Effort Assessment Review
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Kinematics & Dynamics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
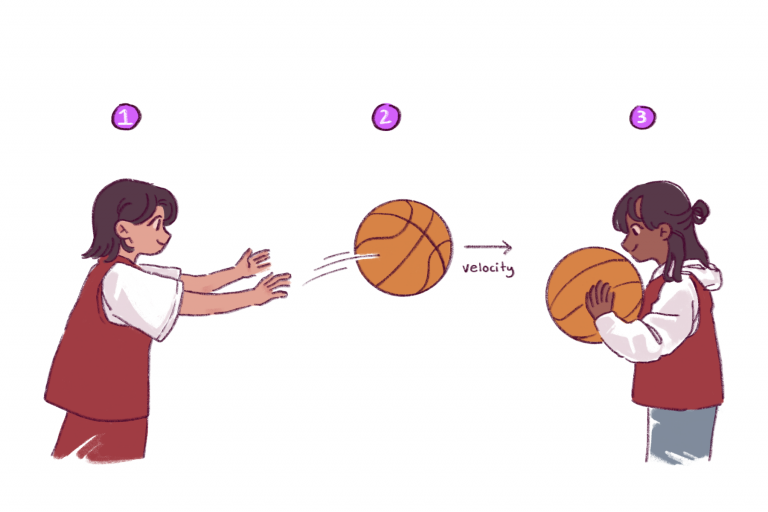
Newton’s First Law
Every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force.
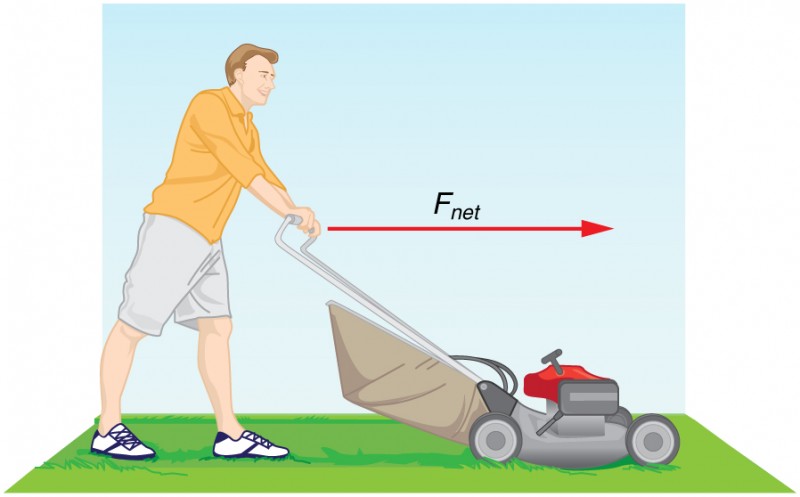
Newton’s Second Law
The force (F) acting on a body is equal to the mass (m) of the body multiplied by the acceleration (a) of its centre of mass,
F = ma
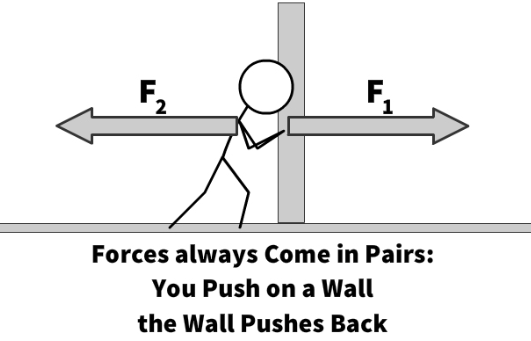
Newton’s Third Law
For every action (force) in nature there is an equal and opposite reaction. If object A exerts a force on object B, object B also exerts an equal and opposite force on object A.
Average Speed
distance / time
d / t
Average Velocity
displacement / time
delta d / t
Horizontal motion as ball is released from rest
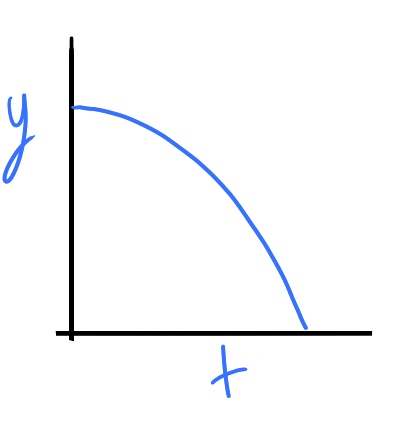
Vertical motion as ball is released from rest
Horizontal motion as ball rolls over table
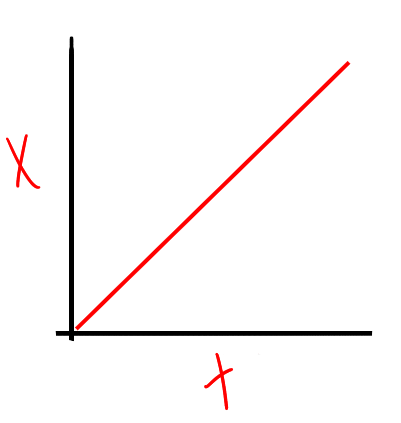
Vertical motion as ball rolls over table
Translation Left
f( x + 2 )
Translation Right
f( x - 2 )