A-Level Physics CIE
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Definition of radian
The measure of the angle subtended at the center of the circle when the radius is equal to the arc length/linear displacement.
Formula for angular speed
ω = dθ/dt = 2π/T
Formulae for tangential/linear speed
v = ωr
v = ds/dt
Formulae for centripetal acceleration
ac = v2/r
ac = ω2r
Formulae for centripetal force
Fc = mac
Fc = mv2/r
Fc = mω2r
Newton’s Law of Gravitation equation for the force between two point masses
Fg = GMm/r2
Newton’s Law of Gravitation definition
The force of attraction between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to their separation squared.
Terms of a satellite in a geostationary orbit
Orbits from West to East (WE)
Orbits directly above the equator
Has and orbital period of 24 hours
Gravitational Field definition
Force per unit mass
Equation for gravitational field strength due to a point mass
g = GM/r2 (M is mass of point mass pulling)
Define the gravitational potential at a point
The work done per unit mass in bringing a small test mass from infinity to the point.
Equation for T/K
θ/ °C + 273.15
Define specific heat capacity
The amount of thermal energy required to raise a substance by 1°C per unit mass.
Define specific latent heat
The amount of thermal energy required to change the state of a substance per unit mass without a change in temperature.
Give the equations of state for an ideal gas
pV = nRT
pV = NkT
What is the equation for the Boltzmann constant k?
R/NA (NA is Avogadro’s constant)
Give the basic assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases (hint: there are 5)
Gas particles are in continuous, random motion
Gas particles have negligible volume compared to the volume of the gas
There are negligible intermolecular forces between the particles, except during collisions
All collisions are perfectly elastic
Time of collisions are negligible in comparison with time between collisions
Formula for the average translational kinetic energy of a gas molecule.
3/2 kT
Define internal energy
The sum of a random distribution of kinetic and potential energies associated with the molecules of a system.
Equation for work done
W = pΔV (at constant pressure of surroundings)
First law of thermodynamics
ΔU = q + W
ΔU = increase in internal energy
q = energy transferred to system by heating
W = work done on the system
Define electric field
Force per unit positive charge.
Equation for force on a charge in an electric field
F = qE
Equation for field strength of the uniform field between charged parallel plates
E = ΔV/Δd (V is potential difference)
Equation for force between two point charges in free space.
Coulomb’s Law
F = Q1Q2 /(4πε0r2)
Electric field strength due to a point charge in free space
E = Q /(4πε0r2)
Define electric potential at a point
The work done per unit positive charge in bringing a small test charge from infinity to the point.
Relate electric field at a point to the potential gradient at that point.
E = - potential gradient = -ΔV/Δd
Equation for electric potential in the field due to a point charge
V = Q /(4πε0r)
Solution to the equation a = -ω²x
x = x₀ sin ωt
x₀ = amplitude
x = displacement
Simple harmonic motion definition
Occurs when acceleration is proportional to displacement from a fixed point and in the opposite direction.
Equation for the total energy of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion.
E = 1/2mω²x₀²
x₀ = amplitude
Define resonance.
The condition in which a maximum amplitude of oscillations occurs when an oscillating system is forced to oscillate at its natural frequency.
Define capacitance.
The ability of a conductor to store charge per unit potential difference.
Formula for capacitance.
C = Q/V
C = capacitance (in Farads, F)
Q = charge (in Coulombs, C)
V = potential difference (in Volts, V)
Formulae for electric potential energy.
W = 1/2QV = 1/2CV²
W = electric potential energy (in Joules, J)
Q = charge (in Coulombs, C)
V = electric potential (in Volts, V)
C = capacitance (in Farads, F)
Formulae for a the time constant for a capacitor discharging through a resistor.
τ = RC
τ = time constant (time take for V, Q, or I to drop to 37% of initial) (in seconds, s)
R = resistance of resistor (in ohms, Ω)
C = capacitance (in Farads, F)
Equation for force on a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
F = BIL sin θ
B = magnetic flux density of the field (in Tesla, T)
I = current in conductor (in Amperes, A)
L = length of conductor (in metres, m)
θ = angle of wire to field lines (°)
Define magnetic flux density.
The force acting per unit current per unit length on a wire placed at right-angles to the magnetic field.
Equation for force on a charge moving in a magnetic field.
F = BQv sin θ
B = magnetic flux density of the field (in Tesla, T)
Q = charge on particle (in Coulombs, C)
v = velocity of particle (in metres per second, m/s)
θ = angle of charge direction to field lines (°)
Define magnetic flux.
The product of the magnetic flux density and the cross-sectional area perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic flux density.
Formulae for magnetic flux.
Φ = BA
Φ = magnetic flux (in Weber, Wb)
A = cross-sectional area (in metres squared, m²)
B = magnetic flux density (in Tesla, T)
Faraday’s law of electomagnetic induction
E.m.f. produced is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage.
ε ∝ NΔΦ / Δt
ε = e.m.f. (in Volts, V)
N = number of turns of coils
Φ = magnetic flux (in Weber, Wb)
t = time taken (in seconds, s)
Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction
The induced e.m.f. is always in such a direction as to oppose the change producing it.
ε = -NΔΦ / Δt
ε = e.m.f. (in Volts, V)
N = number of turns of coils
Φ = magnetic flux (in Weber, Wb)
t = time taken (in seconds, s)
The correlation between mean power in a resistive load and the maximum power.
The mean power in a resistive load is half the maximum power for a sinusoidal alternating current.
Equation for Iᵣ.ₘ.ₛ.
Iᵣ.ₘ.ₛ. = I₀ / √2
Equation for Vᵣ.ₘ.ₛ.
Vᵣ.ₘ.ₛ. = V₀ / √2
Formula for energy of a photon
E = hf
h = Plank’s constant
f = frequency of light (Hz)
E = energy (eV or J)
Photoelectric emission formula.
hf = Φ + 1/2 mvmax 2
hf = energy of photon
Φ = work function energy of electron
De Broglie wavelength formula
λ = h / ρ
h = Plank’s constant
ρ = momentum of particle
Formula for change in energy level during absorption and emission line spectra
hf = E1 - E2
Define mass defect.
The difference between the mass of the nucleus and the mass of the nucleons separated to infinity.
Define binding energy.
The energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons.
Equation for the equivalence between mass and energy
E = mc²
E = energy in joules
m = mass (or change in mass) in kilograms
c = speed of light in meters per second
Define activity
Activity (A) is the decay per unit time.
Define decay constant
The decay constant (λ) is the probability that an individual nucleus will decay per unit time.
Give the activity equation
A = λN
A = activity ΔN/Δt
λ = decay constant
N = number of atoms left in sample
Define half-life
The time it takes for half radioactive atoms to decay.
Define the specific acoustic impedence of a medium
Z = ρc
ρ = density of medium
c = speed of sound wave in medium
Attenuation in matter formula
I₀ = intensity at beginning of medium
x = distance travelled by wave in medium
μ = attenuation coefficient/ absorption coefficient of the medium
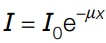
What tracer is used in positron emission tomography (PET scanning)?
Tracer that decays by β⁺ decay.
The inverse square law for radiant flux intensity F in terms of the luminosity L of the source.
F = L/(4πd²)
F = radiant flux intensity (W/m²)
L = luminosity of source
d = distance of source from observer
Wein’s displacement law
λmax ∝ 1/T
T = peak surface temperature of a star (K)
λmax = wavelength of peak emission intensity
Hubble’s Law
v ≈ H₀d
v = recessional velocity of the galaxy (m/s)
H₀ = Hubble constant
d = distance to the galaxy (m)