Understanding Molecular Shapes and VSEPR Theory
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What do Lewis structures represent?
Lewis structures show the structure of molecules in two dimensions (flat).
What is the actual shape of molecules in three dimensions?
Molecules take on a tetrahedral shape in three dimensions.
What theory explains why molecules have three-dimensional shapes?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
What is the principle behind VSEPR theory?
Electron pairs repel one another, causing molecules to adjust their shapes to maximize distance between valence electron pairs.
What types of electron pairs are considered in VSEPR theory?
Both bonding pairs (used in bonds) and non-bonding pairs (lone pairs not used in bonding) are considered.
How do you determine the shape of a molecule using VSEPR theory?
Draw the electron dot or structural formula, count bonding and non-bonding pairs around the central atom, and apply the predicted geometry.
What is the bond angle in a linear molecular shape?
180°.
Give an example of a linear molecule.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an example of a linear molecule.
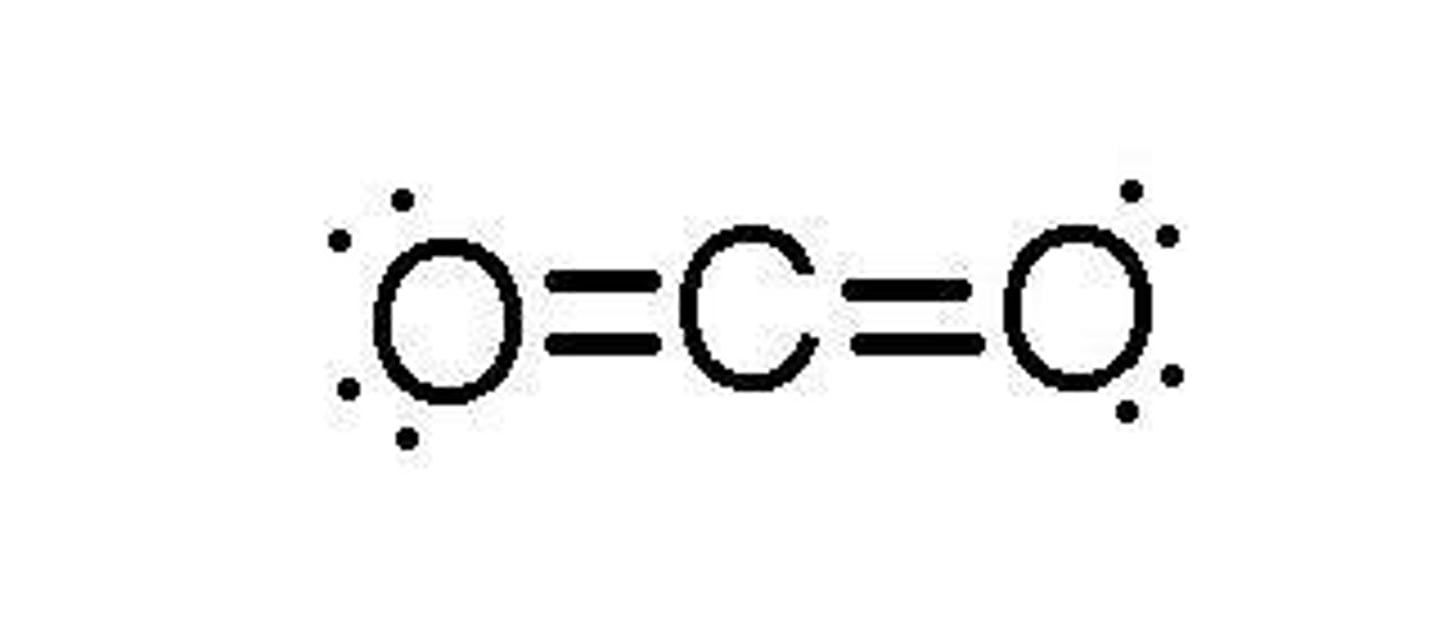
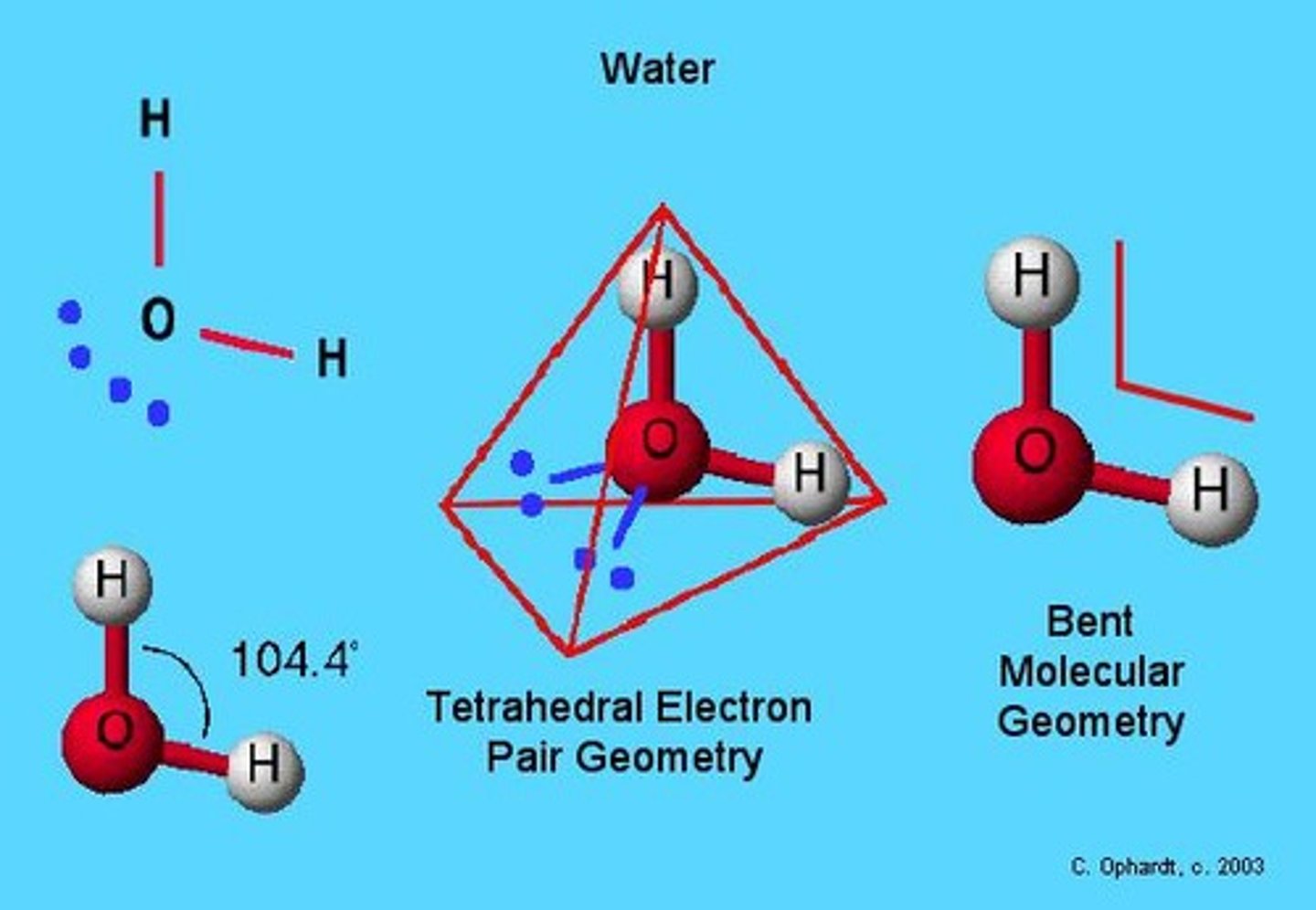
What is the bond angle in a bent molecular shape?
Approximately 104.4°.
Give an example of a bent molecule.
Water (H2O) is an example of a bent molecule.
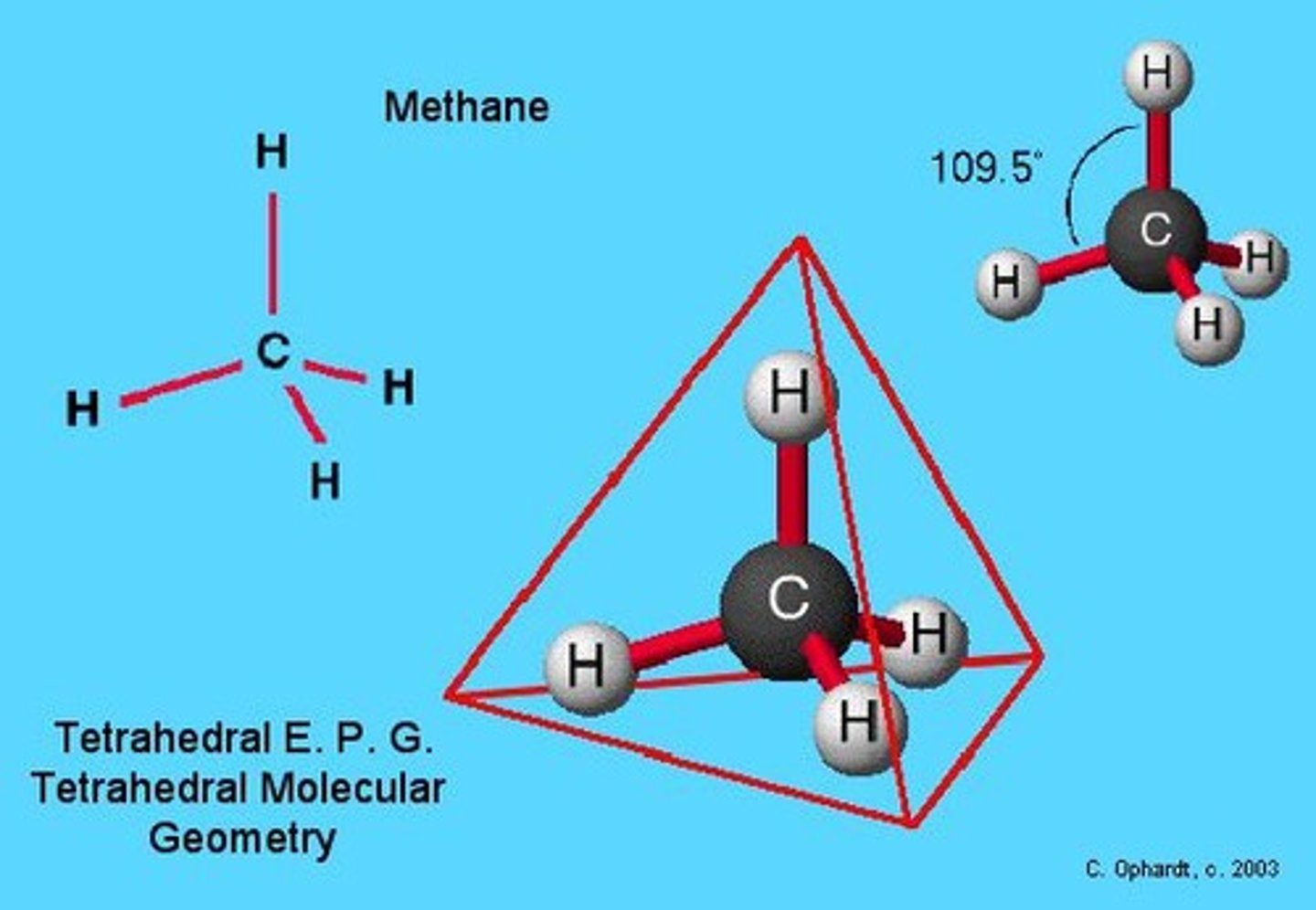
What is the bond angle in a tetrahedral molecular shape?
Approximately 109.5°.
Give an example of a tetrahedral molecule.
Methane (CH4) is an example of a tetrahedral molecule.
What is the bond angle in a pyramidal molecular shape?
Approximately 107.3°.
Give an example of a pyramidal molecule.
Ammonia (NH3) is an example of a pyramidal molecule.
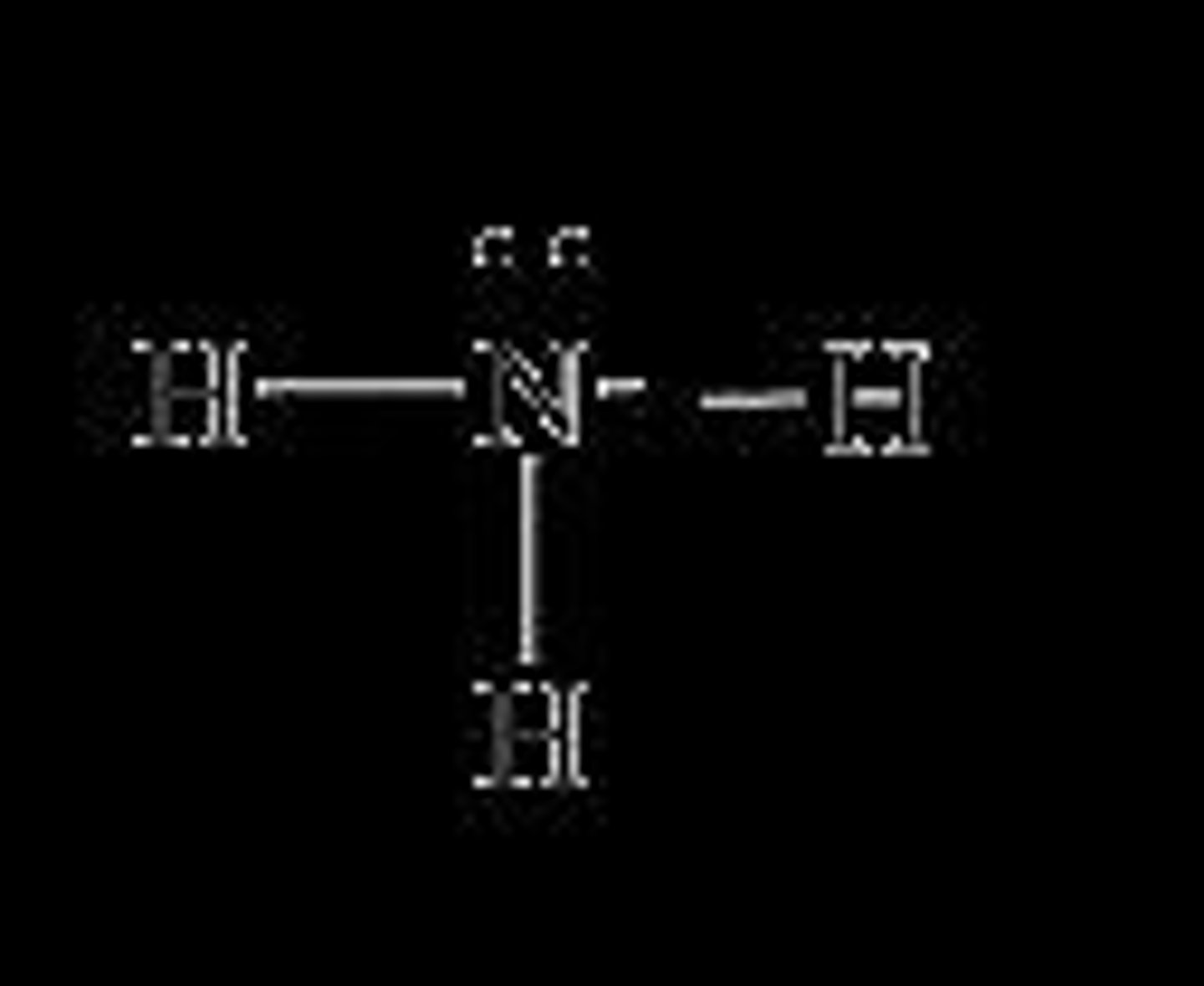
What is the bond angle in a trigonal planar molecular shape?
Approximately 120°.
Give an example of a trigonal planar molecule.
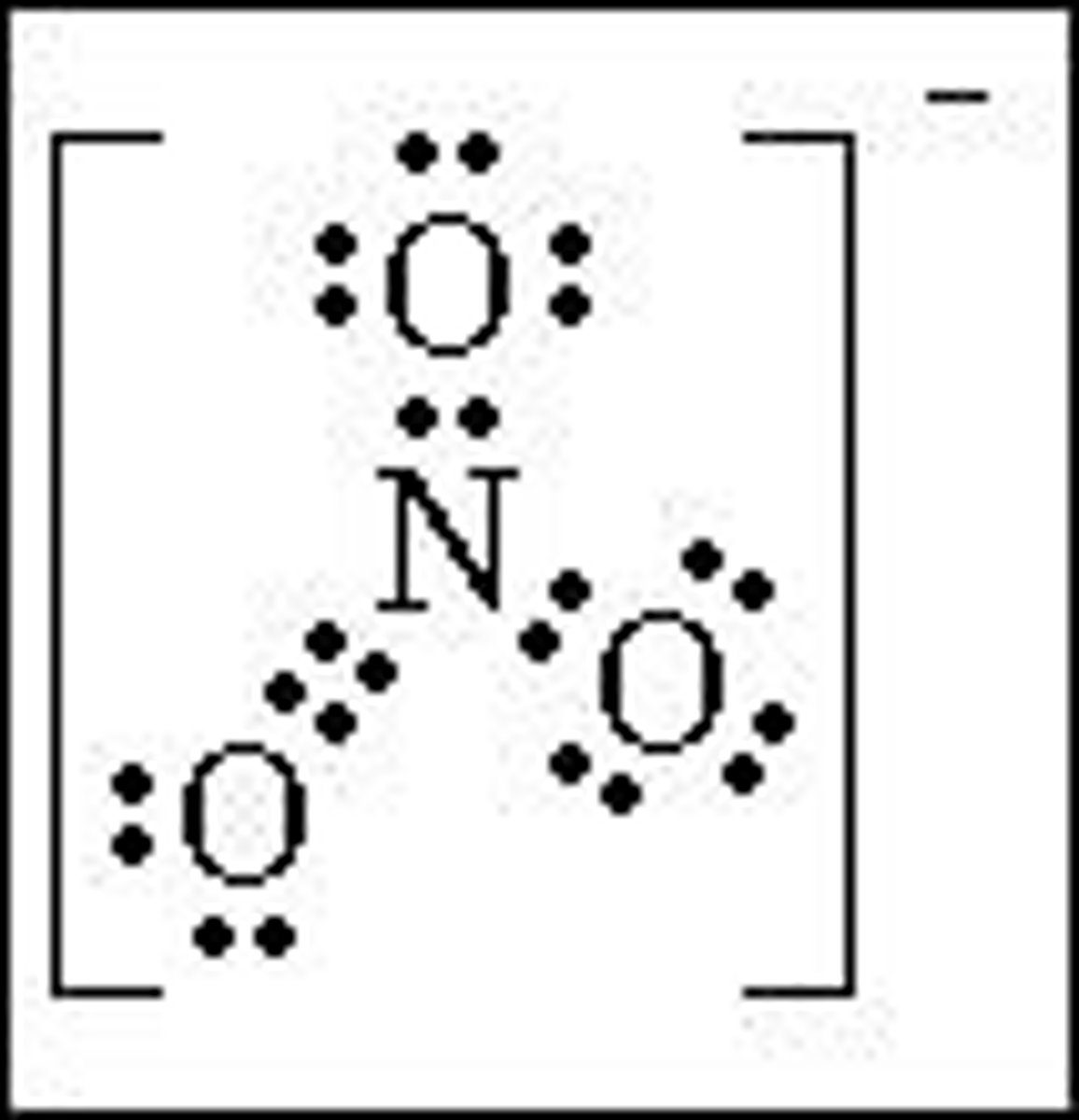
Nitrate (NO3) is an example of a trigonal planar molecule.
What does VSEPR theory assume about electron pairs?
VSEPR theory assumes that electron pairs will be spaced out as far apart as possible due to repulsion.
What is a bonding pair of electrons?
A bonding pair of electrons is an electron pair used in a bond.
What is a non-bonding pair of electrons?
A non-bonding pair of electrons is a lone pair of electrons not used in bonding.
How are multiple bonds counted in VSEPR theory?
Multiple bonds (double, triple) count as one 'location' or 'region' for electron pairs.
What is the significance of electron pair repulsion in molecular geometry?
Electron pair repulsion influences the shape of the molecule, leading to specific geometries.