1- Anatomical Position, Cardinal Planes, & Introduction to Osteology
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
anatomical position
standing upright, with arms at side and palms facing forward. Legs straight, toes pointed forward
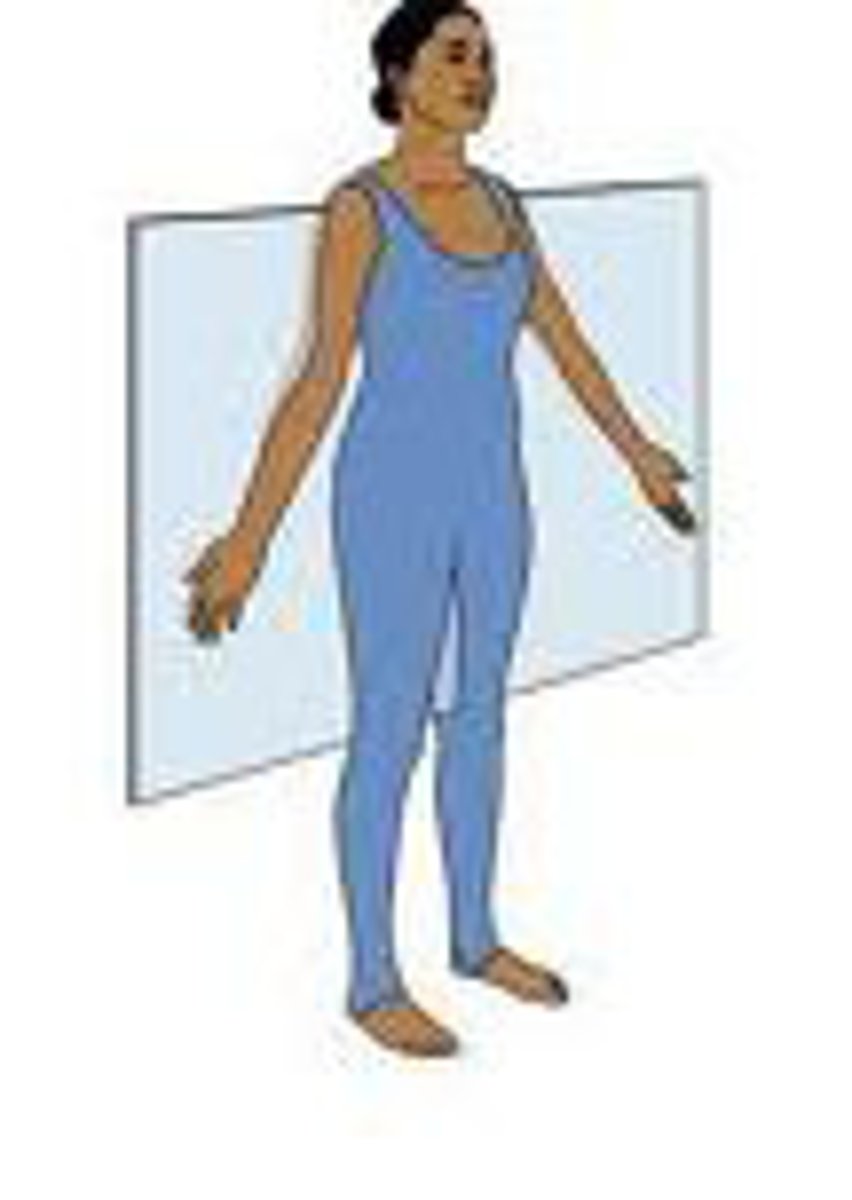
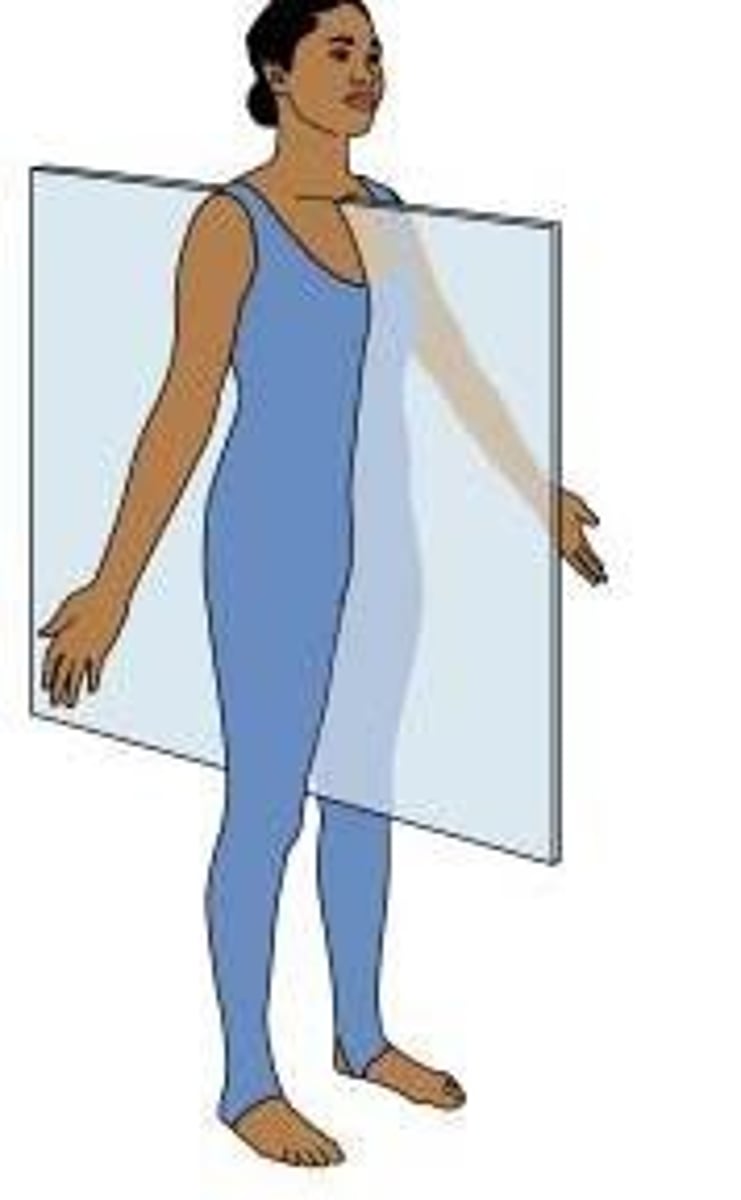
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right

frontal (coronal) plane- divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
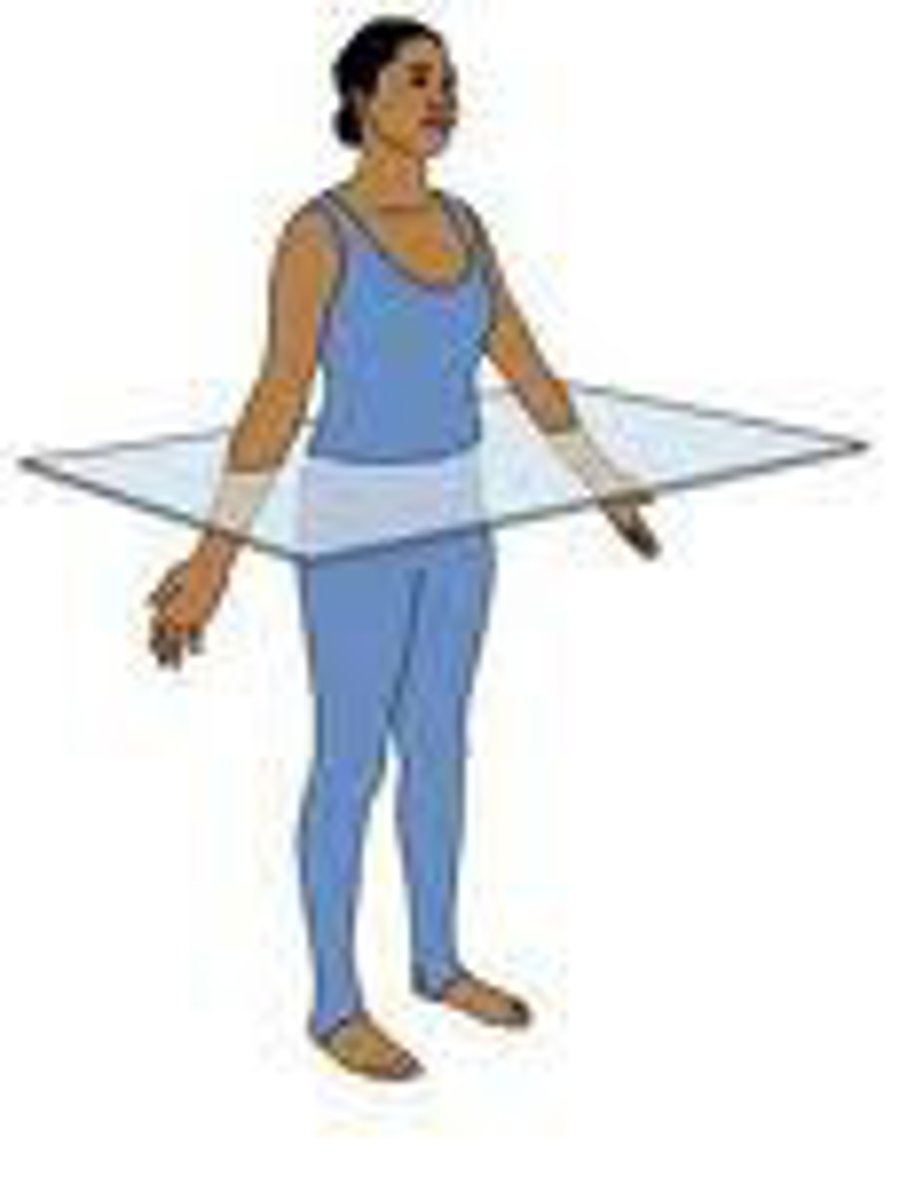
transverse (horizontal) plane
divides the body into upper and lower parts
flexion, extension, dorsiflexion, plantarflexion
motions that occur in the sagittal plane
abduction, adduction, radial deviation, ulnar deviation
Motions that occur in the frontal (coronal) plane
internal rotation, external rotation, horizontal abduction, horizontal adduction, inversion, eversion
Motions that occur in the transverse (horizontal plane)
angle
-sharp bony angulation
-may serve as body or soft tissue attachments
-used for precise anatomical description
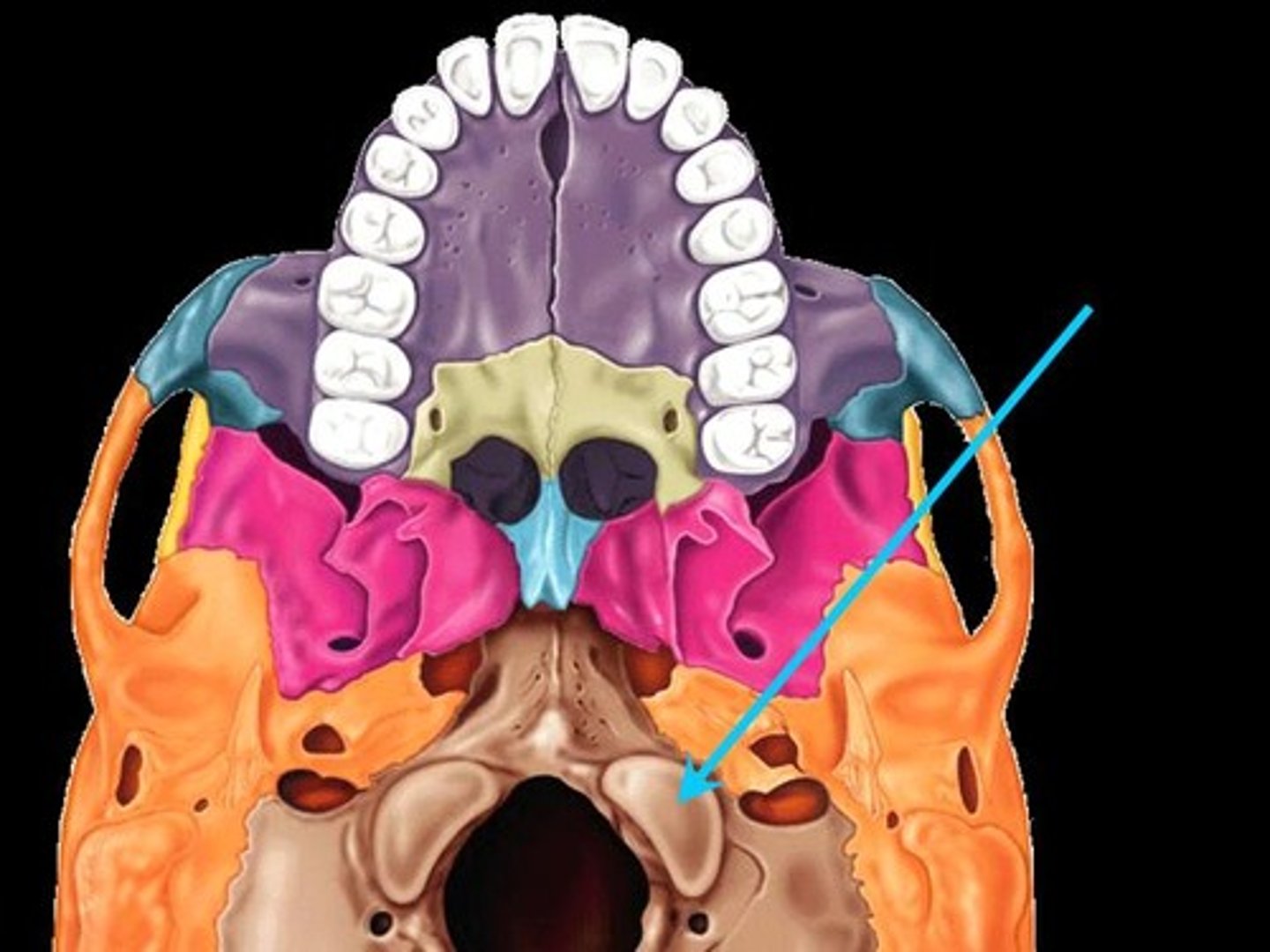
condyle- large round prominence that provides structural support
epicondyle
-prominence superior to a condyle
-attachment for muscles and connective tissues
crest (ridge)
-bone edge's raised or prominent part
-Attachment site for muscle and connective tissue
epiphysis
End of a long bone
diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
facet
smooth, flat surface that glides with another flat bone or facet
foramen
hole through which nerves and blood vessels pass
fossa
shallow depression on a bone surface
fovea
small pit/ depression
groove/sulcus
furrow on the bone surface that houses blood vessels or nerves for protection
head
round, prominent bony extension; main articulating surface in ball-and-socket joints
neck
separates head from bone shaft
an old epiphyseal plate is a _______
anatomical neck
surgical neck
distal to anatomical neck
line
slight, elongated ridge
meatus
-tube-like channel that extends within a bone
-provides passage and protection for nerves and vessels
notch
bony depression that often stabilizes an adjacent bone
process
raised, sharp bony elevation where muscles and connective tissue attach
protuberance
bony projection
ramus
curved part of a bone that gives support to the rest of the bone
spine
sharp process
trochanter
large prominence on one side of a bone where large muscle groups and connective tissue attach
tuberosity
moderately-sized prominence where muscles and connective tissue attach; function similarly to trochanters
tubercle
small, rounded prominence where connective tissues attach