B1: Form and Function Molecules
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Learning outcomes:
descibe nature of covalent bond and that a carbon atoms can form up to four single bonds and other bonds with other atoms
expain macro molecules, such as polysacharides are formed by condensation reaction that link monomers to form a polymer
explain that wa wa molecules are split to provide the -H and -OH groups incorpotated to produce monomers in a hydrolysis reaction
Carbon and the covalent bond
found in cabrs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids
C forms covalent bonds
enables variety of stable compounds to exist. covalent bond = stable
longer chain of C-C bonds the more stable
distinct feature of a fatty acid
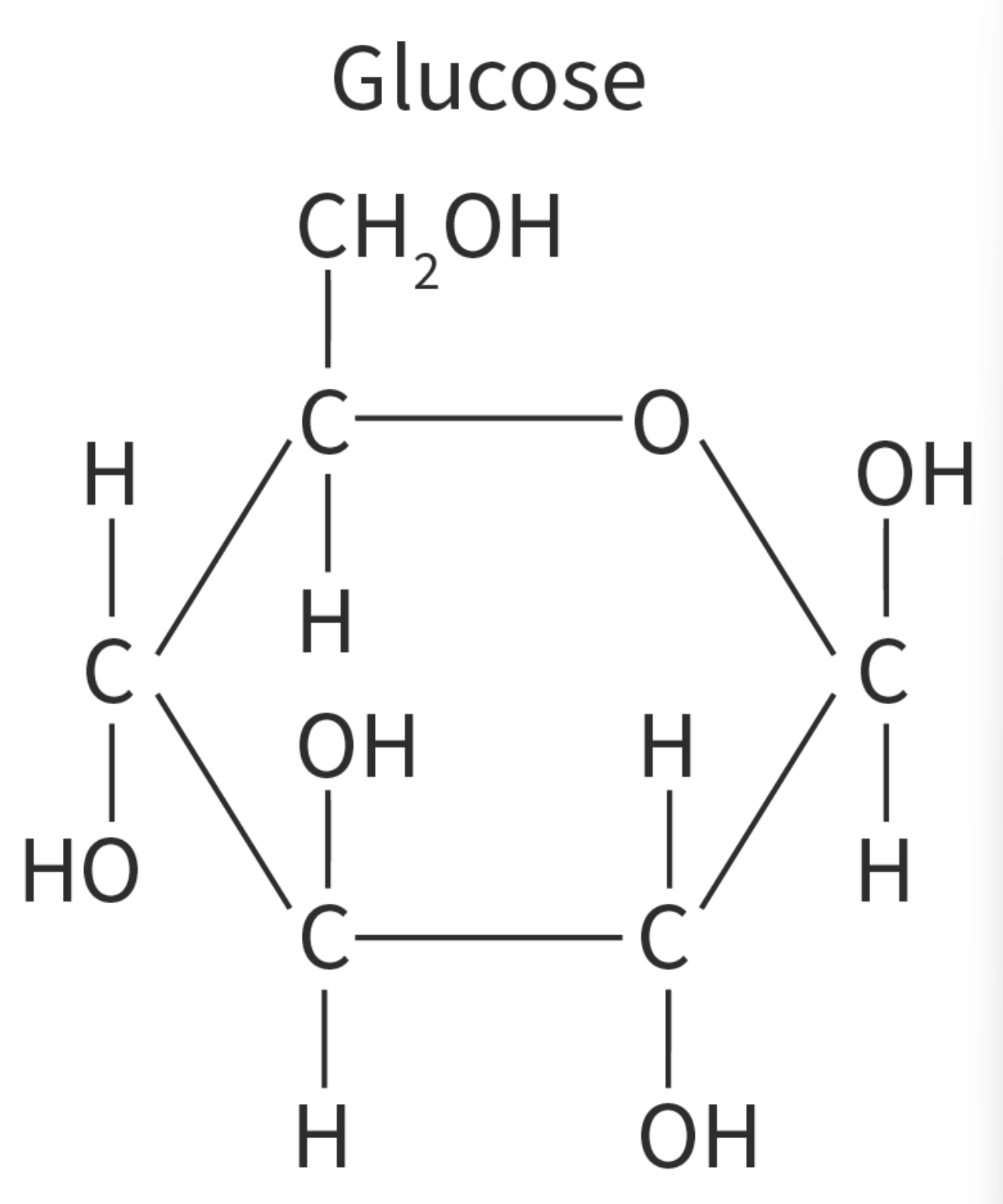
Carbon rings
carbon can also form rings
example of this is glucose
many carbon rings can also join together to form branched structures such as glycogen, which is a polymer of many glucose molecules joined together
Macromolecules
= large molecules made up of smaller building blocks called monomers
individual sub units that can be linked together to form longer chains called polymers
Four main classes of macromolecules:
Carbs
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
Formation of condensation reactions
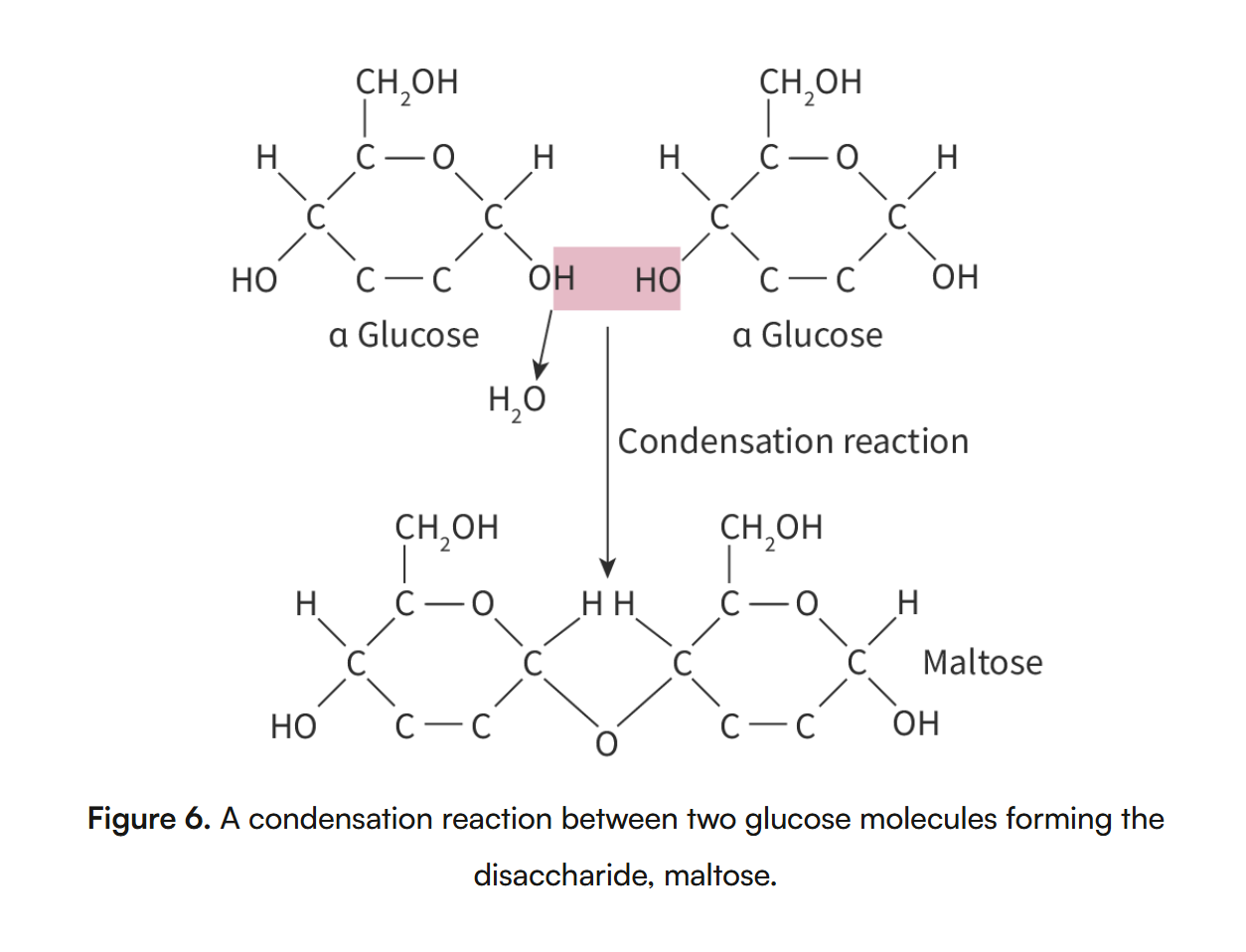
macromolecules formed = monomers must join together by a type of chemical reaction called condensation reaction
condensation reaction = polymersation reaction in which 2 molecules join, one molecule loses a hydroxyl group (-OH) and the other loses a hydrogen atom (-H), forming a water molecule and resulting in the formation of a new covalent bond
condesnation reactions = formation of macromolecules
-Oh group on carbon 1 of glucose molecule attacthed to the -OH group on a carbon 4 of the other glucose molecules, results in a covalent bond between two molecules, and relase of a molcule of water.
glycosidic bond = O atom shared between two glucose molecules that are joined together, when two glucose molecules join together they are called a diashacaride
more then two join together = polysacharide
celluose is an example of polysacharide
Breakdown of hydrolosis reactions
our bodys break down large polymers into constituient monomers to use them for energy or to build new macromolecules ur body needs
process of breaking down macromolecules into monomers = hydrolosis
reverse reaction for the condensation polymerisation reaction
water molecules break the covalent bonds between monomers that make up a polymer making them available for biological processes
Carbohydrates:
recognise monosacharides (pentose and hexoses) and know the properties of glucose (glucose in soluble, stable and can be oxidised).
outline the role of polysacharides as energy storage compounds and as structural components
explain the role of glycoprtiens in cell - cell recognition
Introduction to monosaccharides
monosacharides are dundemental
source of energy for cells
simplest form of a carb, consisting of a single sugar unit that cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis.
Types of monosaccharides
calsified by number of carbon atoms they have
pentoses have 5 carbon atoms, such as ribose, whereas hexose has six, like glucose, galctose and fructose.
Fructose:
sugar naturally found in fruits whereas galactose is a type of sugar that is found in dairy products glucose = most common monosacharide found in nature and is an important source of energy for many organisms.
Properties of glucose
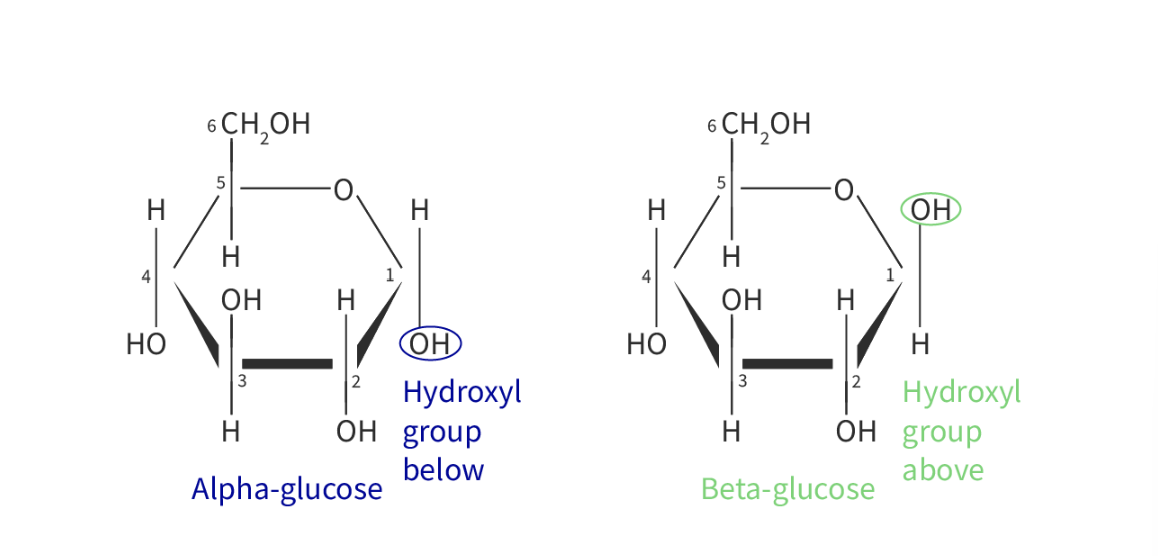
Glucose has two isomers
most common monosaccharide found in nature & properties are esential to its roles
glucose = two isomers = alpha glucose (a-glucose) and beta-glucose (B-glucose)
in the alpha glucose the -OH group is oriented downwards, wheras in beta it is oriented upards
diff structures are a result of diff combinations of the different isomers
Glucose is a soluble molecule
glucose is polar becasue it contains several -OH group
oxygen atom present in the glucose ring has a partial negative charge the carbon - hydrogen (C-H) groups linked to it have a partial positive charge.
in water solution, glucose is in equilibrium with open-chain form, where C1 atom is able to rotate
Glucose is a stable molecule
sturcutal role of the polysaccharide cellulose in plants
Glucose can be oxidised
Oxidation is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of electrons from an atom or molecule
Metabolism
all of the enzye reactions that take place inside a living organism
Anabalism
Def: the sythesis of complex macromolecules from monomers
Energy use: requires input of energy
Type of reactions: condensation reactions
Examples: amino acids from protiens, glucose forms startch
Catabolism
Def: the breakdown of macromolecules into monomers
Energu use: energy is realised in the process
Type of reaction: hydrolysis
Ex: the breakdown of sugars (including glycolysis) or fats to release energy
Hydrolosis
the breaking od chemical bonds by the addition of water molecules
Condensation reaction
reactio in which two smaller organic molecules combine to form a larger molecule with the accomponies formation of water or some other simple molecule
Monosachardies
single sugar monomers used to build larger comples carbs; polar and water soluble
Disaccharides
two sugar monomers joined by a glycosidic bond thru condesation reaction; polar and water soluble
Example: glucose + fructose = sucrose
or glucose + glucose = maltose
Polysaccharides
Macromolecules made of many sugar monomers joined thry condensation reactions; not soluble in water
use glucoe as monomer
very abundant on earth
plants store startch in roots and cells
carbs also make up chitin exosckleleton of isects and crustaceans
Cellulose
beta glucose monomers flip 180 degerss every other glucose to form straight un-branched chain
H bonds between chains provide stability
plants use celluclose as a strucural component, can be used as biofuel
Glycogen
animals use glycogen to store energy
very similar in structure to amylopectin (branched chain of alpha glucose monoers)
Glycoportiens
Def: protiens with one or more carbs attatched to them
Roles include
cell-cell recognition
receptors
ligands
structural support
Properties of lipids
Lipids: class of hydrophobic, non-polar molecules
insoluble in water, will dissolve in other non-polar solvents
Includes triglcerides, wax, steroids & cholesterol
triglycerides: synthesized by liver, found in foods (buuter, lard, olive oil)
wax: high melting point, often solid at room temp; found on surface of leaves to reduce transpiration
Formation of phospholpids
similar to triglycerides except with 2 fatty acid tails and a phosphate group joined to glycerol
Fatty acid structure
Saturated: all single bonds, each C fully saturated with H (4 bonds) —> straight chains that pack together easily —> solid at room temp
Unsaturated: one or more C-C double bonds —> results in kinks or bends in the chain —> harder to pack together —> liquid at room temp
Lipids for energy storage
lipids vs carbs: lipids have higher energy content per gram and are thermal insulators
carbs: 17kL/g vs Fats: 37 kJ/g —> twice the energy per gram
Eg: fat isulated wwhales during winter
Lipids as long term storage:
glycogen (carbs energy stores in animals_ associated with 2g water per gram glycogen
lipids stored w/no addtional water —> smaller contribution to body mass —> lighter overall body mass possible, enhances mobility while retaintaing a lot of energy
can form waterpoof layer in plants and animals
plants store fats (often unsaurated) in seeds as energy for germinating seedling
Phospholipids
negativley charged hydrophilic phospahte head + non-polar long fatty acid tails
hydrophilic + hydrophobic = amphipathic
in water, hydrophobic tails will orite themselves towards other tails (away from water molecules) —> spontanous fomation of bilayers
Membranes as a barrier
core of phospholipid bilayer made of fatty acid tails —> hydrophobic
low permeability to hydrophilic molecules (ions and large polar molecules) because of interactions w/ hydrophobic core
low permeability to large molecules due to size
result: membranes can prevent many kinds of particles from diffusing across without the help of membrane protiens
Steroids
category of hormones which regulate a wide range of functions in the body
share similar carbo 4-ring structure with diff function groups
cholesterol is the base for steriod hormones
hydrophobic —> able to pass thry phospholipid membrane easily —> steroid hormones can deliver their message more efficiently
Proteins: Essential structures for life
huge range of functions:
enzymes
hormones
pumps
receptors
immune protiens (antibodies)
structural protiens
keratin —> hair, nails, claws
Gene
Section of DNA that codes for the amino acid sequence of one polypepetide/protien.
Genes and Protiens
DNA is transcribed as mRNA
mRNA is read (translated) by ribosomes, which build the amino acid chain based on the mRNA instruction
resulting amino acid chain is a polypeptide which will fold innto its final protien configuration
Amino Acids: The building blocks
all protiens are made of chains of amino acids
amino acid structure: central carbo with amino group NH2 carboxyl group (COOH), and R group (20 kinds)
20 Diff Kinds of Amino Acids
Some are essential —> cannot be sythensized in the human body, so must come from outside sources:
Histidine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Threonine
Tryptophan
Valine
Dipeptide
two amino aicds joined by a peptide bond (formed via condensation reaction)
Polypeptide
Def: Many amino acids joined by a peptide bonds
Protiens can be a single polypeptide chain, or several chains combined, like hemoglobin
Peptide bonds
Bonds that join amino acids together
Polypepetide
chain of many amino acids, used interchangeably with protien, usually longer chains folded into secondary structures
Peptide
smaller chains of amino acids, between 2-50
Dipeptide
two amino acids joined by a bond
Polymer
Polymer: general term for a large molecule made of monomers
Examples of polypeptides
Lysozyme: enzyme made of 129 amino acids; found in tears and salvia; disrupts bacteria cell walls
Alpha-neurtoxins: polypeptides in snake venom which target and disrupt nervous system by inhibiting receptors; 60 - 75 amino acids
Glucagon: made of 29 amino acids; secreted by pancreas; increases blood sugar levels by breaking down glycogen stores
Myoglobin: oxygen-binding protien found in muscle tissues; made of 153 amino acids
Optimum temp and pH
devations from optimum temp and pH reduce function and cause denaturation of protiens
Temp: high temps cause denatureation resulting in changed interaction between amun acud R-groups, sometimes irreversible
Optimum pH
very alkaline or acidic solution can break bonds within quaternary, tertiary and secondary structure
Membrane structure
membranes are fluid, flexable and dynamic
maintains internal enviorment of the cell, allows for exchange with outer enviorment
key player in homeostasis
Fluid mosaic model
membranes composed of phospholipid bilayer w/embended protiens and chlesterold
Phospholipid biylaer
two layers of phospholipids( tails on inside, heads on outside)
polar phosphate head —> hydrophilic
two (non-polar) fatty acid tails —> hydrophobic
hydrophilic + hydrophobic = ampipathic
hydrophobic tails “hide” from water between the hydrophilic phosphate heads, which are attratced to water
low permability to hydrophilic molecules because of interactions w/hydrophobic core
low permability to large molecules
membranes can prevent many kinds of particles from diffusing across
Diffusion O2 and CO2
small non-polarticles like O2 and CO2 can diffuse easily across phospholipid bilayer
passive transport
moves down conc gradient from higher to low
Membrane protiens
Intergral: embeded in membrane; amphipathic
Peripheral: attatched to outside of membrane hydrophilic
Chanels: passive transport
Carriers: substrate binds to one side, protien changes shape to carry thru
Recognition: helps cell differentiate between self and non-self
Receptors: relay info from inside or outside cell
Enzymes: increase rate of reactions
Other parts of cell membrane
glycolipids = branching carb attatched to the head of phospholipid
maintain structure, help cells identify “self”
glycoprotien = branching carb attatched to a protien
enormos range of functions
Drawing fluid mosaic model
Represent phospholipids as circle w/ two parallel lines
Represent cholesterol as a short chain of hexagons amongst hydrocarbon tails
Include range of integral and peripheral proteins
Include and label the following structures:
Phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid molecule
Glycoprotein
Glycolipid
Integral and peripheral proteins
Cholesterol
Import and export thru membrane
import materials for metabolism
glucose
hormones
ions
Export toxic wates and useful products made by the cell
other functions: cell defence and homeostasis
Passive transport
Simple diffusion: particles pass directley thru membrane
faciliated diffusion: particles move thry a chanel/carrier protien
larger particles, ions (repelled by hydrophobic tails)
channels and carriers spesific to certain sizes and shapes of molecules
Facilated diffusion of K+ ions
during action potential, K+ floods into axon
axon needs to repolarize by moving K+ out of axon
specialized K+ channels move K+ down its conc gradient
K+ channels are voltage gated
Organelles
structures in a cell that preform spesific functions (like organs in your body).
Membrane bound organelles
many organlles are memrane bound (surrounded by plasma membrane)
only eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles
Compartmentalisation
Def: organising certain functions or processes inside structures bound by plasma membranes
allows for developemnt of specialized cell structures
allows for diff interal conditions
Lysosomes
found in eukaryotic cells: enzyme-filled compartments that break down wastes in cell
Pagocytic vacules
Found in macrophages; use enzymes to break down pathogens into parts (part of immune response)
What isn’t an organelle
organelles need to have specialised function/role: usually related to metabolism
cytoskeleton, cell wall, and cytoplasm are not organelles
Ribosomes
are organelles
they make protiens
not membrane bound
Role of nucleus
DNA is housed in nucleus
DNA —> mRNA —> protien
segments of DNA (genes) are transcribed into mRNA
mRNA leaves nucleus to be translated into protien by the ribosomes in cytoplasm
Role of nucleus in gene expression
before mRNA leaves nucleus, post transcriptional modification
allows modification to be made before ribsomes can access mRNA transcript
prokaryotes are unable to do this
compartmentalisation of nucleus from cytoplasm allows cytoplasm to send signals to nucleus
extrcellular signals like hormones, recieved by cytoplasm
passed to nucleus to alter rate of transcription
Stem Cells
every organism starts as a single, upecialized cell (zygote)
first cells need to be able to differentiate to make specialized tissues of a complate organism
these fist cells are called stem cells
diff kinds based on where they come from and limits of their differentiation
General charactaeristics of stem cells
All stem cells are unspecialises
devide indefitinley to keep making more of that kidn of stem cells
differentiate into difff kinds of cells when given the right stimulus
Differentiation
Def: unspecialised cells developing into cells with a distrinct structure and cell function
certain sections of the genome are turned on for spesific “instructions” for diff kinds of cells
Embryonic development
sperm + egg = zygote
morula: solid ball of cells after first few divisions (16-32)
blastocyst: hollow ball of cells consisting of trophoblast and iner cell mass ICM
trophoblast will become placenta, ICM will become embyro
Other cells “read: their distance away from source in conc grandent thry receptors on surface and devlop accordingly
Result: early embryonic cell differentiations
From Unicellular to multiceullular organisms
Since organisms has multiple cells, those cells could specialise thru differientiation
Stem cell niche:
Def: the micromoment within the organism with adult stem cells live and recieve instructions
Includes cell-to-cell interactions between cell na d extracellular fluid
Signaling molecules can activate, or prevent genes from transcribing → leads to activation of supression of cells.
Bone marrow/blood cell niche
Bone barrow niche consits of cells that make bloof cells and supportive cells
Hair follicles:
Have cycles of degeneration growth and rest so that your body is alwaus covered with mature hair shaft
These are stem cells responsible for the proliferation of hair found in the “buldge”
Surface to colume ratio: cells
Will eventually be to much volume to be supported by not enough surface area
Wont be enough membrane space allow enough nutrients in watses out to maintian full volume of the cell