economic growth/policies
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
economic growth
an increase in national output as measured by rGDP
occurs in the long term or long term
short term economic growth
occurs when there are any changes to the components of AD (C+I+G+(X-M))
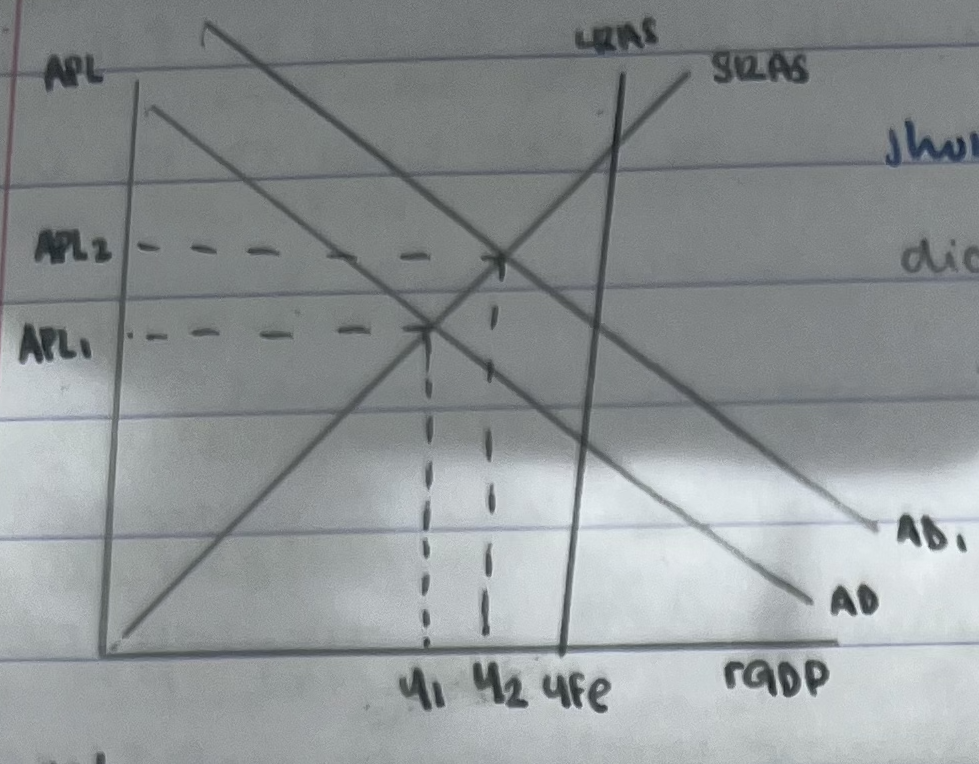
short term economic growth on AD/AS diagram
an increase in C,I,G, net exports has caused AD curve to shift to the right AD-AD1
the current real output has increased from y1-y2 which represents economic growth
increase in rGDP= economic growth
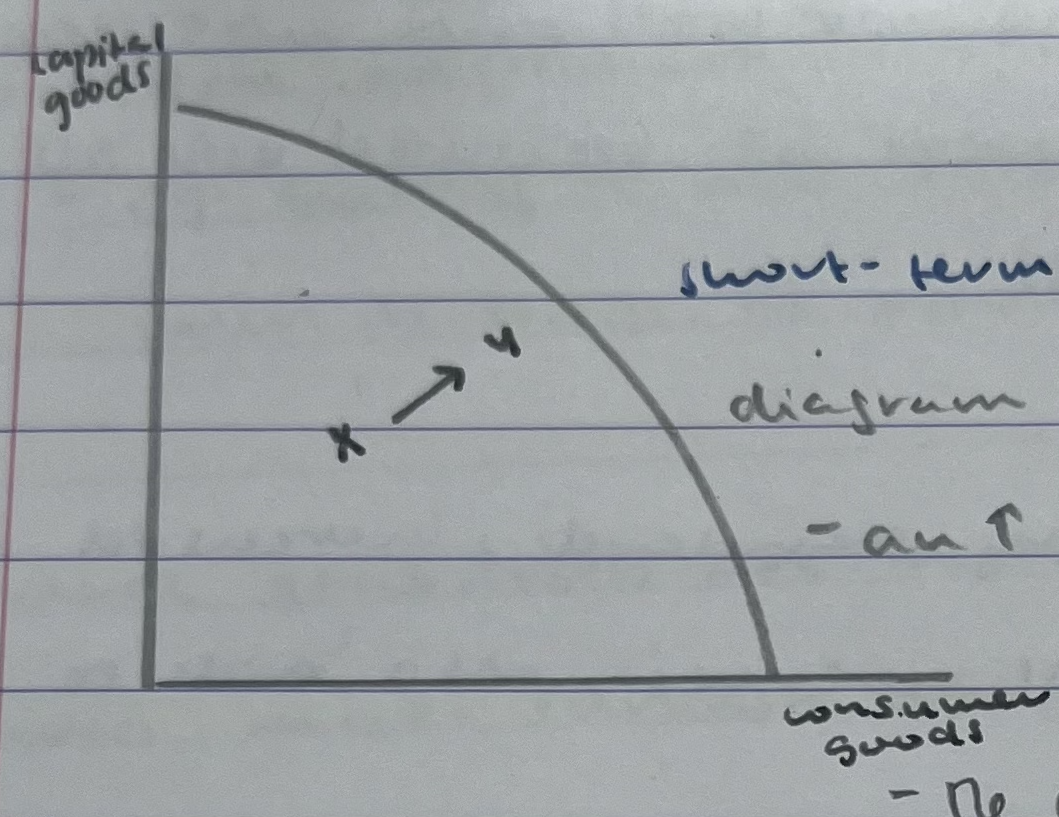
short term economic growth on PPC
an increase in production has caused a shift in the production combinations X-Y
the current real output has increased moving closer to the maximum possible output of the economy
represents an increase in rGDP
increase in rGDP= economic growth
long term economic growth
caused by any improvements to the determinants of AS
changes in quality and quantity of FOPs
technological advances
efficiency improvements
changes in institutions
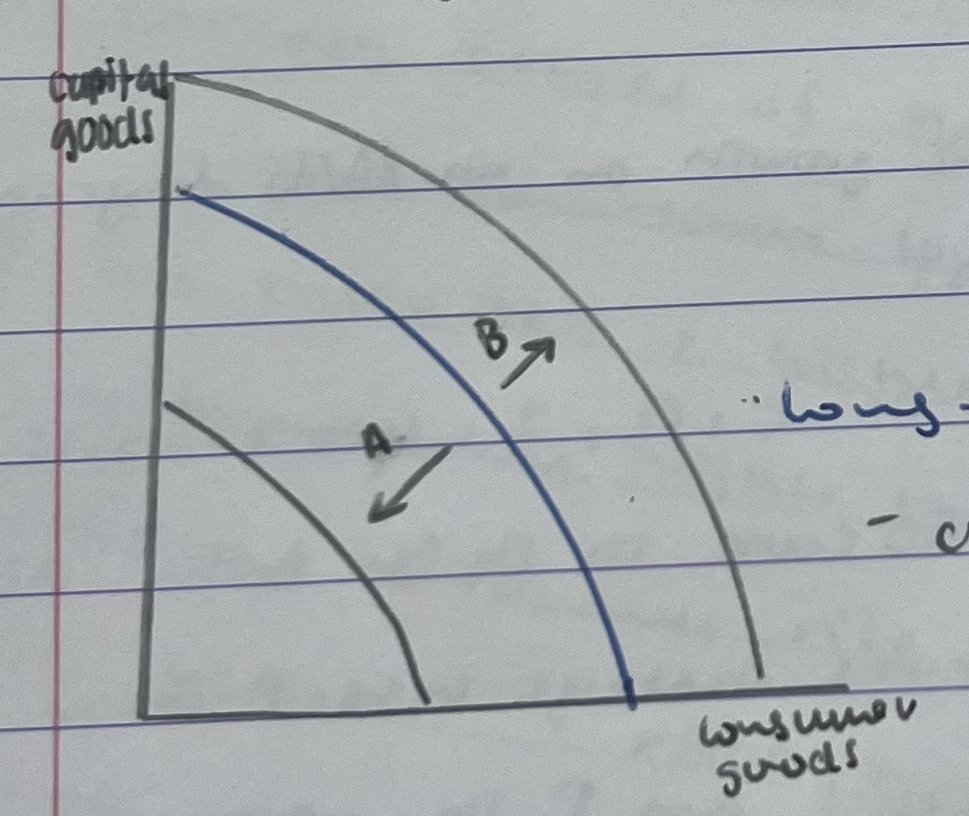
long term economic growth on PPC
changes in AS determinants have increased the potential output of the economy, demonstrated by the outward shift of the entire curve
more consumer and capital goods can now produced using all available resources
A: inward shift: economic decline
B: outward shift: economic growth
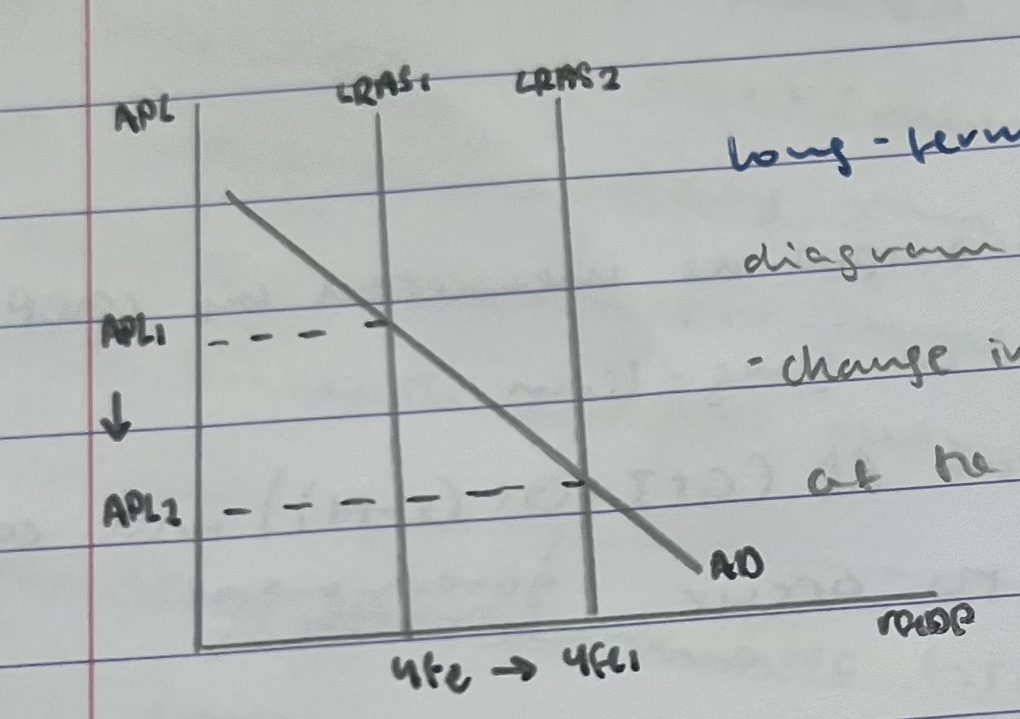
long term economic growth on an AD/AS diagram
changes in AS determinants have increased the potential output of the economy yfe-yfe1
what does economic growth lead to?
higher living standards
increased employment opportunities
improved government revenues
aids reduce poverty and inequality over time
nominal GDP ($)
C+I+G+(X-M)
using expenditure approach
rGDP($)
(nominal GDP/price deflator)x100
if < 100: deflation
if > 100: inflation
strengths of fiscal policy
spending can be targeted at specific industries
highly effective in restoring confidence in an economy during a deep recession
redistributes income through taxation
increased consumption of merit goods/services
automatic stabilizers
automatic fiscal changes, that occur as the economy moves through stages of the business cycle
in a recession: automatically lowers tax revenue, as income falls, households are taxed less + higher unemployment benefits = increase in rGDP
in a boom: automatically higher tax revenue due to the nature of progressive taxation - as income rises households are taxed more + less unemployment benefits + rGDP being lower
weaknesses of fiscal policy
political pressure: policies can fluctuate significantly when new governments are elected: long term projects such as infrastructure may lack follow-through
unsustainable debt: increased government spending can create budget deficits which are added to national debt
time lags: It is difficult to predict exactly when the desired effect on the economy will occur
fiscal policy will take longer time to plan and implement than monetary policy
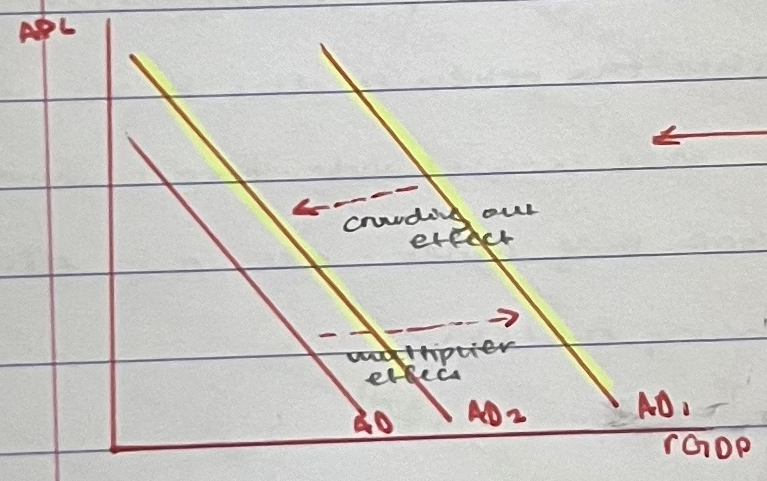
crowding out
the phenomenon where expansionary fiscal policy, particularly government spending can result in a reduction of private sector spending or investment
governments borrowing results in competition with others in the economy who want to borrow the limited amount of savings available
diagram:
private forms are crowded out of the market
as investment falls, AD shifts back to AD2
expansionary fiscal policy
when the government increases the money supply in the economy using budgetary instruments to either raise spending or cut taxes: generatce further economic growth
contractionary fiscal policy
occurs when the government raises the tax rates or cuts government spending, shifting AD to the left: slowing down economic growth
strengths of monetary policy
central banks can operate independently (without government intervention)
can consider the long-term outlook
takes less time than fiscal policy to plan and implement
contractionary policy is often effective when there is an inflationary gap
targets inflation and maintains stable prices
rate changes can quickly be condemned or reversed in necessary
weaknesses of monetary policy
C+I might be interest inelastic
limited effectiveness when the economy is in a deep recession
instead of borrowing, firms and consumers might simply repay debts
conflicting government objectives
falling growth might require expansionary monetary policy however high inflation might suggest contractionary monetary policy is needed
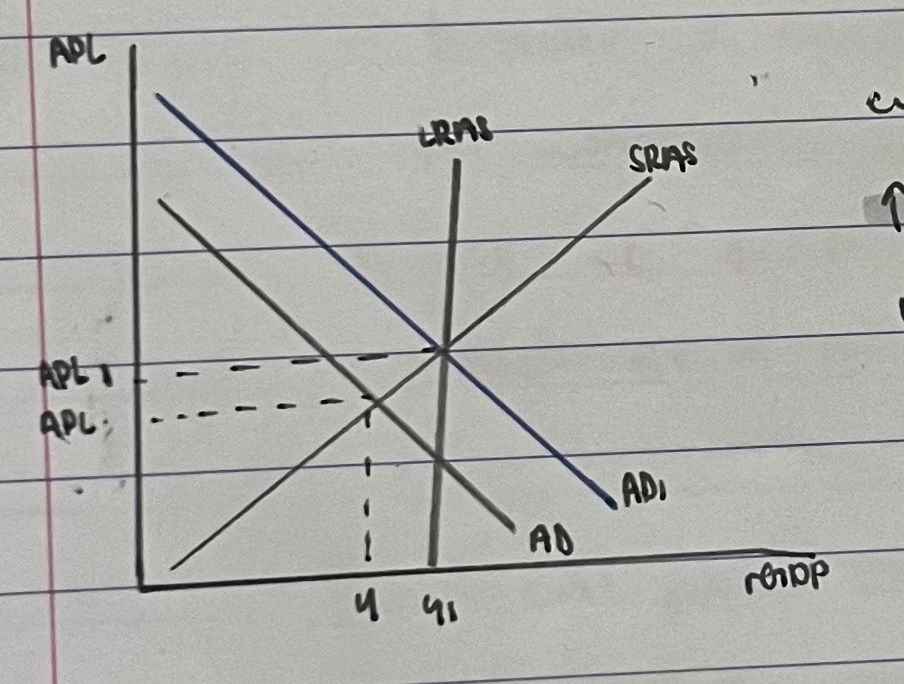
expansionary monetary policy diagram
economy if experiencing a deflationary gap
therefore, the central bank increases money supply
this decreases interest rates
which results in more people borrowing and investing
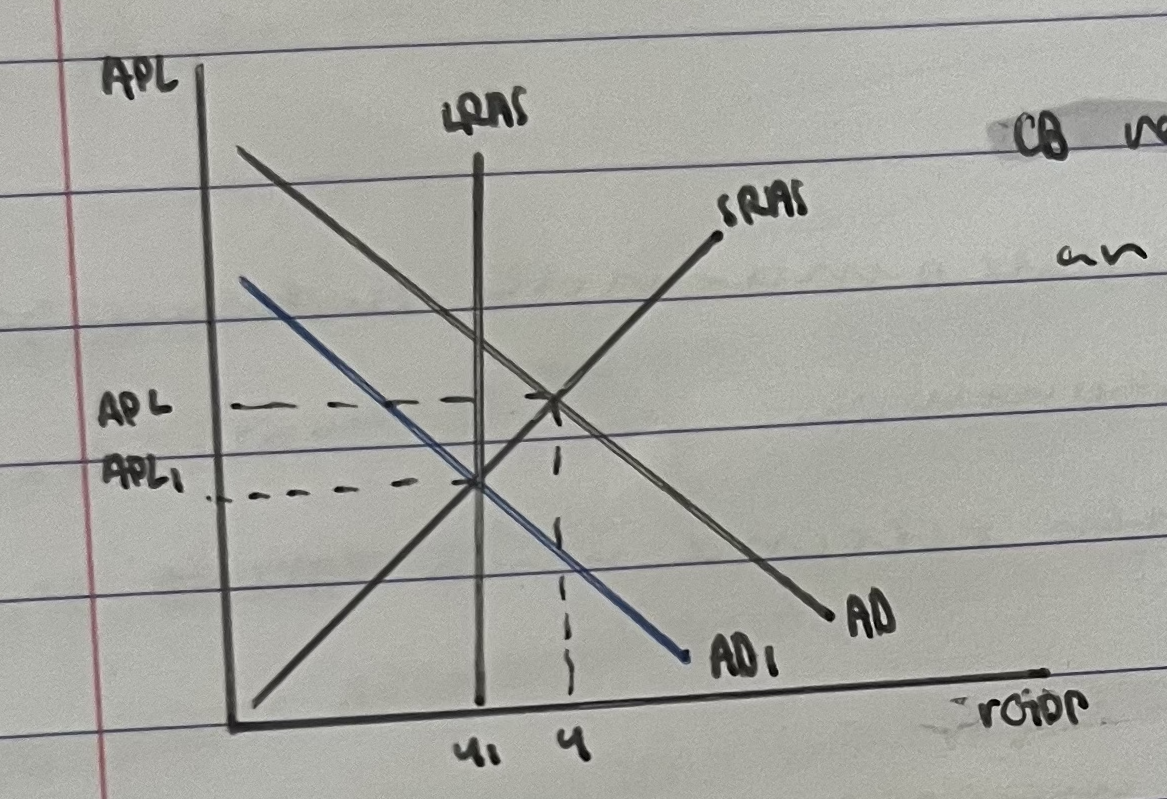
contractionary monetary policy diagram
central bank reduces money supply when the economy is experiencing an inflationary gap
expansionary monetary policy
expand monecy supply and boost economic activity by keeping interest rates low to encourage borrowing by consumers, individuals and banks
contractionary monetary policy
reduces government spending or rate of monetary expansion by cenmtral bank
monetary policy
the control of the quantity of money available in an economy and the channels by which new money is supplied
economic growth strengths
living standards:
increased income = better living standards
increased employment = resolves some of the social impacts of unemployment
income distribution:
decreased levels of absolute poverty
increased levels of employment = more tax revenue to redistribute or welfare payments
the environment
improvements in the quality/quantity of environmentally friendly tech
economic growth weaknesses
living standards:
rising AD causes demand-pull inflation and purchasing power of some people on fixed income might fall
increased income usually leads to greater consumption of demerit goods
income distribution:
lack of equity in the distribution of income - the rich get richer and the poor get poorer
environment:
damage caused by negative externalities of production and consumption
resources are depleted rapidly
constant price
price levels that have been adjusted for inflation
current prices
nominal price levels
challenges of sustaining economic growth
high inflation erodes purchasing power and can lead to uncertainty reducing investment and consumption
central banks must strike a balance between stimulating growth and controlling inflation through monetary policy
policies leading to short-term growth
expansionary fiscal
expansionary monetary
policies leading to long-term growth
supply-sside policies
market based
interventionist based
supply-side policies
government policies which seek to increase the productivity and efficiency of the economy
aim to increase long-term competitiveness and productivity
in the long run, supply-side policies can help increase the level of employment in an economy as firms expand and grow.
market based policies strengths
improved resource allocation: focus on improving the workings of the market system based on the operation of demand and supply, therefore expected to = in improved efficiency in resource allocation
may not burden the government budget: do not need government funds to be implemented as they are based on private initiative
ability to reduce inflationary gap
market based policies weaknesses
time lags
negative impacts on the environment
negative effects on equity
interventionist based supply-side policies weaknesses
time lags
negative impact on government budget: heavily based on government spending, therefore might create a budget deficit for the nation
interventionist based policies strengths
direct support of sectors important for growth
ability to create employment: enables workers to aquire skills, provide assistance to workers to relacate (structural)
potential ability to reduce inflationary gap
privatization
transfer of ownership of a firm from the public to the private sector
can increase efficiency due to improved management and operation of privatized firms
intervenstionist supply-side policies
presupposes that the free market economy alone cannot achieve the desired results in terms of increased potential output and therefore governments intervention is required