Cholesterol Metabolism
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
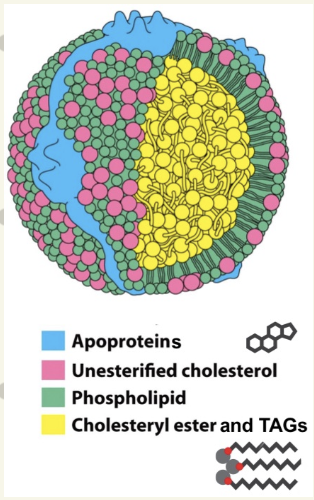
What are lipoproteins? what’s the structure?
transports TAG produced in liver into bloodstream
center: transport molecule carrying TAGs & Cholesterol esters
outside: thin monolayer of phospholipids & cholesterol
surface: apoproteins
what are cholesterol made from? what does it require? How is it regulated?
from acetyl-CoA using C from fat/protein/carbohydrate metabolism
requires NADPH & ATP
regulated by inhibiting HMB-CoA reductase via phosporylation / statins
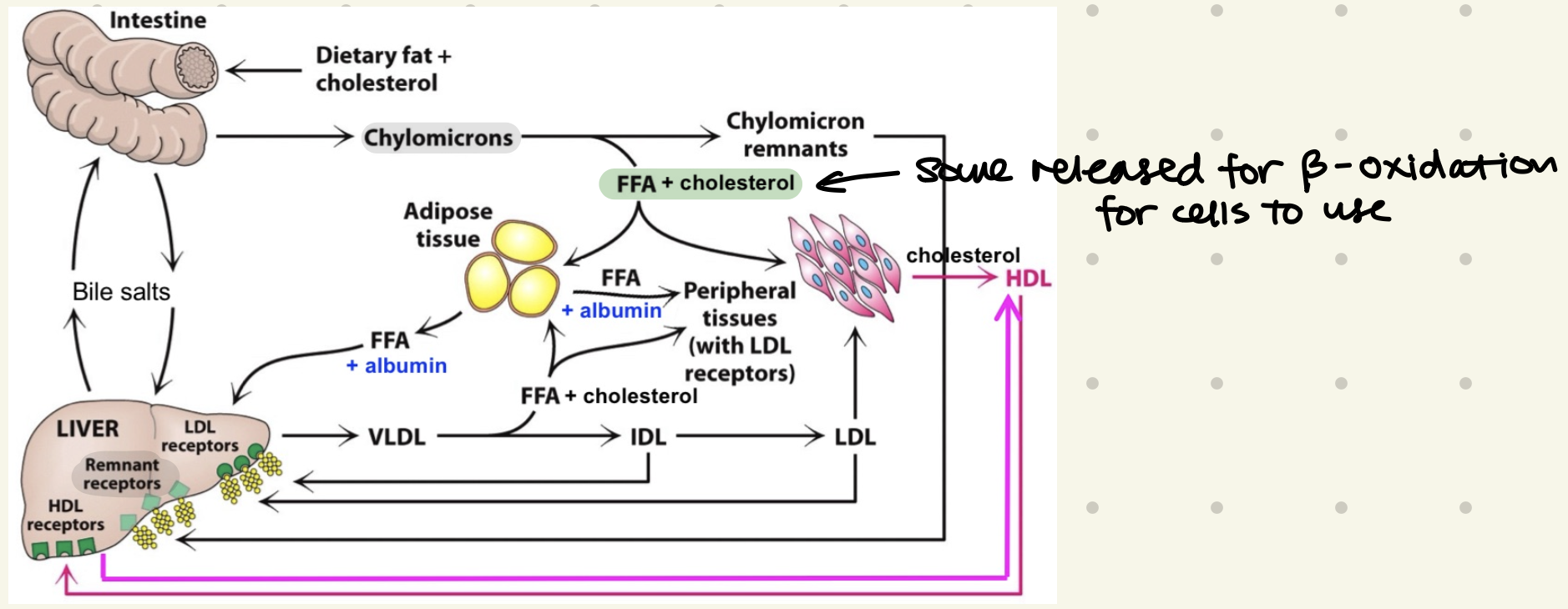
what are the 3 types of lipoproteins?
Chylomicrons
made in small intestine
largest
contain most TAGs
VLDL
sent by liver
distribute TAGs & cholesterol
binds lipoprotein lipase → hydrolyze & release TAGs
producing Intermediate Density Protein (IDL) → Low Density Protein (LDL) “bad cholesterol”
HDL
“good cholesterol”
contains LCAT enzyme → picks up cholesterol for transport back to liver (break down & recycling)
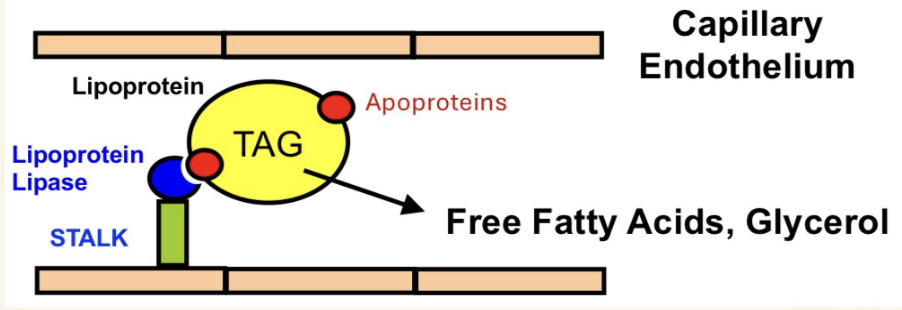
What is lipoprotein’s mechanism in circulation?
lipoprotein lipase (LPL) is located on capillary wall
bound by apoproteins (non-covalent)
LPL hydrolyzes TAGs into FFA & glycerol
what is the biochemical logic behind how exercise can lead to inhibition of fat synthesis via kinases?
exercise leads to:
⬆epinephrine → phosphorylation
⬆AMP (due to ATP hydrolysis) → activates AMP Kinase → phosphorylates ACC = ⬇malonyl-CoA = ⬆CATI activity = ⬆beta-oxidation = ⬆fat degradation = ⬇fat synthesis