4th Quarter Vocabulary - Life Science - 7th Grade
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

67 Terms

Abiotic
Nonliving part of an organism’s habitat or ecosystem.

Apex Predator
Top carnivore that has no other predators.
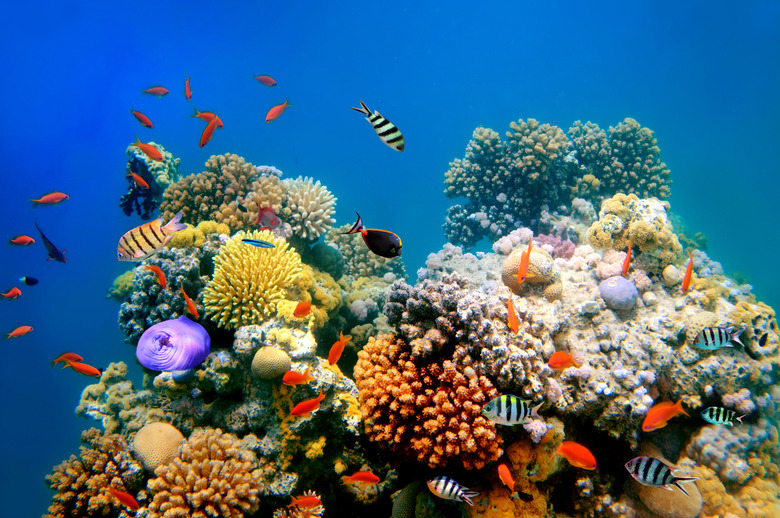

Aquatic
Found in or around bodies of water.

Autotroph
A living thing that makes its own food, like a plant.
Biodiversity
The variety of different organisms living in a particular area.

Biome
A group of ecosystems with similar climates and organisms.

Biotic
A living or once living part of an organism’s habitat or ecosystem.

Boreal Forest
A forest in cold northern areas with long winters, mostly made up of evergreen trees.
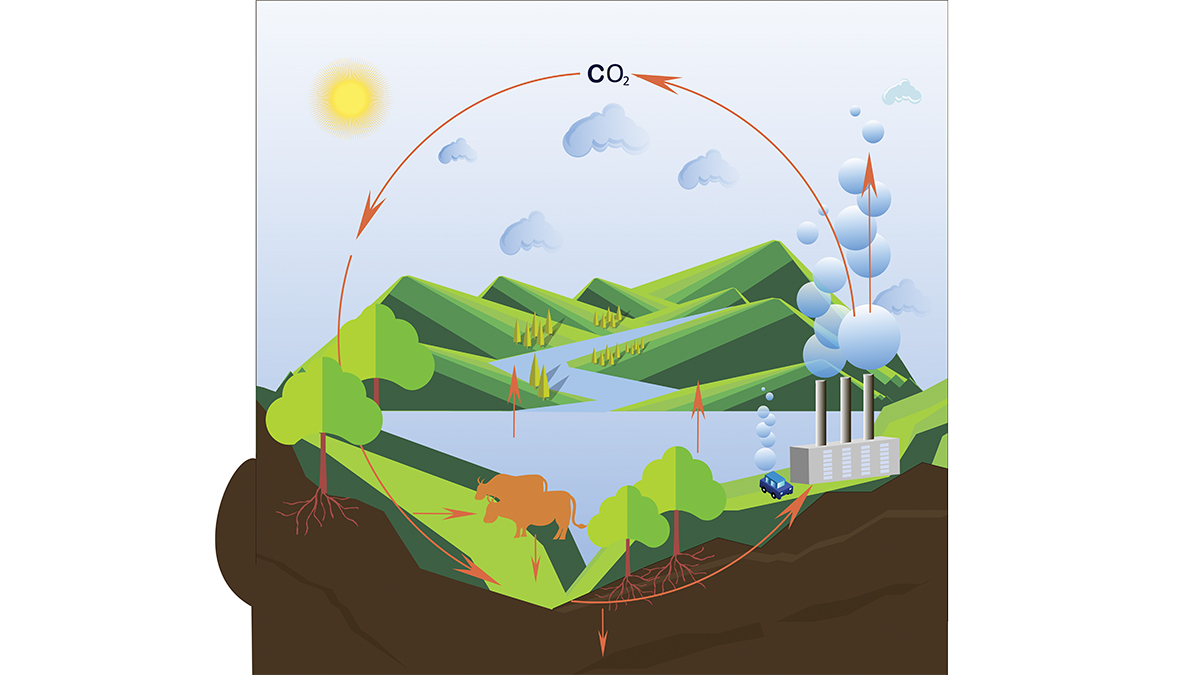
Carbon Cycle
The process that moves carbon between plants, animals, and microbes; minerals in the earth; and the atmosphere.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Reactant needed by plants to carry out photosynthesis.
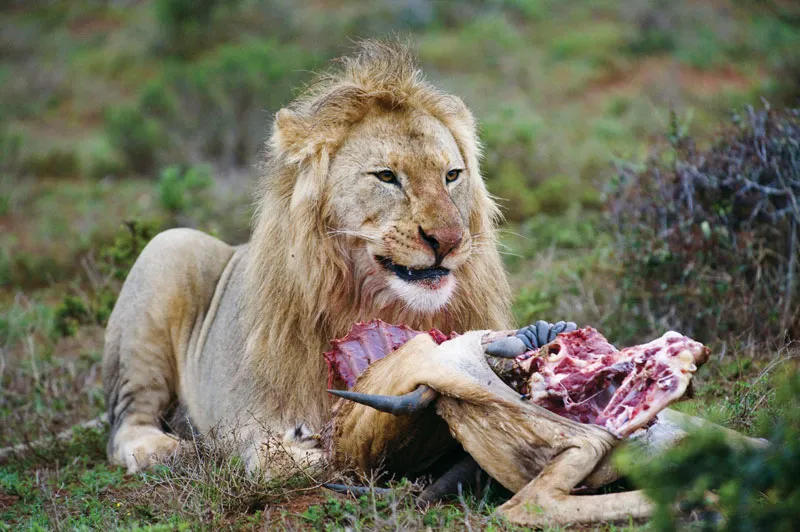

Carnivore
An animal that only eats meat.
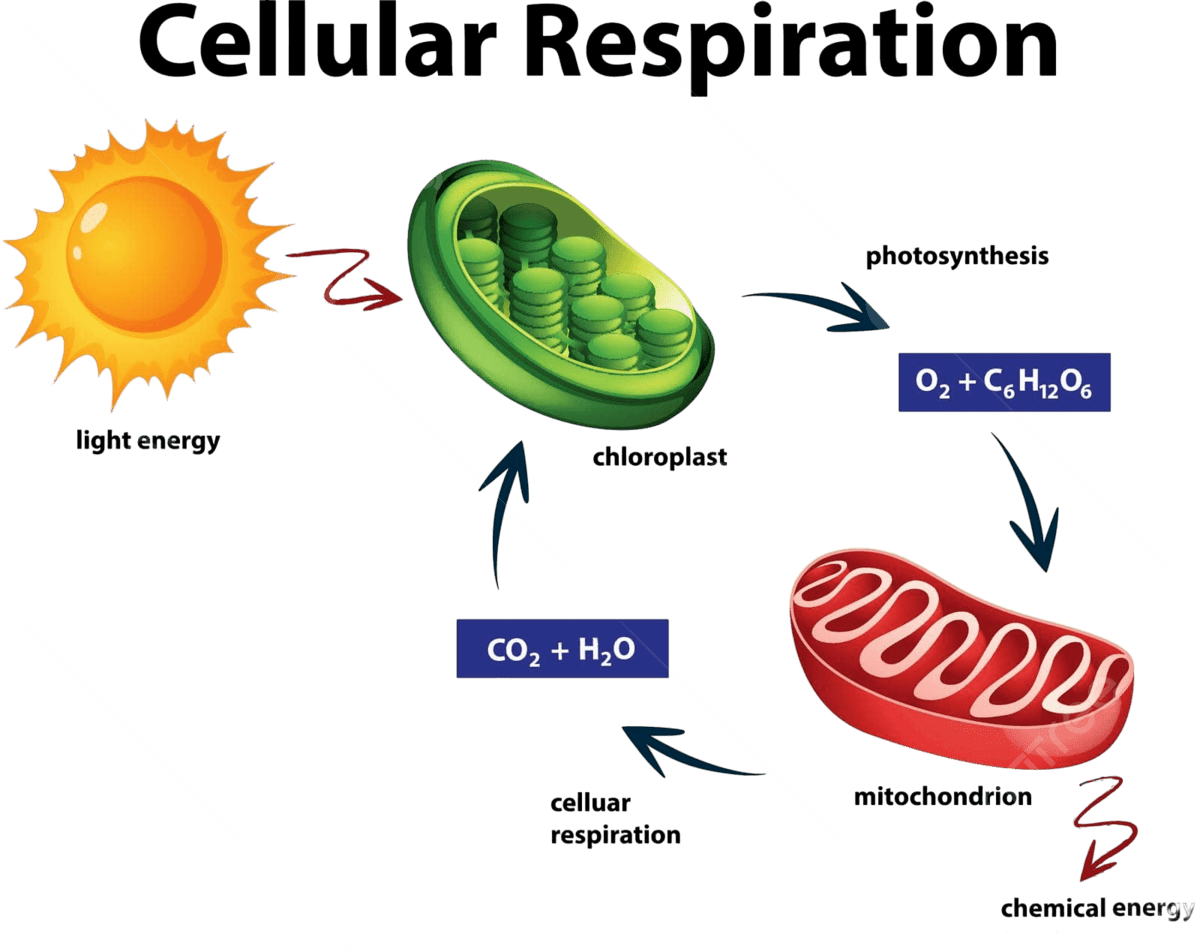
Cellular Respiration
How cells use food and oxygen to make energy.
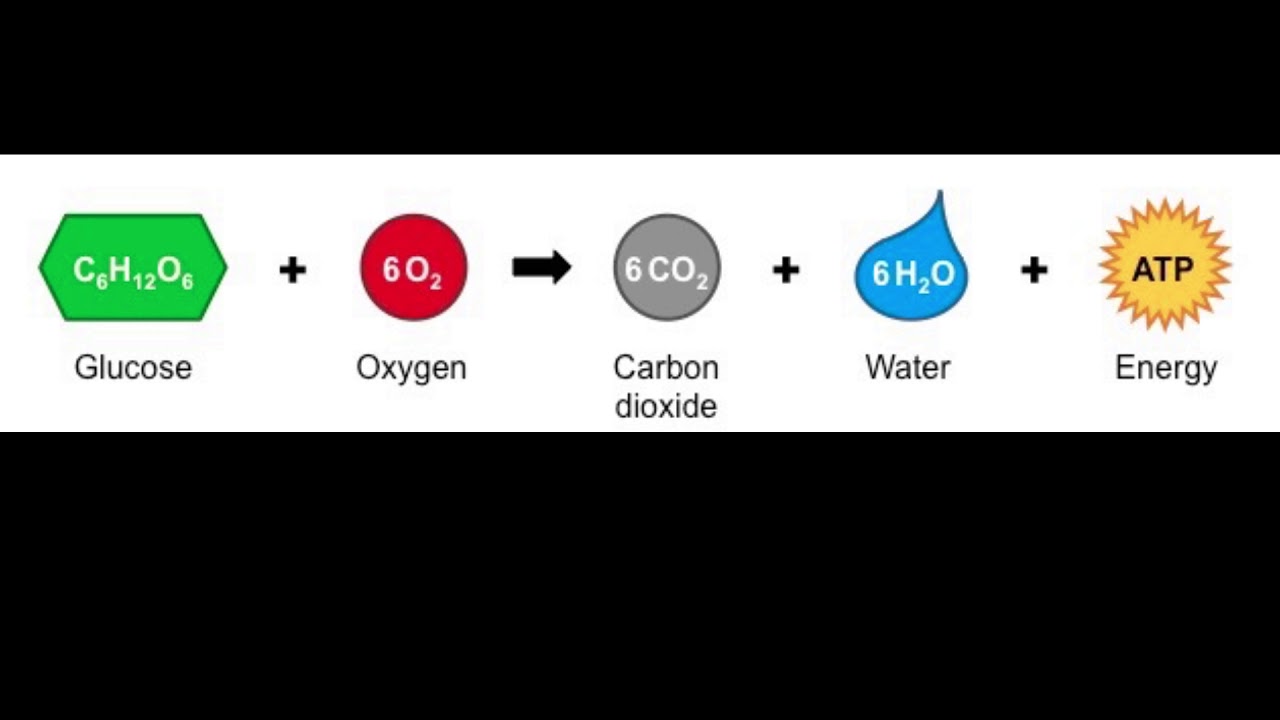
Chemical Formula
Symbols that show the elements and the ratio of atoms in a compound.

Chlorophyll
The green pigment in plants that helps them catch sunlight.

Climate
The average annual conditions of temperature, precipitation, and clouds in an area.
Community
All of the different populations that live together in a particular area.

Coniferous Forest
A forest made mostly of trees with needles and cones.

Consumer
An organism that gets energy by eating other organisms.
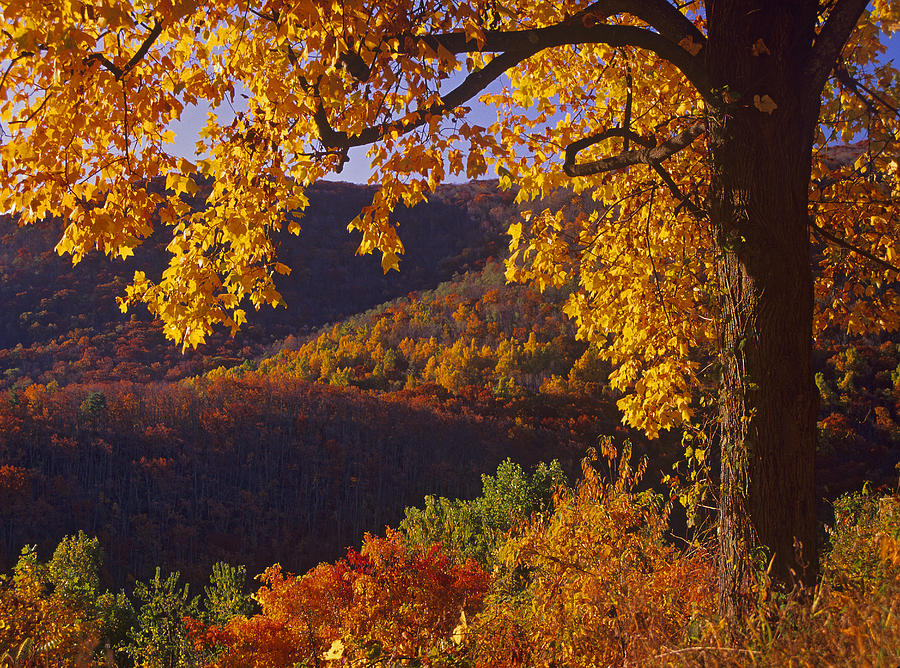

Deciduous Forest
A forest made of trees that lose their leaves each year, usually in winter.
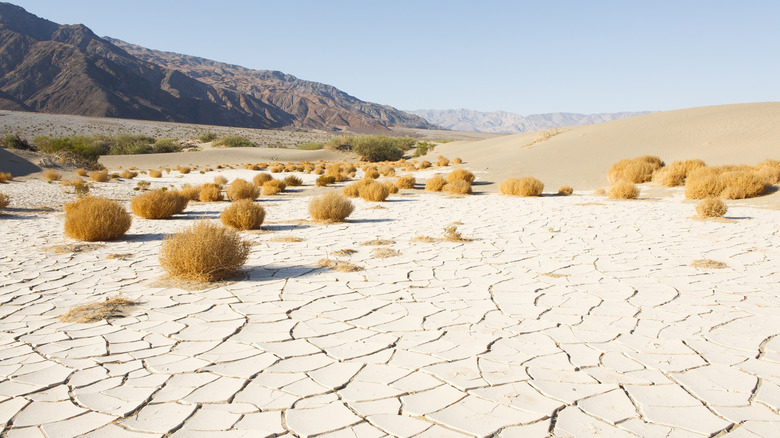

Desert
Any large, arid area of land where little to no rainfall occurs.
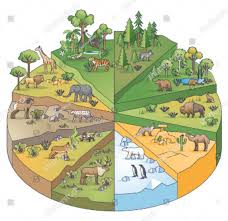
Ecological Biodiversity
The variety of ecosystems on land and in water.
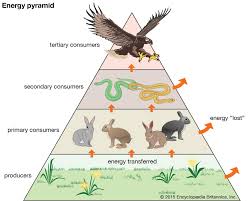
Energy Pyramid
A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web.
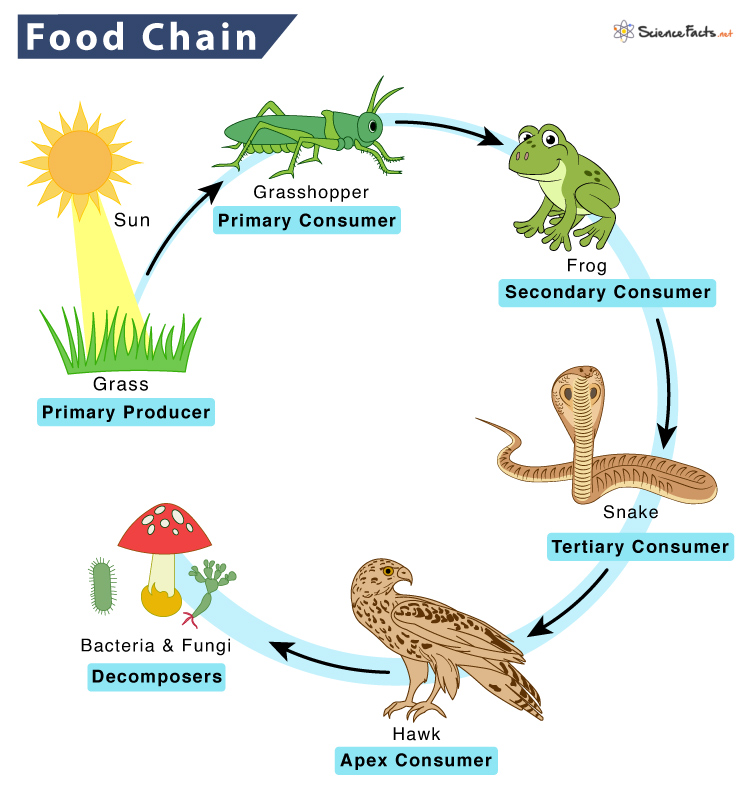
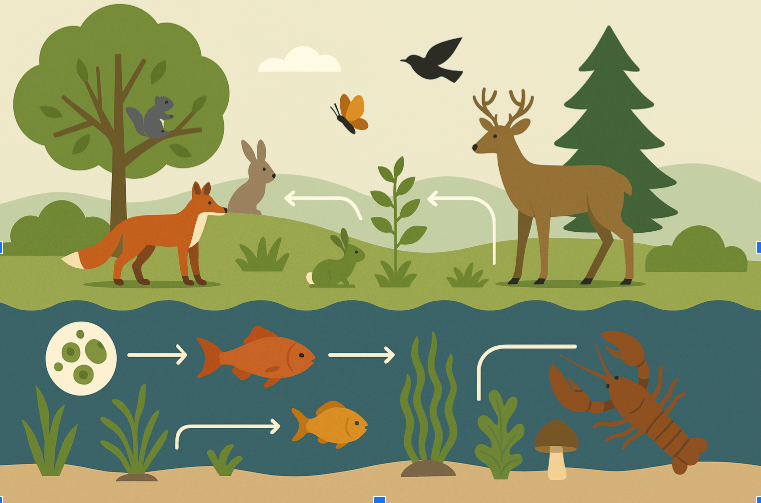
Food Chain
A path that shows how energy moves when one living thing eats another.
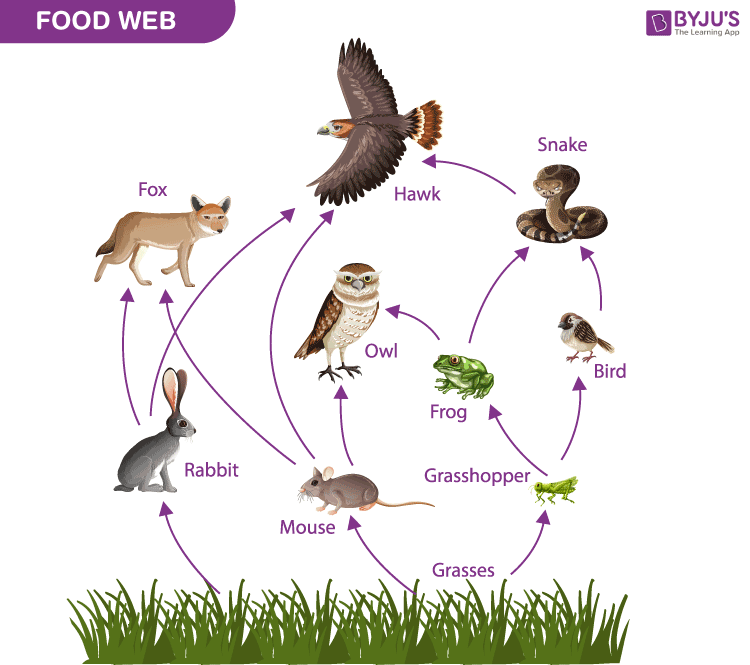
Food Web
A group of connected food chains in an ecosystem.

Freshwater
Water with low concentrations of salt.
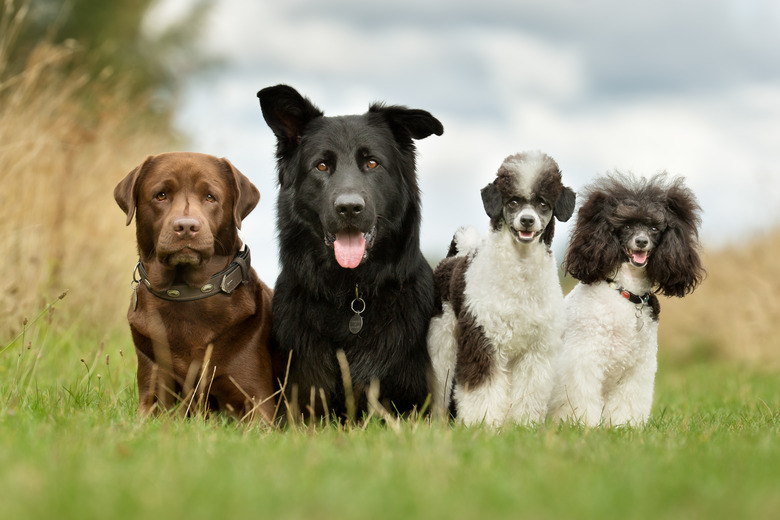

Genetic Biodiversity
The biological variation that occurs within species.
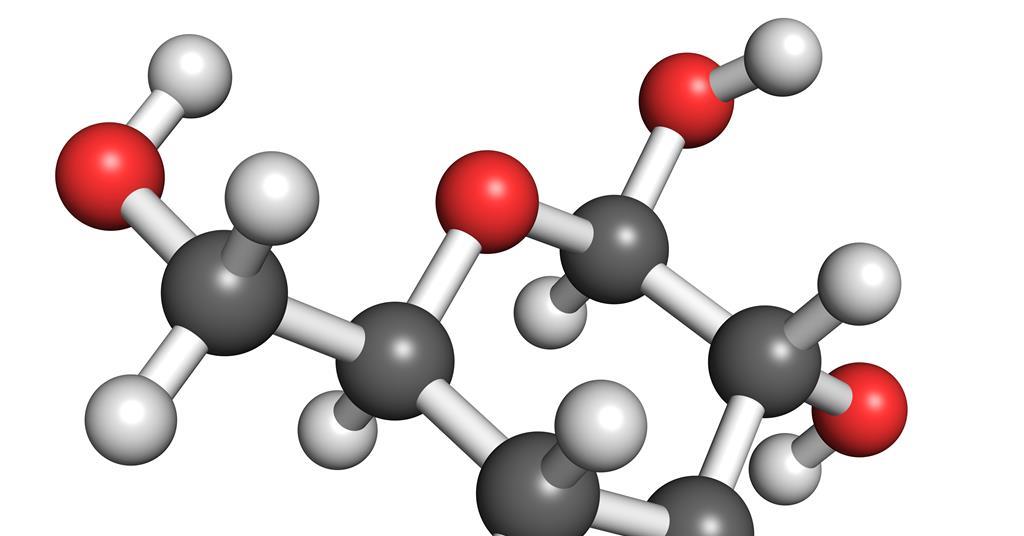
Glucose (C6H12O6)
Product produced by plants in the process of photosynthesis.

Grassland
Generally open and continuous, fairly flat areas of grass.

Habitat
The natural home or environment of an organism.
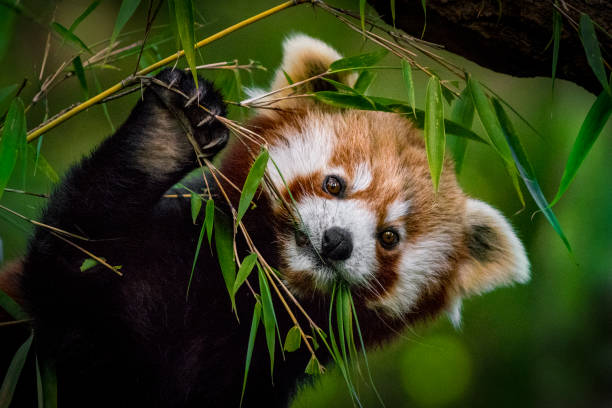

Herbivore
A consumer that gets energy by eating only plants.
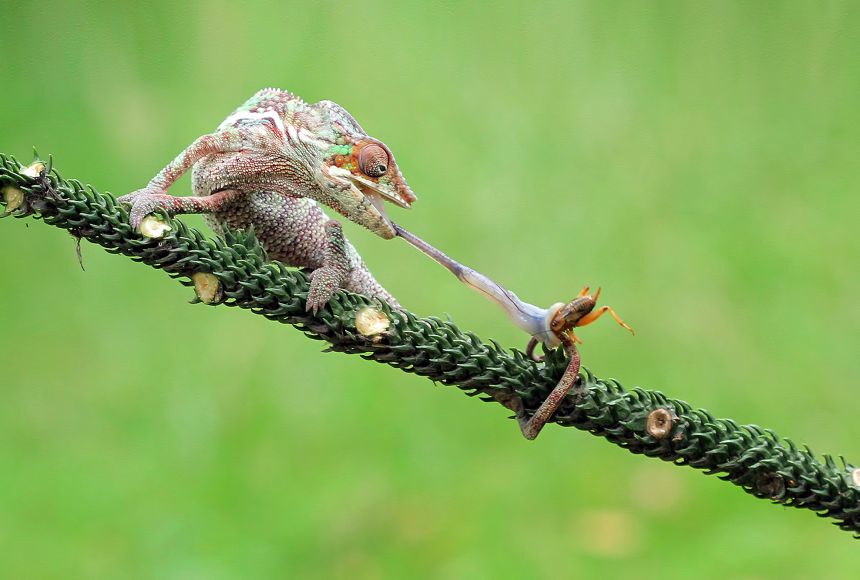

Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food and gets food by eating other living things.

Marine
Saltwater environments.
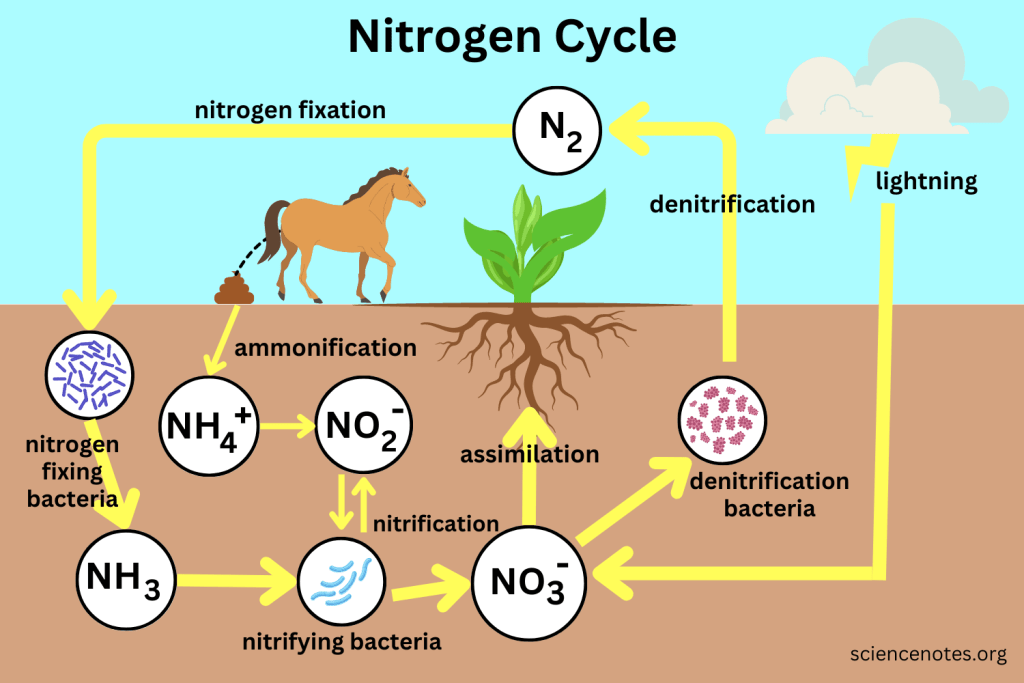
Nitrogen Cycle
Describes how nitrogen moves between plants, animals, bacteria, the atmosphere, and soil.

Omnivore
A consumer that gets energy by eating both plants and animals.
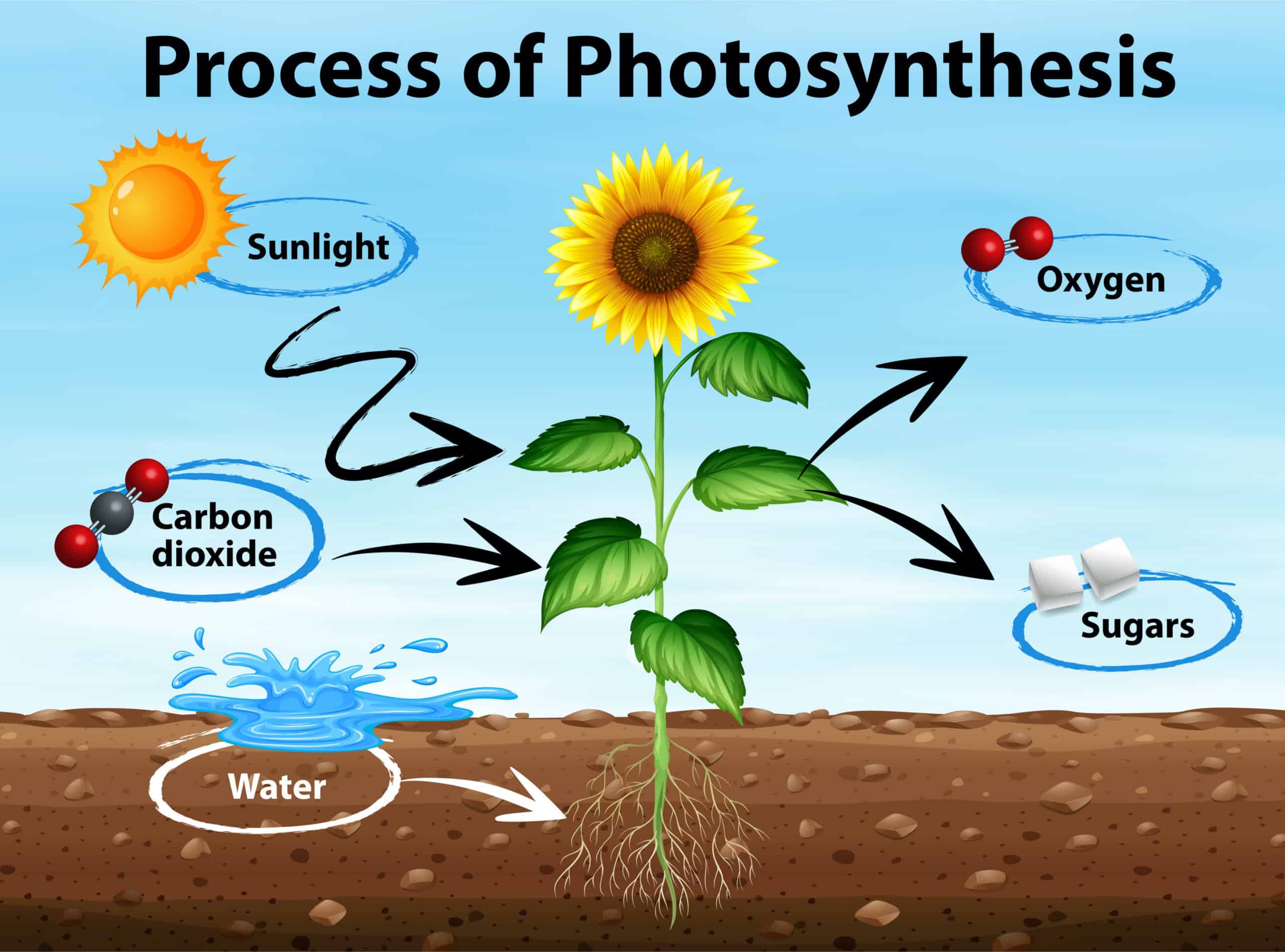
Oxygen (O2)
A product of photosynthesis.
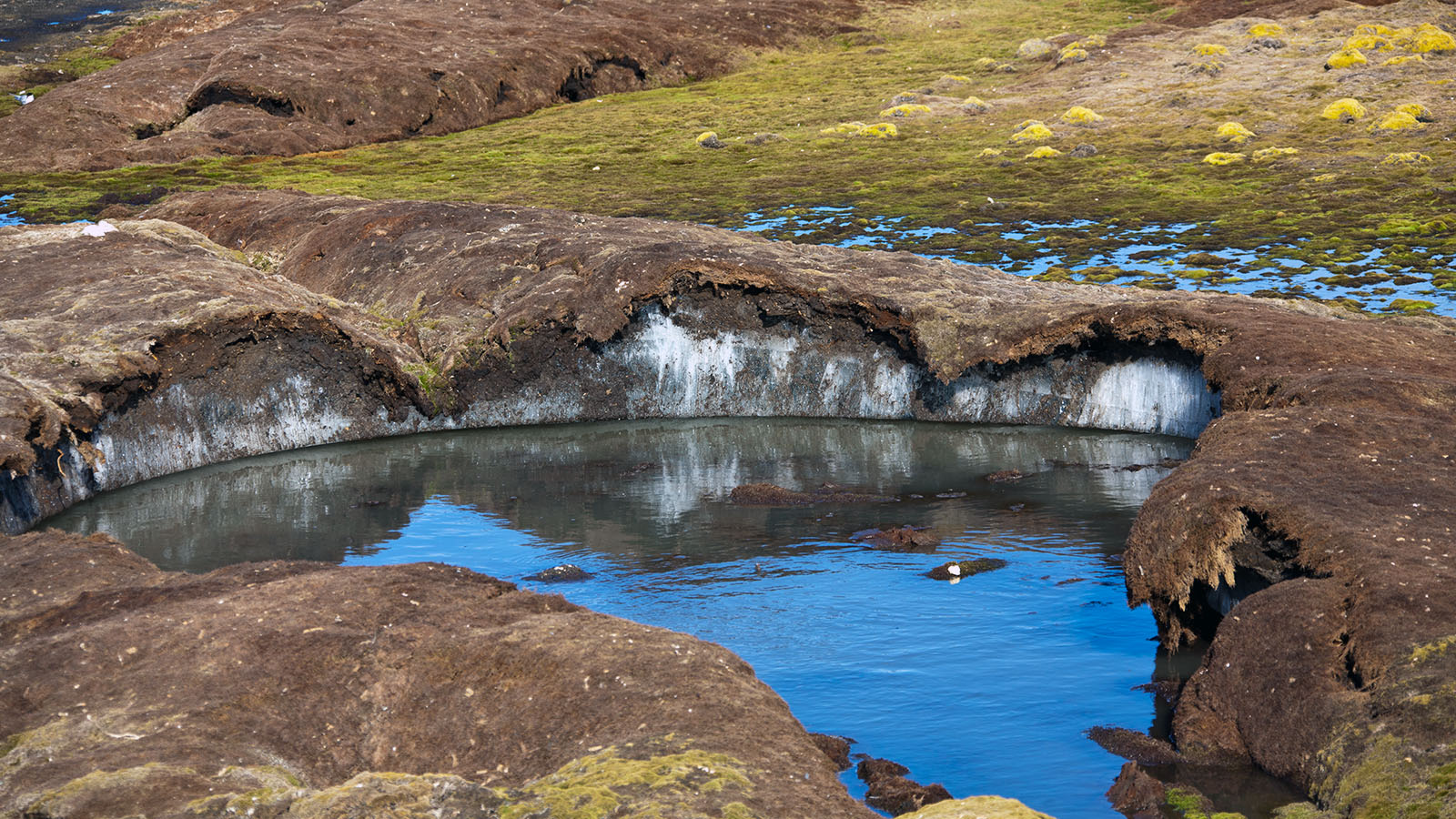

Permafrost
A permanently frozen layer on or under Earth's surface.
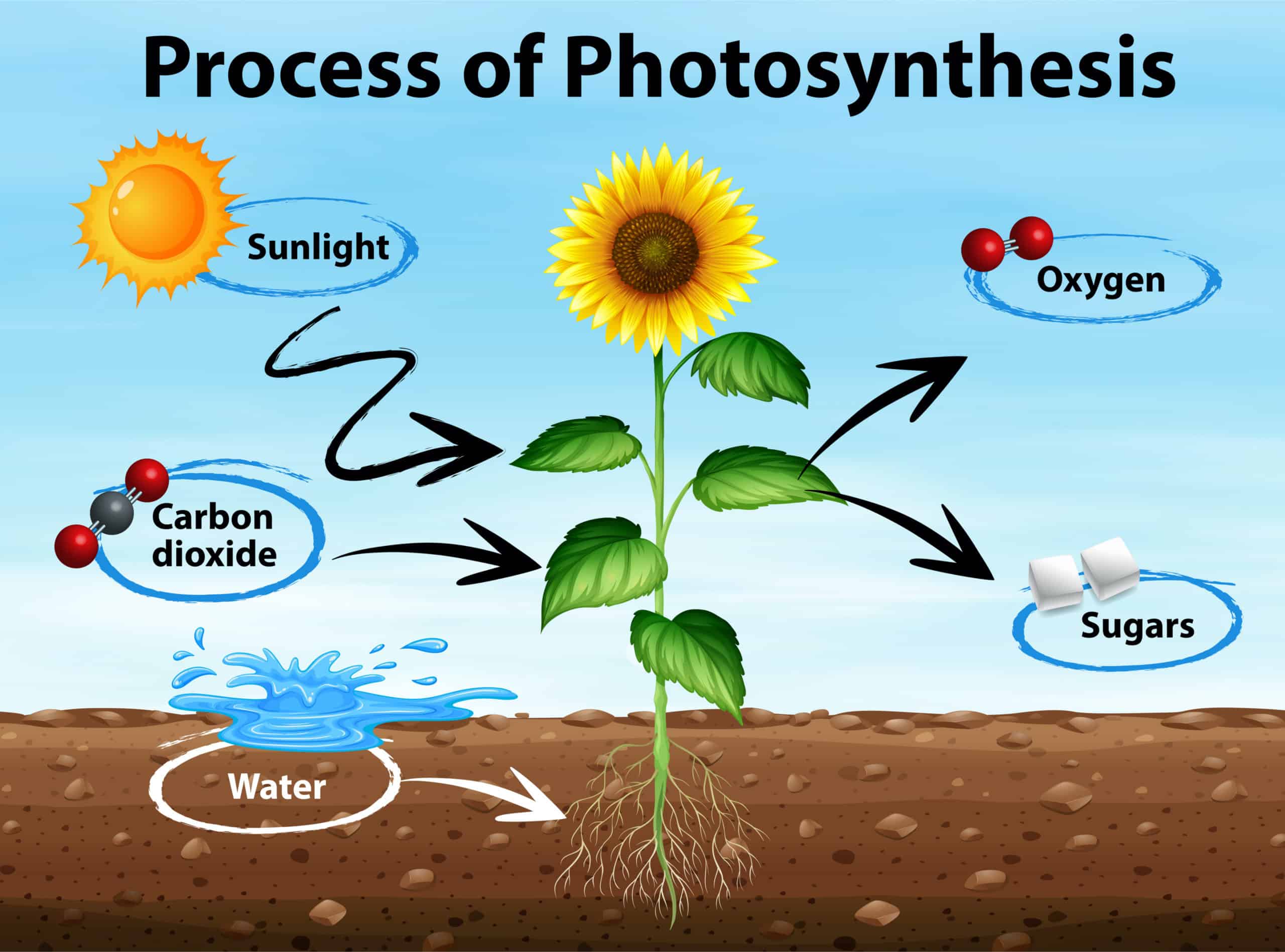
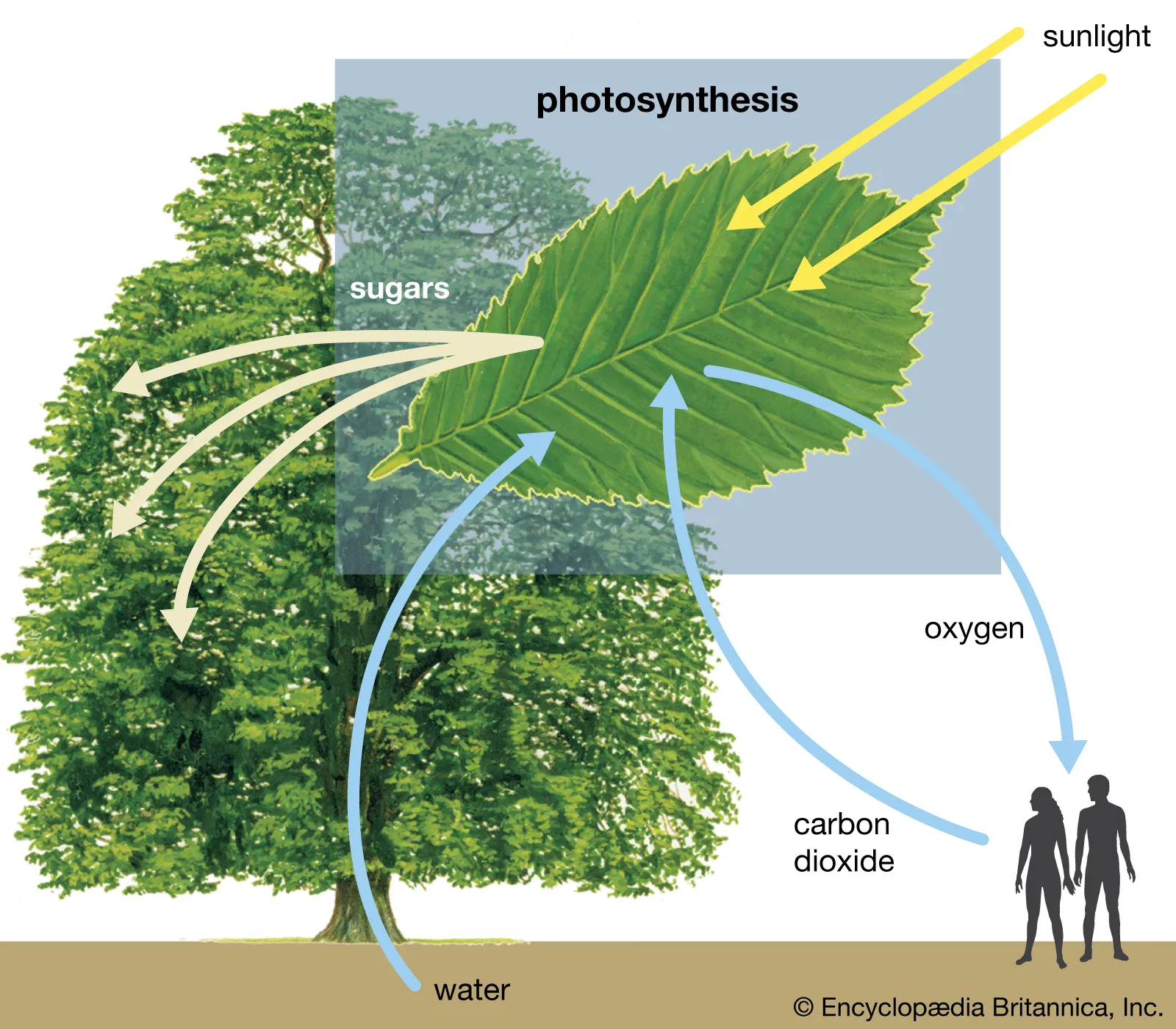
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants and other autotrophs capture and use energy from the sun to make food.
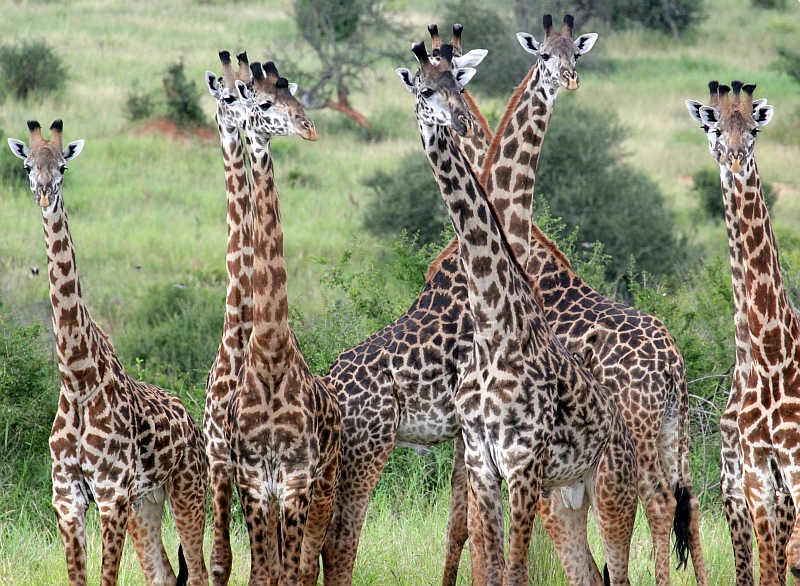

Population
All the members of one species living in the same area.

Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth’s surface.

Predator
An animal that hunts, catches and eats other animals.
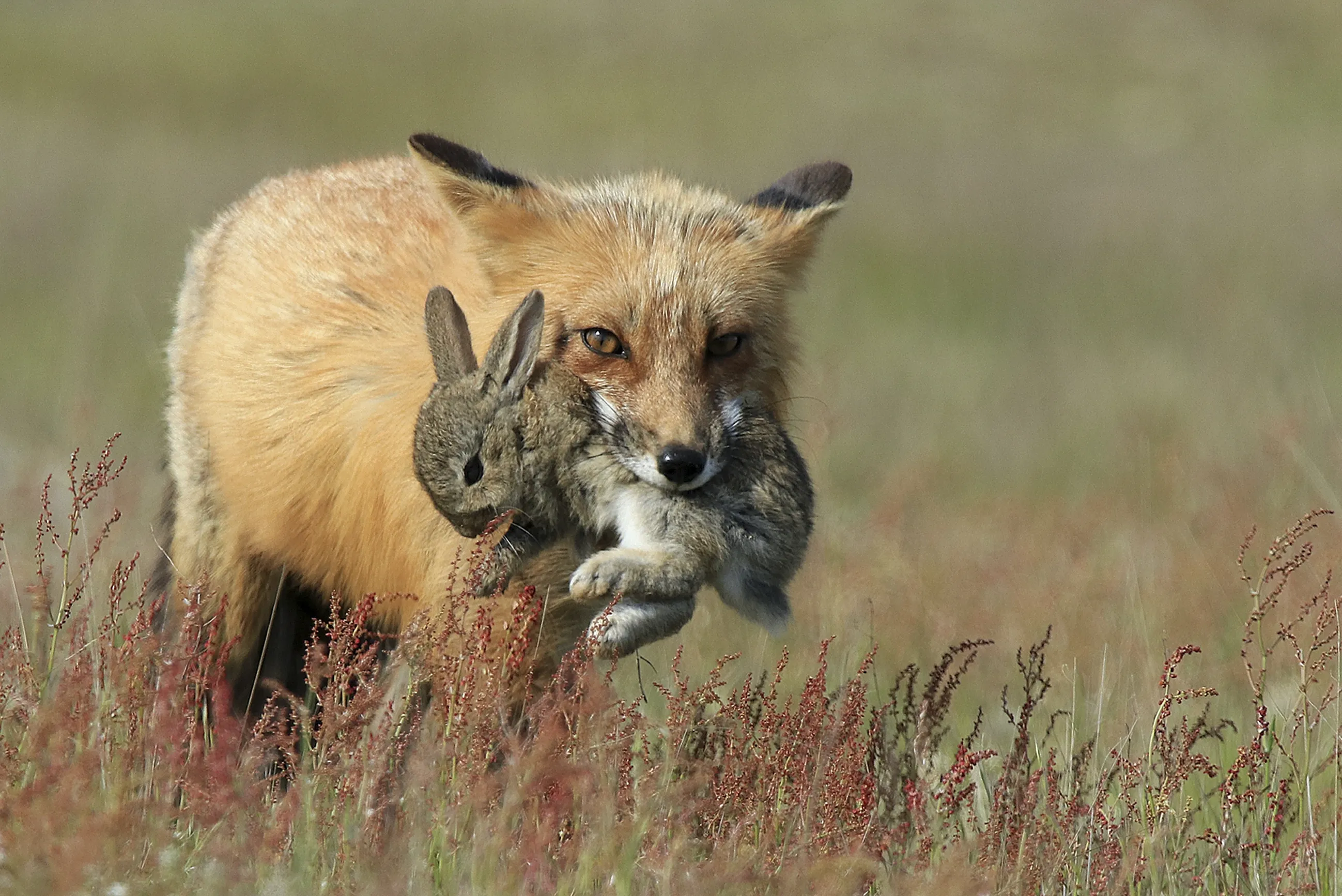

Prey
An animal that is hunted by another animal for food.
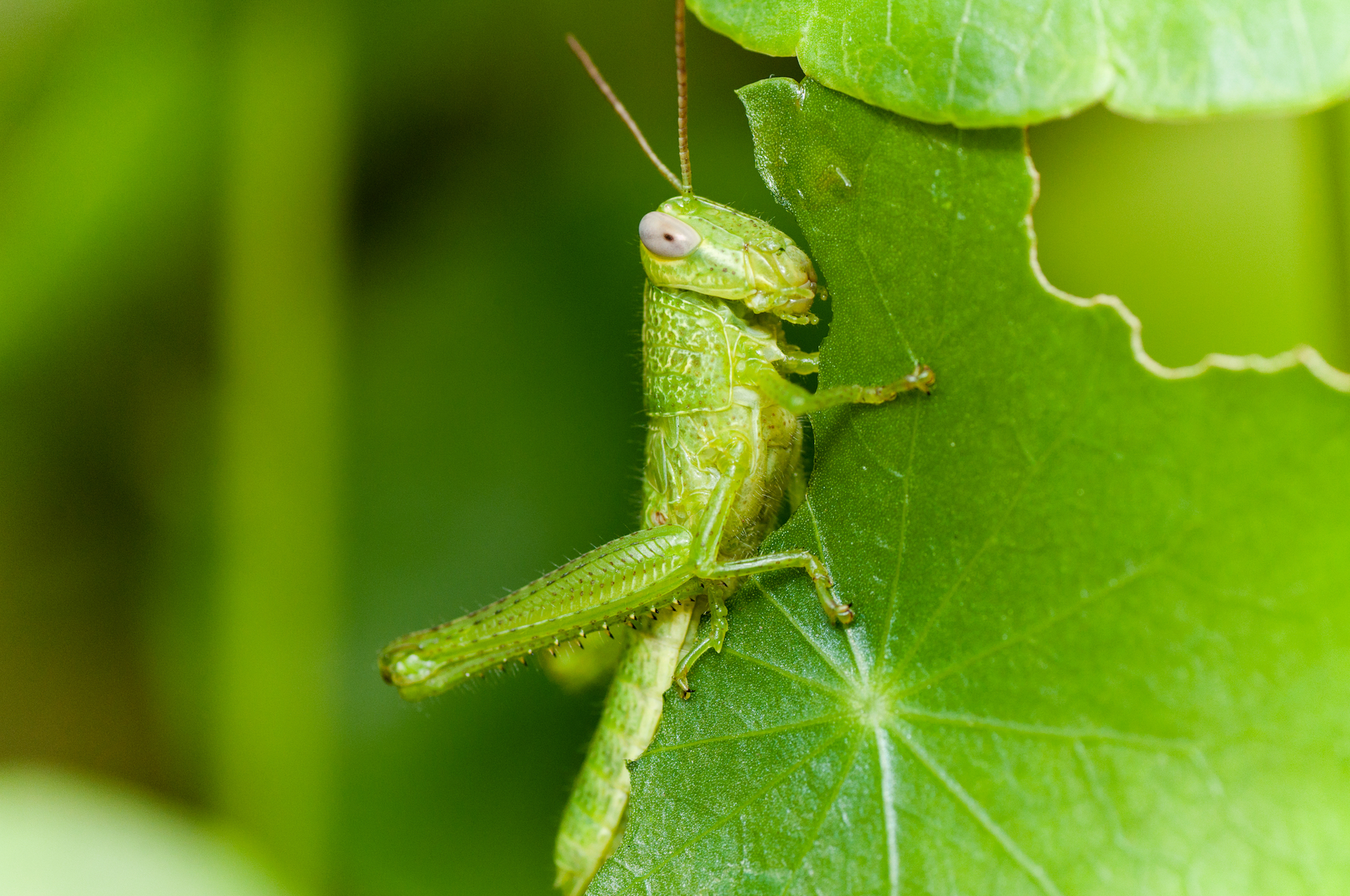

Primary Consumer
Organisms that only eat the producers in a food chain.

Producer
An organism that can make its own food.
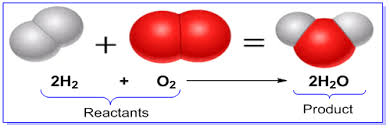
Product
A substance formed as a result of a chemical reaction.

Rain Forest
A forest that receives a large amount of rainfall each year.
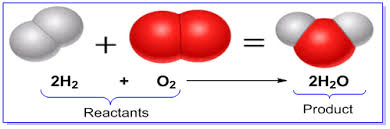
Reactant
A substance that enters into a chemical reaction.
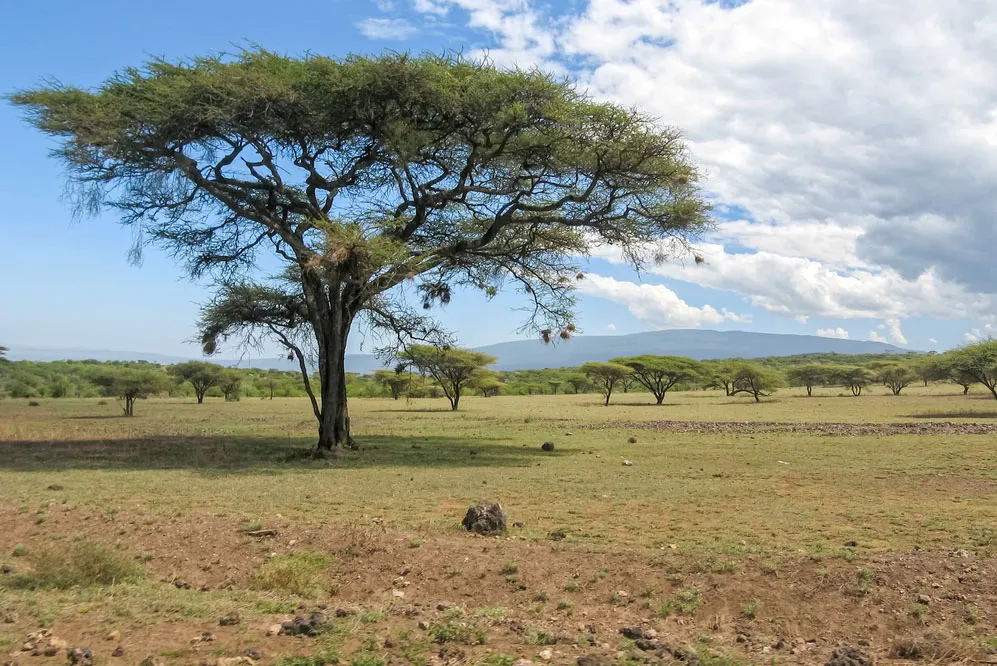

Savanna
Flat grasslands with scattered trees and shrubs.
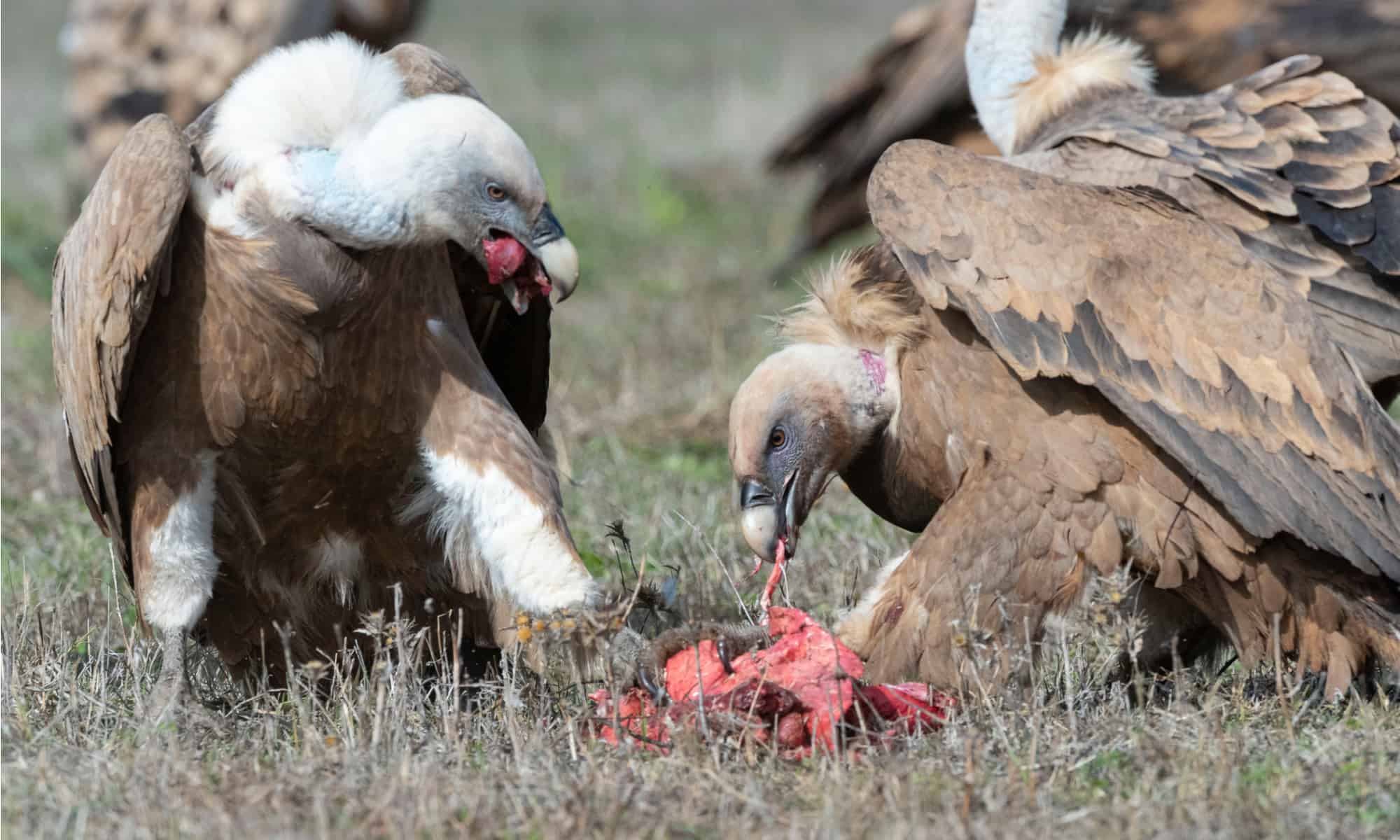

Scavenger
A carnivore that feeds on the bodies of dead or decaying organisms.
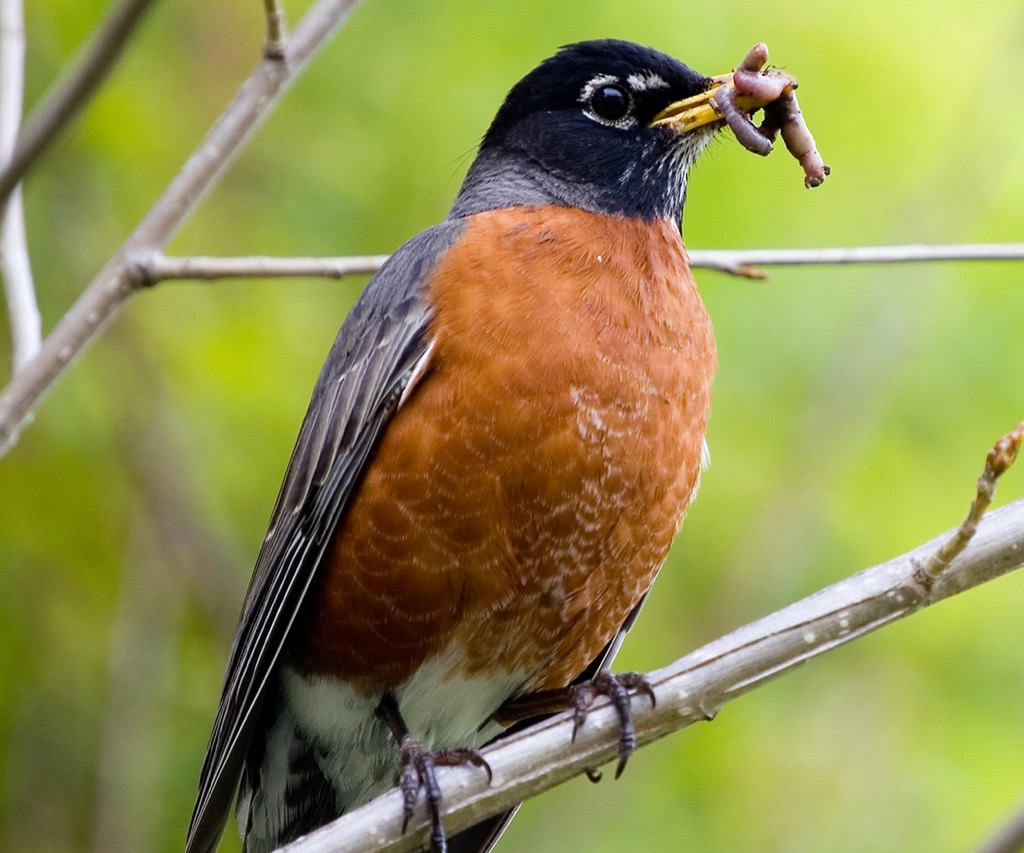

Secondary Consumer
Mostly carnivores that feed on primary consumers.
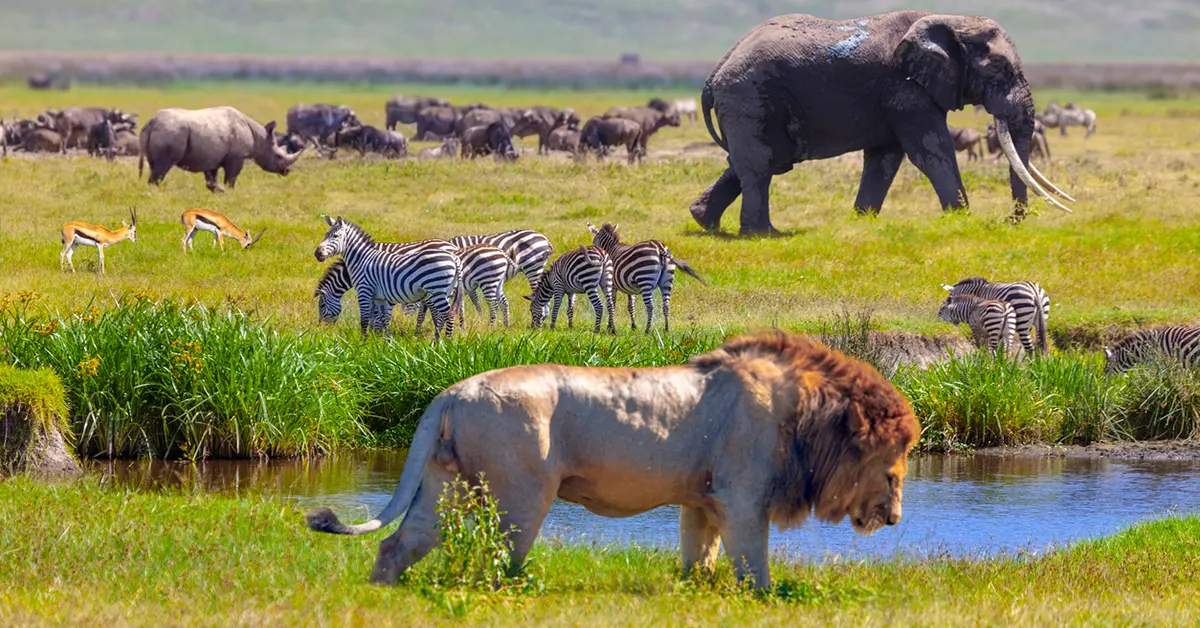

Species Biodiversity
The variety of different organisms living in a particular area.
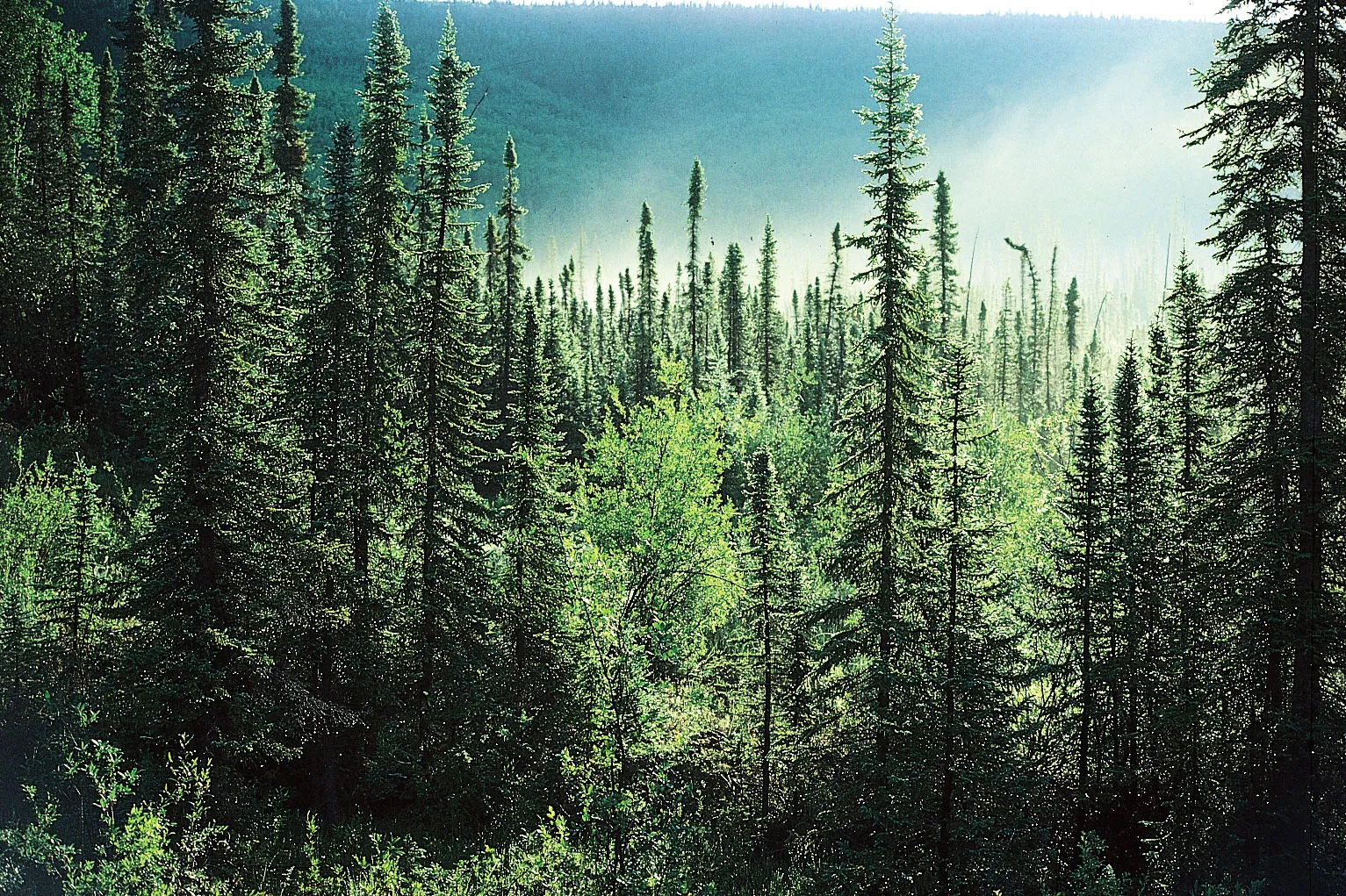

Taiga
A coniferous forest growing on swampy ground.

Temperature
How hot or cold something is.
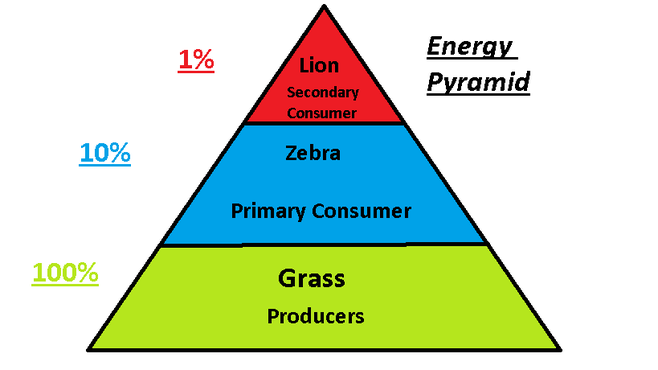
Ten Percent Rule
Only 10% of the total energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
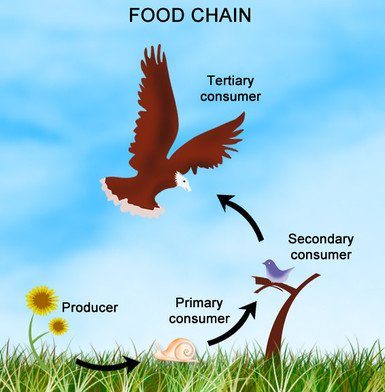
Tertiary Consumer
Carnivores that eat primary or secondary consumers.

Tundra
A very cold, treeless region where the ground stays frozen most of the year.

Adaptation
A special characteristic or behavior that helps a living thing survive.
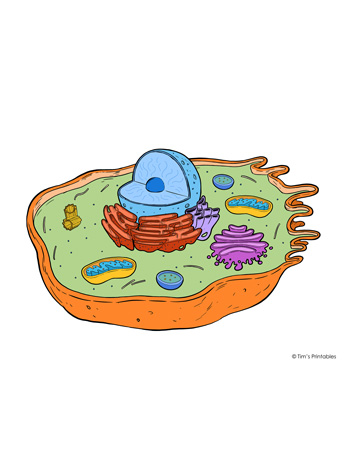
Cell
The tiny building block that makes up all living things.
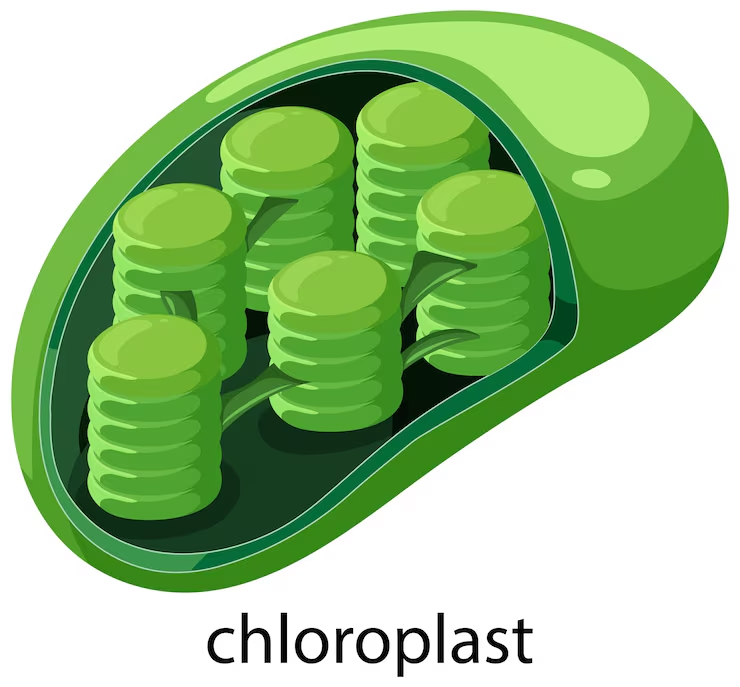
Chloroplast
The part of a plant cell that uses sunlight to make food.
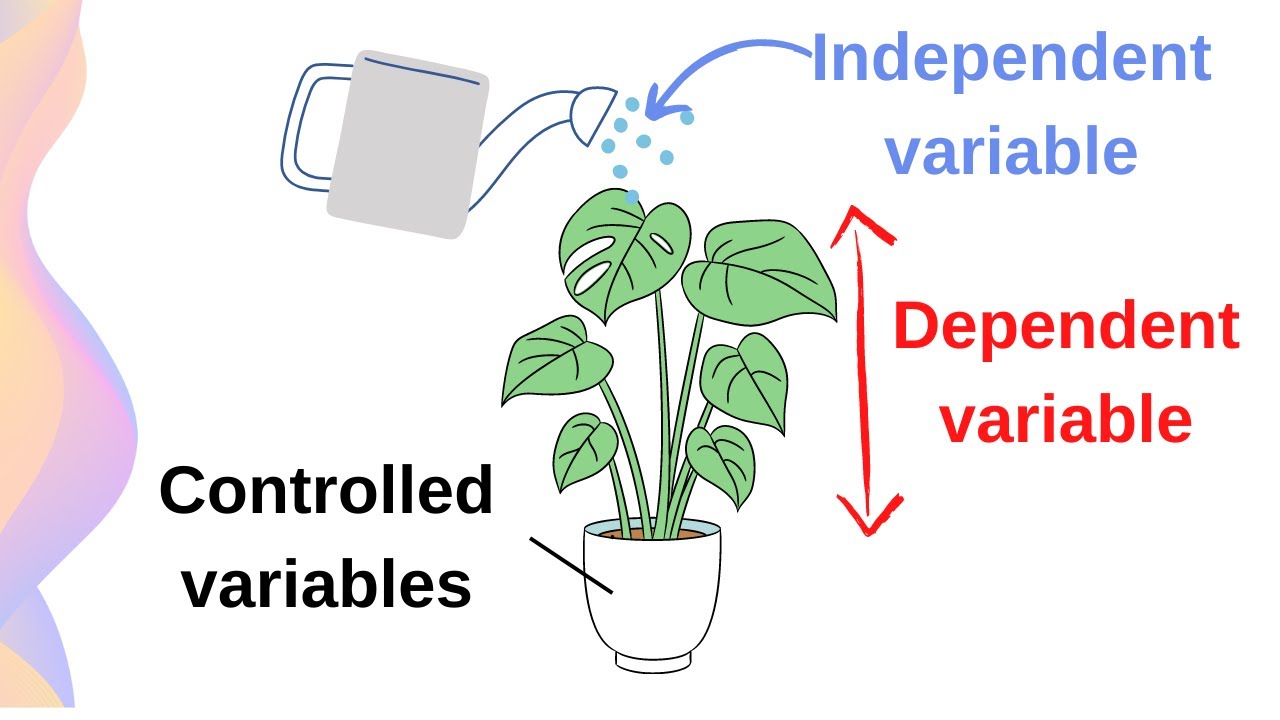
Dependent Variable
In an experiment, the factor that you measure in response to changes you make.

Ecosystem
The community of organisms that live in a particular area along with their nonliving environment.
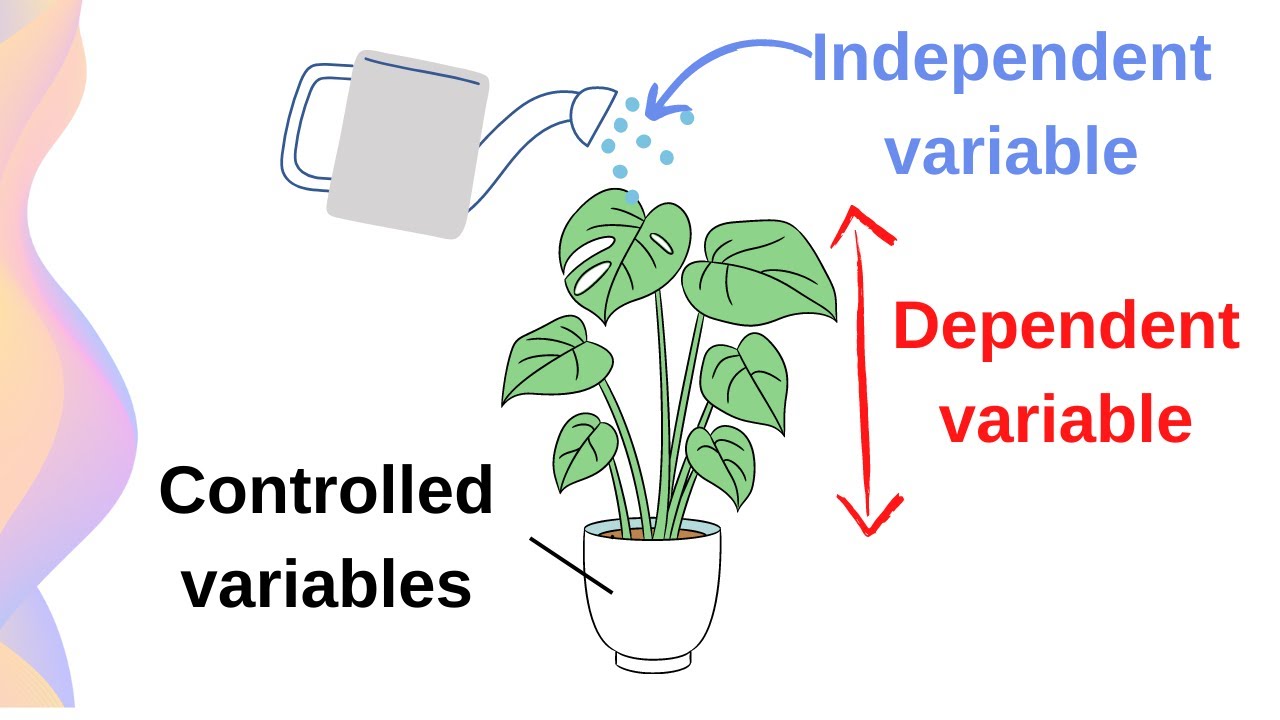
Independent Variable
The factor you change in an experiment to see how it affects the outcome.
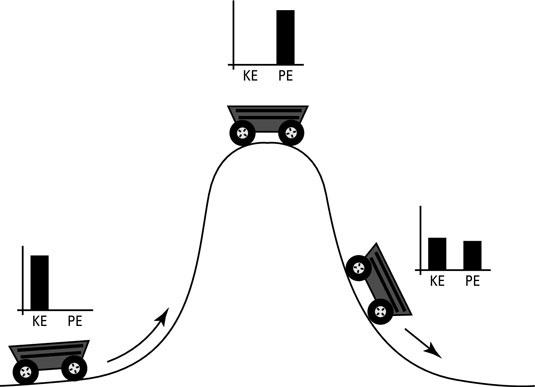
Law of Conservation of Energy
The amount of energy is neither created nor destroyed.
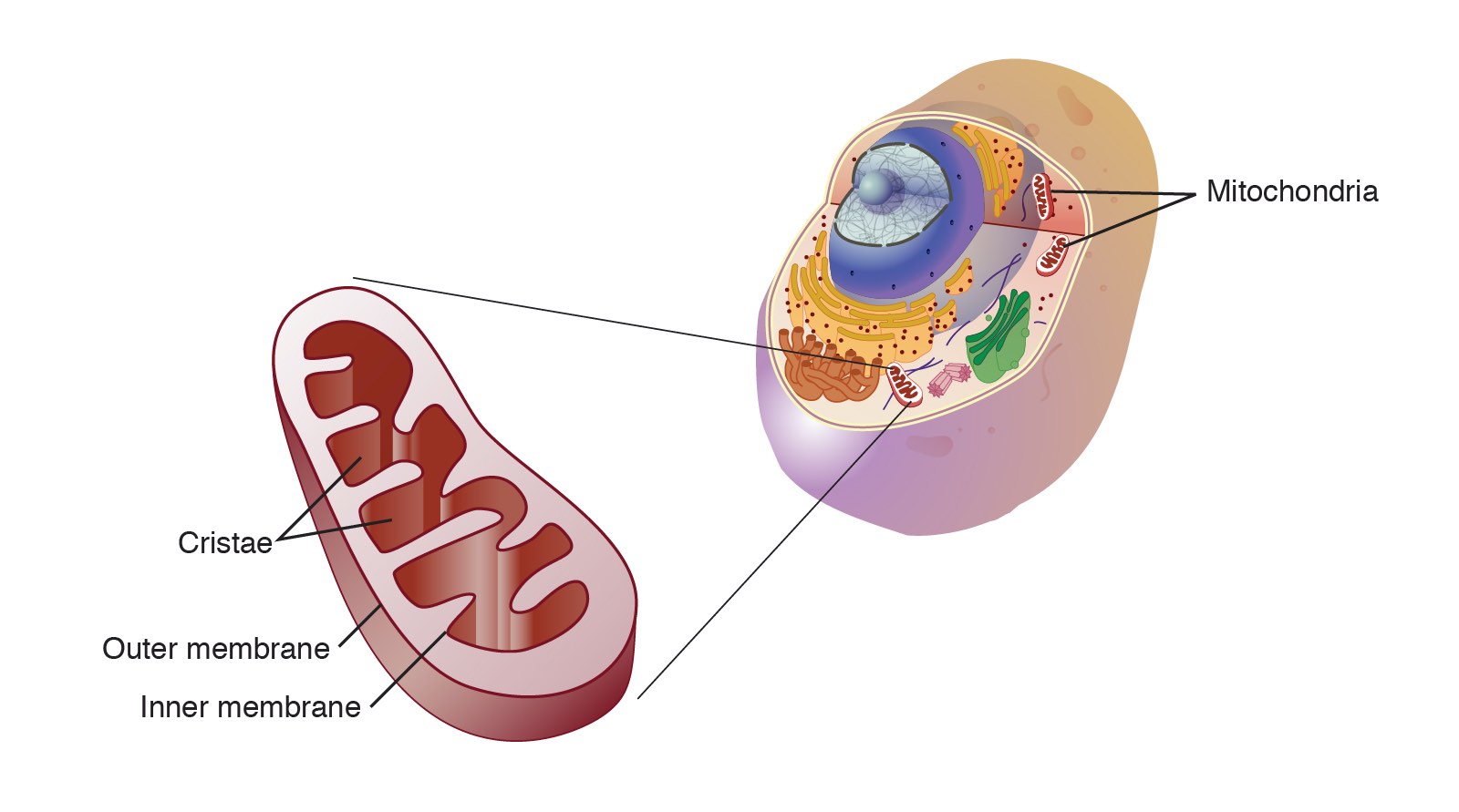
Mitochondria
The part of the cell that makes energy.
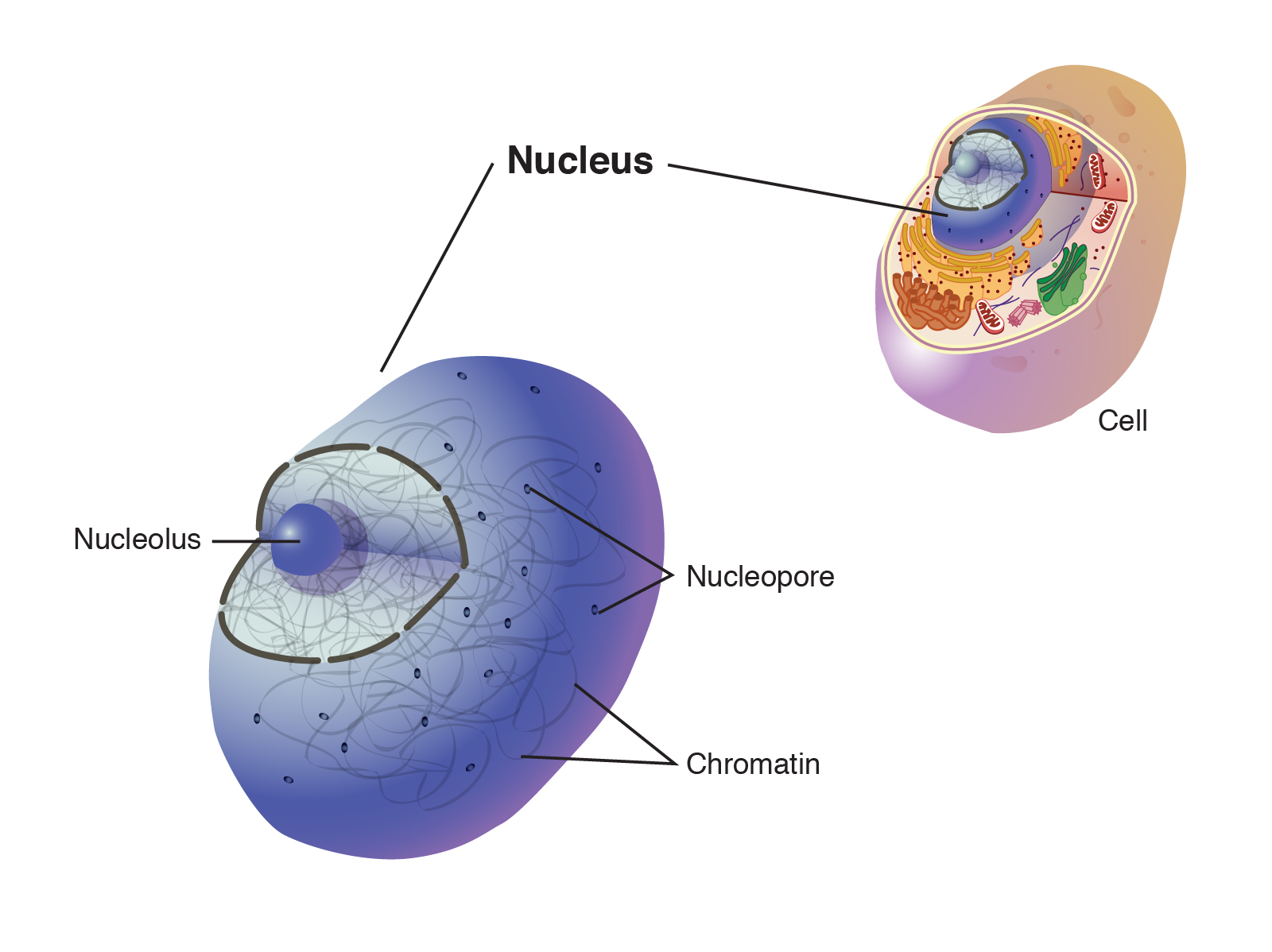
Nucleus
The 'boss' of the cell that tells the cell what to do.
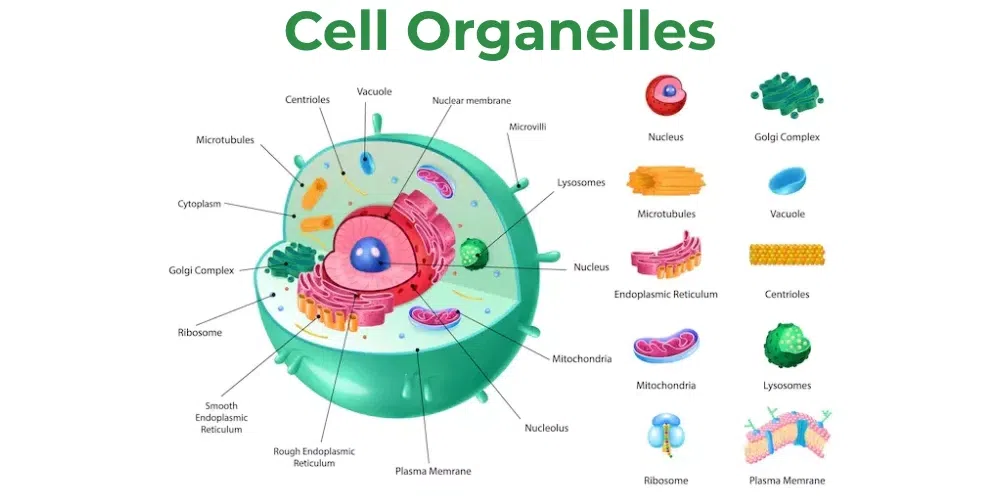
Organelle
The small parts inside a cell that each have a special job.
Organism
Any living thing.
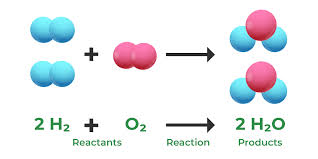
Law of Conservation of Matter
Matter is not made or lost; it only changes form.