Lecture 1-3 (Cardiac Muscle)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
describe cardiac muscle characteristics
Single nucleus bust post-mitotic
Striated muscle
Intercalated discs have desmosomes and gap junctions
Generates synchronized and forceful contractions via gap junctions
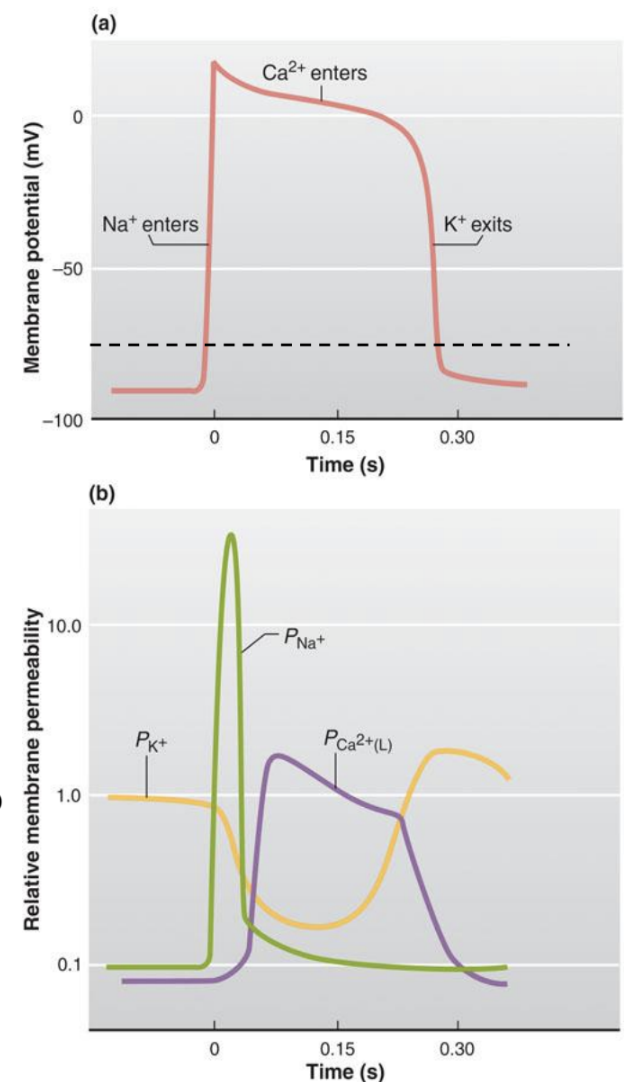
ventricular muscle fiber action potential (steps and channels involved)
at resting potential, Kir channels open and contributes to very negative resting potential
V-gated Na+ channels open → rapid depolarization to threshold
At peak, V-gated Na+ channels inactivate
Just after peak, L-type Ca2+ channels (V-gated) open. Ca2+ balances K+ efflux = plateau
Near end of plateau: L-type Ca2+ channels inactivate. Delayed-rectifying V-gated K+ channels open (slow to open) → rapid repolarization
Kir channels maintains hyperpolarized Vm
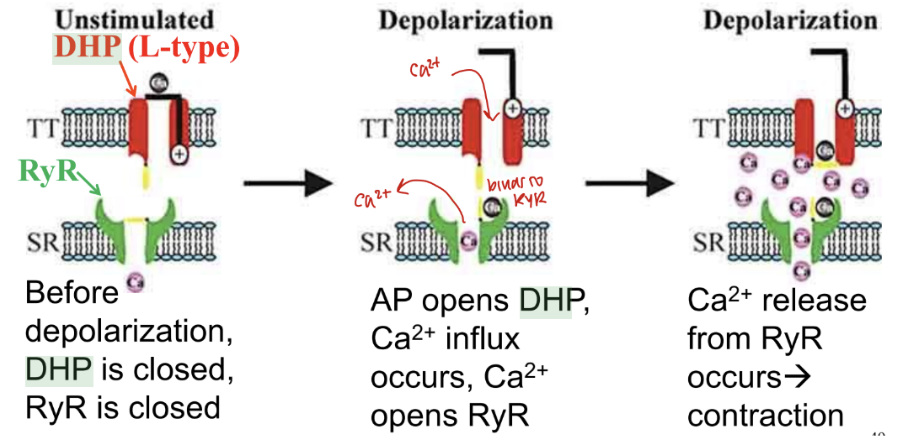
how are DHP receptors in ventricular muscles similar and different to skeletal muscles
Ventricular muscle cells have DHP receptors in plasma membrane T-tubules, BUT they are NOT physically connected to RyR
what are DHP receptors in ventricular muscle membranes also referred as
L-type Ca2+ channels (V-gated channels): they open and allow Ca2+ influx from the ECF. Ca2+ then binds to and opens RyR on the SR membrane
what is Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release
Opening of L-type Ca2+ channels (DHP receptors) causes Ca2+ influx. Ca2+ binds to RyR on the SR membrane. Most of the Ca2+ for contraction is released from the SR.
draw out DHP and RyR channels during CICR
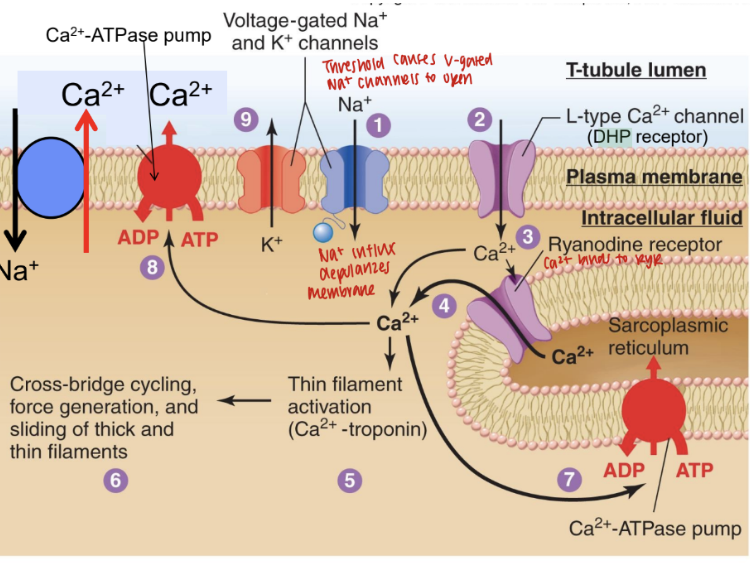
what is on the sarcolemma
Ca2+-ATPases and Na+-Ca2+ exchangers
what is located on the SR membrane
SERCA and RyR
cardiac excitation-contraction coupling and relaxation steps
V-gated Na+ channels open (depolarizing phase of AP)
L-type Ca2+ channels (DHP receptors) open (plateau phase of AP)
Ca2+ influx → Ca2+ binds to RyR → RyR opens →
Ca2+ release from SR →
Ca2+ binds to troponin →
Cross-bridge cycling starts → force production
Ca2+ is removed by 3 active transporters to ECF or SR → relaxation
Simultaneous with Ca2+ removal (step 7), delayed V-gated K+ channels open and L-type Ca2+ inactive then close → membranes repolarizes → V-gated Na+ channels close → another AP can be generated
why is it important for cardiac muscles to have a longer refractory period
cardiac muscle cannot undergo fused tetanic contractions (maintained contraction w/o relaxation)
desmosomes
hold the muscle cells together so they are not pulled apart during contraction