Viral epidemiology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Epidemiology- definition
Study of frequency, distribution, determinants of disease in populations
POPULATION level impact
Biological V mechanical vector
Biological → virus replicates inside vector
Bluetongue → virus replicates inside midge and ruminant
Mechanical → virus only moved by vector (living or fomite)
Myxoma virus → flea moves it between hosts
Common viral strategy control
Enhance surveillance
Change host movement
Control zone (3km radius)
culling, testing
Surveillance zone (10km radius)
movement restrictions, testing
Quarantine
Physical measures
disinfection
barrier - wall off → hens in barns
fencing to protect from env reservoirs
Change host demography
Increase proportion protected → vaccination → herd immunity
Reduce population infected → culling
Notifiable diseases
Key notifying reasons:
International trade
Public health
Animal welfare
Legal requirement to notify APHA
Suspicion or confirmation (which is earlier)
Rapid and coordinated action to reduce spread
Movement restrictions
Culling
Onsite restrictions
Rabies key info
(Order → Mono-nega-virales)
(Family → Rhab-do-viridae)
Species → Lyssavirus rabies
Rod shaped
Enveloped
Helical capsid
Group V → -ve sense ssRNA
Rabies epidemiology
Domestic dogs and bats
US/Europe → free of domestic dog rabies
US many wild rabies
UK rabies epidemiology
Rabies free
Notifiable
Largest threat → illegal animal imports (e.g. domestic dogs)
GB not part of EU pet travel scheme since Brexit → no pet passports
Rabies control from GB → EU (post Brexit) requirements
Rabies vaccinated post 21 days
Microchipped
Animal health certificate issued within 10 days before travel
Rabies control into GB requirements
EU
GB pet health certificate/passport
Issued from UK or EU
USA
GB pet health certificate
Kenya (other countries)
Antibody test 30+ days after vaccination documented on health cert
Wait 3 months from vaccination before travelling
Valid if booster schedule kept
If no controls met → 4 months quarantine
Period between animal first bitten and symptoms shown
Rabies vaccination
injectable vaccines (inactivated)
oral vaccines (mostly live attenuated)
FMDV general facts
(Order → Picornavirales)
(Family → Picornaviridae)
Genus → Aph-tho-virus
7 serotypes
Spread between most cloven hoofed animals
sylvatic in subsaharan Africa
FMDV modes of transmission [5]
VERY INFECTIOUS
Direct contact with infected animals
Animals may shed asymptomatically
Short incubation period
Contact with infected animal secretions
vesicles
semen
milk
Wind movement
Meat and offal (pigs)
Fomites
FMDV impact
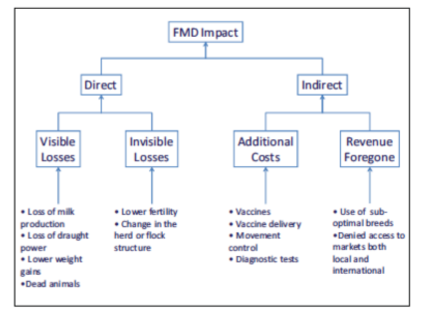
FMDV distribution
Asia and Africa endemic
UK, N America, Europe free from FMDV without vaccination
FMDV impact- disease free zone
Much higher trade impact → threatens disease free status
Rapidly stamp out single case and investigate intensively
pre-emptive cullings
FMDV impact- endemic zone with sylvatic reservoir
Less impactful → already disease there
Doesn’t change trading status, less possible to control
General FMDV control
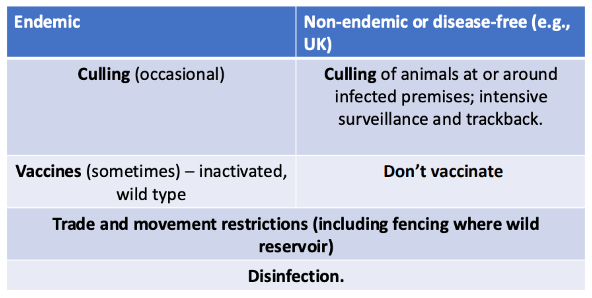
UK Vaccination
Emergency
UK legislation allows emergency use
serve prophylaxis
protect high yielding dairy cattle
already lost access to global market so doesnt matter if antigen positive for FMDV
FMDV serologial tests for no exposure
cannot differentiate btw vaccine antibodies and infection antibodies
Prophy;axis
enzootic countries protect production animals (high-yielding dairy) from clinical illness
FMDV vaccination info
Provides 4-6 month protection against specific serotypes
Only protects against clinical illness → vaccinated animals could be carriers
Reduced access to global markets
Herd immunity necessary to reduce transmission
Poor thermostability of vaccine
Risk of viral reintroduction from wildlife reservoirs