Advanced Biology Exam 2 - Vocab
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Genetics
The study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics.
The genetic properties or features of an organism, characteristic, etc.
Blending
an outdated theory that suggested offspring inherit traits as an average of their parents' traits
genotype
genotype refers to an organism's complete set of genes, or its genetic makeup.
probability
helps predict the likelihood of inheritance patterns and trait occurrences in offspring
F1
the first generation of offspring produced when two different parent strains or types are crossed
Codominance
two different alleles of a gene are both fully expressed in the phenotype, meaning both traits are visible.
trait
a specific characteristic or feature of an individual, often influenced by genes and/or environmental factors
dominant
A dominant allele is a variant of a gene that will be expressed, even if the other allele for that gene is different. A dominant trait is a characteristic that appears in an offspring if at least one parent contributes the dominant allele for it.
Phenotype
The observable characteristics or traits in an individual based on the expression of their genes.
punnet sq.
A visual tool used in genetics to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a cross between two individuals
F2
F2 represents the second filial generation in genetics, meaning the offspring of the F1 generation.
sex-linked
characteristics (or traits) that are influenced by genes carried on the sex chromosomes.
Mendel
In his monastery garden, Mendel performed thousands of crosses with pea plants, discovering how characteristics are passed down from one generation to the next — namely, dominant and recessive traits. Mendel's early experiments provided the basis of modern genetics.
recessive
a trait or allele that is not expressed in an individual unless two copies of the trait are present
homozygous
a situation where an individual has two identical versions (alleles) of a gene for a specific trait. This means both copies of the gene, one inherited from each parent, are the same.
heterozygous
an individual or cell having two different versions, or alleles, of a specific gene. This means that the individual inherited one version of the gene from each parent.
Mendel’s Laws
Law of Dominance, Segregation, and Independent Assortment
Law of Dominance
in a pair of contrasting traits, one trait, the dominant trait, will mask or conceal the other trait, the recessive trait.
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
states individuals possess two alleles, and a parent passes only one allele to his/her offspring.
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
states that the inheritance of one pair of factors ( genes ) is independent of the inheritance of the other pair.
hybrid
The offspring of a cross between two individuals of different breeds, varieties, species, or even genera.
genes
The fundamental unit of heredity, a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for making a specific protein.
alleles
a variant of a gene that occupies a specific location (locus) on a chromosome.
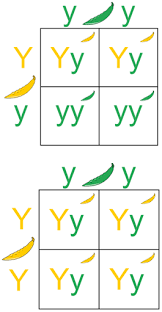
test cross
a genetic experiment used to determine the genotype of an individual with a dominant phenotype.
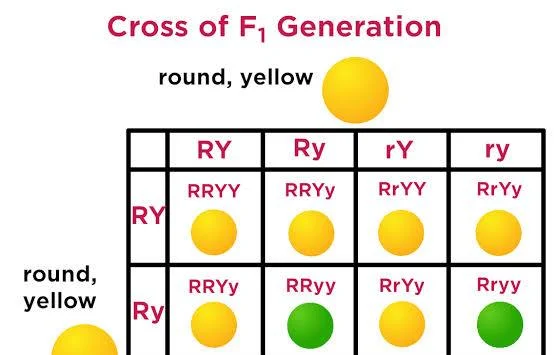
dihybrid
a mating experiment between two individuals that are both heterozygous (hybrid) for two different traits
P
the parental generation in a genetic cross experiment
Multiple Alleles (blood is an example)
a situation where a single gene has more than two different versions or alleles within a population, but an individual can only carry two alleles for that gene.
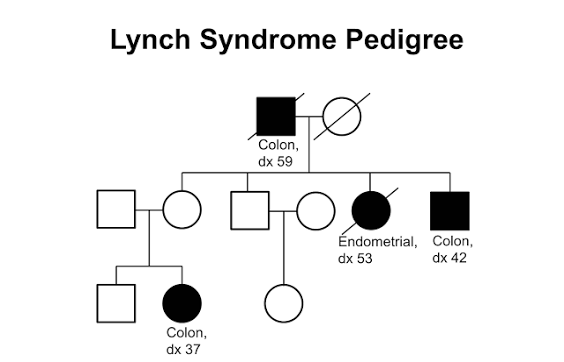
pedigree
the recorded ancestry, especially upper-class ancestry, of a person or family.
carrier
an individual who carries a mutated gene associated with a genetic disorder but does not exhibit symptoms or only mild symptoms of the disease.
Adenine
building blocks of DNA, forming base pairs that determine the genetic code, matches with thymine
guanine
building blocks of DNA, forming base pairs that determine the genetic code, matches with cytosine
cytosine
building blocks of DNA, forming base pairs that determine the genetic code, matches with guanine
thymine
building blocks of DNA, forming base pairs that determine the genetic code, matches with adenine
Uracil
a nitrogenous base found in RNA, pairs with adenine and replaces thymine in DNA during transcription
phosphate
a molecule containing a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms
Deoxyribose
a five-carbon sugar that is a fundamental component of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
DNA
a self-replicating material that is present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information.
helicase
an enzyme that separates double-stranded nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) into single strands, typically for processes like DNA replication, repair, transcription, and RNA processing
histones
a group of alkaline proteins that play a crucial role in organizing and packaging DNA within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. They help condense long DNA strands into a more compact structure called chromatin.
Watson
discovery of the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Crick
He is best known for his work with James Watson, which led to the discovery of the double-helix structure of DNA in 1953.
Wilkins
Professor Maurice Wilkins. Wilkins is most well-known for beginning the X-ray diffraction images of DNA that contributed to Watson and Crick's discovery of the double-helix structure of DNA.
Franklin
used X-ray photographs to study DNA fibers, revealing critical information about the molecule's structure
Replication
the process where a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA, ensuring that each new cell created during cell division inherits the same genetic information.
regulation
the process by which a cell controls which genes are turned on (expressed) and which are turned off.
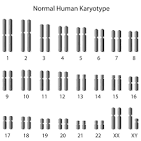
Karyotype
a picture of all of an individual's chromosomes, arranged in pairs and numbered.
exo1
Plays a crucial role in various DNA metabolism processes, including DNA repair and replication. Does replication, repair, and recombination. Key enzyme that removes mutated pieces so DNA polymerase can come back and put in the correct nucleotides.
leading strand
The strand that DNA polymerase builds from continuosly
lagging strand
The strand of DNA that DNA polymerase builds on in small segments in reverse
DNA polymerase
Enzyme which attatches free nucleotides to single strand of DNA during replication
A base, sugar, and phosphate form one _____.
nucleotide
mutations
changes in the DNA sequence of an organism
deletion
when a nucleotide or piece of information is removed.
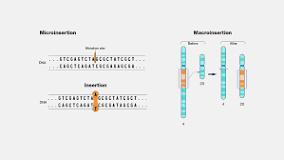
insertion
a mutation where extra nucleotide base pairs are added to a DNA sequence.
substitution
when one nucleotide is replaced by another
frame shift
When nucleotides are inserted or deleted and it makes the entire sequence move up or down
inversion
when a piece of DNA in a chromosome gets reversed
translocation
a type of chromosomal abnormality where a piece of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome
mutagens
a chemical or physical agent capable of inducing changes in DNA called mutations. Examples of mutagens include tobacco products, radioactive substances, x-rays, ultraviolet radiation and a wide variety of chemicals.
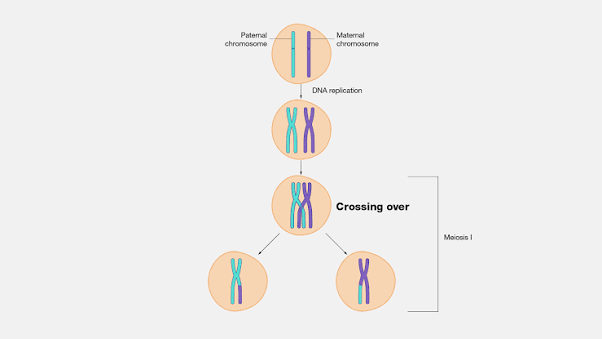
crossover
the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
independent assortment
how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop.
RNA
______ is usually single-stranded and involved in protein synthesis.
RNA polymerase
a vital enzyme that synthesizes RNA molecules from a DNA template during transcription. It plays a crucial role in gene expression, converting DNA's genetic information into RNA.
ribose
a natural five-carbon sugar (pentose) that is a building block of RNA and a component of ATP, the primary energy currency of cells
amino acids
the basic building blocks of proteins, which are essential for life
Transcriptiontr
the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence.
translation
The process by which a cell uses genetic information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) to synthesize proteins.
Ribosome
the cellular machinery responsible for making proteins.
Protein
made up of one or more long, folded chains of amino acids (each called a polypeptide), whose sequences are determined by the DNA sequence of the protein-encoding gene.
codon
section of three bases in mRNA that code for an amino acid
anticodon
sequence of three bases in tRNA that compliment mRNA
tRNA