physics 30 - atomic physics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
john dalton
proposed that matter is composed of indivisible particles
* billiard ball model
* billiard ball model
2
New cards
eugene goldstein
* experimented with gas-discharge tubes attached to high voltage induction coils where electrons travelled from the cathode to the anode
* conducted experiments on the geissler beam and gave it the name cathode ray
* found that the cathode ray travelled through thin metal foils and travelled much further through air than atoms, thus concluding that cathode rays were very small in mass
* discovered the proton
* conducted experiments on the geissler beam and gave it the name cathode ray
* found that the cathode ray travelled through thin metal foils and travelled much further through air than atoms, thus concluding that cathode rays were very small in mass
* discovered the proton
3
New cards
william crookes
* performed an experiment called the bent tube experiment using an L-shaped tube
* found that the cathode ray beam was most intense at the elbow of the tube, confirming that cathode rays travel in straight lines
* also found that when a magnet was introduced near the beam of cathode rays, they bent in a direction indicating they were negatively charged particles
* found that the cathode ray beam was most intense at the elbow of the tube, confirming that cathode rays travel in straight lines
* also found that when a magnet was introduced near the beam of cathode rays, they bent in a direction indicating they were negatively charged particles
4
New cards
jj thomson
* proposed plum pudding model
* designed a special cathode ray tube that allowed the beam to be exposed to magnetic and/or electric fields
* the path of the cathode ray is straight and horizontal, indicating that gravity has very little effect, so cathode rays must have a very small mass
* **Fe = Fm - determine speed of cathode rays**
* **Fm = Fc - once speed is measured, the electric field is turned off and the radius of curvature can be measured**
* thomson confirmed the particle produced by goldstein in his geissler tube was a proton
* renamed cathode rays electrons
* designed a special cathode ray tube that allowed the beam to be exposed to magnetic and/or electric fields
* the path of the cathode ray is straight and horizontal, indicating that gravity has very little effect, so cathode rays must have a very small mass
* **Fe = Fm - determine speed of cathode rays**
* **Fm = Fc - once speed is measured, the electric field is turned off and the radius of curvature can be measured**
* thomson confirmed the particle produced by goldstein in his geissler tube was a proton
* renamed cathode rays electrons
5
New cards
millikan
* conducted a series of experiments known as the **oil drop experiments** where a negatively charged oil drop is introduced between two charged plates
* millikan discovered the elementary charge
* combining millikan’s and thomson’s discoveries, we can find the mass of a proton and electron
* when forces are balanced: Fg = Fe
* millikan oil with acceleration: fnet = ma = Fe - Fg
* millikan assumed that:
1. all electrons are identical - same charge
2. the mass of each electron is so small that +/- of a few will not significantly change the mass of the oil droplet
3. the amount of charge on the oil droplet will be whole a number multiple of the charge of one electron
* millikan discovered the elementary charge
* combining millikan’s and thomson’s discoveries, we can find the mass of a proton and electron
* when forces are balanced: Fg = Fe
* millikan oil with acceleration: fnet = ma = Fe - Fg
* millikan assumed that:
1. all electrons are identical - same charge
2. the mass of each electron is so small that +/- of a few will not significantly change the mass of the oil droplet
3. the amount of charge on the oil droplet will be whole a number multiple of the charge of one electron
6
New cards
ernest rutherford
* proposed the planetary model
* began a series of experiments to verify thomson’s atomic model known as the **gold foil scattering experiments**
* gold foil was used because it could be pounded down to a layer only a few atoms thick
* alpha particles were fired at the gold foil. behind the gold foil was a zinc sulfide screen. any particle hitting the zinc sulfide caused a glow of light which could be observed
* many alpha particles were deflected including some at large angles, making rutherford’s experiment **not supportive** of thomson's model
to account for disparities, rutherford proposed a nuclear atom where most of the mass and all of the positive charge was concentrated at the center of the atom and that the electrons orbited around the positive nucleus
* began a series of experiments to verify thomson’s atomic model known as the **gold foil scattering experiments**
* gold foil was used because it could be pounded down to a layer only a few atoms thick
* alpha particles were fired at the gold foil. behind the gold foil was a zinc sulfide screen. any particle hitting the zinc sulfide caused a glow of light which could be observed
* many alpha particles were deflected including some at large angles, making rutherford’s experiment **not supportive** of thomson's model
to account for disparities, rutherford proposed a nuclear atom where most of the mass and all of the positive charge was concentrated at the center of the atom and that the electrons orbited around the positive nucleus
7
New cards
light spectra
patterns produced when light is either dispersed through an equilateral glass prism or is diffracted apart by a diffraction grating - i.e. light is separated into its colours
8
New cards

continuous spectrum
* when a solid or liquid is heated up, white light is emitted.
* when this light passes through a prism it is dispersed into its colours
* the short wavelengths (violet, blue) are refracted more by the prism than the longer wavelengths (orange, red)
* result is continuous spectrum of light from violet to red
* when this light passes through a prism it is dispersed into its colours
* the short wavelengths (violet, blue) are refracted more by the prism than the longer wavelengths (orange, red)
* result is continuous spectrum of light from violet to red
9
New cards
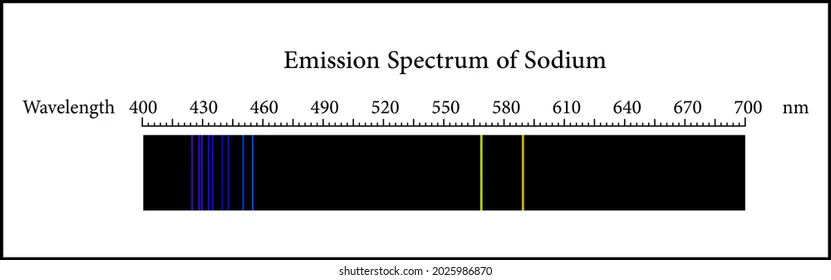
emission / bright-line spectrum
* gases will produce light when heated to a high temperature
* they produce a spectrum that is composed of bright coloured lines against a black background
* the colour and locations of the bright lines are different when different gases are used
* they produce a spectrum that is composed of bright coloured lines against a black background
* the colour and locations of the bright lines are different when different gases are used
10
New cards
spectral analysis
* each gas has a characteristic bright line spectrum so elements can be identified by their spectrum
* elements like cesium and rubidium were discovered using this technique
* elements like cesium and rubidium were discovered using this technique
11
New cards
fraunhofer lines
hundreds of dark lines formed on the continuous solar spectrum
12
New cards
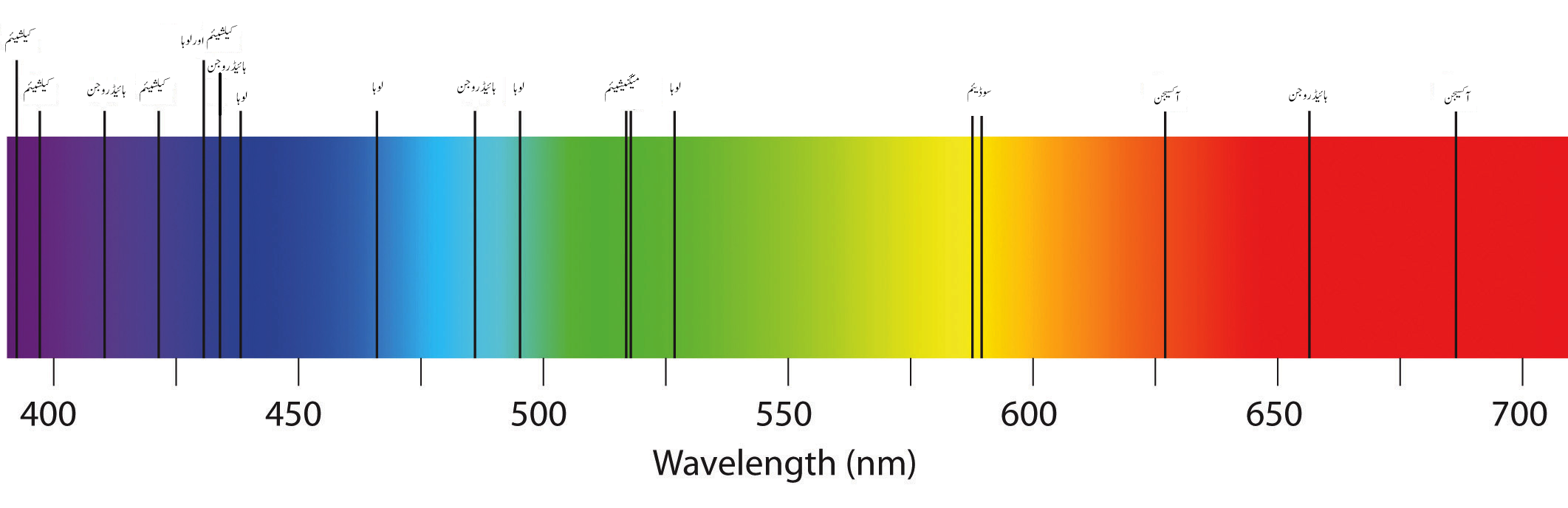
absorption / dark-line spectrum
when white light is passed through a cold, dilute gas and then allowed to go through a prism, an absorption spectrum is produced
* the chemical composition of the outer region of the sun and of distant stars and galaxies has been determined by this process
* the chemical composition of the outer region of the sun and of distant stars and galaxies has been determined by this process
13
New cards
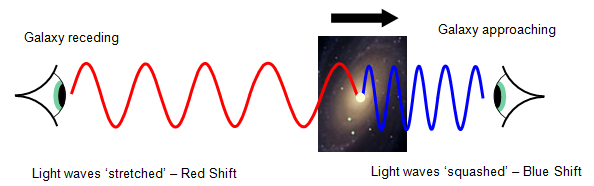
doppler effect
when spectra were recorded and analyzed from galaxies, it was found they were shifted from their normal positions
* some were shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum, while others were shifted toward the red
* some were shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum, while others were shifted toward the red
14
New cards
red-shifted
indicates the galaxy was moving away (stretched, longer wavelength)
* the vast majority of galaxies are red-shifted, indicating we live in an expanding universe (big bang theory)
* the vast majority of galaxies are red-shifted, indicating we live in an expanding universe (big bang theory)
15
New cards
blue-shifted
indicates movement towards Earth (squished, shorter wavelength)
16
New cards
why are there always more lines in the emission spectrum than in the absorption spectrum?
17
New cards
franck - hertz experiment
the experiment consisted of gradually increasing the accelerating voltage and, for each value, measuring the electric current passing through the mercury vapour and collected by the plate.
* as the accelerating voltage was increased slowly from zero, the current gradually increased as well
* then, at voltages of 4.89V, 6.67V, 8.84V and 9.8V the current drops
the results indicated that for certain values of electron energy, the electrons do not “make it” through the mercury vapour
* as the accelerating voltage was increased slowly from zero, the current gradually increased as well
* then, at voltages of 4.89V, 6.67V, 8.84V and 9.8V the current drops
the results indicated that for certain values of electron energy, the electrons do not “make it” through the mercury vapour
18
New cards
19
New cards
20
New cards
21
New cards
22
New cards
23
New cards
24
New cards
25
New cards