B cell? NO, excel 🤩
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
What are the types of lymphocytes (3)
T cell, B cell, NK cell
2
New cards
Where are the lymph nodes found?
Linguine, axillary, cervical regions
3
New cards
Lymph node function?
Remove foreign debris, house lymphocytes, macrophages, filters blood
4
New cards
Two parts of lymph node
Cortex, medulla
5
New cards
What does the parathyroid secrete and when?
Secretes PTH when Ca levels low
6
New cards
Where are chief cells found?
Parathyroid
7
New cards
Where are oxyphil cell found?
Parathyroid
8
New cards
What are the types of leukocytes (3)
Granulocytes, monocytes, lymphocytes
9
New cards
fas ligand
makes cells do apoptosis
10
New cards
what 2 antibodies are the receptors for b cells. which one is better
igM, igD. better = igM
11
New cards
self recognition vs self tolerance
self recognition: recognize your own MHC. self tolerance: they react to the MHC
12
New cards
What are the types of granulocyte (3)
Eosinophil, basophil, mast cell
13
New cards
What is the cell involved in allergic reactions & asthma?
Basophil
14
New cards
What is the cell involved in allergies and autoimmunity?
Mast cell
15
New cards
What are the types of phagocytes? (3)
Neutrophil, macrophage, dendritic
16
New cards
What does histamine do?
Exudation (swelling) by vasodilation
17
New cards
What do kinins cause?
Chemotaxis and pain
18
New cards
What inhibits prostaglandins?
Aspirin
19
New cards
What does hyperemia cause?
redness and heat
20
New cards
What does exudate mean?
swelling
21
New cards
What are the 4 steps of phagocytosis mobilization?
Leukocytosis, margination, diapedesis, chemotaxis
22
New cards
What are IFNs?
Proteins secreted by virus-infected cells to protect non-infected cells
23
New cards
What do complements do?
Plasma proteins that circulate the blood in an inactive state.
24
New cards
What is the classical complement pathway triggered by?
Pathogen or antibody binding
25
New cards
What is the lectin pathway triggered by?
Binding of pattern-recognition molecules
26
New cards
What is the alternative pathway triggered by?
Hydrolysis of internal C3 thioester bond
27
New cards
What kind of antigen can be anything (polysacc, lipid, microorg)?
Complete
28
New cards
What kind of antigen causes immune responses only when attached to large carriers?
Hapten/incomplete
29
New cards
Where do lymphocytes originate from?
Red bone marrow
30
New cards
Where do B cells mature?
Red bone marrow
31
New cards
Where do T cells mature?
Thymus
32
New cards
Where does B/T cell activation occur
Lymph node/spleen
33
New cards
What are the types of APCs (3)?
Dendritic, macrophage, B cell
34
New cards
What do T cells do?
Secrete lymphokines
35
New cards
What is B cell’s primary target?
Bacteria, fungi, parasite, virus
36
New cards
What is T cell’s primary target?
Cancer, virus
37
New cards
macrophages that bind to ct is called
histiocytes
38
New cards
chemokine vs cytokine
Chemokine signal more distant cells
39
New cards
function of ifn
signal the cells that surround the cells of a virally infected cell to release anti viral proteins
40
New cards
What does double negative mean?
Earliest stage of T cell, neither CD4/8
41
New cards
What is it called when T cells only react to self-MHC proteins?
Positive selection
42
New cards
What is it called when T cells don’t recognize self-antigens displayed on self-MHC, making sure they don’t attack their own cells?
Negative selection
43
New cards
autoimmune disease are malfunction in what
self recognition
44
New cards
white pulp vs red pulp spleen in their composition
white: Lymphoid tissue; Dense in lymphocytes & distant from blood supply
\
red: CT w/ sinusoids full of blood
\
red: CT w/ sinusoids full of blood
45
New cards
white pulp fx
Prolif lymphocytes, initiate active immu response
46
New cards
red pulp fx
Filter blood & remove waste
47
New cards
why do antibodies not work on viruses
virus don’t have metabolic pathways for antibiotic to target, they cant’ penetrate virus’ cell wall, viruses don’t reproduce on its own they go inside the host cell in reproduce in there
48
New cards
what would you call the cytokine factories
helper t cell
49
New cards
innate immunity
natural, always present, non-specific responses, no immunological memory, can be inherited from parents, recognizes less diverse group of antigens, does not produce allergic reactions
50
New cards
adaptive immunity
antigen-specific immune response, memory B-cells will possess immunological memory and cell memory, the response usually is delayed 5-6 days, higher diversity of pathogens/ antigens recognized, develops allergic reactions, cannot be inherited and must be acquired.
51
New cards
both innate and adaptive involve these 2 cells
t, nk
52
New cards
the disease mono is a swelling of what
posterior cervical ln
53
New cards
What type of receptors do macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells have?
toll like
54
New cards
adenoid fx
trap pathogens that enter from the mouth or nose and then produce antibodies
55
New cards
adenoid loc
entrance of respiratory tract and GI tract
56
New cards
another word for platelet
thrombocyte
57
New cards
platelets are
fragments of the cytoplasm which are derived from megakaryocytes
58
New cards
fx of spleen
removes old RBC from blood, recycles iron, produces lymphocytes
59
New cards
What antigens are targeted in hashimoto’s
thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin
60
New cards
what are the large cells in bone marrow called
megakaryocytes
61
New cards
what happens after the antibody is secreted
the antibody circulates the bloodstream to find the pathogen to caused it to be secreted in the first place
62
New cards
what are the 2 things antibodies do
1) neutralize 2) flag for phagocytes or complement system
63
New cards
where are antigens bound to
the mhc protein on the surface of an APC
64
New cards
how to tell the difference btn b and t
b has lots of rough er, t doesnt
65
New cards
antibodies vs cytokines
antibodies are widely distributed across blood, cytokines are local
66
New cards
what is the molecule that you have to inject to have artificial immunity
adjuvant
67
New cards
what part of plasma cells makes antibodies
rough er
68
New cards
What cells kill cancerous/infected cells by looking for class 1 MHC protein?
T cytotoxic cell
69
New cards
clonal selection
antigen binding to only t cells that have receptors specific that that antigen
70
New cards
What cell dampens the immune response by direct contact/releasing cytokines?
T memory cell
71
New cards
What type of immunity is by injecting antibodies harvested from a donor?
Passive artificial
72
New cards
What MHC is on the surface of all cells except RBC?
Class 1 MHC
73
New cards
What MHC interacts with CD8?
MHC 1
74
New cards
What MHC is only on the surface of cells that make antigens to CD4, mature B, APCs, and T cell?
MHC 2
75
New cards
Type 1 Hypersens is caused by
IgE, allergy
76
New cards
Type II Hypersens is caused by
IgG, IgM, autoantibodies
77
New cards
Type III Hypersens is caused by
Antibody-antigen complexes
78
New cards
Type IV Hypersens is caused by (ex TB tuberculin skin test)
CD4, T cell
79
New cards
AIDS stands for
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
80
New cards
Recurrent infections and low antibody levels in adults
Common variable immunodeficiency
81
New cards
Type of inflam myopathy
Dermatomyositis
82
New cards
Graves is caused by too much
Thyroxine
83
New cards
Sausage fingers, depression in nail (pitting)
Psoriasis arthritis
84
New cards
Hashimoto is caused by
Thyroid atrophy
85
New cards
Itchy rash
Contact dermatitis
86
New cards
Collection of microorganisms in organism (confined to skin, mouth, digestive tract, vagina)
Microbiota
87
New cards
When do lymphatic tissues begin to develop?
End of 5th week of gestation
88
New cards
Difference between B and T cell activation is that T cell is *_ and* _
Short distance, direct
89
New cards
What soluble pattern recognition proteins that function as poisoning enhance phagocytosis? 4
C-reactive protein, Ficolin, MBL, surfactant proteins A & D
90
New cards
4 steps of tumor growth/metastasis
Initiation, promotion, progression, metastasis
91
New cards
Osteocytes do what (2)
maintain healthy bones, control calcium release
92
New cards
what enhances immune response and makes it weaker
Adrenaline
93
New cards
look at me
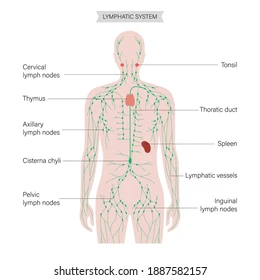
94
New cards
Five types of pathogen
Virus, bacteria, parasite, fungi, helminth
95
New cards
T cells respond to antigens by
Recognition site
96
New cards
What are the roles of surfactant
Alveolar collapse, surface tension, coats alveoli, immune response
97
New cards
3 properties of immune system
Inducibility/primary response, memory/secondary response, specificity for antigen, no autoreactivity
98
New cards
What organ system does the thoracic duct connect the lymphatic system to
Cardiovascular
99
New cards
Waht is the largest mass of lymphoid tissue
GALT
100
New cards