Pharm tech - parenteral & transdermal
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
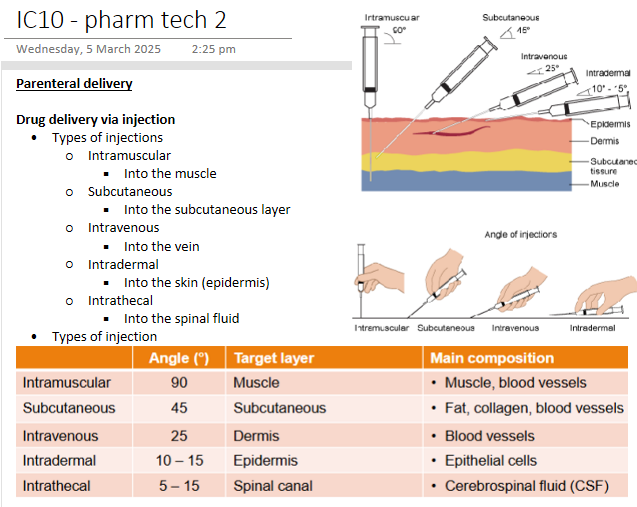
Parenteral delivery - Drug delivery via injection
Parenteral delivery - Parenteral to brain access

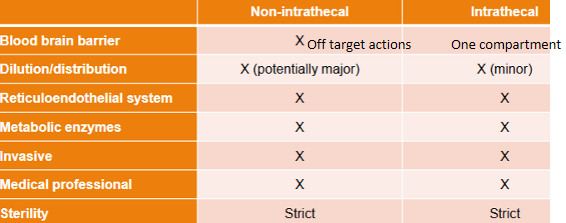
Parenteral delivery - Barriers and disadvantages
Parenteral delivery - Advantages
Bypasses hepatic first pass metabolism
Can control dosage - cause you know the blood conc
Relatively low drug concentration (and low toxicity)
Direct access to brain (intrathecal)
Sustained release (intramuscular depots, intrathecal reservoirs)
Ideal for non-compliant, unconscious or dysphagic patients - guarantee med was given
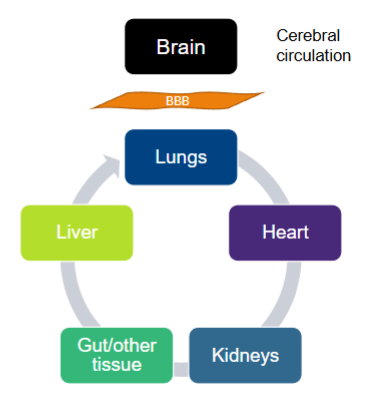
Parenteral delivery - Blood to brain transport
Drug solution flows through circulatory system
Reticuloendothelial system (RES)
Unless there is active targeting, drug will distribute everywhere
Drugs must bypass the blood brain barrier (BBB) to access the brain. Coats every blood vessel
Parenteral delivery - blood brain barrier
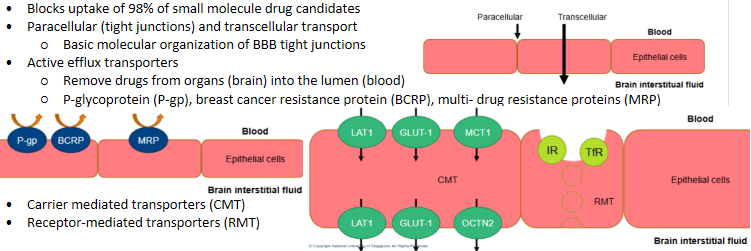
Parenteral delivery - Ideal drug candidates for parenteral (non-intrathecal)
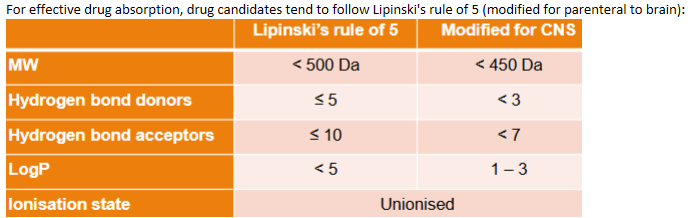
Parenteral delivery - Delivery systems (formulations)

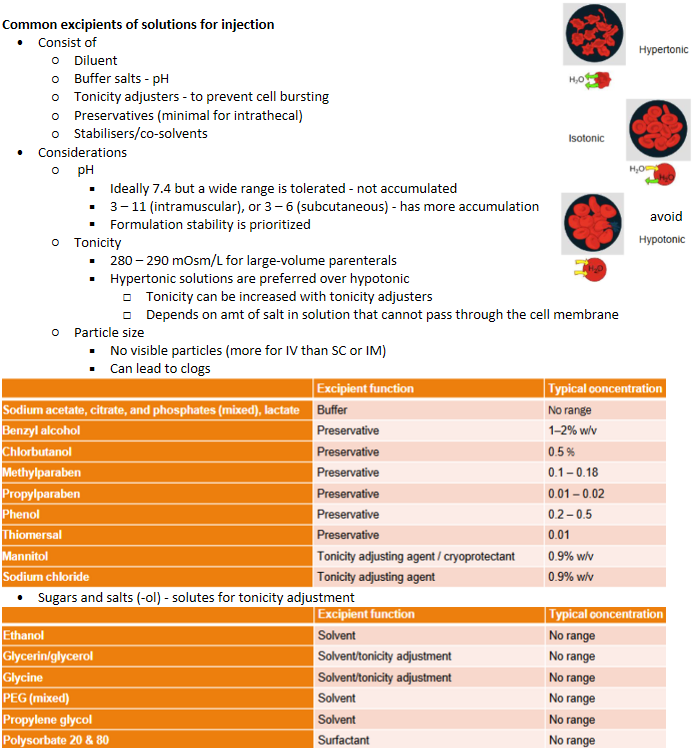
Parenteral delivery - Common excipients of solutions for injection
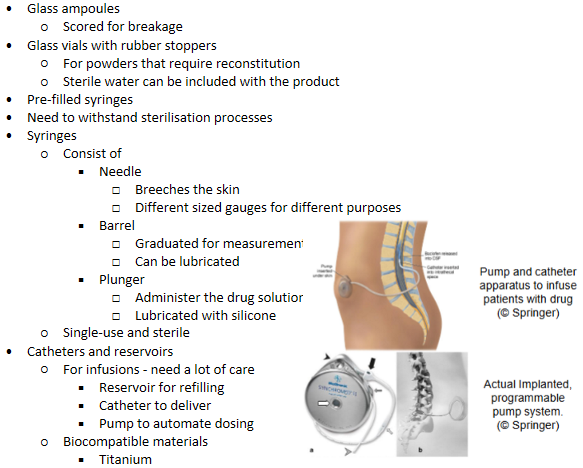
Parenteral delivery - Packaging & storage
Parenteral delivery - Haloperidol/Hadol
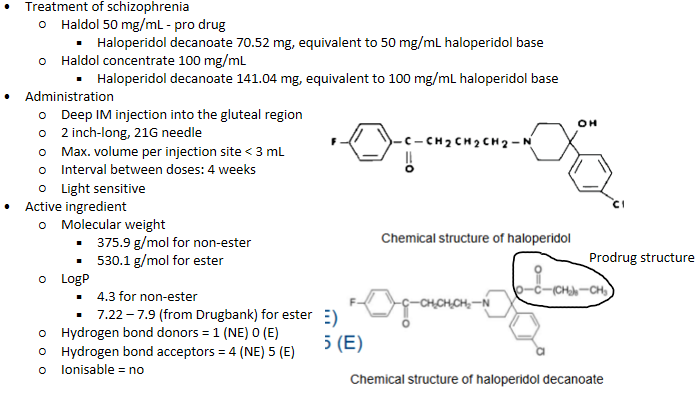
IM Haloperidol/Hadol - composition
Sesame oil - solvent
Benzyl alcohol - preservative
Haloperidol
No pH, osmolality (lipophilic)
IM Haloperidol/Hadol - PKPD
Sustained release from depot - long term, as chronic condition
Steady state plasma levels reached within 2 – 4 mths
Half-life = 3 weeks
Metabolised in liver
Plasma protein binding ~ 88 – 92%
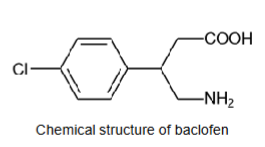
Parenteral delivery - Baclofen/Lioresal

IV/PO Baclofen/Lioresal - Active ingredient
Molecular weight = 213.67 g/mol
LogP = 1.3
Hydrogen bond donors = 3
Hydrogen bond acceptors = 4
Ionisable = yes
pKa, 1 = 3.87 (carboxyl group)
pKa, 2 = 9.62 (amino group)
IV/PO Baclofen/Lioresal - composition
Water - solvent
Sodium chloride - tonicity
Baclofen - AI
pH: 5 – 7
Osmolality: 270 - 300 mOsm/kg (0.05 mg/mL) - NaCl + baclofen
IV/PO Baclofen/Lioresal - PKPD
Baclofen concentration in CSF is ~100x higher than after oral administration
Infusion - for minor effects, chronic
Antispastic action seen ~6 – 8 hrs after administration (infusion)
Maximum efficacy observed ~24 – 48 hrs
Bolus - emergency, may have other SE
Onset ~ 0.5 – 1 hr after administration
Peak antispastic effect ~ 4 hrs after dosing and last 4 – 8 hrs
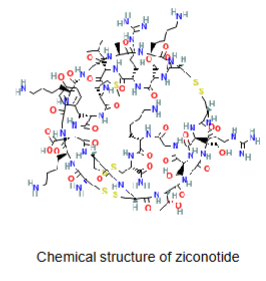
Parenteral delivery - Ziconotide/Prialt
N-type voltage-gated calcium channel blocker
Management of severe chronic pain
PRIALT: one vial per carton
25 μg/mL in glass vial (20 mL)
100 μg/mL in glass vial (1 or 5 mL)
Medtronic SynchroMed® II infusion system or CADD-Micro ambulatory infusion pump
IV Ziconotide/Prialt - active ingredient
Molecular weight = 2639.2 g/mol
LogP = -2 or -23 (from DrugBank) - very hydrophilic
Hydrogen bond donors = 42
Hydrogen bond acceptors = 46
Ionisable = yes
Many a.a. - polypeptide
IV/IT Ziconotide/Prialt - composition
Water - solvent
Sodium chloride - tonicity
L-methionine - antioxidant (peptide stability)
Ziconotide acetate
pH: 4 – 5
Isotonic
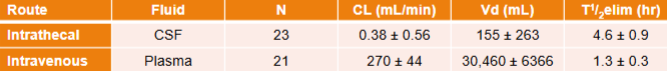
IV Ziconotide/Prialt - PK
Half-life: 4.6 ± 1.8 hrs
Metabolised by peptidases/proteases
VD ~ 140 mL (volume of CSF)
50% bound to human plasma proteins
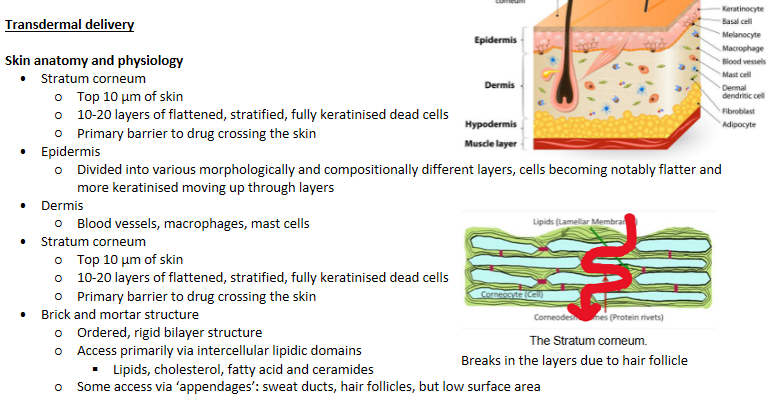
Transdermal delivery - Skin anatomy and physiology
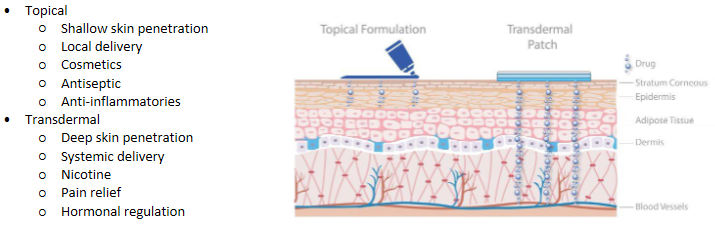
Transdermal delivery - Transdermal vs topical delivery
Transdermal delivery - Advantages
Controlled release (reservoirs, duration of contact). Decreased dosing frequency
No GI degradation/irritation
Bypasses hepatic first pass effect
Easy termination of input
Non-invasive
Transdermal delivery - Disadvantages and barriers
Variability between people and location of administration on body - genetic variations
Stratum corneum - Slow absorption
Skin irritation (interactions and removal)
Could be removed by the patient
Metabolic enzymes
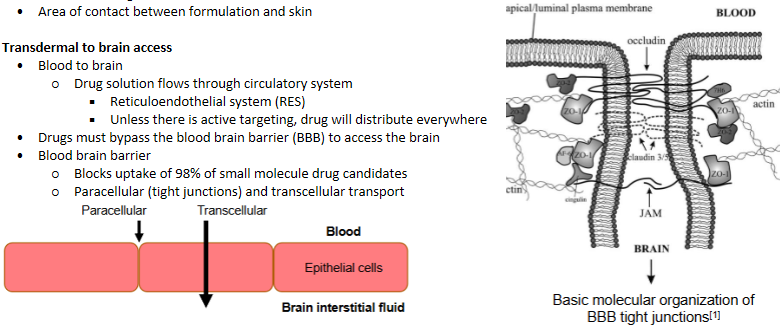
Blood brain barrier (via systemic delivery)
Systemic side effects
Transdermal delivery - Factors that affect delivery
Skin condition: age, disease, injury, site
Skin thickness (thickness of diffusion layer)
Hydration of skin (stratum corneum) - Natural or “manufactured” (occlusive: physical/chemical)
Stimulation of the skin (phonophoresis/ultrasound, iontophoresis, heat)
Physicochemical properties of drug (lipophilicity, diffusion coefficient)
Permeation enhancers - Reversible reduction in the barrier resistance of the stratum corneum without damaging viable cells
Concentration gradient
Area of contact between formulation and skin
Transdermal delivery - Transdermal to brain access
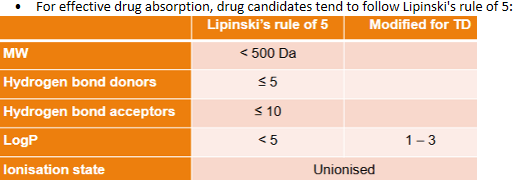
Transdermal delivery - Ideal drug candidates
Transdermal delivery - Delivery systems (formulations)
Some types include:
Topical
Gel, creams (water-based/oil-based) and ointments
Transdermal
Patches (solutions/suspensions in reservoirs)
Patches (polymer matrix) - provide occlusion, increase retention time
Transdermal delivery - Products on the market
Transdermal patches
Rotigotine/Neupro
Management of Parkinson’s
Treatment of restless leg syndrome
Fentanyl/Duragesic
Pain relief
Estrogen/Estraderm
Hormone replacement therapy
Nicotine/Nicotinell
Nicotine replacement therapy
Transdermal delivery - Common excipients of solutions for patches
Preservatives
Solvents/co-solvents
Viscosity modifier
Permeation enhancers
Adhesives
Transdermal delivery - Polymer matrices
Drug release dependent on
Diffusion coefficient of drug
Surface area
Concentration
Porosity/tortuosity of polymer matrix - Determined by intramolecular interactions (crosslinking, hydrogen bonds)
Transdermal delivery - Packaging & storage
Patches sealed in individual pouches
Plastic/polymer lining
Aluminium lining
Sealed packaging
Maintain integrity of adhesive
Maintain integrity of product
Maintain hydration
Transdermal delivery - Design of patches

Transdermal delivery - special considerations for patches
Release rate of drug from patch
Potential for leaching and extraction of drug into backing/other layer
Temperature - 25c
Crystallinity of drug over time
Strength of adhesion (between layers, influence of sweat, hair etc.)
Disposal
High concentrations
Transdermal delivery - Rotigotine/Neupro
Dopamine receptor agonist
Treatment of Parkinson’s
Cartons of 30 patches
Rotigotine/Neupro patches - application
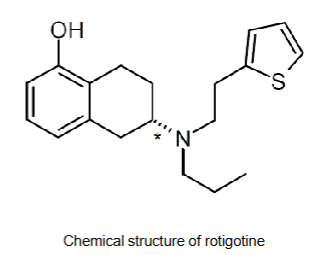
Rotigotine/Neupro patches - active ingredient
Molecular weight = 315.48 g/mol
LogP = 4.7
Hydrogen bond donors = 1
Hydrogen bond acceptors = 3
Ionisable? Yes OH
Rotigotine/Neupro patches - composition
Ascorbyl palmitate - fatty acid. Antioxidant
Povidone - viscosity
Silicone- adhesive
Sodium metabisulfite - preservative/antioxidant
DL-alpha-tocopherol - antioxidant
Rotigotine - AI
What is the design of the patch? - drug in adhesive
Rotigotine/Neupro patches - PK
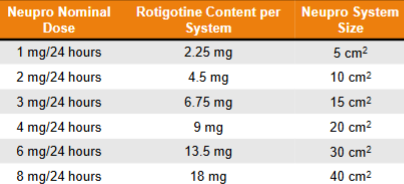
~45% released in 24 hrs (0.2 mg/cm2)
Cmax dependent on patch dose
Removal of patch: plasma levels decreased with a terminal half-life of 5 – 7 hrs
Transdermal delivery - Fentanyl/Duragesic
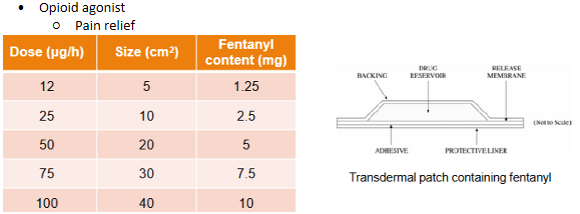
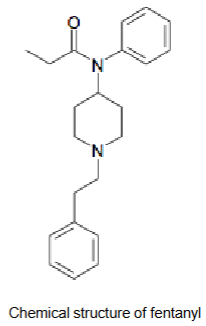
Fentanyl/Duragesic patches - Active ingredient
Molecular weight = 336.5 g/mol
LogP = 4.05
Hydrogen bond donors = 0
Hydrogen bond acceptors = 2-3
Ionisable? y, tert amine
Fentanyl/Duragesic patches - composition
Alcohol* - permeation enhancer
Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer - membrane
Hydroxyethyl cellulose - suspending agent
Polyester - backing layer
Silicone
*minute amounts
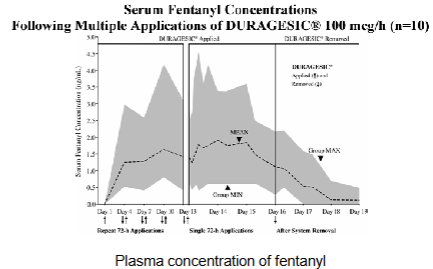
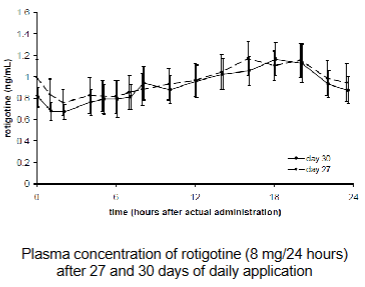
Fentanyl/Duragesic patches - PK
Steady state plasma concentrations after ~3 days
Plasma concentration dependent on patch dosage
Half-life ~ 7 hrs after removal of patch