Facilitated Diffusion
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is facilitated diffusion?
The passive movement of molecules across the cell membrane via a membrane protein.
What types of molecules utilize facilitated diffusion?
Molecules that can’t cross the phospholipid bilayer freely.
What are the two types of proteins that aid in facilitated diffusion?
Channel proteins and carrier proteins.
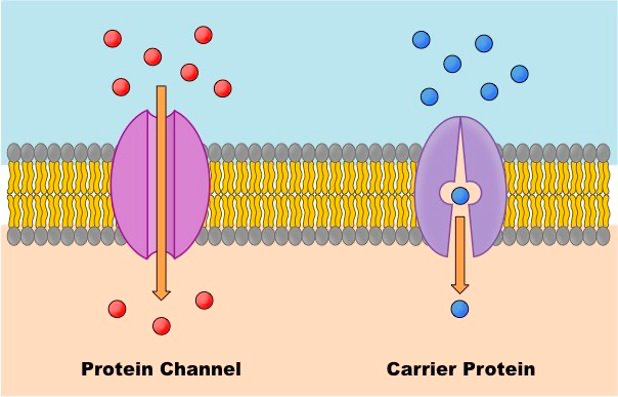
What do channel proteins do in facilitated diffusion?
They are specific to certain ions/molecules based on size, charge, or other characteristics and only move molecules along a concentration gradient.
How do carrier proteins function in facilitated diffusion?
They bind to a solute and undergo a conformational change to move the solute across the membrane, often involving energy (ATP) and can move against a concentration gradient.
Why are channel proteins considered selective gates?
Their structure allows them to enable the passage of specific substances while blocking others.
What can channel proteins be selective based on?
Charge, size, and the binding of a solute, voltage and more
What is an example of a channel protein?
Potassium channels found in nerve cells.
How do voltage-gated channels react to changes in transmembrane voltage?
They open and shut.
What is significant about the structure of potassium channels?
They are comprised of four subunits, and the inner pore contains a selectivity filter that restricts passage of alternative ions.