CEN4020 final
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
Software engineering is to make _____ software
RIGHT
What is Software Engineering (v.s. Programming)?
engineering discipline that
is concerned with the practicalities of planning,
developing, testing and delivering useful and reliable
software.
Software engineering is involved with _____-person
development of _____-version programs
multi
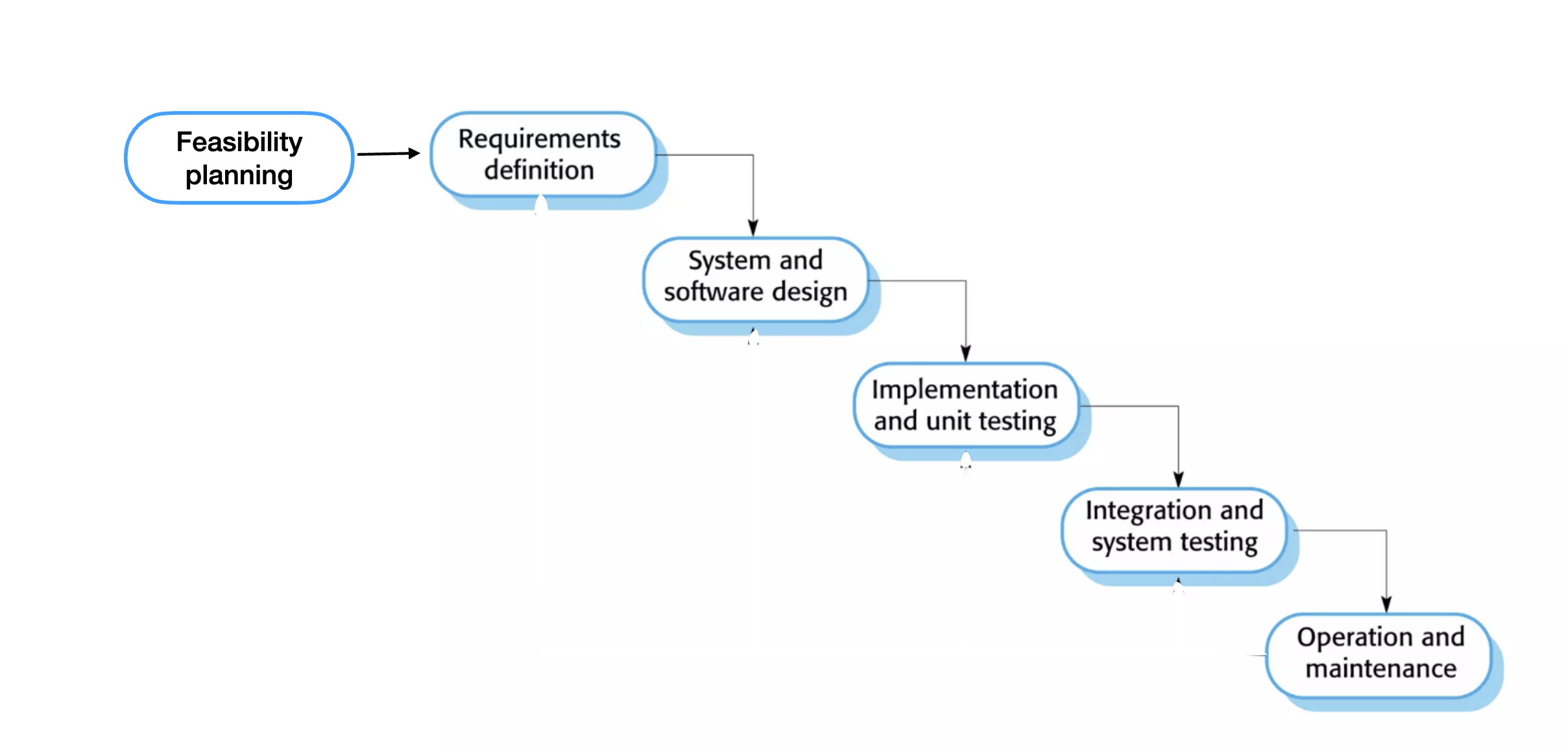
Process model - Modifed Waterfall
Linear and sequential process.
Each phase must be completed before moving to the next.
Best for projects with clear, fixed requirements.
Limited flexibility for changes.
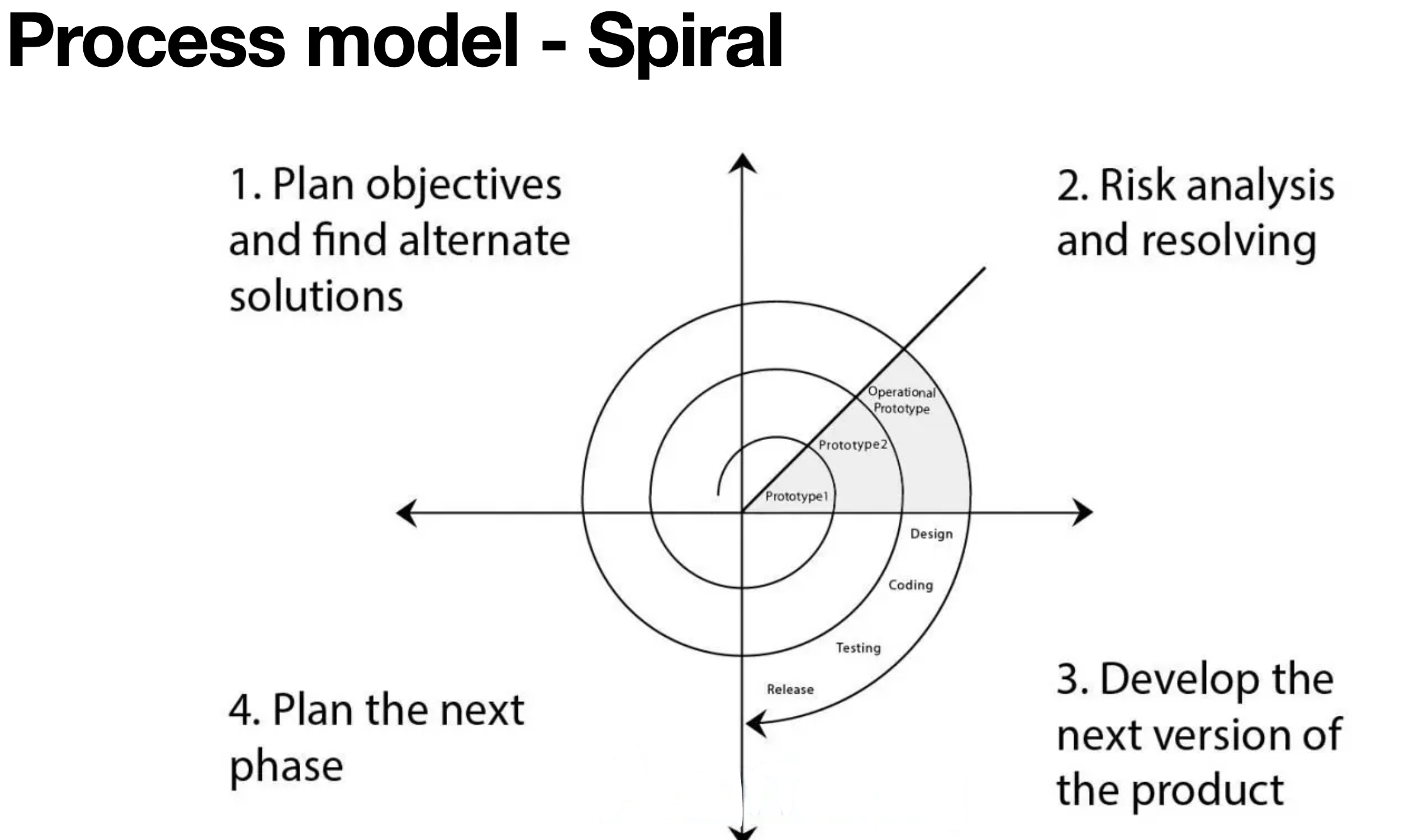
Process model - Spiral
Iterative and risk-driven approach.
Focuses on continuous risk assessment and development in cycles.
Suitable for complex projects with evolving requirements.
Requires careful risk management.
Process model - Agile
Program specification, design and implementation are light and interleaved.
How is the process model - Agile system developed?
as a series of versions or increments with clients involved in version specification and evaluation.
What are the Agile Manifesto - 4 values?
individuals and interactions over process and tools
working software over comprehensive documentation
customer collaboration over contract negotiation
responding to change over following a plan
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Agile helps them to collaborate and solve any problems that arise
Working software over comprehensive documentation
Agile values documentation, but values working software more.
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Agile enables the coordinated teams to align better with the customer requirements.
Responding to change over following a plan
Agile adapt quickly in order to deliver a quality product and ensure their client’s satisfaction.
Incremental planning
Requirements are recorded on story cards and the stories to be included in a release are determined by the time available and their relative priority. The developers break these stories into development ‘Tasks’.
Small releases
The minimal useful set of functionality that provides business value is developed first.
Releases of the system are frequent and incrementally add functionality to the first
release.
Simple design
Enough design is carried out to meet the current requirements and no more.
Test-first
development
An automated unit test framework is used to write tests for a new piece of functionality
before that functionality itself is implemented.
Refactoring
All developers are expected to refactor the code continuously as soon as possible code
improvements are found. This keeps the code simple and maintainable.
Pair programming
Developers work in pairs, checking each other’s work and providing the support to
always do a good job
Collective
ownership
The pairs of developers work on all areas of the system, so that no islands of expertise
develop and all the developers take responsibility for all of the code. Anyone can change
anything.
Continuous
integration
As soon as the work on a task is complete, it is integrated into the whole system. After
any such integration, all the unit tests in the system must pass.
Sustainable pace
Large amounts of overtime are not considered acceptable, as the net effect is often to
reduce code quality and medium term productivity
On-site customer
A representative of the end-user of the system (the customer) should be available full
time for the use of the XP team. In an extreme programming process, the customer is a
member of the development team and is responsible for bringing system requirements to
the team for implementation.
Scrum
agile framework that focuses on managing iterative development
rather than specific agile practices.
- leading agile development methodology
The Scrum Team consists of three roles:
Product Owner, the Development Team, and
a Scrum Master
Product Owner
represents the product’s stakeholders and the voice of the customer.
S/he creates a prioritized, dynamic wish list (user stories) called a product backlog and
is the sole person responsible for managing it.
Development Team
is responsible for delivering the increments of the product. The
team Is self-organizing. No one tells the Development Team how to turn the Product
Backlog into Increments of functionality.
Scrum Master
is a facilitator who arranges daily meetings, tracks the backlog of work
to be done, records decisions, measures progress against the backlog and
communicates with customers and management outside of the team.
product backlog
The starting point for planning, which is the list of
work to be done on the project
What happens during the selection phase in a sprint?
The project team and the customer work together to select features and functionality from the product backlog to create the Sprint Backlog, which is developed during the sprint.
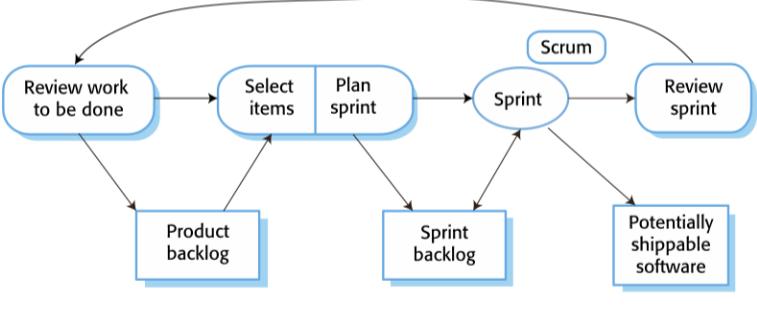
daily meetings (Scrums)
where all team
members share information, describe their progress since the last meeting,
problems that have arisen and what is planned for the following day
What is a key advantage of Centralized Version Control Systems (CVCS)?
Easier to administrate and control backups, access, and progress.
What is a major disadvantage of Centralized Version Control Systems (CVCS)?
Single point of failure.
Why can CVCS be inefficient?
It is slow, and one error can affect everyone.
Why is a network connection necessary in CVCS?
Because everything requires a network connection to the central server.
What is a key benefit of Distributed Version Control Systems (DVCS)?
It allows you to work offline.
How does DVCS support individual development?
Each developer can have their own repository.
When is a network connection required in DVCS?
Only for collaboration purposes.
Why is DVCS faster than CVCS?
Because many operations are done locally.
What is a downside of DVCS regarding project coordination?
Integration is often delegated.
What are the three tree architectures in Git?
Working directory, staging index, repository
Working directory
It is the local copy of the repository where the user
can make changes locally.
Staging index
It is the place where a commit will be prepared. We can
add changes in the staging index before committing them as one
single commit.
Repository
it is the place where committed changes are stored
Atomic Commits
small changes related to specific aspects of the
project, so your team can review, merge, or revoke them easily
Atomic Commits organizes the work by only making changes to the:
relative files
to a specific task, keeping other files clean, and then committing these
changes in a single commit.
What are the two categories of requirements?
functional and nonfunctional requirements
functional requirement
specifies an action that the software product must be able to
perform (what the system is supposed to do)
- Often expressed in terms of inputs and outputs
nonfunctional requirement
specifies constraints of the software product (how the
system is supposed to be) that are measurable.
In requirements specification, what is an actor?
An actor is a type of user that represents the role of someone who interacts with the system.
What do user actors typically do in a system?
They require help from the system to perform tasks and run the system's functions.
Give an example of a user actor in a train system.
Passenger: A person in the train
OR
Conductor: A person who checks tickets in the train
Give an example of a user actor in a video game system.
A person who plays a video game.
In requirements specification, what is an external system actor?
An external system actor represents an external system, database, API, platform, client, server, cloud platform, device, or sensor that interacts with your system.
What does a GPS satellite represent in a requirements specification?
An external system that provides the system with GPS coordinates.
How is a database considered an external system actor?
It is an external database that contains data, like payment records, that the system accesses.
What is the role of a financial API as an external system actor?
It is an external API used to post payments to bank accounts.
What is a use case in requirements specification?
A use case represents a functionality provided by the system.
What does each use case typically represent?
One functional requirement of the system.
How should a use case be named?
Using a Verb + Noun/Noun Phrase (e.g., "Process Payment") to indicate an action of the system.
What makes a use case name effective?
It must be sufficiently descriptive and clearly express the action being performed.
How are actors and use cases related?
Each actor must be linked to at least one use case.
Can a use case exist without being directly linked to an actor?
Yes, some use cases may be triggered by another use case rather than directly by an actor.
What does an association represent in a use case diagram?
The participation of an actor in a use case.
How is an association shown in UML diagrams?
By a solid line connecting an actor to a use case.
What is the most basic type of relationship in UML diagrams?
An association.
What does the system boundary represent in a use case diagram?
A rectangular box that indicates the scope of your system.
Where should the system name be placed in a use case diagram?
At the top, inside the system boundary rectangle.
What does it mean if something is inside the system boundary?
It is part of your system.
What does it mean if something is outside the system boundary?
It is not part of your system.
What is software architecture?
It represents the big picture of the system, including structure, subsystems, interactions, and tools.
What are architectural patterns in software architecture?
Reusable solutions to common high-level system organization problems.
What are subsystems in software architecture?
Independent components or modules that perform specific functions within the system.
What do interaction principles refer to in software architecture?
Rules and methods that define how subsystems communicate and work together.
What is the allocation of modules to subsystems?
The process of assigning specific modules to designated subsystems.
What are data storage paradigms?
The models and strategies used to store, manage, and retrieve data (e.g., relational, NoSQL, flat files).
Why are recovery systems important in software architecture?
They ensure the system can recover from failures and maintain availability and data integrity.
What should be listed regarding tools in a software architecture document?
Frameworks, tools, and programming languages used.
What is OO-Design (Object-Oriented Design)?
A detailed view of the system focused on classes, their attributes, methods, and interactions.
What should be included for each class in OO-Design?
Methods and attributes.
What is included in the method list in OO-Design?
Each method with its stereotype (e.g., constructor, getter, setter).
What is included in the attribute list in OO-Design?
Each attribute with its data type.
What is pseudocode used for in OO-Design?
To describe the logic of each method in a human-readable, language-agnostic format.
What are module interactions in OO-Design?
The ways in which different classes or components communicate with one another.
What are design patterns?
Proven solutions to common software design problems (e.g., Singleton, Observer, Factory).
What are programming idioms?
Commonly used coding techniques or conventions in a specific language.
Why are algorithms part of OO-Design?
They define the step-by-step logic used in methods to solve specific problems.
What is UML?
UML (Unified Modeling Language) is a standardized specification language for object-oriented analysis and design.
Is UML a model or a language?
UML is a language, not a model.
What is the purpose of UML?
UML is a general-purpose notation used to visualize, specify, construct, and document the design of software.
How does UML help software developers?
It allows developers to visualize the software design and architecture.
What are some open-source tools for UML modeling?
Gliffy Online, draw.io, yuml, ArgoUML, and Umbrello UML Modeller.
What have we already learned in UML?
we have already learned how to create use case diagrams using UML.
What does a UML class diagram represent?
it represents the structure of the system, models application domain concepts, and specifies the detailed behavior and attributes of classes and their relationships.
What are the key components of a class in a UML class diagram?
Class Name
Attributes
Methods
What is an example of an attribute in a UML class diagram?
name: String
age: int = 0
What is an example of a method in a UML class diagram?
+ getName() : String
+ setName(in/out n: String)
What does the access level "+" represent in UML class diagrams?
Public – The member is visible to all code in the application.
What does the access level "−" represent in UML class diagrams?
Private – The member is visible only to code inside the class.
What does the access level "#" represent in UML class diagrams?
Protected – The member is visible only to code inside the class and any derived classes.
What does the access level "∼" represent in UML class diagrams?
Package – The member is visible only to code inside the same package.