Chapter 1: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
Unlimited wants, scarce resources
Economics - Social science of how individuals, institutions, + society make choices under scarcity
- Opportunity cost - Value of the good, service, or time forgone to obtain something else
- “There is no free lunch”
Economic perspective - Economic way of thinking
- Utility - Pleasure/happiness/satisfaction from consuming good/service
- Purposeful behavior - People make decisions w/ desired outcomes in mind
- Consumers + institutions make rational decisions by comparing marginal costs + marginal benefits
- Marginal analysis - Comparisons of marginal benefits + marginal costs for decision making
Economists use the scientific method -- Form + test hypotheses of cause & effect relationships → Generate theories, laws, + principles
- Economic principle - Widely-accepted theory; statement about economic behavior that allows for predictions of effects of certain actions
- Combine theories into representations called models
- Economic principles are generalizations
- Other-things-equal assumption - Assumption that factors other than those being considered do not change
Microeconomics - Concerned w/ individual units (person, household, firm, industry)
- Observes details of small part of economy
- “The sand and shells”
Macroeconomics - Examines either the entire economy or basic aggregates (gov’t, business sectors)
- Aggregate - Collection of specific economic units treated as 1 unit
- General overview of economy + relationships of major aggregates
- “The beach”
Positive economics - Facts + cause-and-effect relationships
- Avoids value judgements
- Scientific statements
- “What is”
Normative economics - Value judgements about what the economy SHOULD be like
- Desirability of certain parts of the economy
- Expresses support for certain economic policies
- “What should be”
Economizing problem - Need to make choices because economic wants exceed economic means
- Unlimited desires, limited income
- Budget line - Schedule or curve that shows various combos of 2 products that can be purchased with specific money income
- Inside budget line = Attainable
- Outside budget line = Unattainable
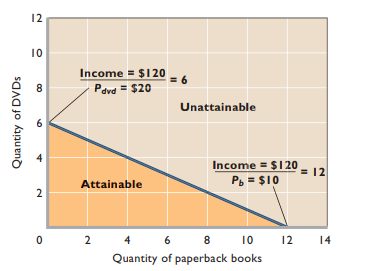
- Trade-offs - Must give something up to get something else
- Choice - Choose what to buy + what to forgo
- Income changes - Budget line shifts w/ changes in income
Economic resources - All natural, human, manufactured resources used for production of goods and services
- Land - All natural resources
- Labor - Physical + mental talents of individuals used in production
- Capital - All manufactured aids used in production (ex. tools, machinery, etc.)
- Entrepreneurial ability - Strategic business decisions, innovation, strategically combining resources, etc.
Production possibilities model
- Consumer goods - Products that satisfy wants directly
- Capital goods - Products that satisfy wants indirectly
- Production possibilities curve - Graph that shows different combos of goods + services that can be produced in fully employed economy
- Assumes resource quantity, resource quality, and technology are fixed
- Shows limit of attainable outputs
- Bowed out from origin
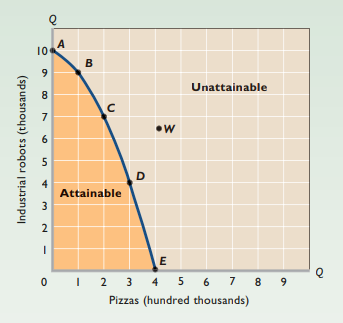
Law of increasing opportunity costs - As production of a good increases → Opportunity cost of producing an additional unit rises
- Gain of one type of good or service → Always accompanied by loss of one type of another good or service
- Resources not equally adaptable to different uses → Shifting resources from one use to another → Increasing opportunity costs
Optimal allocation where Marginal Benefit = Marginal Cost (MB = MC)
- Most desirable mix of goods
Unemployment represented by point inside original production possibilities curve
Economic growth - Growth of economic capacity; larger total output
- Increased resource supplies
- Advances in technology
More focus on capital goods over consumer goods → Production possibilities curve further to the right
International specialization + trade → Economy can consume MORE than production possibilities curve
- International specialization - Directing resources at output that nation is efficient in producing
- International trade - Exchange of goods for goods produced abroad