5.2.2 Respiration
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
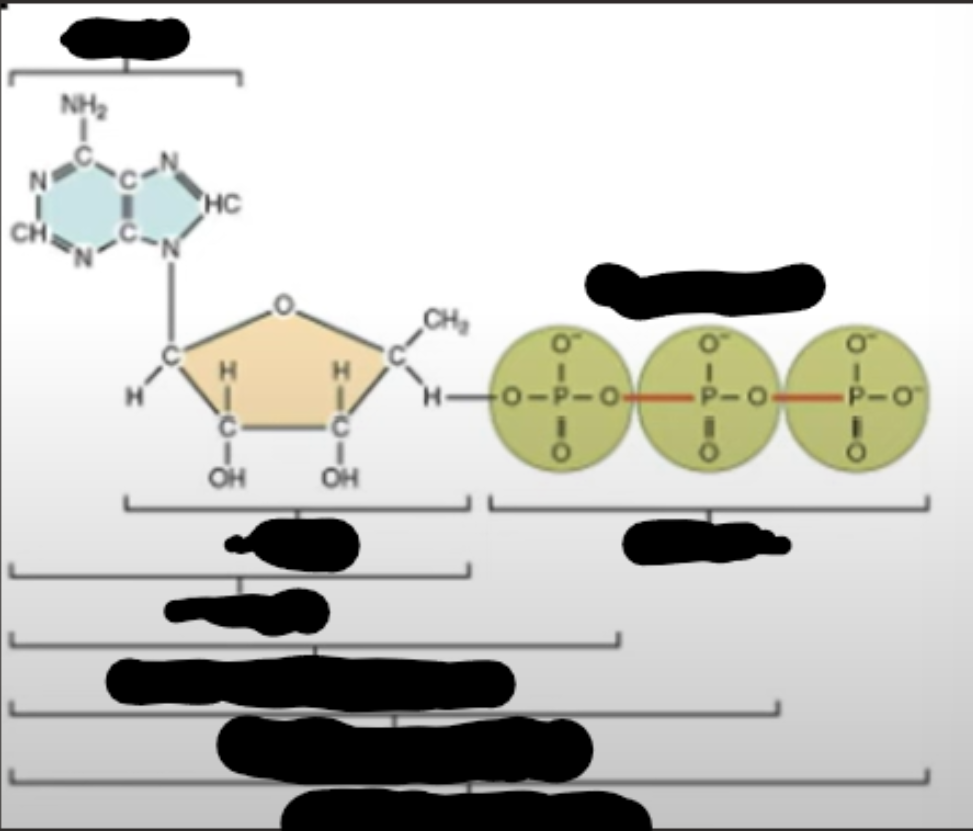
ATP is used for (7)
-movement
-active transport
-endo/exocytosis
-cell division: mitosis & meiosis
-synthesis of biological molecules
-DNA replication
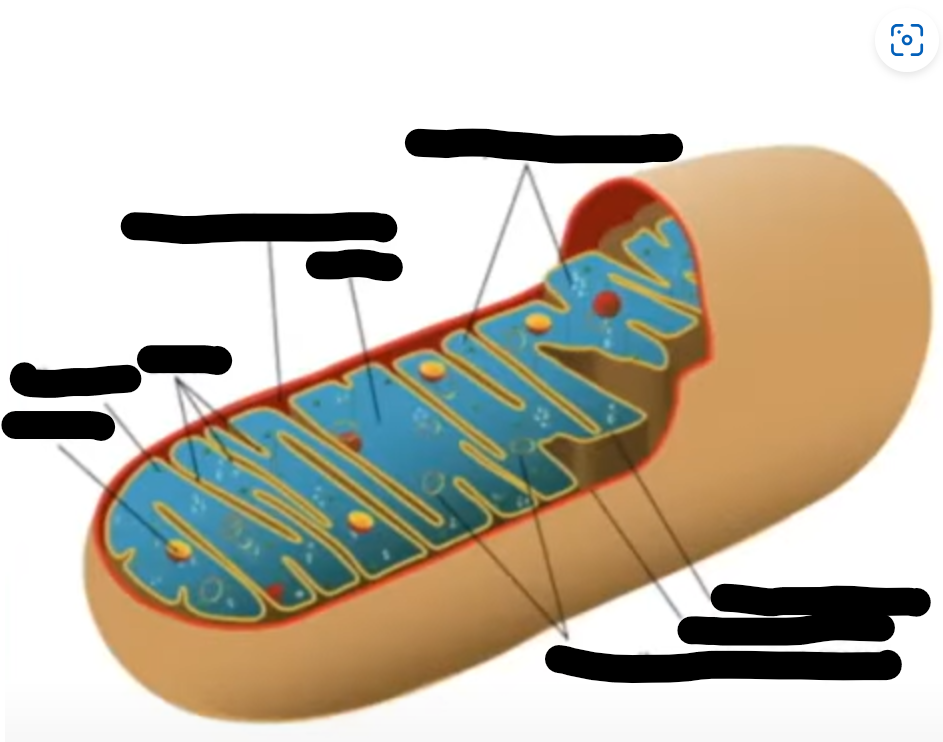
aerobic respiration steps (4)
glycolysis (cyto)
link reaction(mito matrix)
krebs cycle(mito matrix)
oxidative phosphorylation(mito inner membrane cristae)
glycolysis
-first step for anae/aerobic respiration
-anaerobic process
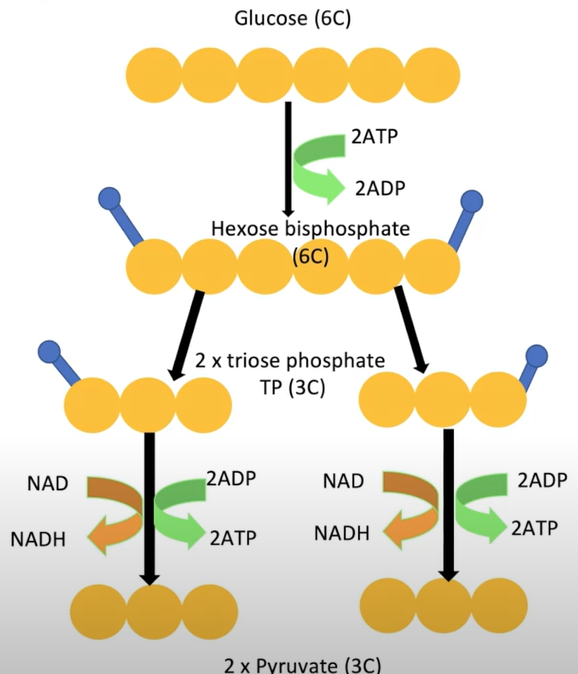
glycolysis process
-phosphorylating glucose to hexose bisphosphate
-using 2 ATP and hydrolysing them to release phosphate group
-this binds to glucose (phosphorylating it)
-makes the glucose molecule gain energy and become more reactive
-therefor splits into 2 molecules of triose phosphate
-which undergoes oxidation as NAD picks up H from triose phosphate
-triose phosphate loses a phos grp each and gives to ADP to make ATP
-NAD reduced, triose phosphate oxidised to pyruvate
-pyruvate and NADH actively transported from cyto to mito matrix
products of glycolysis
2x pyruvate
net gain of 2 ATP
2 x reduced NAD
glycolysis diagram
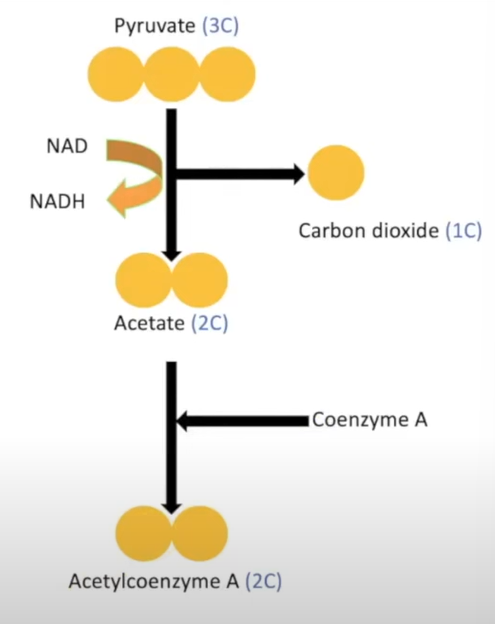
link reaction
-pyruvate further oxidised into acetate (2C)
-NAD picks up H (from pyruvate) and becomes reduced NADH
-decarboxylation; removal of C molecule from pyruvate to form CO2
-acetate combines w/ coenzyme to produce acetylcoenzyme a
-happens so coenzyme can help acetate enter krebs cycle
how many times does link reaction occur per molecule of glucose
twice
products of link reaction
2x acteylcoenzyme a
2x CO2
2x reduced NAD
link reaction diagram
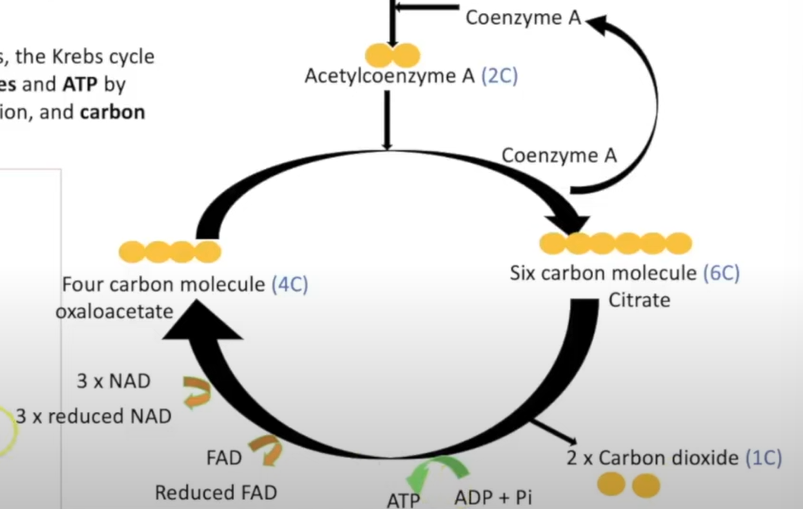
krebs cycle
acetyl(2C) grp released from conenzyme
combines w/ oxaloacetate(4C) to form citrate (6C)
citrate decarboxylated and dehydrogenated to produce 5C compound
releases CO2 and NADH
5C compound further decarboxylated and dehydrogenated to 4C compound
substrate level phosphorylation occurs to phosphorylate ADP to ATP
releases CO2 and NADH
4C compound combines with conenz A temporarily then is released
ATP produced
4C compound dehydrogenated stays 4C
produces reduced FAD
4C catalysed by enzyme and further dehydrogenated
NAD gets reduced
produces oxaloacetate
products made per krebs cycle

products per glucose molecule

krebs cycle diagram
total coenzymes from 1 glucose molecule
10 red. NAD
2 red. FAD
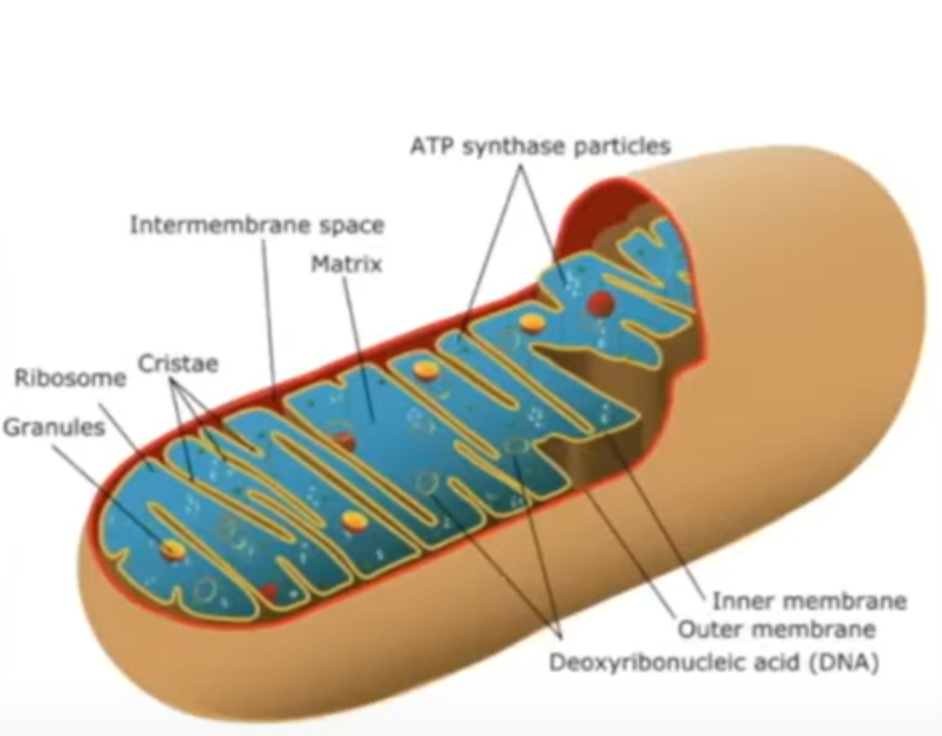
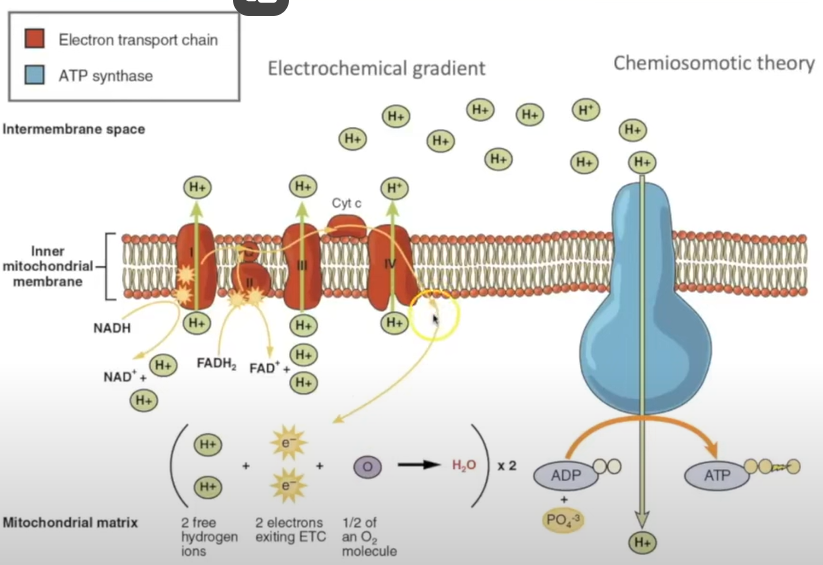
oxidative phosphorylation
NADH dehydrogenised
H split into e- and protons
e- picked by proteins embedded in inner mito membrane and passed along e- transfer chain
every time electron is passed along to next protein
releases enough energy to transport proton to intermembrane space
results in electrochemical gradient due to build up of protons
protons move down this gradient through ATP synthase
as protons move down conc gradient via facilatated diffusion
this will catalyse the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP
at the end of e- transport chain, O collects e- and some protons so chain can continue
to form water
oxidative phosphorylation diagram
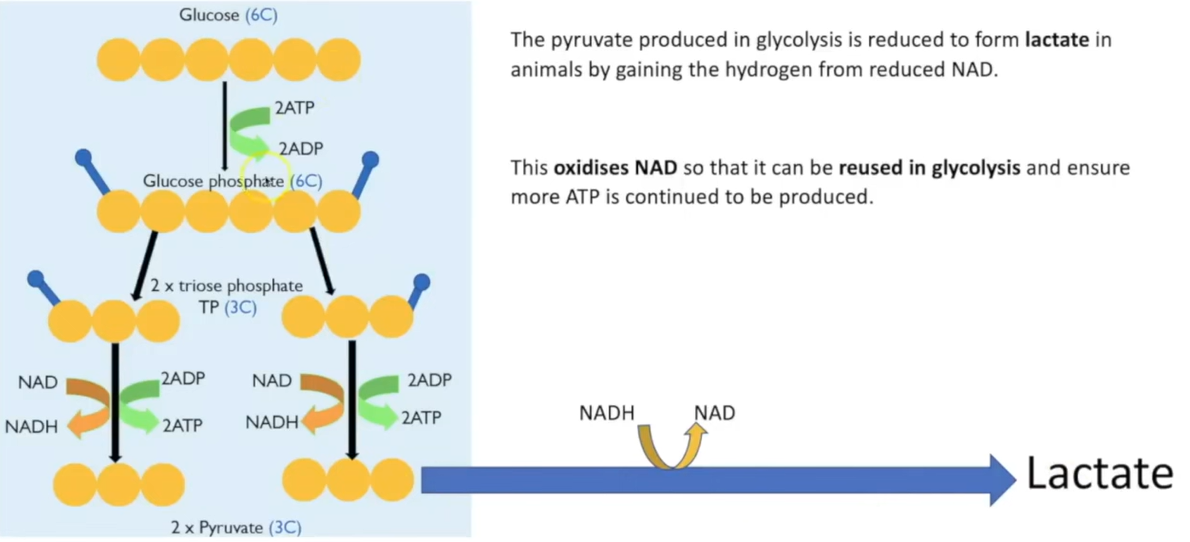
anaerobic respiration animal
occurs in cyto of cell
pyruvate produced in glycolysis
stays in cyto
reduced to lactate
by gaining H from NADH
oxidises NAD so can be reused in glycolysis
so more ATP produced
anaerobic respiration animal diagram
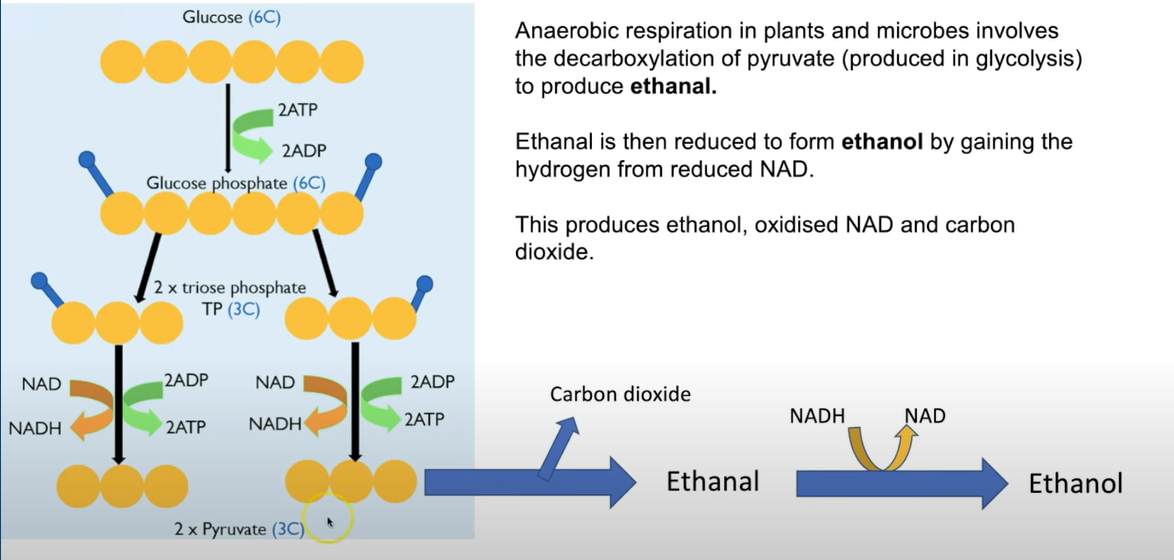
anaerobic respiration plant and microbes
pyruvate decarboxylated to produce ethanal
reduced to produce ethanol by gaining H from NADH
anaerobic respiration plant diagram
respiratory substrate
organic molecule that can be used in respiration to produce ATP
glucose most common
respiratory substrate (carbs)
used in glycolysis
glucose or starch( plants)
glycogen (animals)
can be hydrolysed to release glucose
respiratory substrate (lipids)
hydrolysed into glycerol and fatty acids
glycerol converted into triose phosphate
enters glycolysis to make pyruvate
fatty acids combine w/ coenzyme A
then converted to acetyl coenzyme a to enter krebs cycle
respiratory substrate (proteins)
hydrolysed to amino acids
deaminated to release keto acids
used in krebs
respiratory quotient
ratio of CO2 molecules produced compared to O molecules produced in respiration
RQ formula
CO2 produced/ O2 produced
RQ of carbs
1.0
RQ lipids
0.7
RQ proteins
0.8-0.9
RQ anaerobic respiration
above 1.0
what does RQ show
substrate being used in aerobic respiration
respirometer
device used to measure the rate of exchange of O and/or CO2 in living organism during aerobic respiration