study guide chapters 18-20
1/418
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
419 Terms
Endocrine glands
-Secrete chemical substances called, hormones.
-Ductless glands; secrete hormones directly into the blood & not into ducts.
Hormones
-Chemical messenger that influences/controls the activities of other tissues or organs
islets contain
secreting cells
Gonads produce
gametes (oocytes and sperm respectively)
gonads are
ovaries and testes
ovaries produce
two estrogens (estradiol and estrone), progesterone, relaxin, and inhibin
Testes produce
testosterone
Melatonin helps to
regulate the body's biological clock
The thymus is located
behind the sternum between the lungs
thumus produces
thymosin, thymic humoral factor (THF), thymic factor (TF), and thymopoietin
These hormones promote maturation of the immune system's T cells
function of hormones
Help regulate metabolic processes involving carbohydrates, proteins, & fats
-Help in growth & reproduction
-Help regulate water & electrolyte balance
-Help your body meet the demands of infection, trauma, & stress
Exocrine glands secrete their products into what
ducts
The posterior pituitary gland does not synthesize any
hormones
it stores and releases from axon terminals
what 2 hormones are produced by the neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus:
Oxytocin (OT)
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Axons from the neurosecretory cells form
the hypothalamohypophyseal tract
The amount of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secreted
varies
with blood osmotic pressure
An increase in blood volume
causes a decrease in ADH secretion
A decrease in blood volume
causes an increase in ADH secretion
ADH decreases
urine output
osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus monitor
blood osmotic pressure
The thyroid gland is a butterfly- shaped gland
located inferior to the larynx and anterior to the trachea
It has right and left lateral lobes
connected by an isthmus
Some glands also have a pyramidal lobe projecting from
the isthmus
exocrine glands do not include any
hormones
Thyroid hormones:
Increase basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Help maintain normal body temperature
Stimulate protein synthesis
Increase the use of glucose and fatty acids for ATP
productionUpregulate beta (β) receptors that attach to
catecholaminesWork with hGH and insulin to accelerate body growth
Parathyroid glands contain 2
types of cells:
chief cells and oxyphil cells
• Chief cells (principal cells
produce parathyroidhormone (PTH, parathormone)
Oxyphil cells
secrete excess PTH in cases of parathyroid cancer
suprarenal glands are covered by
a connective tissue capsule
The glands are divided into two regions:
The outer cortex
The inner medulla
Testosterone Inhibits secretion
of FSH from anterior pituitary.
ovarian hormones inhibit
secretion of FSH from anterior pituitary.
The pancreas is located
in the curve of the duodenum
the pancreas is both
an endocrine and exocrine gland
Exocrine glands include
sudoriferous glands, sebaceous glands, mucous glands, digestive glands and several others throughout the body
what glands secrete hormones
endocrine gland
how do endocrine gland secrete their hormones
directly into the interstitial fluid that surrounds them
how do hormones diffuse into the blood
by the capillaries which then carry the hormone to target cell throughout the body
Secretion of glucocorticoids help control:
Protein breakdown
Glucose formation
Lipolysis
Resistance to stress
Inflammation
Immune responses
Almost all of the exocrine cells of the pancreas
are arranged in clusters called acini
Acini produce
digestive enzymes that are delivered to the gastrointestinal tract through duct
where are islets found
Scattered among the acini
The major androgen secreted by the suprarenal cortex is
dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
In males, after puberty
the hormone testosterone is secreted in much larger quantities so DHEA has virtually no effect
In females, DHEA and other adrenal androgens play a major role in
promoting libido and are converted to estrogens
In menopausal women, all female estrogens come from
adrenal androgens
The adrenal medulla is stimulated by
sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Chromaffin cells secrete
epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
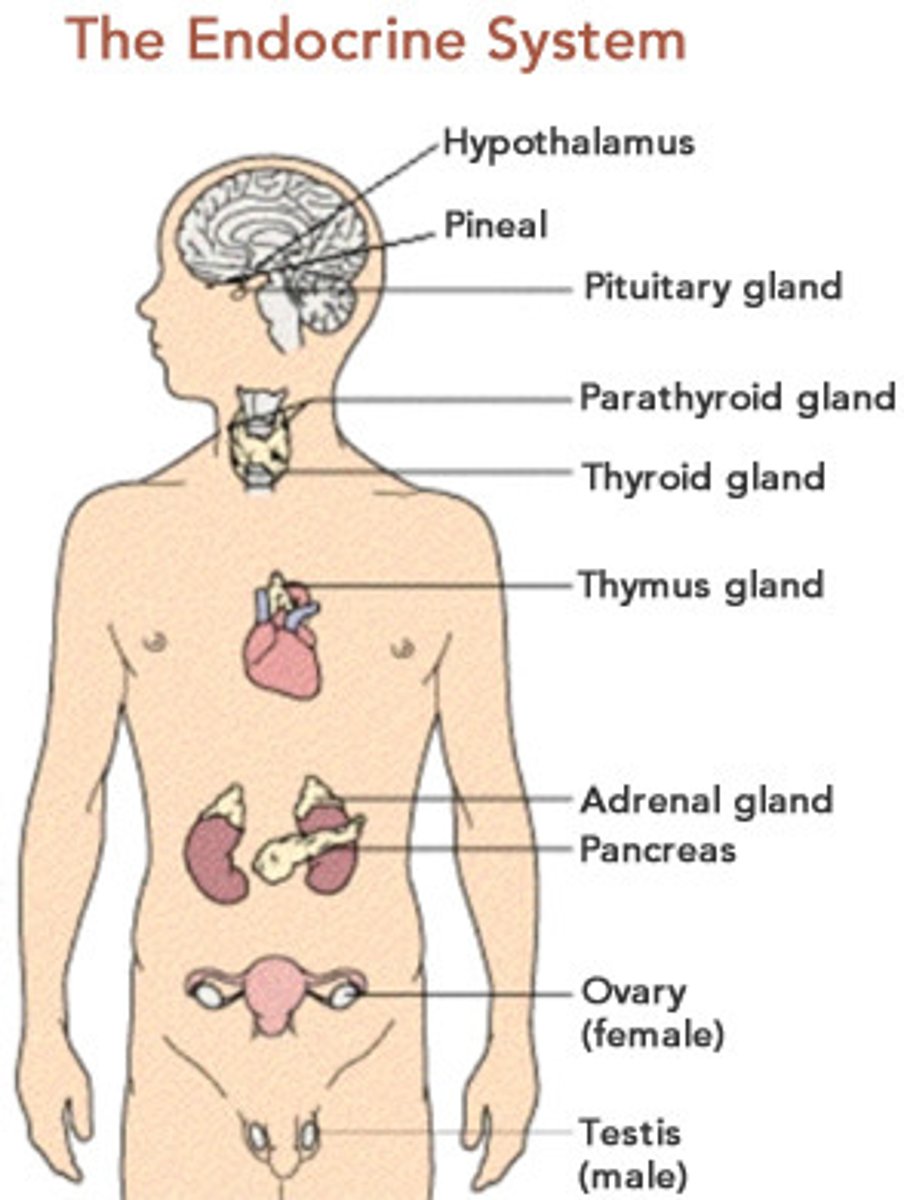
Endocrine glands include
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal and pineal glands
Certain organs and tissues that are not part of the
endocrine system also secrete hormones because
they contain secreting cells
Secreting cells can be found in
hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, ovaries, testes, kidneys, stomach, liver, small intestine, skin, heart, adipose tissue and
placenta
• Receptors may be down-regulated
in the presence of high concentrations of hormone
• Receptors may be up-regulated
in the presence of low concentrations of hormone
Hormones that don’t circulate
are local hormones called paracrines
Those that act on the same cell that secretes them
are autocrines.
lipid soluble hormones
steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, nitric oxide
water- soluble hormones
amine hormones, peptide and protein hormones, eicosanoid hormones
Water-soluble hormones circulate
freely in the plasma
Lipid-soluble hormones circulate
by binding to transport proteins
Steroid hormones include
Aldosterone, cortisol, androgens, Calcitriol, Testosterone, Estrogens, progesterone
Calcitriol is the
active form of vitamin D
Aldosterone, cortisol, and androgens is secreted by
Suprarenal cortex.
Calcitriol secreted by
Kidneys
Testosterone is secreted by
Testes
Estrogens, progesterone is secreted by
Ovaries
Thyroid hormones include
T3 ,T4
T3 and T4 are secreted by
thyroid glands
what cells in thryoid gland secrete T3 T4
thyrocytes or t cells
Gas hormones include
Nitric oxide (NO), Prostaglandins, leukotrienes.
NO is secreted by
Endothelial cells lining blood vessels.
Prostaglandins, leukotrienes are secreted by
All cells except red blood cells.
Amines hormones include
Epinephrine, norepinephrine (catecholamines), Melatonin, Histamine, Serotonin
Epinephrine, norepinephrine (catecholamines) is secreted by
Suprarenal medulla
Melatonin is secreted by
Pineal gland
Histamine is secreted by
Mast cells in connective tissues
Serotonin is secreted by
Platelets in blood
peptides and proteins include
All hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones, oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone, growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, melanocyte-stimulating hormone, insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide, Parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, GIP (glucose- dependent insulinotropic peptide), Erythropoietin, Leptin.
All hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones secreted by
Hypothalamus
Oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone secreted by
Posterior pituitary
Growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, melanocyte stimulating hormone secreted
Anterior pituitary
Insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide secreted by
pancreas
parathyroid hormone is secreted by
parathyroid glands
Calcitonin is secreted by
thyroid gland
what cells secrete calcitonin
thyrocytes specifically C cells
Gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide) is secreted by
Stomach and Small intestine specifically enteroendocrine cells
Erythropoietin is secreted by
kidneys
Leptin is secreted by
Adipose tissue
what is the basic sex hormone
aldosterone
what happens when a molecule can’t sneak past the membrane
it needs a messenger system to relay the info to the hormone
Responses to the same hormone may vary depending on
the hormone itself and the target cell.
The response may be
• Synthesis of new molecules
• Changing permeability of the cell membrane - in or out of the memb.
• Stimulating transport of a substance into or out of
the cell
• Altering the rate of metabolic actions - how quick or slow you use it
• Causing contraction of smooth or cardiac muscle
target cell responds to a hormone is based on
The hormone’s concentration in the blood
The number of hormone receptors on the target cell
influences exerted by other hormones
Some hormones work more effectively when a
second hormone is present to assist themSome hormones oppose the action of others
hormones are secreted in
short bursts when needed
hormones are secreted regularly by
signals from NS, chemical changes in blood, other hormones
what is most of the feedback that occurs
negative feedback
what are the positive feedback
childbirth, lactation, and blood clots
withdraw additional hormone when
blood concentration is back to normal
what 2 glands work together to control other endocrine glands
hypothalamus and pituitary glands
adenohypophysis makes up
75% of the pituitary glands weight
how many hormones do adenohypophysis secrete
7
what are the 7 hormones secreted by the adenohypophysis
• Human growth hormone (hGH) - all tissue
• Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) - thyroid gland
• Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) - reproductive tissue
• Luteinizing hormone (LH) - reproductive tissue
• Prolactin (PRL) - specific
• Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) - suprarenal/ adrenal glands
• Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) - production of melanin