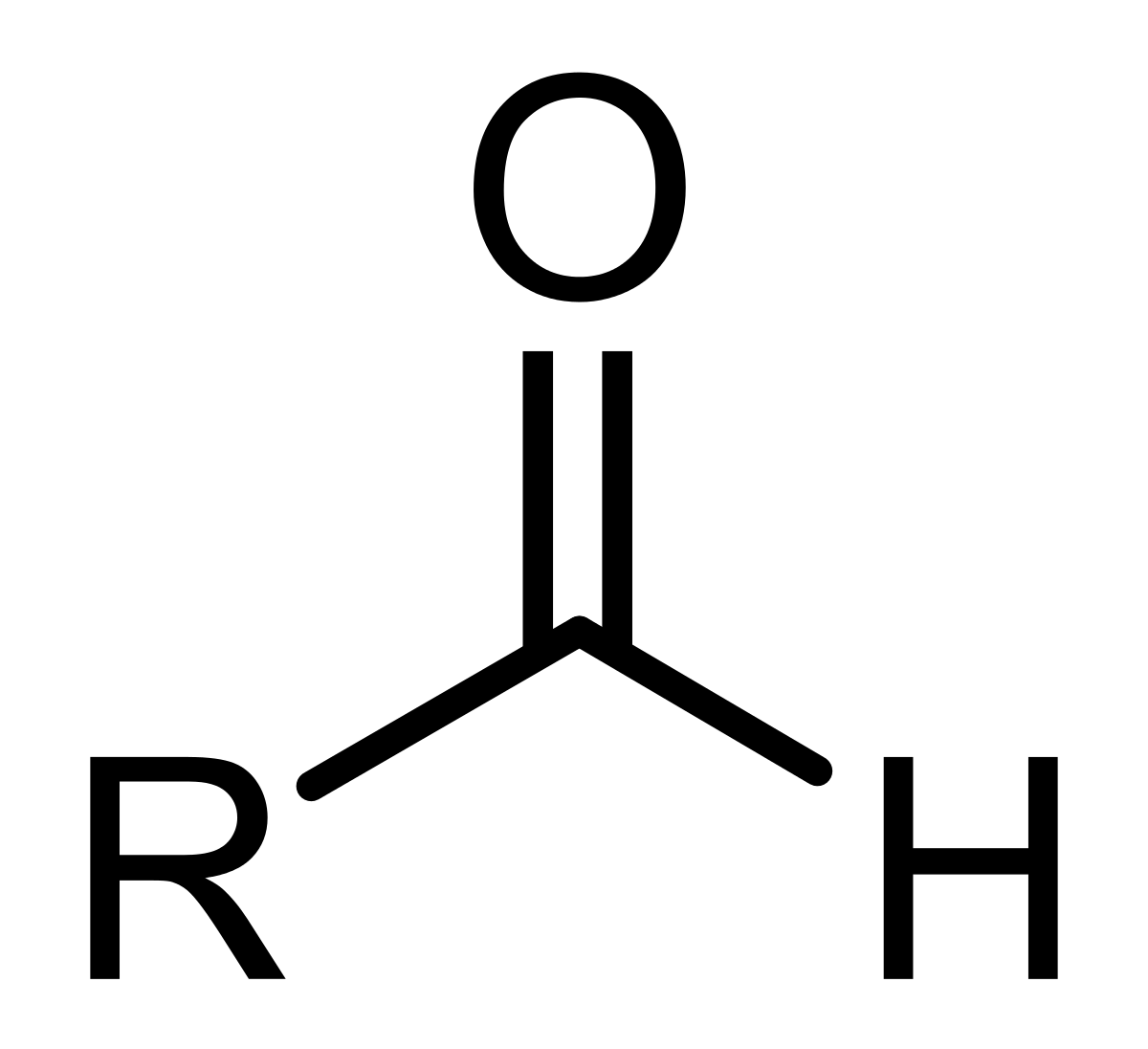
What is/are the R(s) in the Aldehydes Functional Group?
R → H or C-Containing Group
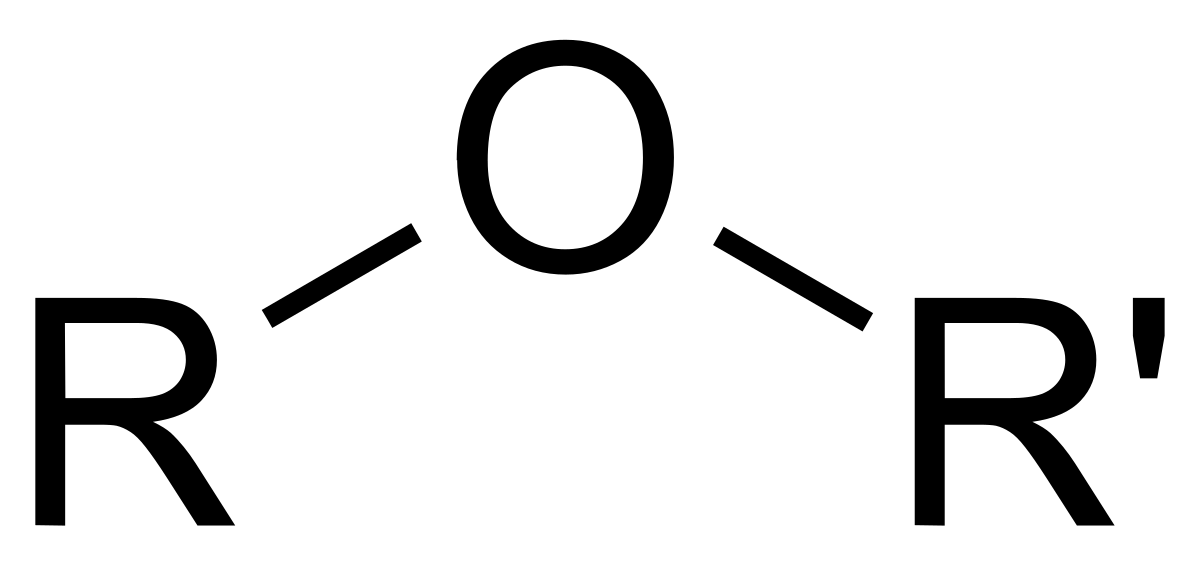
What is/are the R(s) in the Ethers Functional Group?
R and R’ → Both are C-Containing Groups; Same or Different
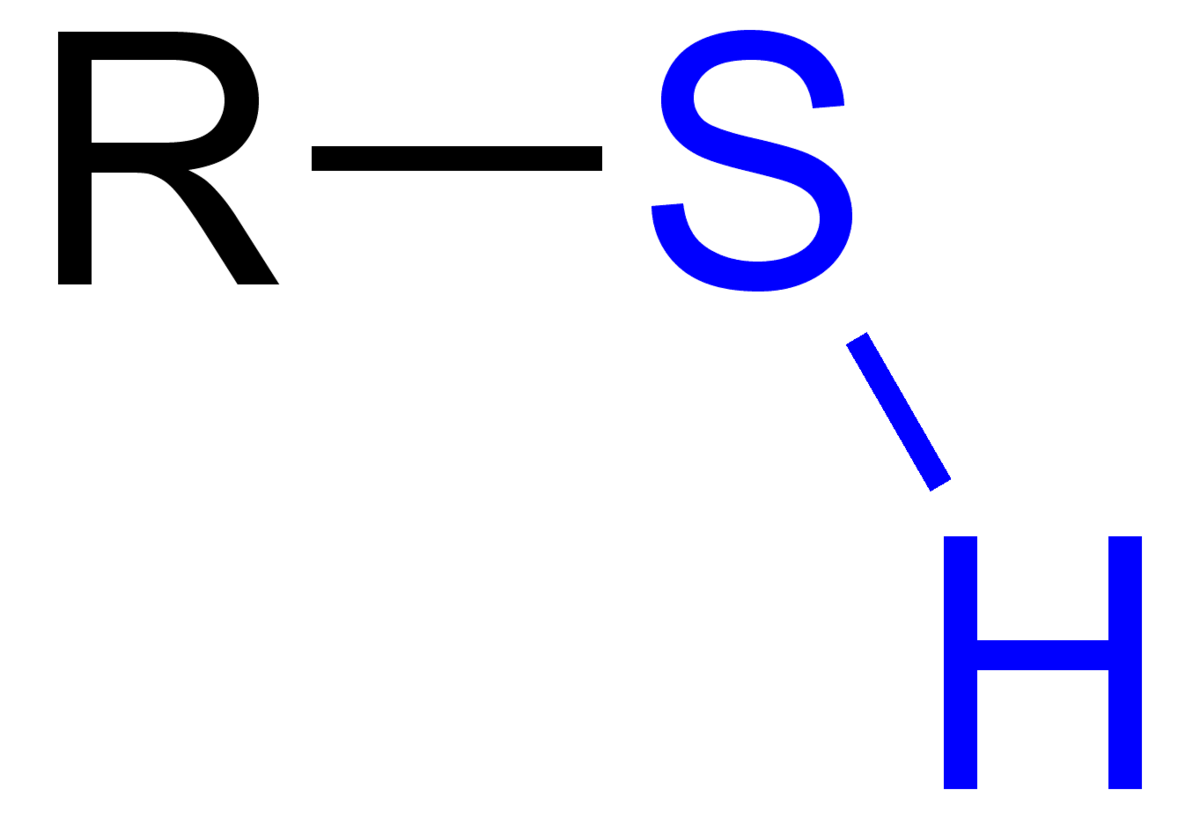
What is/are the R(s) in the Thiols Functional Group?
R → C-Containing Group
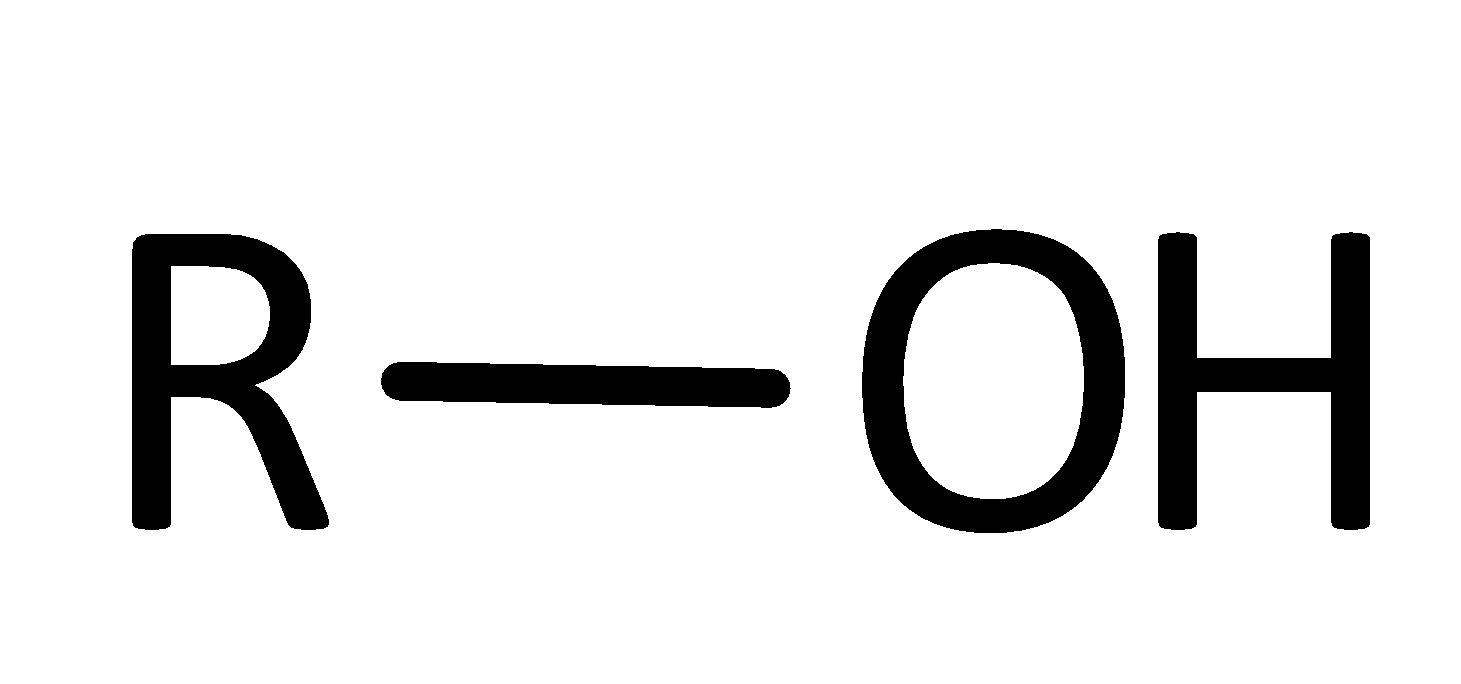
What is/are the R(s) in the Alcohols Functional Group?
R → Has to be some C-Containing Group