Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is the functional group of a carboxylic acids?
COOH, carbonyl (C-O double) and OH acid
How are carboxylic acids produced?
Oxidation of primary alcohols under reflux
What happens to carboxylic acids when they are in solution?
they are weak acids so dissociate slightly, forming a H+ ion and a carboxylate ion (RCOO-)
How do carboxylic acids react with carbonates?
They react as acids to produce a carboxylate salt, water and CO2
Why are small chain carboxylic acids soluble in water?
They can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules (between the lone pair on an oxygen atom and the positive part of the hydrogen atom)
How are esters formed and what is it called?
When carboxylic acids react with alcohols in the presence of a strong acid catalyst
Esterification
What molecule is each part of the water molecule removed from in esterification?
The OH is removed from the acid and the H from the alcohol
What are esters?
Sweet smelling compounds used in food flavourings and perfumes
What are the relative boiling points of esters?
Low
Vegetable oils and fats are esters of what naturally occurring alcohol?
Glycerol (propane - 1,2,3 - triol)
What is formed when glycerol undergoes esterification?
Triglyceride esters
What is ester hydrolysis?
When a water molecule is added across an ester to split it into multiple products
What happens to an ester when it is hydrolysed in acidic conditions?
The alcohol and carboxylic acid that make up the ester are reformed
What happens when an ester is hydrolysed under basic conditions?
The alcohol is reformed and the carboxylic acid reacts further to form a carboxylate salt
What is the formation of a carboxylate salt from an ester called?
Saponification
State a common application of carboxylate salts and why.
Soap
They have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties
What is acylation?
The introduction of an acyl group to another molecule
What is an acyl group?
An R group bonded to a C-O double bond
State what 2 types of molecules acyl group can come from.
Acyl chlorides
Acid anhydrides
What is an acyl chloride?
A molecule with a C-O double bond directly bonded to a Cl atom
What is an acid anhydride?
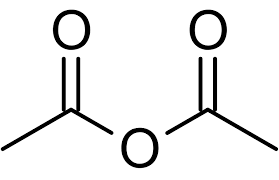
State the general reaction for acylation.
Nucleophile + Acyl —> Nucleophile - C[O]R + leaving group
State the conditions for an acylation reaction.
Room temp, no catalyst, anhydrous
What products are made during an acylation reaction using water as the nucleophile?
Carboxylic acid + HCl (hydrogen chloride)
What products are made during an acylation reaction using an alcohol as the nucleophile?
Ester + HCl
What products are made during an acylation reaction using ammonia as the nucleophile?
Amide + HCl
What products are made during an acylation reaction using a primary amine as the nucleophile?
N-substituted amide + HCl
What is the name of the mechanism for acylation?
Nucleophilic addition elimination
What is the suffix for an acyl chloride?
-oyl chloride
What is the formula for an acyl chloride?
RCOCl
What is the suffix for a primary amine?
-ylamine
State the formula for a primary amine.
RNH2
What is the suffix for an amide?
-amide
What is the formula for an amide?
RCONH2
What is the suffix for an N-substituted amide?
N -yl -amide
What atom should be included in the structural formula of an N-sub amide that is not normally included?
The H on the nitrogen
Describe the mechanism of acylation with any nucleophile.
The lone pair on the nucleophile bond to the carbon in the acyl group and the C-O double bond breaks
The double bond is reformed, the electrons in the C-Cl bond move to the Cl (or other leaving group) and the Cl leaves the molecule
The electrons in an N-H or O-H bond move to the O+/N+ and the H leaves the molecule
The final products are formed