Pancreas pathology
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
What is pancreatitis?
Inflammation of the pancreas
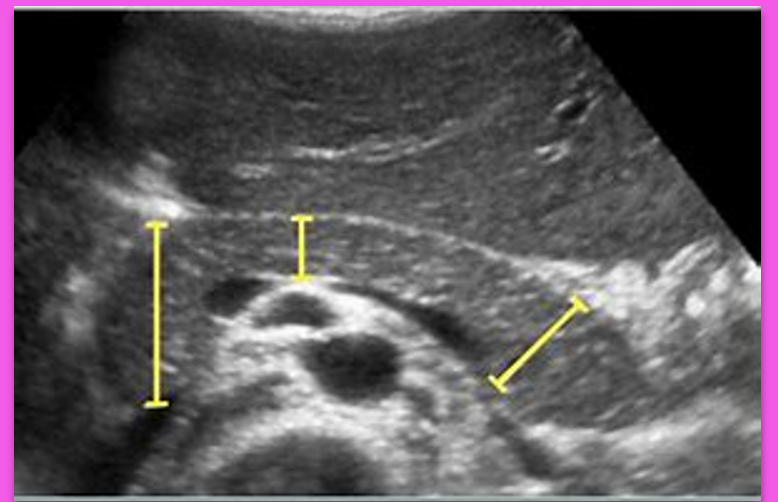
Normal measurements of the Pancreas are:
Head: ____ cm
Neck: ____ cm
Tail: _____ cm
3
2
2
Pancreatitis may be ______ or _______
Acute; chronic
Pancreatitis occurs when pancreas becomes _______ and _______ s a result of increased _______ and _______ of ducts
damaged; malfunctions; secretion; blockage
_________ occurs when pancreas becomes damaged and malfunctions as a result of increased secretion and blockage of ducts
Pancreatitis
Acute Pancreatitis is caused by inflamed ______ releasing pancreatic _______ into the surrounding pancreatic _______
Acini; enzymes; tissue
_____ pancreatitis does not last more than several days
Acute
A patient with _____ pancreatitis may be at risk for ______ and _______ secondary to the pancreatitis
acute; abscess; hemorrhage
The most common cause of pancreatitis in the United states is ______ tract disease
biliary
_______ abuse is the _____ most common cause of pancreatitis
Alcohol; second
Gallstones are present in _____ to _____ of patients, and ____ of patients with gallstones have ______ pancreatitis.
40%;60%; 5%; acute
________ are present in 40% to 60% of patients, and 5% of patients with _______ have acute pancreatitis
Gallstones; gallstones
Less common causes of pancreatitis are:
Tra____
Inflammation from adjacent peptic _____
______ infection
Pre______
Mu______
Tu______
Con_______ causes
Vas_______ thrombosis
Em______
Dr_______
Trauma
Inflammation from adjacent peptic ulcer
Abdominal infection
Pregnancy
Mumps
Tumors
Congenital causes
Vascular thrombosis
Embolism
Drugs
An _____ attack of pancreatitis is commonly related to _______ tract disease and ________
Acute; biliary; alcoholism
______ pancreatitis symptoms begin with ______ pain that occurs after a ______ meal or ______ binge
Acute; severe; large; alcohol
Serum _______ rises within 6 to 12 hours of the onset of _____ pancreatitis.
Amylase; acute
Serum amylase _____ within ____ to _____ hours of the onset of acute pancreatits
rises; 6;12
Serum _____ rises within 4 to 8 hours of the onset of symptoms for acute pancreatitis
lipase
Serum lipase _____ within ___ to ____ hours of the onset of symptoms for _____ pancreatitis
Rises; 4;8; acute
Acute pancreatitis may go on to develop other complications:
P______ formation
F____/pa_____/bl_____ vessel necrosis
Ab____
He______
Du______ obstruction
Pseudocyst formation
Fat/parenchymal/blood vessel necrosis
Abscess
Hemorrhage
Duodenal obstruction
_____ pancreatitis may go on to develop other complications:
Pseudocyst formation
Fat/parenchymal/blood vessel necrosis
Abscess
Hemorrhage
Duodenal obstruction
Acute
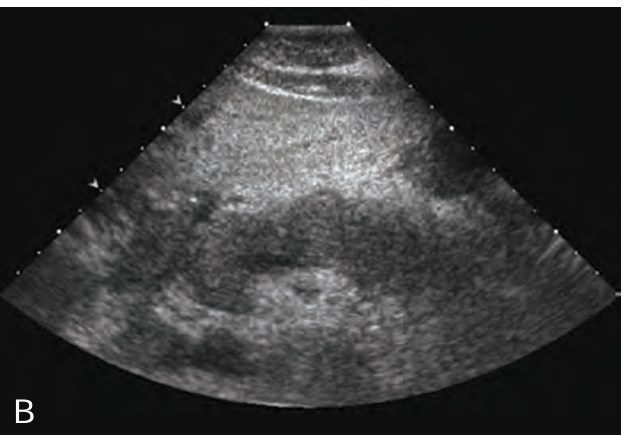
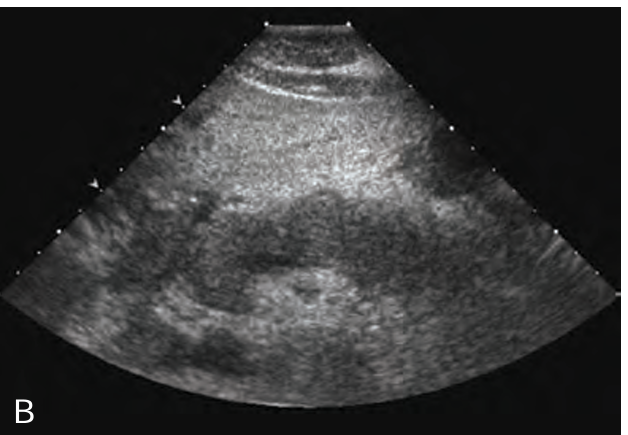
In the early stages of _____ pancreatitis, the sonographic appearance of the gland may _____ show _______ on sonography.
acute; NOT; swelling
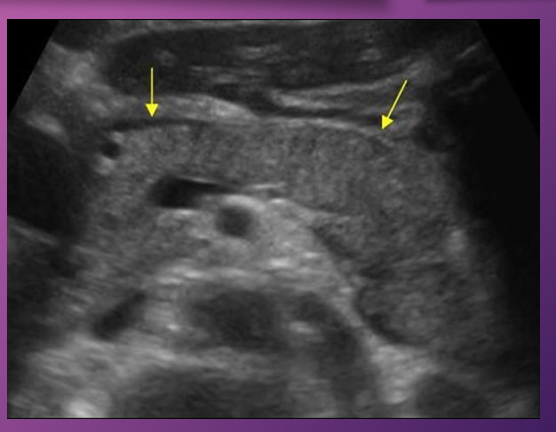
When swelling does occur in acute pancreatitis, the sonographic appearance of the gland becomes ______ to _____ and is less _____ than the ______
hypoechoic; anechoic; echogenic; liver
When _____ does occur in _____ pancreatitis, the sonographic appearance of the gland becomes hypoechoic to anechoic and is less echogenic than the liver
Swelling; acute
_____ pancreatitis will have somewhat ______ but ________ borders, sonographically.
Acute; indistinct; smooth
Acute pancreatitis will have somewhat indistinct but smooth ______, sonographically
Borders
The pancreatic duct may be obstructed in acute pancreatitis due to ________, ______, ______, swelling of the ______, or _______ formation
inflammation, spasm, edema, papilla, pseudocyst
The pancreatic duct may be _______ in _____ pancreatitis due to inflammation, spasm, edema, swelling of the papilla, or pseudocyst formation
obstructed; acute
____-_______ fluid collection with ______ pancreatic enzymes is ______ suggestive of _____ pancreatitis
Peri-pancreatic; abnormal; acute; acute
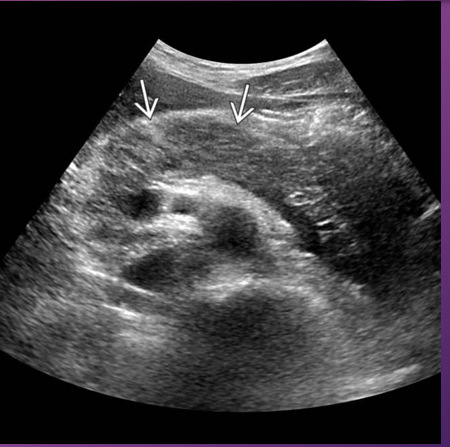
_____ pancreas is more easily _____ because of ____ body fat to interfere with visualization
Pediatric; seen; less
Normally, LLL is more ______ and pancreatic gland is more _____ than ________
prominent; isoechoic; hyperechoic
With ____ pancreatitis in children, the gland is _____ with _____ pattern and an _______ outline
acute; enlarged; hypoechoic; indistinct
Findings of _____ collections and _____ are common with ______ acute pancreatitis
fluid; edema; severe
The most common sites for fluid collections are found in the lesser _____, anterior _______ spaces , me______, ______ spaces, and __________ soft tissue spaces.
sac; pararenal; mesocolon; perirenal; peripancreatic
The formation of pseudocyst occurs when the fluid collection develops into a well-_____,______-off fluid collection of _______
defined; wall; amylase
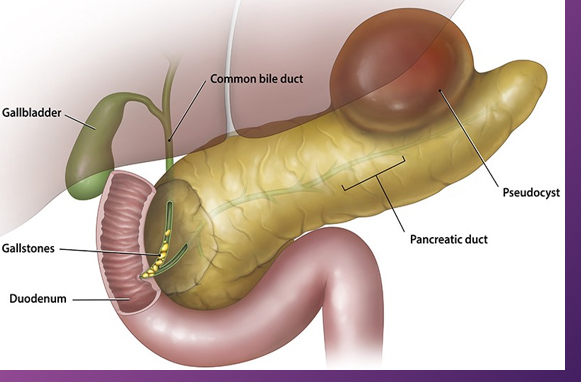
A ______ is a collection of fluid that arises from the loculation of ________ processes, _______, or _______
pseudocyst; inflammatory; necrosis; hemorrhage
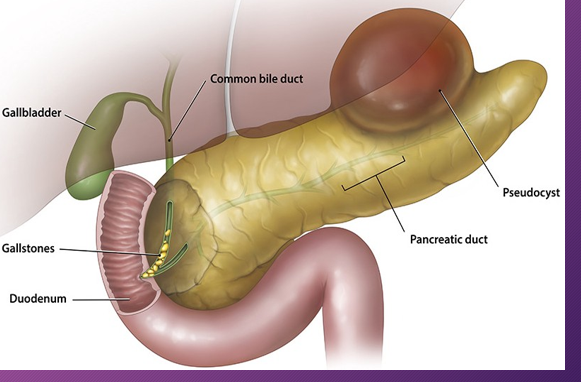
A pancreatic ______ is a ___-filled mass that develops ______ of the pancreas
pseudocyst; fluid; outside
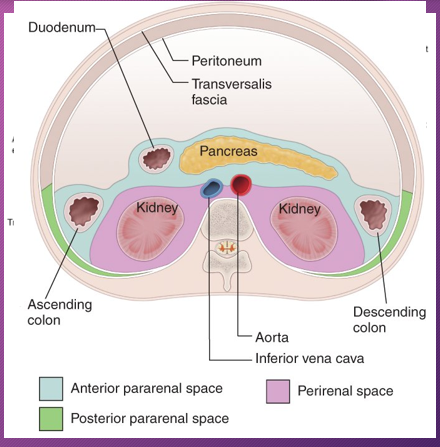
The most common location of a pseudocyst is in the ______ sac ______ to the _______ and ______ to the _______
lesser; anterior; pancreas; posterior; stomach
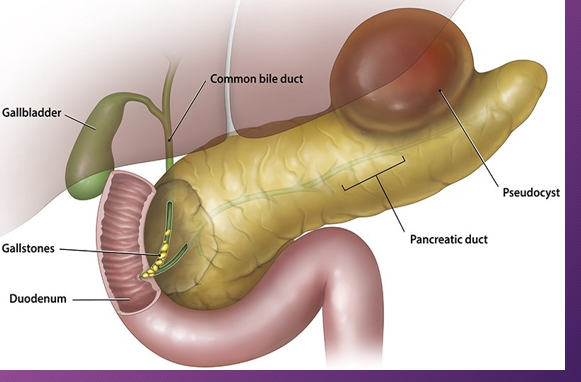
A ______ is a result from _____ to the gland or _______
pseudocyst; trauma; pancreatitis
A _______ takes contour of the available _____ around them
pseudocyst; space
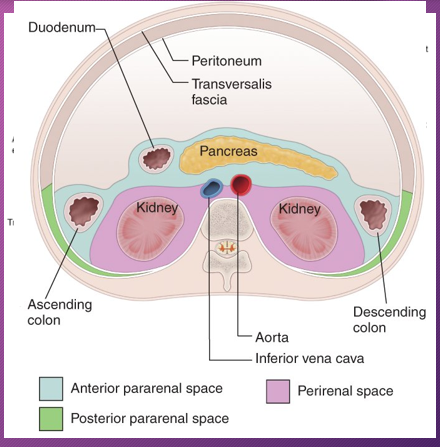
The second most common location of a pseudocyst is the _____ _____ space that is _______ to the _____ sac and bounded by ______ fascia
anterior; pararenal; posterior; lesser; Gerota’s
______ occurs more commonly in the _____ pararenal space than in the _______
Fluid; LEFT; right
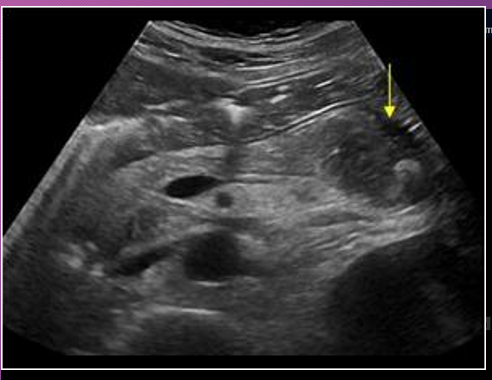
Sonographically, pseudocysts appear as ____-_____ masses, _______ with increase through _______
well-defined; anechoic; transmission
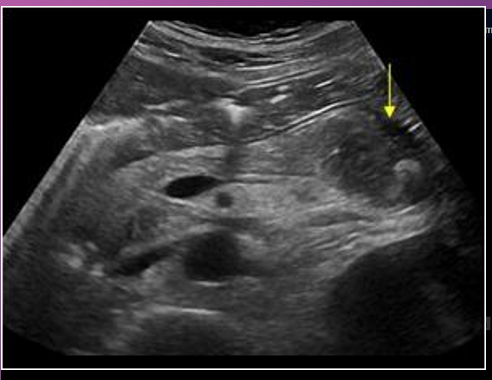
______ seen within the pseudocyst may occur from complications of ______ or _______
Debris; infection; hemorrhage
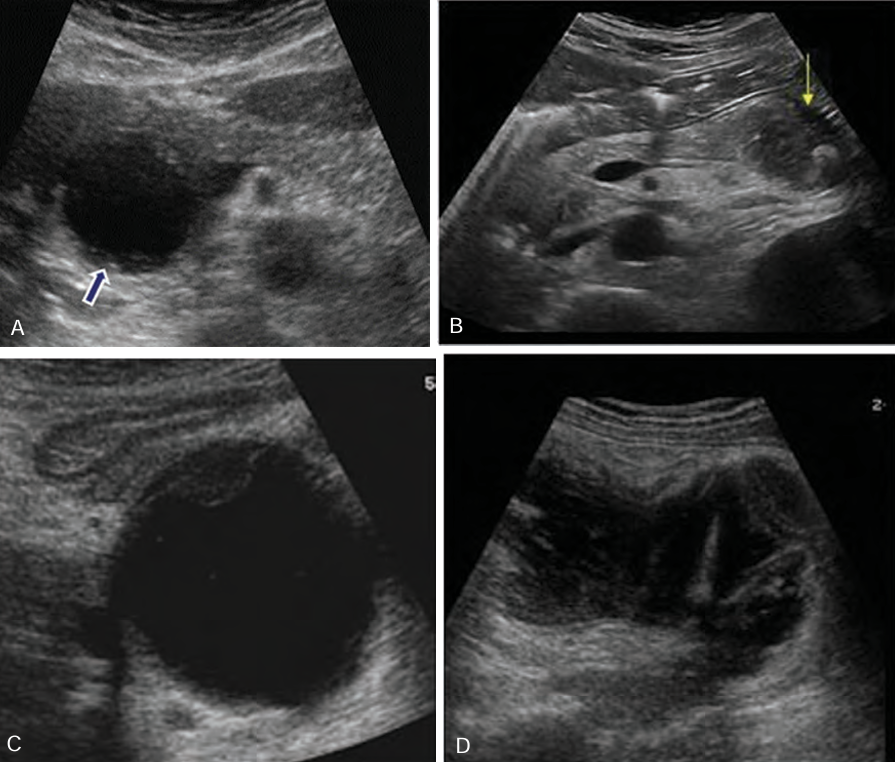
Borders of pseudocysts are very _______, and they usually are _____ than other simple cysts. ________ may develop _____ the walls of the pseudocyst
echogenic; thicker; Calcification; within
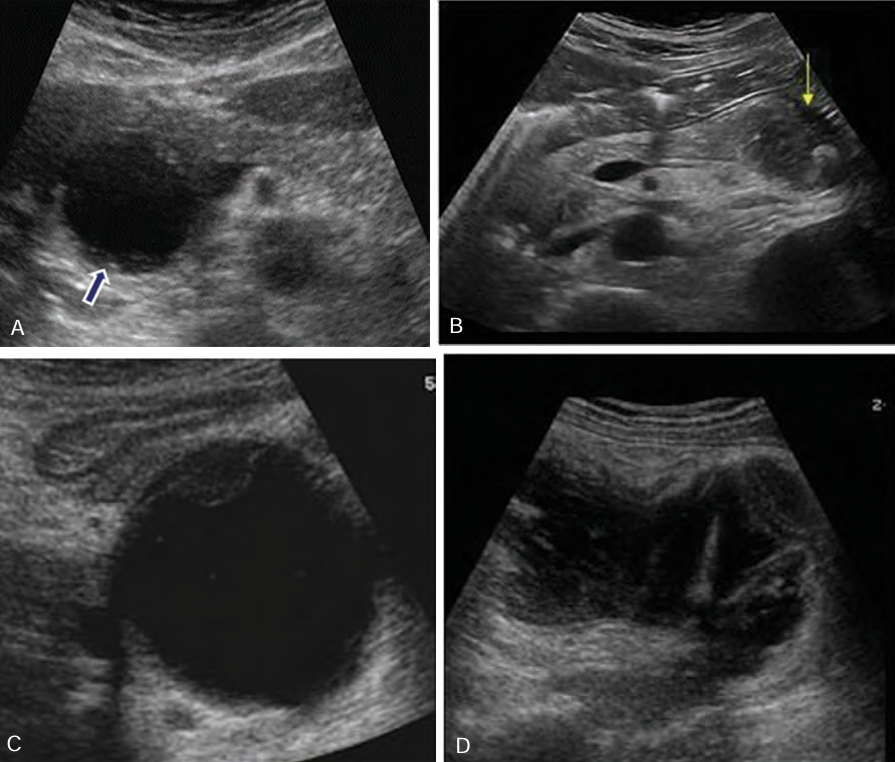
When a suspected pseudocyst is located near the stomach, the stomach should be _______ so the cyst is not ______ for a _____-filled stomach
drained; mistaken; fluid
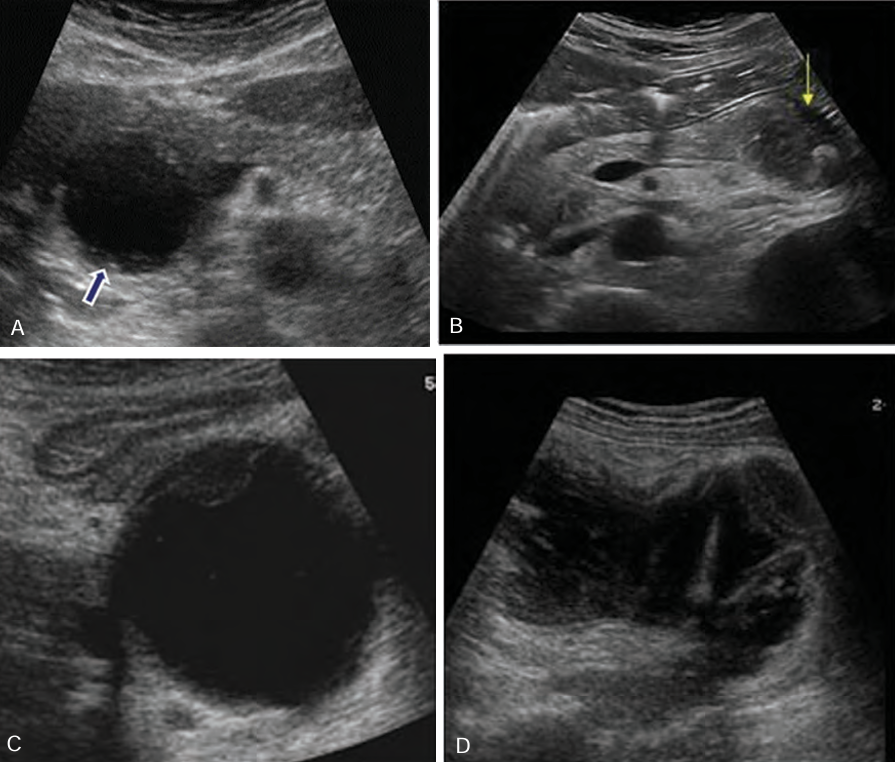
Be sure not to confuse a fluid filled stomach with what?
Pseudocyst
A ________ rupture is the most common complication of a pancreatic ________, occurring in ____ of patients.
Spontaneous; pseudocyst; 5%
Clinical symptoms of a _______ rupture of a pancreatic pseudocyst are _____ and _______.
spontaneous; pseudocyst; shock; peritonitis
The mortality rate of a _______ rupture is _____
spontaneous; 50%
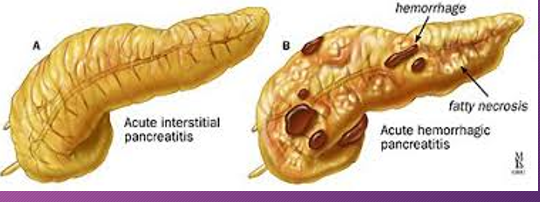
Hemorrhagic pancreatitis is a rapid progression of ______ pancreatitis with _______ of pancreatic ______ and subsequent __________
rapid; acute; rupture; vessels; hemorrhage
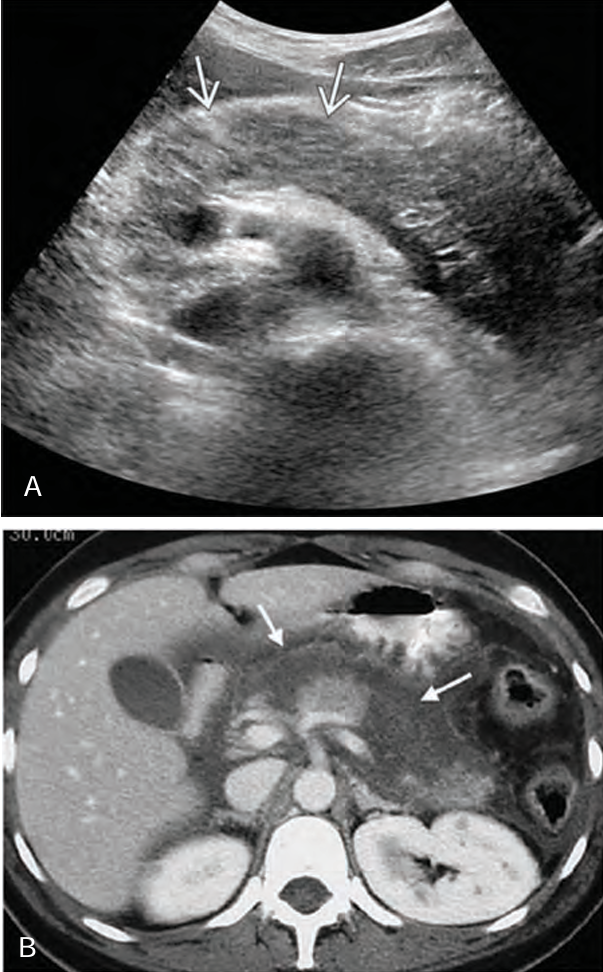
In _______ pancreatitis, there is diffuse _____ destruction of the pancreatic substance caused by a sudden escape of ______ pancreatic ________ into the ______ parenchyma
hemorrhagic; enzymatic; active; enzymes; glandular
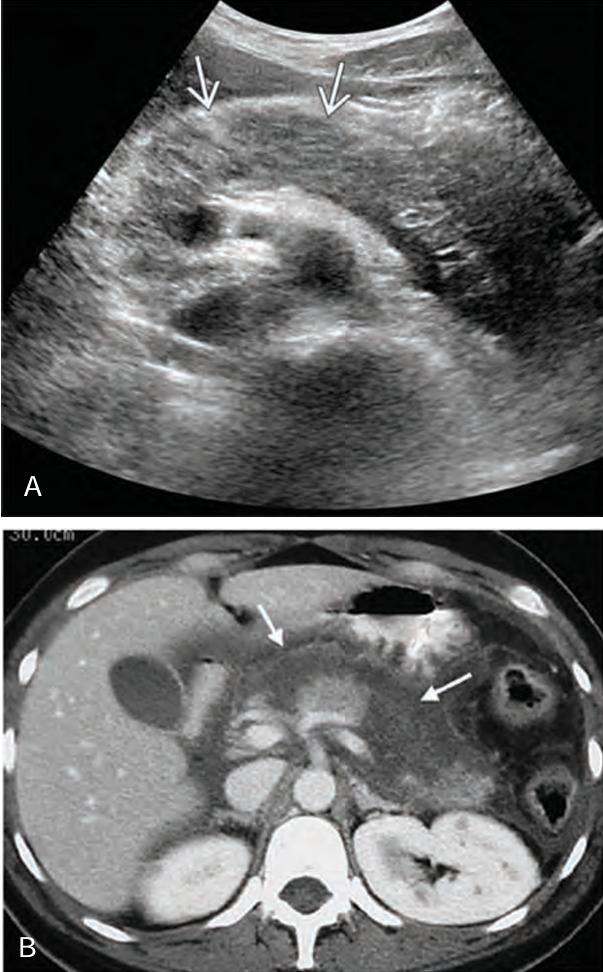
Pancreatic enzymes cause focal areas of fat ______, _____ and ______ the pancreas, which leads to _____ of pancreatic ______ and _______
necrosis; in and around; rupture; vessels; hemorrhage
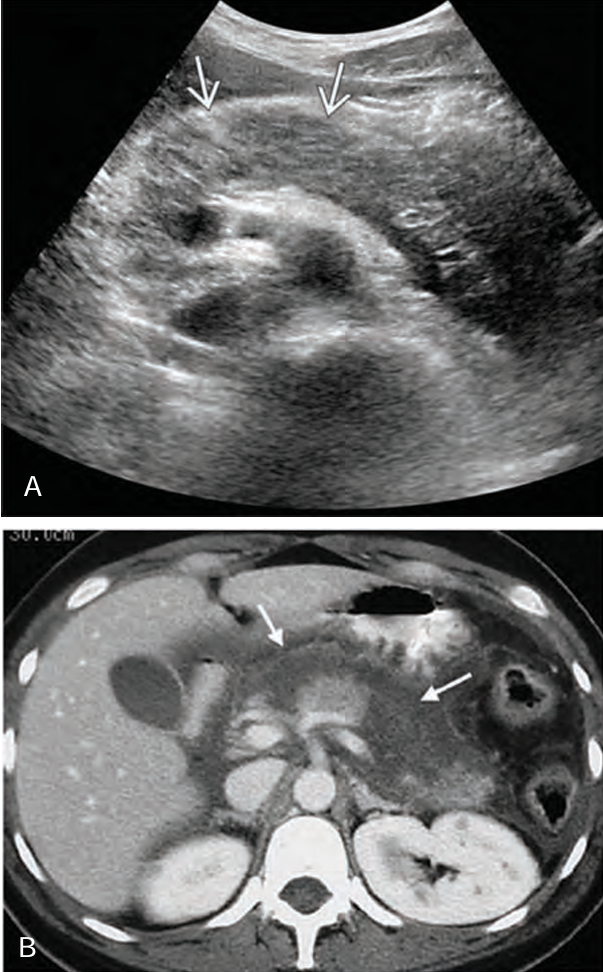
Patients with ______ pancreatitis has sudden _______ destruction of the pancreas AFTER an ______ binge or an excessively _____ meal
hemorrhagic; necrotizing; alcoholic; large
Sonographically, hemorrhagic pancreatitis depends on the ____ of the hemorrhage
age
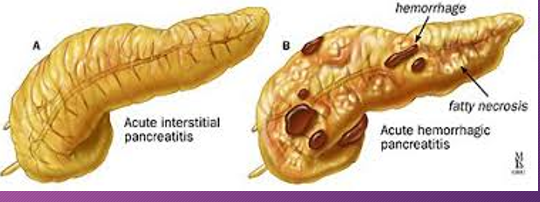
Sonographically, a ______ necrosis may be seen as a ___- defined, ________ mass in the area of the pancreas
fresh; well; homogenous
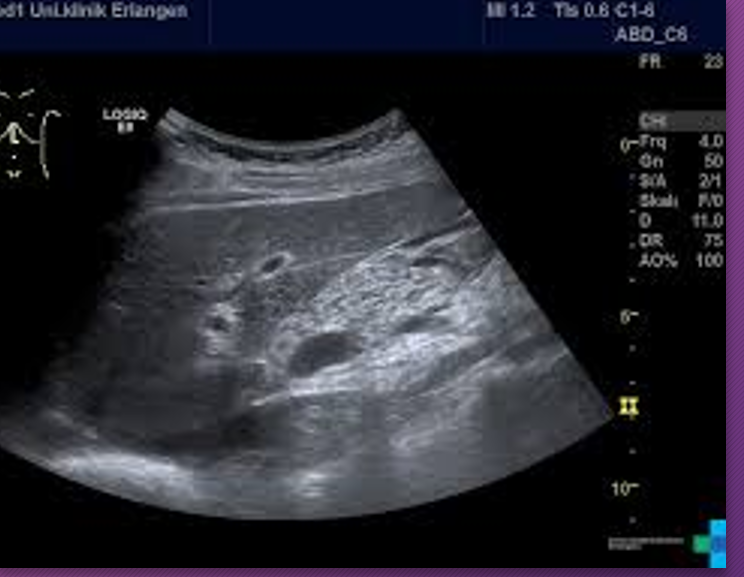
Sonographically, at ____ week, the mass (hemorrhage) may appear ____ with ____ elements or _______
1; cystic; solid; septation
Sonographically, after _____ weeks, the hemorrhage may appear ______
several; cystic
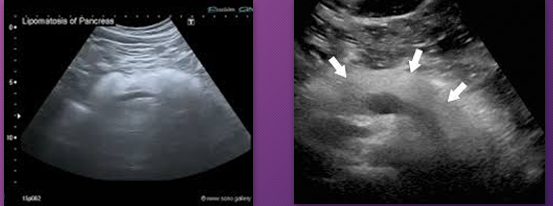
Pancreatic _______ is fat that replaces or infiltrates the pancreas
lipomatosis
Pancreatic lipomatosis is _____ that _____ or _____ the pancreas
fat; replaces; infiltrates
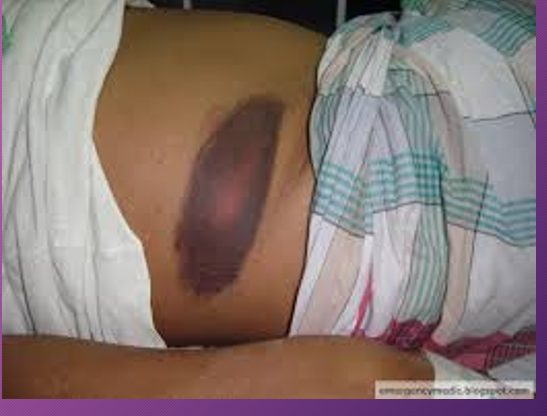
______ ______ sign is an uncommon subcutaneous manifestation of intra-abdominal pathology that manifests as discoloration of the flanks.
Gray Turner’s
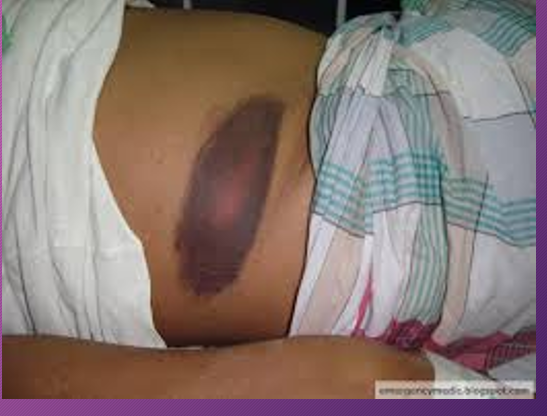
Gray Turner’s sign is an uncommon _________ manifestation of intra-abdominal pathology that manifests as _______ of the _____.
subcutaneous; discoloration; flanks
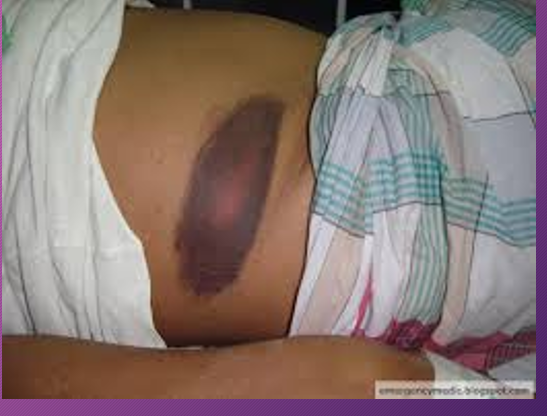
Gray turner’s sign causes discoloration of what?
Flanks
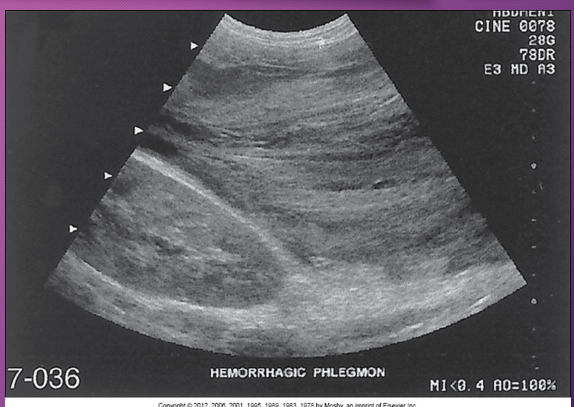
A _______ pancreatitis is an _______ process that spreads along _____ pathways, causing localized areas of diffuse inflammatory _____ of soft tissue that may proceed to necrosis and suppuration
phlegmonous; inflammatory; fascial; edema
______ pancreatitis occurs in ___-___ of patients with _____ pancreatitis
Phlegmonous; 18-20%; acute
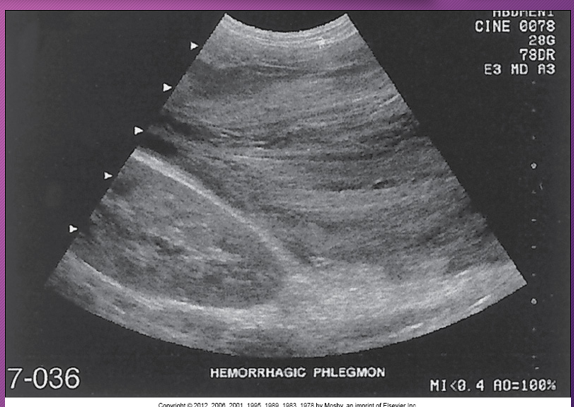
Sonographically, phlegmonous tissue appears ______ in texture with good through-_____
hypoechoic; transmission
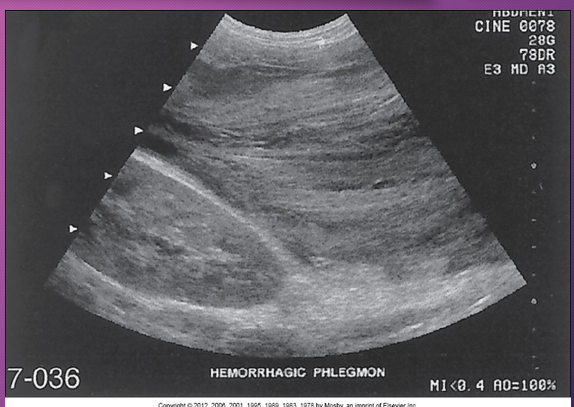
Sonographically, how does phlegmonous tissue appear?
Hypoechoic with good through transmission
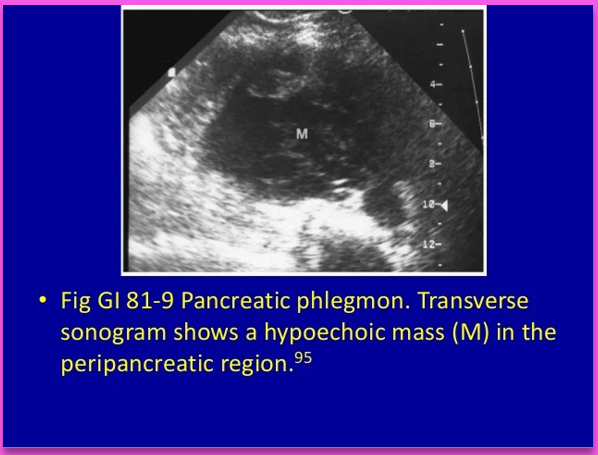
Phlegmonous pancreatitis usually/commonly involves the ____ sac, ____ anterior _____ space, and transverse ______.
lesser; left; pararenal; mesocolon
Pancreatic abscess has a ___ incidence
low
Pancreatic abscess is a condition that is related to the degree of tissue _______
Necrosis
Majority of patients develop abscesses ______ to _______ that develops from _____-_____ procedures
secondary; pancreatitis; post-operative
Pancreatic ______ has a very _____ mortality rate IF left ______
abscess; high; untreated
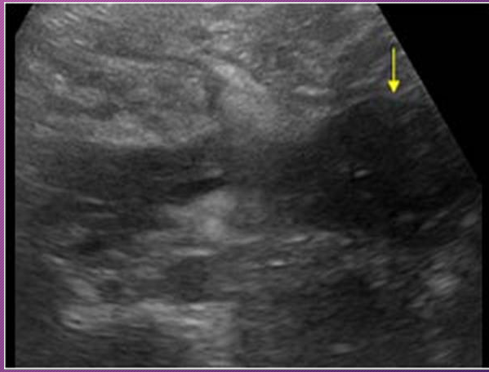
A pancreatic abscess may be ________ or ________
abscess; unilocular; multilocular
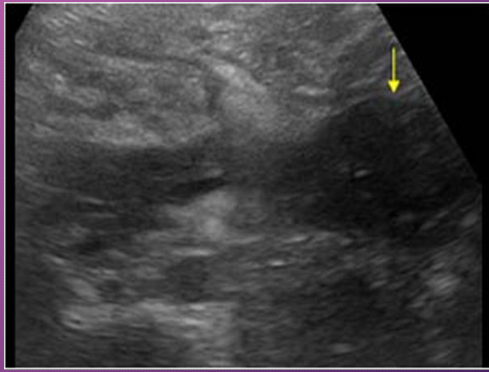
A pancreatic abscess can spread _______ into the _______, ______ to transverse mesocolon, or down to the ________ into the______
superiorly; mediastinum; inferiorly; retroperitoneum; pelvis
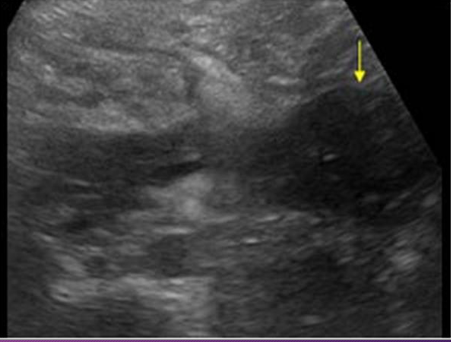
Sonographically, a pancreatic abscess is a poorly defined ______ mass with ______ or _______ thick walls, causing few _____ echoes
hypoechoic; smooth; irregular; internal
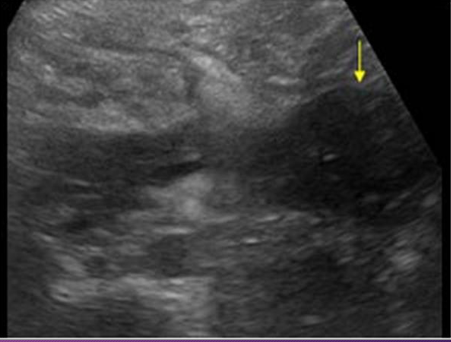
Sonographically, if ____ _____ are present in a pancreatic ______, an ______ region with a ______ posterior is imaged
air bubbles; abscess; echogenic; shadow
Chronic pancreatitis results from _____ attacks of ____ pancreatitis and causes continuous ______ of the pancreatic parenchyma
recurrent; acute; destruction
Patients with chronic pancreatitis may be _______
asymptomatic
Clinical findings of chronic pancreatitis include _______ pain radiating to the back and _______
epigastric; nv
Chronic pancreatitis is generally associated with chronic _______ or ______ disease
alcoholism; biliary
Patients with ________ (elevated calcium levels) and ________ (elevated fat levels) are more _______ to _______ pancreatitis
Hypercalcemia; hyperlipidemia; predisposed; chronic
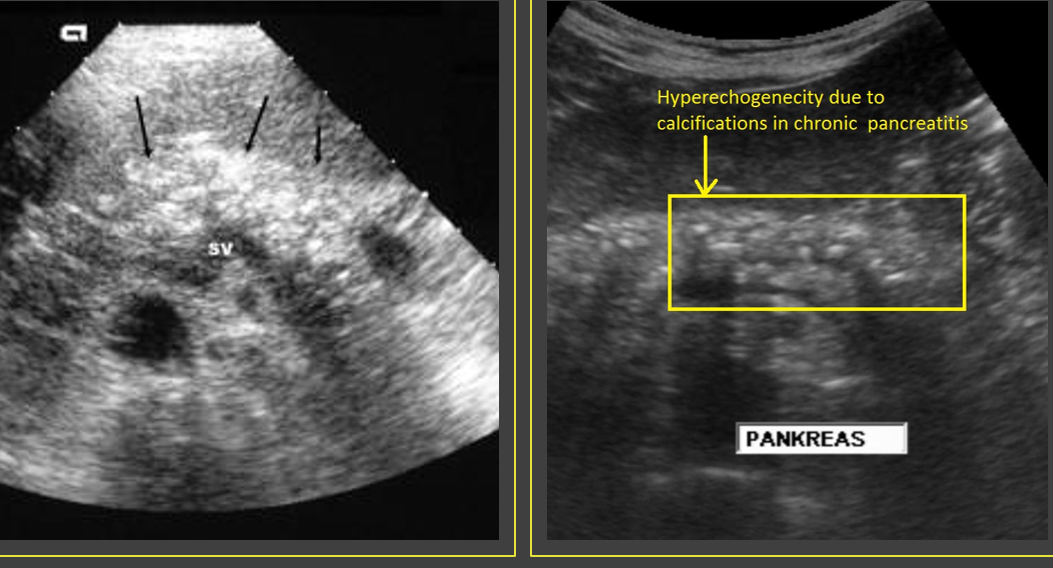
Chronic ______ pancreatitis causes increased pancreatic _____ secretion with subsequent ______ obstruction resulting in chronic ______ pancreatitis.
alcoholic; protein; ductal; calcifying
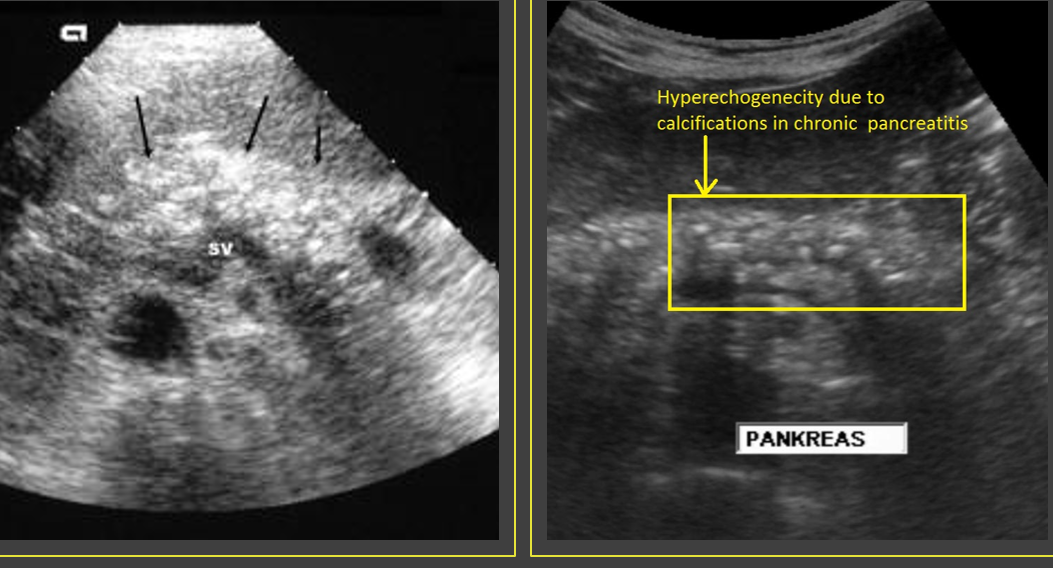
Chronic ______ pancreatitis has fibrous _____ tissue that rapidly grows around the ____ and between _____ that results in ______. This leads to a _______, _____ surface of the pancreas
Alcoholic; connective; ducts; lobules; scarring; nodular; irregular
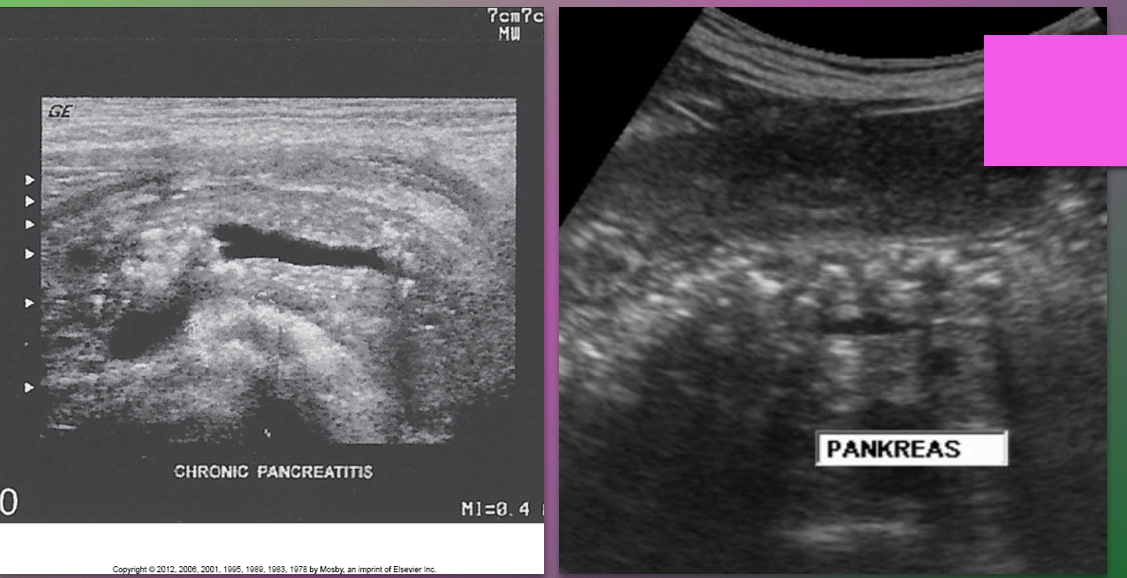
A chronic obstructive pancreatitis is caused by ______ of the sphincter of _____ by ______ or pancreatic _____
stenosis; Oddi; cholelithiasis; tumor
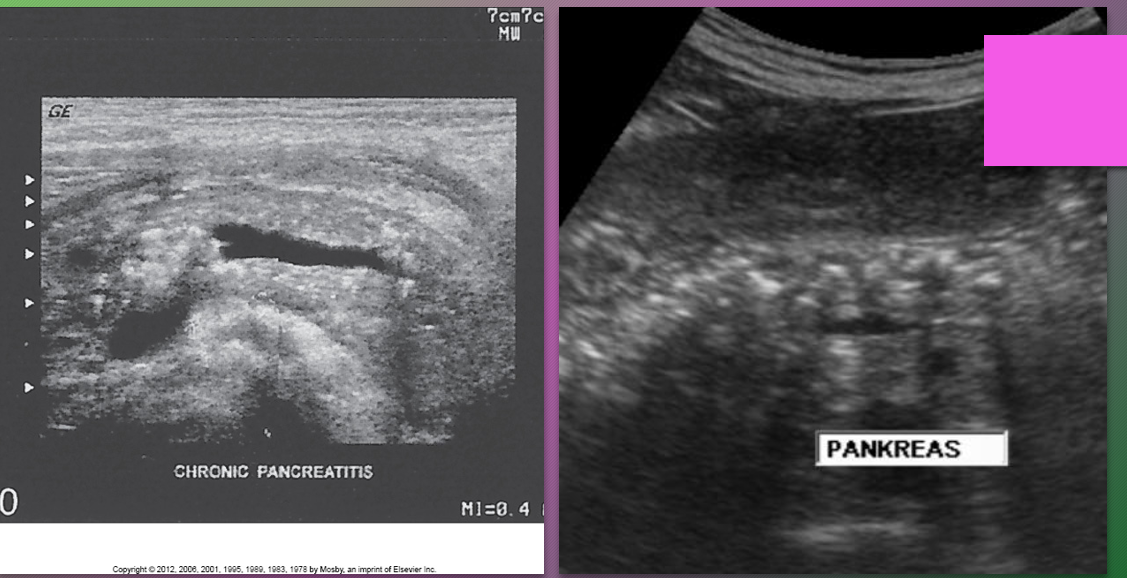
Chronic obstructive pancreatitis presents with non-______ distribution, less ductal _______ damage and ______ stones
lobular; epithelial; calcified
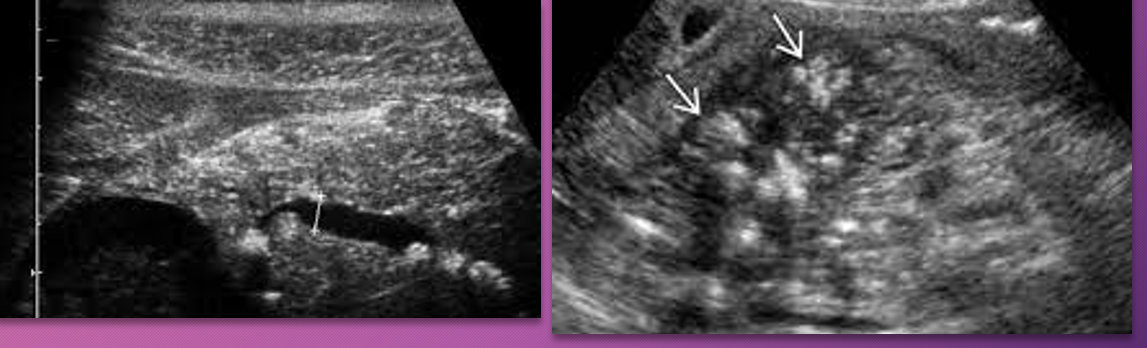
____-____ of patients with _____ pancreatitis develop ________
25-40%; chronic; pseudocysts
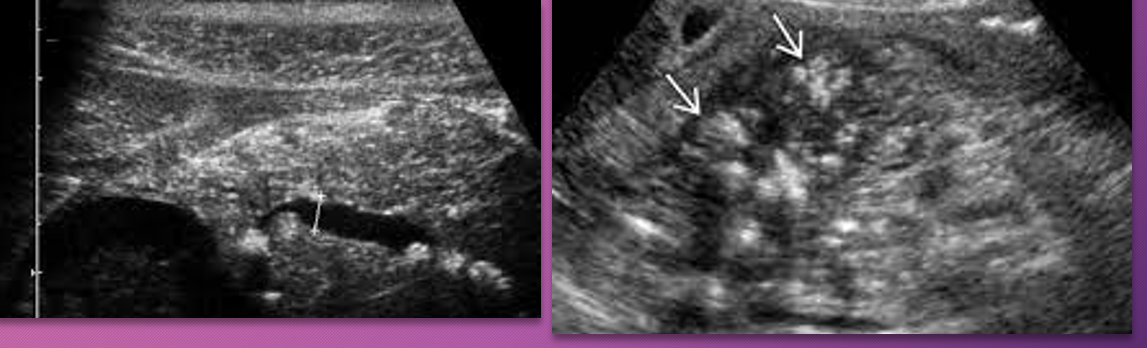
Patients with chronic pancreatitis may develop pseudocysts, a dilated ________, or _______ of the ______ vein with extension into the _______ vein.
CBD; thrombosis; splenic; portal
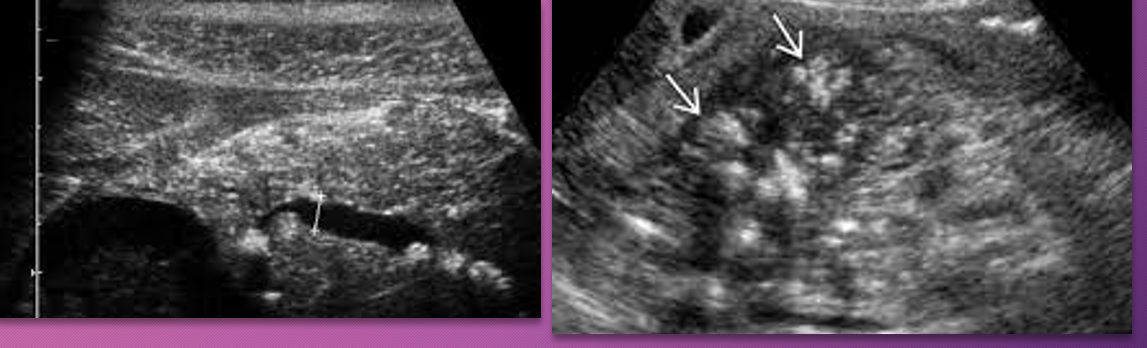
Patients with ______ pancreatitis have an ______ risk of developing pancreatic ______
chronic; increased; cancer
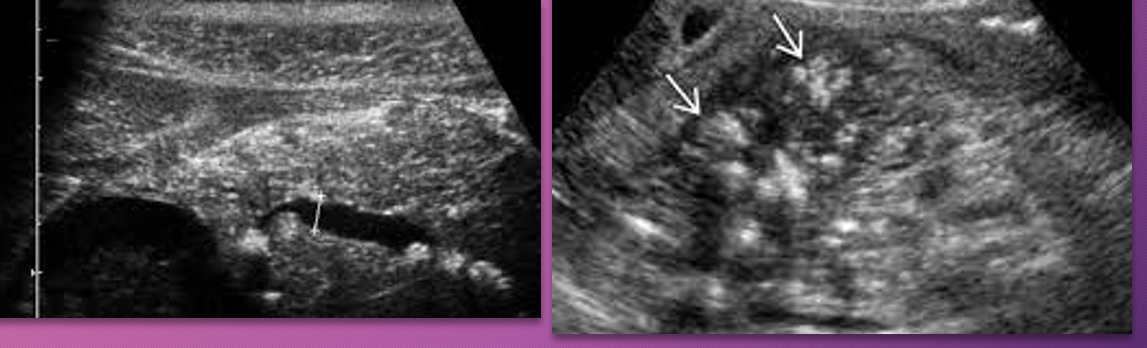
Sonographically, chronic pancreatitis may appear _____ or ______ with increased ______, size _____, ______ borders, and ______ duct
localized; diffuse; echogenicity; reduced; irregular; dilated
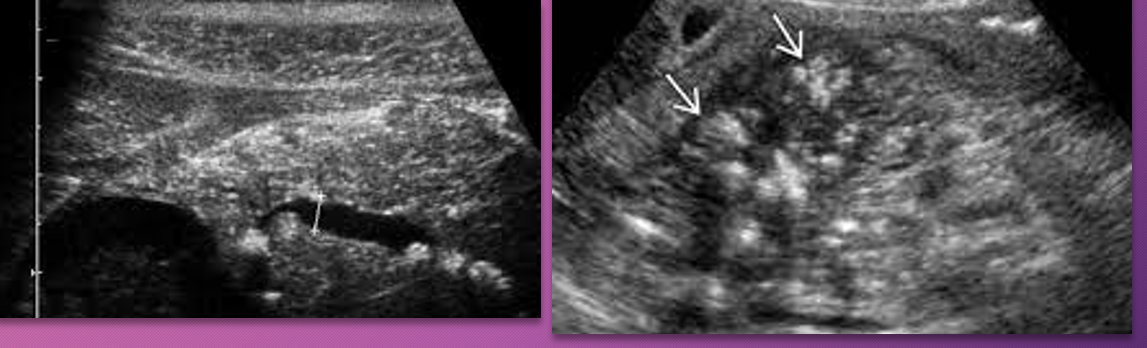
What is a classic finding of chronic pancreatits?
Calcification
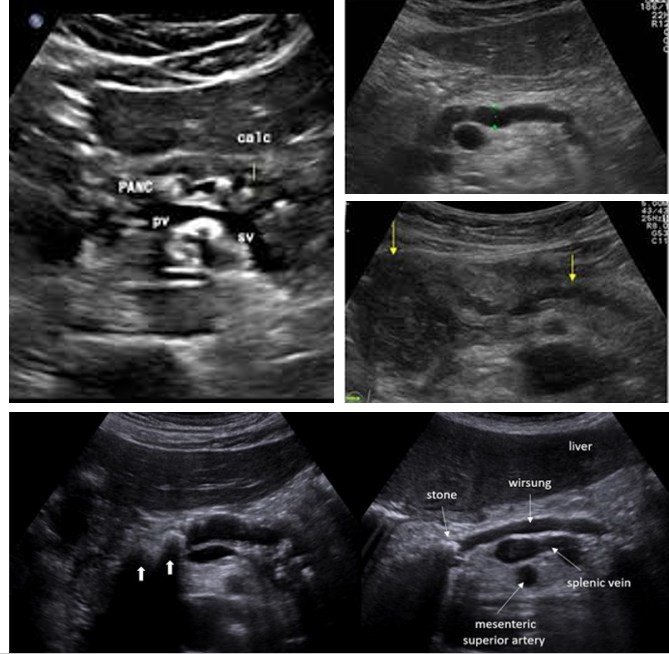
Normal Pancreatic duct measurement:
Head: ___-____ mm
Body: ___-____ mm
Tail: ___-___ mm
3-3.5; 2-2.5; 1.5-2
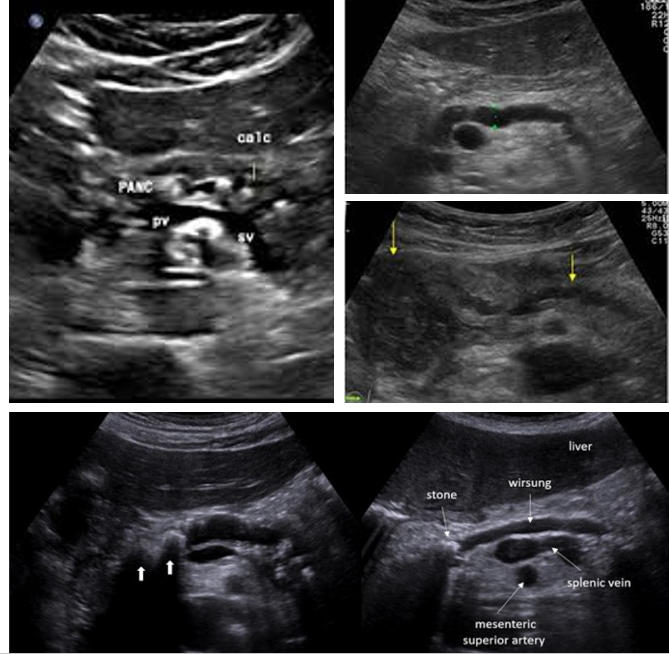
What causes pancreatic ductal dilation?
Acute/chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic neoplasms
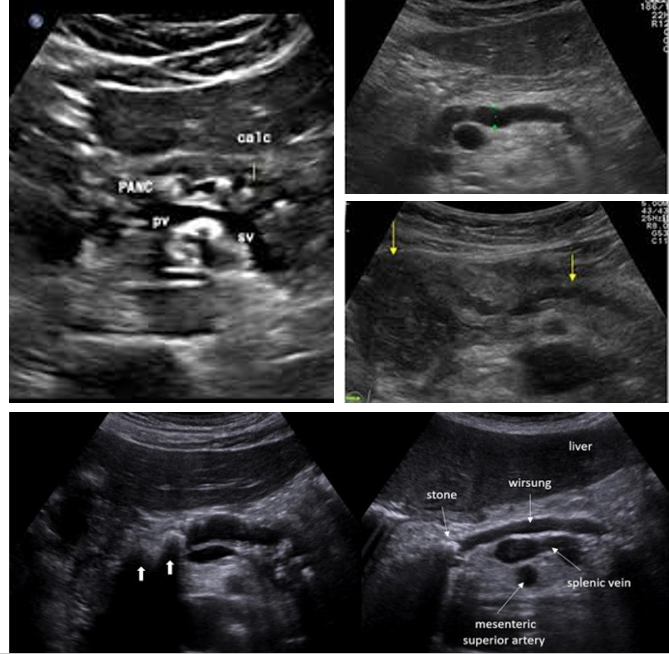
Check pancreatic ducts for what?
Choledocholithiasis
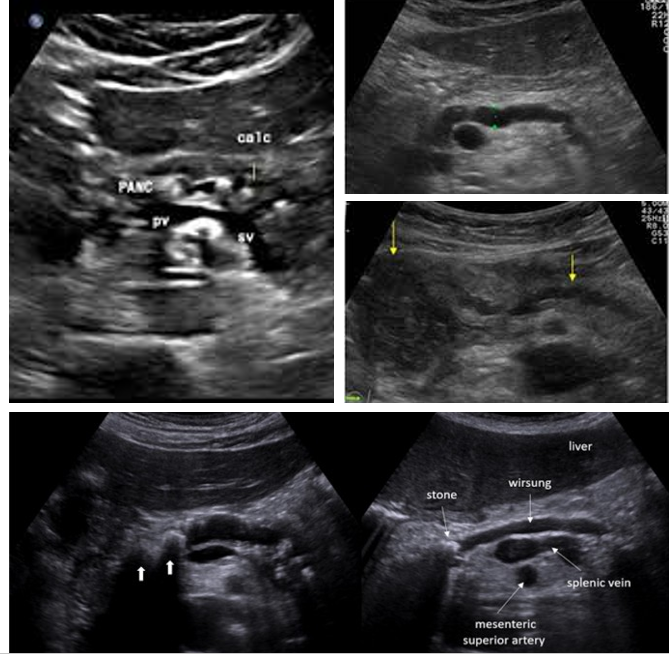
Check gallbladder for ________ with pancreatic duct dilation
gallstones
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic disease is characterized by the presence of multiple small ____ in the _____ and _____ and rarely in the _____
cysts; kidney; liver; pancreas
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic disease have cysts that vary from _______ to several _______ in diameter and with _______ size, may _____ the normal pancreatic tissue
microscopic; centimeters; increasing; destroy
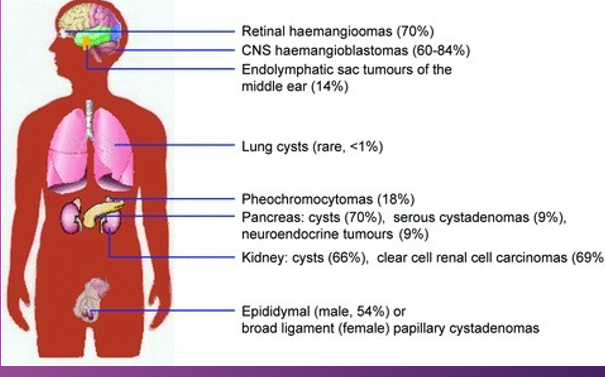
von Hippel–Lindau syndrome is an _____ disorder characterized by the formation of _____ and _____ sacs (cysts) in many different parts of the ______
inherited; tumors; fluid-filled; body
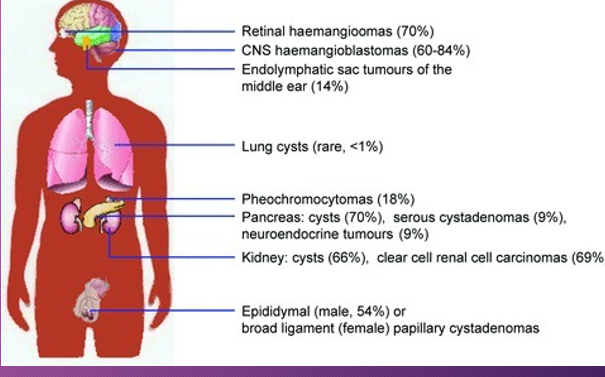
People with von Hippel–Lindau syndrome commonly develop cysts in the ______, _____, and______ tract.
kidneys; pancreas; genital
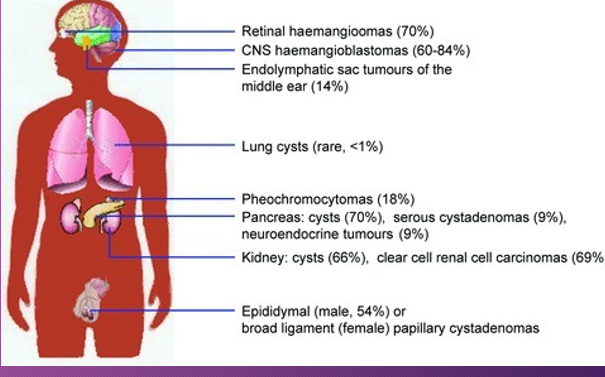
Von Hippel-Lindau have tumors that may either be _________ or _______ and most frequently appear during _____ adulthood
noncancerous; cancerous; young
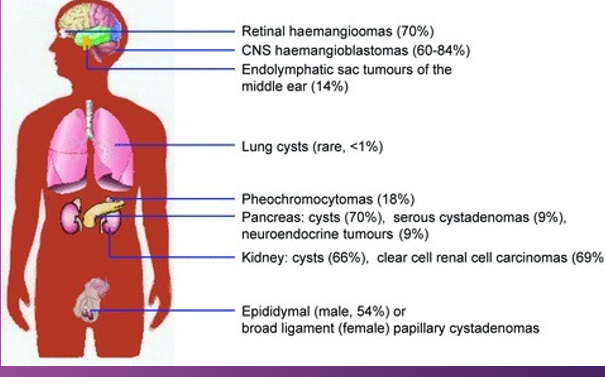
Patients with Von-Hippel Lindau syndrome have an _____ risk of developing pancreatic ________ tumor
increased; neuroendocrine