Overview of Anxiety Disorders and Neural Mechanisms
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
What are the five main types of anxiety disorders?
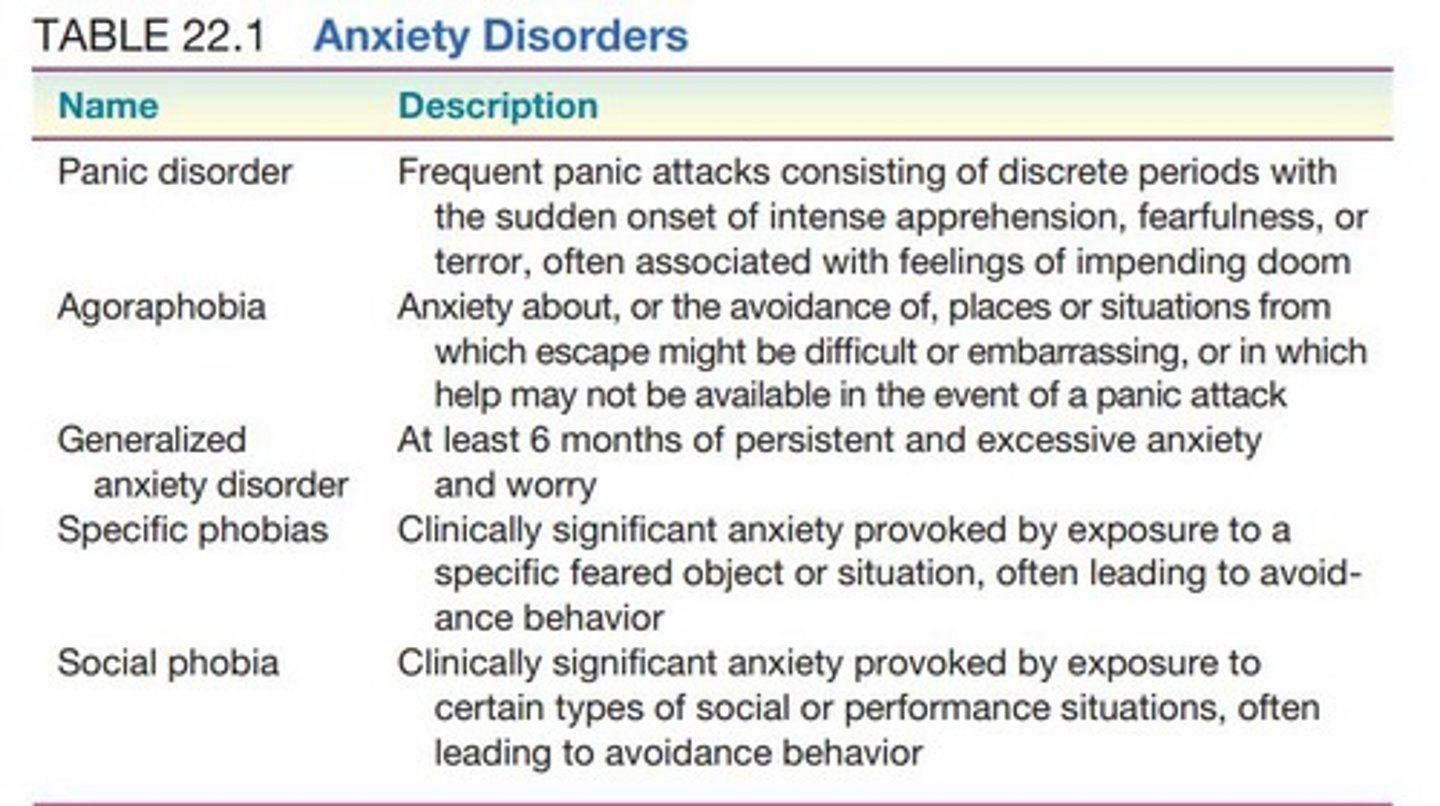
1. Panic disorder: Sudden, recurrent panic attacks with physical symptoms. 2. Agoraphobia: Anxiety about being in places where escape may be difficult, often leading to avoidance of public areas. 3. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): Excessive, uncontrollable worry lasting at least six months without a specific trigger. 4. Specific phobias: Intense fear and avoidance of specific objects or situations. 5. Social phobia (social anxiety disorder): Fear of social or performance situations where one may be judged.
What is the biological basis for anxiety disorders?
Anxiety disorders involve dysregulation of the brain's stress response system, particularly the HPA axis. The hypothalamus releases CRH, stimulating the pituitary gland to secrete ACTH, which triggers cortisol release from the adrenal glands. The amygdala becomes hyperactive, causing exaggerated reactions, while the hippocampus, which normally inhibits the HPA axis, can be damaged by chronic stress, leading to increased cortisol and intensified anxiety.
What role does neural activity play in the phases of pathway formation?
Neural activity is involved in the phases of pathway formation, particularly in the adjustment of synaptic connections based on experience.
How does Ca++ contribute to synapse formation and rearrangement?
Ca++ is thought to contribute to synapse formation and rearrangement by: 1. Activating signaling pathways that promote synaptic growth. 2. Modulating the release of neurotransmitters. 3. Influencing the insertion of receptors into the synaptic membrane.
What is metaplasticity?
Metaplasticity refers to the change in the rules governing long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) based on prior synaptic activity, adjusting the threshold for inducing LTP or LTD.
How does metaplasticity affect synaptic response?
In metaplasticity, heightened synaptic activity raises the threshold for LTP, making it harder to achieve, while reduced activity lowers the threshold, making LTP easier.
What is synaptic scaling?
Synaptic scaling is a homeostatic mechanism that globally adjusts all synaptic weights by multiplying or dividing them by the same factor, preserving relative strengths while changing absolute values.
How do metaplasticity and synaptic scaling differ?
Metaplasticity adjusts the synaptic modification threshold based on prior activity, while synaptic scaling adjusts all synapses on a neuron simultaneously without regard to individual activity history.
What is the role of CaMKIV in synaptic scaling?
CaMKIV is involved in gene expression that regulates receptor insertion or removal, facilitating synaptic scaling.
What are the time scales over which metaplasticity and synaptic scaling operate?
Both metaplasticity and synaptic scaling operate over longer timescales (hours to days) compared to LTP and LTD.
What properties characterize long-term potentiation (LTP) in CA1?
LTP in CA1 is characterized by a persistent increase in synaptic strength following high-frequency stimulation, involving NMDA receptor activation and calcium influx, leading to various intracellular signaling pathways.
What mechanisms drive long-term potentiation (LTP)?
LTP is driven by mechanisms such as calcium influx through NMDA receptors, activation of protein kinases, and changes in receptor trafficking and gene expression.
What is the role of the amygdala in anxiety disorders?
The amygdala initiates the stress response and becomes hyperactive in many anxiety disorders, leading to exaggerated fear responses.
What is the function of the hippocampus in the context of anxiety?
The hippocampus contains glucocorticoid receptors that normally inhibit the HPA axis by sensing cortisol levels, providing negative feedback.
How does chronic stress affect the hippocampus?
Chronic stress can damage hippocampal neurons, weakening its ability to regulate the HPA axis and increasing anxiety symptoms.
What is the relationship between cortisol and anxiety?
Increased cortisol release due to dysregulation of the HPA axis can intensify anxiety symptoms.
What triggers the release of cortisol in the stress response?
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) released by the hypothalamus triggers the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary gland, which in turn stimulates cortisol release from the adrenal glands.
What is the significance of the NR2A/NR2B ratio in metaplasticity?
The NR2A/NR2B ratio affects the threshold for LTP and LTD, with changes in this ratio influencing synaptic plasticity based on prior activity.
How do experience-dependent plasticity and memory formation relate to metaplasticity and synaptic scaling?
Both metaplasticity and synaptic scaling allow for memory formation and experience-dependent plasticity while preventing excessive potentiation or depression that could disrupt stimulus selectivity.
What is the impact of avoidance behavior in anxiety disorders?
Avoidance behavior in anxiety disorders can lead to increased anxiety and reinforce the disorder by preventing exposure to feared situations.
How long must excessive worry persist for a diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)?
Excessive worry must persist for at least six months for a diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
What is long-term potentiation (LTP) and where does it occur?
LTP is a synaptic mechanism thought to underlie learning and memory, occurring in the CA1 region of the hippocampus.
What are the key properties of LTP at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapse?
LTP is input-specific, can be induced rapidly by high-frequency stimulation (tetanus), and is long-lasting, persisting for weeks or even a lifetime.
What is the concept of cooperativity in LTP induction?
Cooperativity refers to the requirement that presynaptic activity and postsynaptic depolarization occur simultaneously for LTP induction.
What principle does LTP follow regarding neuronal firing?
LTP follows Hebb's principle: 'cells that fire together, wire together.'
What receptors mediate excitatory transmission in LTP?
Excitatory transmission is mediated by AMPA receptors.
What is the critical trigger for LTP and how does it work?
The critical trigger for LTP is Ca²⁺ influx through NMDA receptors, which open when glutamate binds and the postsynaptic neuron is depolarized.
What are the two major effects of Ca²⁺ activation in LTP?
1. Phosphorylation of existing AMPA receptors to enhance their conductance. 2. Insertion of additional AMPA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane.
What structural changes contribute to the long-term maintenance of LTP?
Growth of new dendritic spines and synapses.
What is the role of the HPA axis in stress response?
The HPA axis involves the hypothalamus releasing CRH, which causes the anterior pituitary to release ACTH, leading to cortisol release from the adrenal glands.
What are the symptoms of anxiety disorders?
Symptoms include panic attacks and agoraphobia, which is the fear of not being able to escape a situation.
What are the two types of reinforcement in behavior?
Positive reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, while negative reinforcement decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
What are some common treatments for depression?
Common treatments include tricyclics and SSRIs.
What are anxiolytic drugs and name a few?
Anxiolytic drugs include lithium, MAOIs, SSRIs, and NSRIs (norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitors).
How does lithium work in bipolar disorder?
Lithium works by preventing the breakdown of certain molecules within the lipid bilayer, mitigating the euphoria associated with bipolar disorder.
Who created the drug arsphenamine and what was its significance?
Paul Ehrlich created arsphenamine, which destroyed the Trypanosoma bacteria that caused insanity, prior to the discovery of penicillin.
What is the order of cortical layer formation in the brain?
Cortical layers are formed beginning with layer VI and progressing to layer I as neurons travel through the cortical plate.
What is the role of the amygdala in stress response?
The amygdala exacerbates the stress response.
What is the role of the hippocampus in stress response?
The hippocampus suppresses the stress response.
What are the symptoms of panic attacks?
Symptoms of panic attacks can include rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, shortness of breath, and feelings of impending doom.
What is the significance of the HPA axis in relation to stress and the immune system?
Activation of the HPA axis produces cortisol, which can induce stress and suppress the immune system.
What is the relationship between the hypothalamus and amygdala in the HPA axis?
The hypothalamus and amygdala have a push and pull relationship in regulating the HPA axis.
What happens to the cortical plate during development?
The cortical plate disappears, resulting in the formation of 6 layers.
What are some examples of chemoattractants and chemorepellents?
Netrin, agrin, and musk.
What is synaptic rearrangement and what are its types?
Synaptic rearrangement involves increasing synaptic strength through mechanisms such as increased receptor expression, phosphorylation of channels, increased myelination, and axon terminal sprouting due to neurotrophic factors.
Why do some neurons undergo apoptosis?
Neurons undergo apoptosis due to insufficient trophic factors.
What is the role of trophic factors in synaptic strength?
Trophic factors undergo retrograde transport to the neuron, leading to protein synthesis that strengthens synapses.
What are ocular dominance columns?
Ocular dominance columns are structures in the visual cortex that can be eliminated if an eye is deprived of stimulation, affecting both the tectum and occipital lobe.
What is the significance of retinocortical synapses?
Retinocortical synapses are crucial for visual processing and the formation of ocular dominance columns.
What is synaptic capacity?
Synaptic capacity refers to the finite number of synapses that can occur on dendrites, roughly estimated to be around 10,000.
What is the difference between apoptosis and necrosis?
Necrosis is cell death due to damage, while apoptosis is programmed cell death, often influenced by the excitability of AMPA receptors.
What causes neurons to be pruned away during development?
Neurons are pruned away due to competition for neurotrophic factors released by the postsynaptic neuron.
What role does Slit play in neural development?
Slit is released within the spinal cord and guides growth cones to specific regions in the midbrain.
What is the subplate in cortical development?
The subplate is the first layer containing precursor cells for neurons, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and astrocytes.
What was the key finding in the monkey experiment regarding activity levels?
The experiment showed increased activity when the monkey grabbed food or when a human grabbed food, but less activity when using forceps.
What is the trisynaptic circuit and its pathway?
The trisynaptic circuit consists of the pathway: EC → dentate gyrus → CA3 → CA1, which is involved in long-term potentiation (LTP).
What is unique about NMDA receptors that allows LTP to occur?
NMDA receptors allow calcium influx, which is necessary for synaptic rearrangement and strengthening.
What is encoding in the context of sensory information?
Encoding is the process by which sensory information is transformed into neural impulses.
What is metaplasticity?
Metaplasticity refers to the plasticity of synaptic plasticity itself, influencing how synapses can change.
What is the role of calcium in NMDA receptor activation?
Calcium influx through NMDA receptors is required for the activation of signaling pathways that lead to synaptic strengthening.
What is the biological basis of anxiety disorders?
Anxiety disorders are often linked to dysregulation of neurotransmitter systems, particularly involving monoamines.
What is the role of LTP in the CA1 region?
LTP in the CA1 region is crucial for memory formation and synaptic strengthening.
What is the most common psychiatric disorder?
Anxiety disorders.
What does the monoamine hypothesis suggest about mood disorders?
The monoamine hypothesis suggests that depression is a consequence of dysregulation in monoamine neurotransmitter systems, particularly norepinephrine and serotonin.
How would a behaviorist treat maladaptive behavior disorders?
A behaviorist would treat maladaptive behaviors by reinforcing new behaviors or employing extinction techniques.
What was a symptom of general paresis of the insane?
Symptoms included cognitive decline and emotional disturbances, affecting 10-15% of institutionalized psychiatric patients.
What are common symptoms of panic attacks?
Frequent panic attacks consisting of discrete periods, depression, and stressful behavior.
What is a typical symptom associated with mania?
Decreased need for sleep.
What are adverse effects of PCP intoxication?
Hallucinations, paranoia, and other symptoms of schizophrenia.
True or false: Schizophrenia is associated with enlarged lateral ventricles.
True.
What neurochemical triggers the release of ACTH from the anterior pituitary gland?
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH).
What is positive reinforcement of behavior?
An increase in the probability of a type of behavior when it satisfies a craving.
What are common symptoms of OCD?
Recurrent, intrusive thoughts, images, or impulses perceived as inappropriate, grotesque, or forbidden.
What is a disadvantage of ECT?
Relief typically requires many sessions.
What is the role of the hippocampus in the stress response?
Suppresses the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus.
Which structure in the temporal lobe is affected by ECT?
Hippocampus.
What characterizes hypomania in some people?
An increase in efficiency, accomplishment, or creativity.
What is the role of the central nucleus of the amygdala in the stress response?
Activates hypothalamic stimulation of the HPA axis and the sympathetic nervous system.
What is a common symptom of acute anxiety?
Panic attacks.
What behavior is associated with the cognitive deterioration in depression?
Stressful behavior.
What is a common treatment for acute anxiety?
Benzodiazepines.
What is a symptom of mania that involves judgment?
Enhanced judgment skills is not typical; decreased need for sleep is.
What are symptoms of major depression?
Periods of major depression and insomnia.
What is a common fear associated with panic attacks?
Overwhelming fear of dying or 'going crazy'.
What is a common behavior in OCD?
Avoidance of situations irrationally perceived as threatening.
What is the effect of ECT on memory?
ECT disrupts memories of events occurring about 6 months before treatment.
What is a characteristic of hypomania?
An increased efficiency, alternating with periods of depression.
What activates avoidance behavior in the stress response?
Activation of periaqueductal gray matter.
What provokes anxiety in performance situations?
Anxiety provoked by exposure to certain performance situations.
What are sudden feelings of intense terror that occur without warning called?
Panic attacks.
What are compulsions that neutralize anxiety?
Compulsions are behaviors performed to reduce anxiety.
What does reexperiencing an extremely traumatic event refer to?
It refers to symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Which drug did Paul Ehrlich establish could kill Treponema pallidum without harming the human host?
Arsphenamine.
What is the effect of lithium on the nervous system?
Lithium facilitates the actions of adenylyl cyclase in the neuron.
What are common symptoms of schizophrenia?
Delusions, hallucinations, lack of emotional expression, disorganized behavior, incoherent speech, and peculiarities of voluntary movement.
How would a behaviorist treat maladaptive behavior disorders?
By reinforcing new behaviors.
True or false: The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia reflects diminished activation of NMDA receptors in the brain.
True.
True or false: Schizophrenia is associated with enlarged lateral ventricles due to brain tissue shrinkage.
True.
What is a symptom of major depression?
Loss of appetite.
True or false: Type II bipolar disorder is characterized by hypomania and marked impairments, while type I is characterized by manic episodes with major depression.
False.