Vocal Ped midterm
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
phonation happens during
adduction
respiration happens during
abduction
bernoulli principle
bigger space (lungs/vocal tract) has lower velocity and higher pressure while smaller space (larynx) has higher velocity and lower pressure, forcing the vocal folds to adduct (with help from muscles)
thyroid cartilage
The largest cartilage in the larynx, commonly known as the Adam's apple, that provides structure and protection for the vocal folds.
cricoid cartilage
A ring-shaped cartilage located below the thyroid cartilage in the larynx, providing support and structure to the airway and serving as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments.
hyoid bone
A U-shaped bone located in the neck, serving as an anchor for the tongue and supporting the larynx.
thyroarytenoid muscle
A muscle in the larynx that plays a crucial role in voice production by adjusting the tension of the vocal folds. (aka TA/vocalis muscle)
cricothyroid muscle
A muscle in the larynx that alters the tension of the vocal folds by moving the cartilages, lengthens folds to affect pitch
interarytenoids
Muscles in the larynx that aid in the adduction of the vocal folds by bringing the back of the arytenoids together (aids LCA)
cricoarytenoids
Muscles in the larynx that control the opening and closing of the vocal folds, essential for regulating airflow during phonation.
lateral cricoarytenoids
assist in adduction by swiveling the arytenoid cartilages to bring the vocal folds together
posterior cricoarytenoids
muscles in the larynx that work in opposition to abduct the vocal folds by moving the arytenoid cartilages apart, allowing for increased airflow during breathing.
pitch change is caused by
length change via the CT muscle
loudness/intensity change is caused by
change in vocal fold thickness and breath pressure (TA muscle)
vocal register
a series of contiguous pitches produced in the same way with the same timbre
Mode 1
vocal register characterized by thicker and shorter folds, a lower more robust sound, and the TA/vocalis muscle
Mode 2
a vocal register characterized by a higher sound, utilizes the CT muscle to stretch the folds
range
all the notes an individual can produce
tessitura
the range of pitches that once can sing most comfortably and that sound the best
passaggio
vocal event in which a threshold is reached in the voice, triggers a change in production (minor ones every 3-4 half steps)
resonance
intensification and enrichment of a musical tone by supplementary vibration
belt
a quality of sound over top of production, NOT a type of production
the vocal tract is comprised of
the pharynx (back of throat), oral cavity, and nasal cavities
harmonics are produced where?
the vocal folds, happen first and come from the source
formants are produced where?
the vocal tract, resonance of the filter, based on the shape of the resonator
what is the singer’s formant?
creates a resonant sound by clustering together F3,4,5 so one can sing over instruments or in large spaces, creates a ringing quality, likely produced in the space between the vocal folds and the epiglottis
what happens when formants are in alignment with harmonics?
sound waves are amplified rather than attenuated, determines perceived vowel sound and tone quality
what is the glottis?
the space between the vocal folds when abducted
the thyrohyoid membrane and cricothyroid membrane do what?
hold the cartilages and bone together (thyro+hyoid, crico+thyroid)
where are the two major passaggios (primo + secondo)?
at the top of the chest voice (mode 1) and bottom of head voice (mode 2), primo is higher than secondo
how many registers does McCoy suggest there are?
two
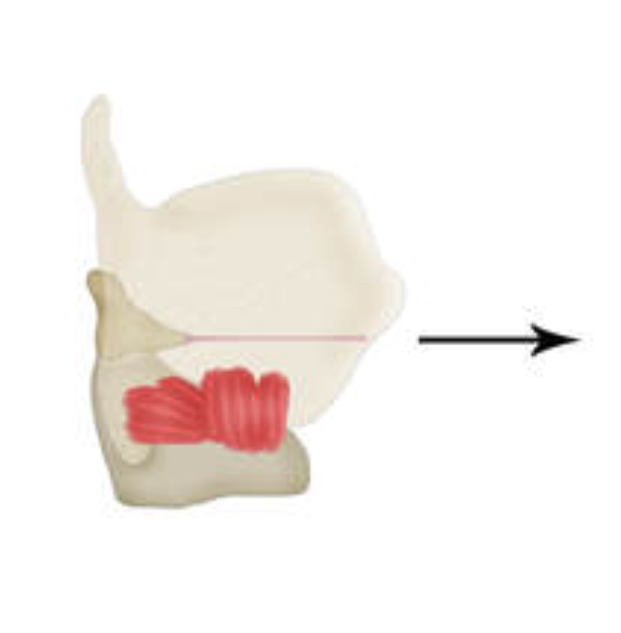
what is this muscle? what does it do?
cricothyroid (CT), stretches vocal folds
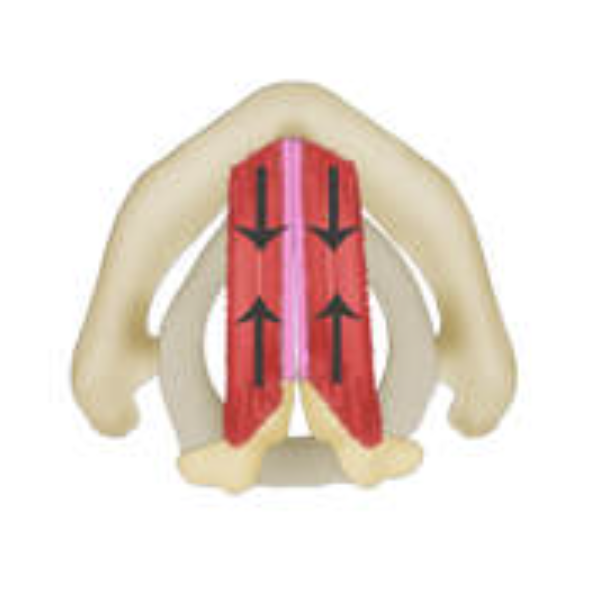
what is this muscle? what does it do?
thyroarytenoid (TA), thickens vocal folds
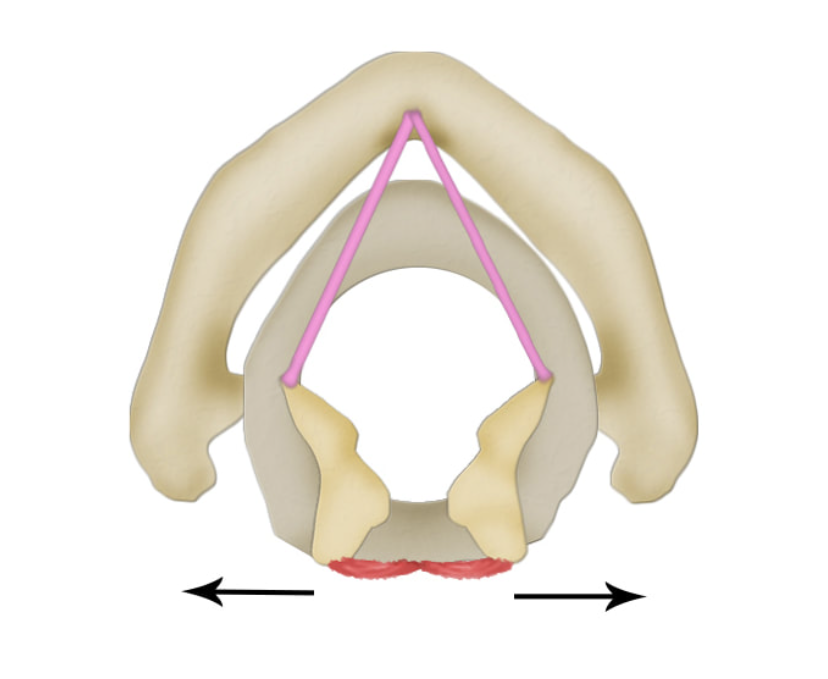
what is this muscle? what does it do?
posterior cricoarytenoid (PCA), opens/abducts
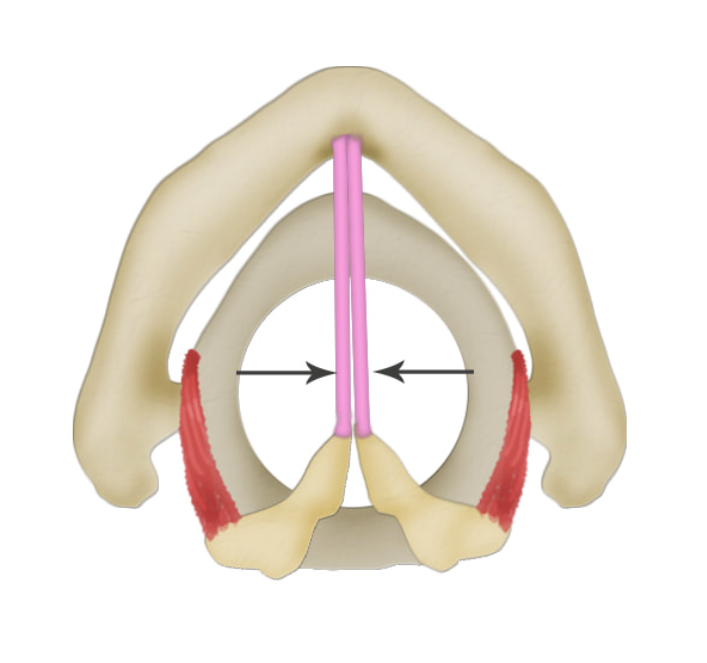
what is this muscle? what does it do?
lateral cricoarytenoid (LCA), brings together/ adducts
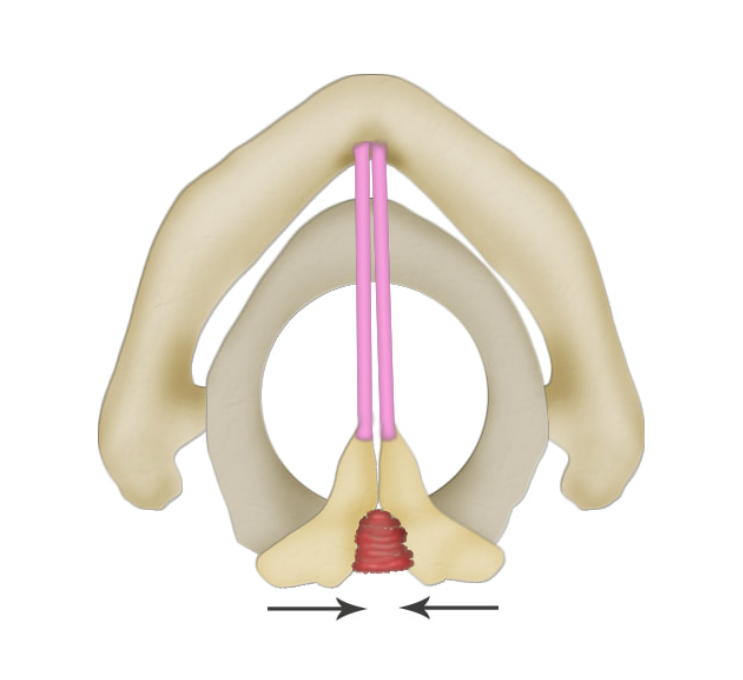
what is this muscle? what does it do?
interarytenoid (IA), brings together/ adducts
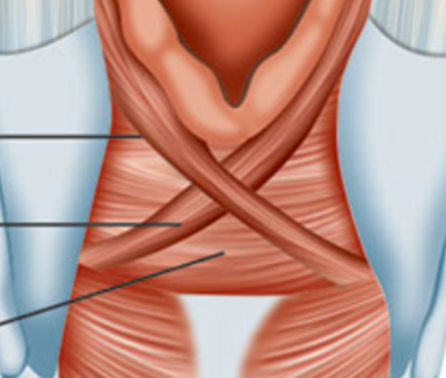
what are these muscles? (sorry this is a bad pic)
transverse and oblique arytenoids, close the larynx and adjust vocal folds