Unit 1 Organic Chemistry and Macromolecules: Key Concepts for Biology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Organic Chemistry
The study of compounds that contain bonds with carbon atoms.
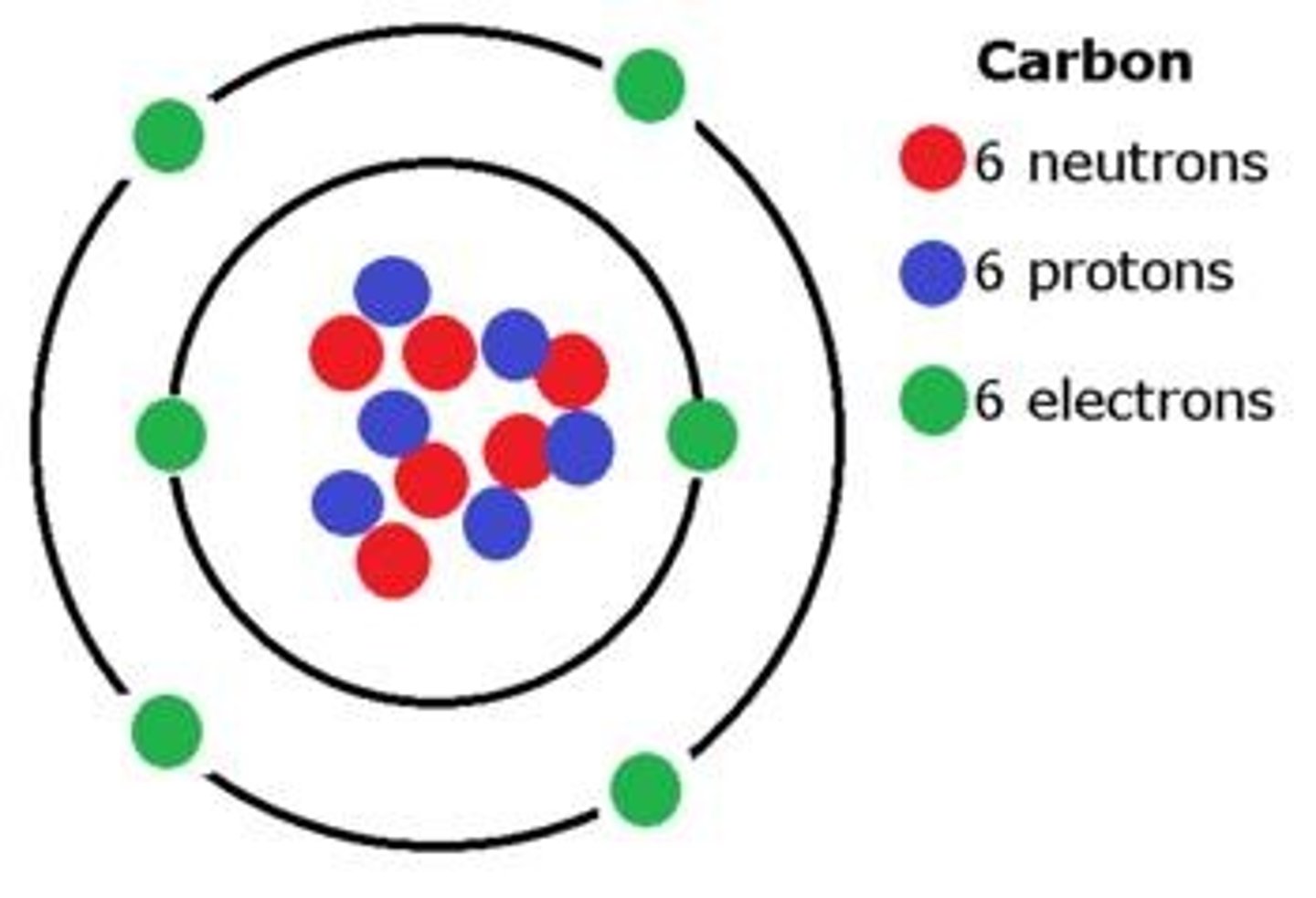
Carbon
The element of life that contains 4 valence (outer) electrons and forms strong covalent bonds with other elements.
Macromolecules
Large organic compounds formed from hundreds or thousands of smaller molecules called monomers.
Monomers
Single molecules of a carbon compound.
Polymerization
The process of joining smaller monomers to create larger molecules.
Polymers
Long chains formed when monomers join together.
Dehydration Synthesis
The process where monomers are joined together through covalent bonds to make polymers, with water lost as a byproduct.

Hydrolysis
The process where polymers are broken down into monomers using water molecules.
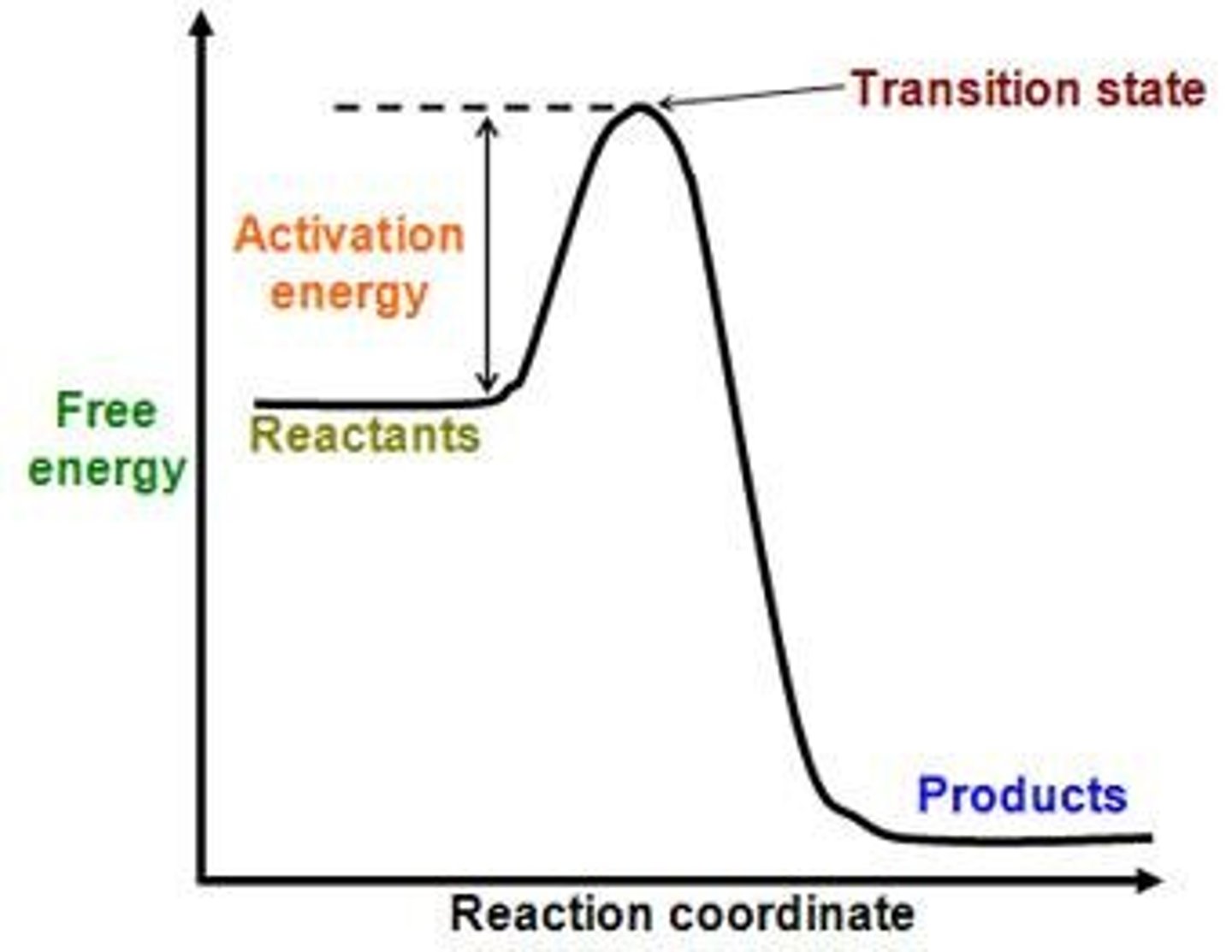
Activation Energy
The energy needed to start a reaction.
Anabolic Reactions
Chemical reactions that build larger molecules from smaller ones.
Catabolic Reactions
Chemical reactions that break down larger molecules into smaller ones.
Endergonic Reactions
Reactions that require energy input.
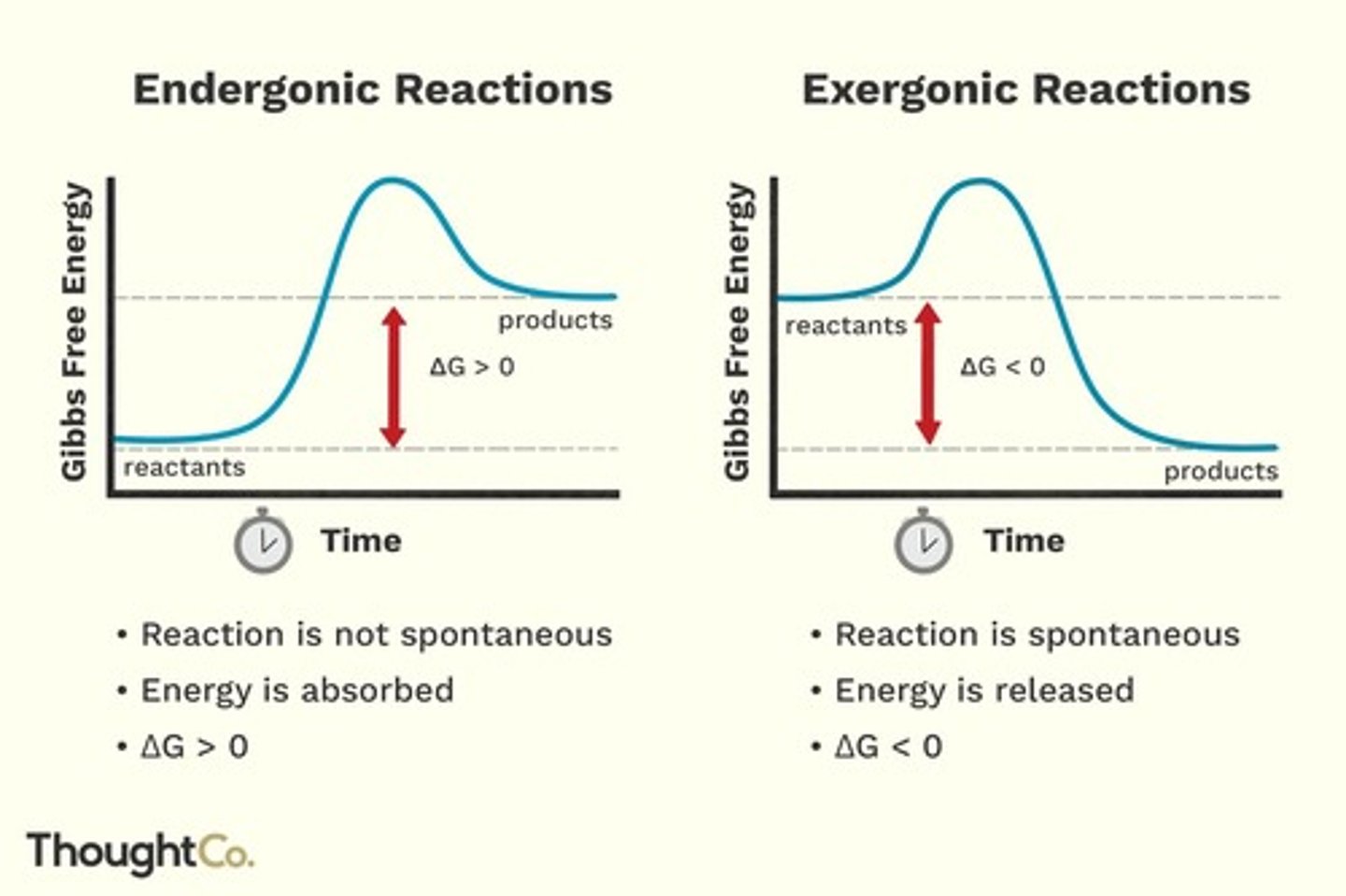
Exergonic Reactions
Reactions that release energy.
Carbohydrates
Macromolecules consisting of sugars and starches, usually colorless, water soluble, and crystalized.
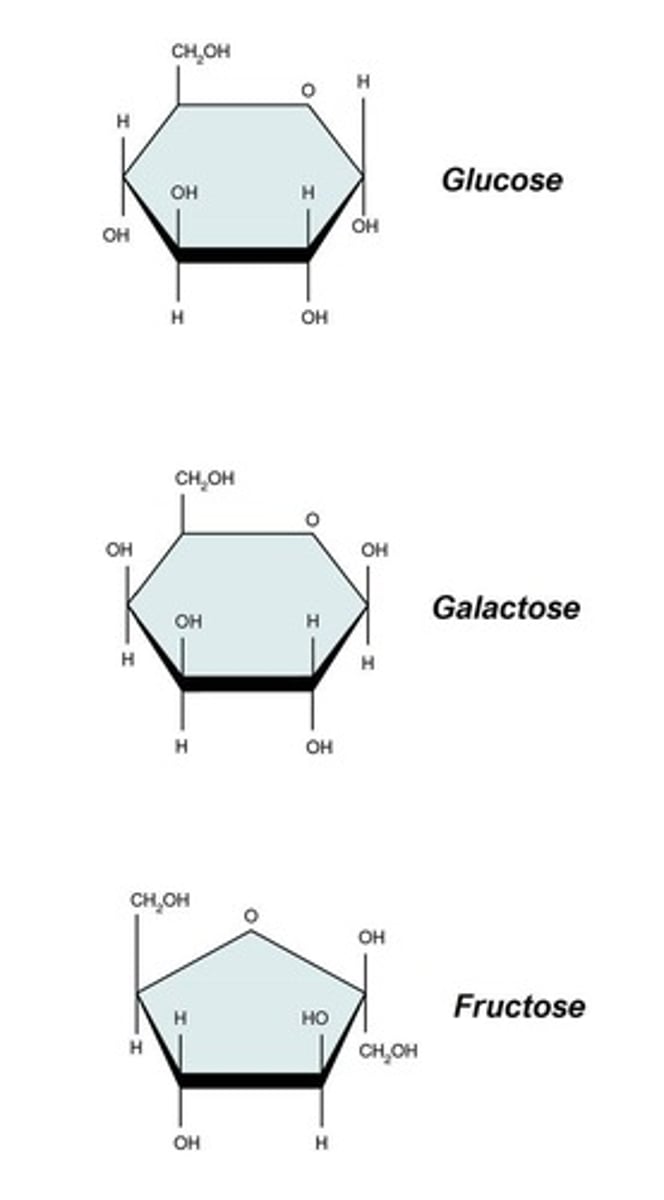
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars that contain a single monomer.
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates that contain 2 monosaccharides chemically combined.
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that contain 3 or more monomers.
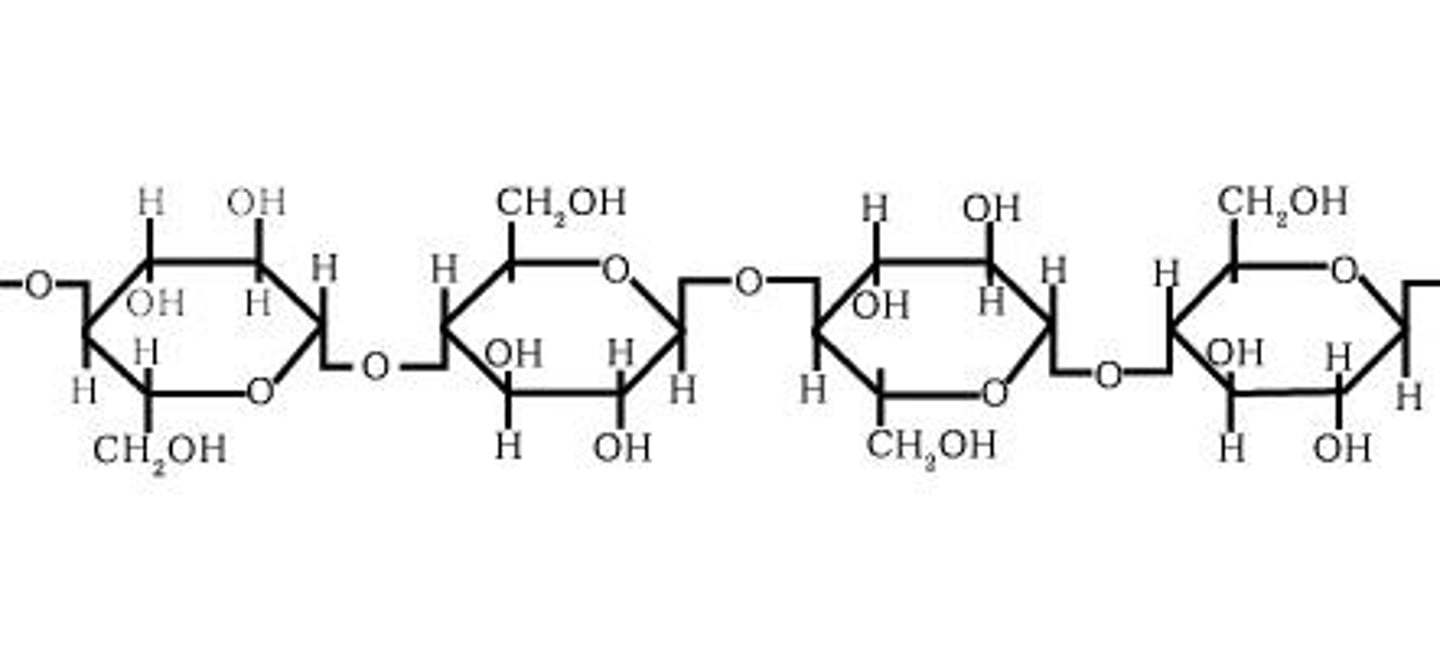
Glycogen
A form of energy storage in animals, primarily found in liver and muscle cells.
Starch
A form of energy storage in plants.
Glycoproteins
Molecules formed by the bonding of carbohydrates with proteins, important in cell membranes.
Glycosidic Bond
The bond between 2 monosaccharides.
Structural Isomers
Compounds that share the same formula but have different structures.
Elemental Ratio of Carbohydrates
1:2:1, representing the ratio of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen in carbohydrates.
Maltose
product of starch digestion, malt or beer sugar= glucose + glucose
Lactose
sugar in milk = galactose + glucose
Sucrose
common table sugar = glucose + fructose
Cellulose
Builds cell walls for plants and bacteria. Gives plants strength and flexibility.
Chitin
Insects, other arthropods, and crustaceans use chitin in their exoskeletons. Fungi use chitin in their cell walls.
Lipids
All lipids contain Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen atoms (CHO), and are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water.
Monomer of Lipids
Fatty Acids & Glycerol
Polymer of Lipids
Fats, Oils, Waxes, Steroids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids
Functions of Lipids
Long-term Energy Storage, Make Up Cell Membranes, Prevent water from soaking plant tissue and bird feathers
Saturated Fats
Solid at room temperature
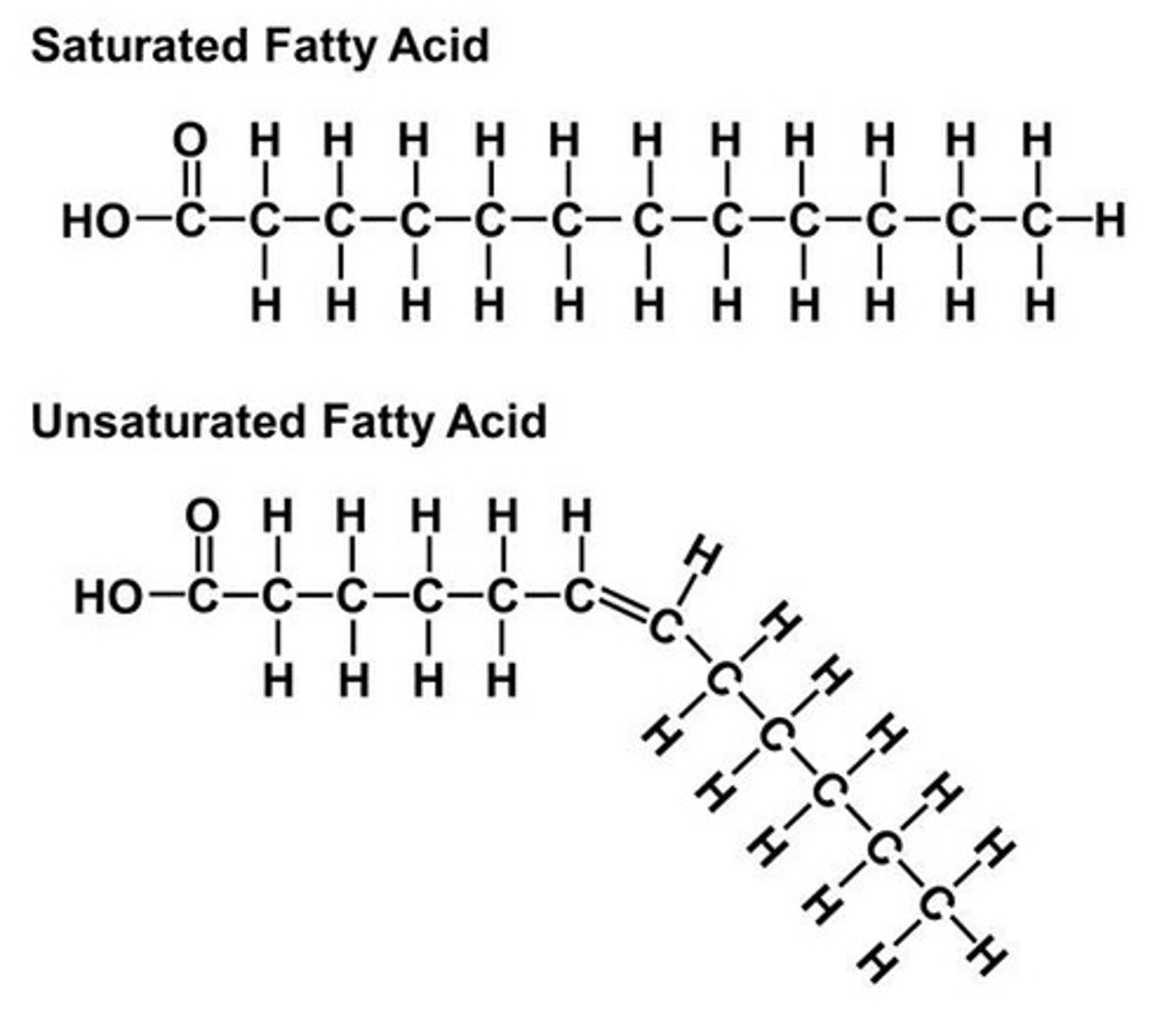
Unsaturated Fats
Liquid at room temperature
Proteins
Composed of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen Atoms - CHON
Monomer of Proteins
Amino Acids
Polymer of Proteins
Polypeptide
Functions of Proteins
Form Cell Structures, Transport substances around the body, Enzymes control the rate of reactions in an organism, Hormones coordinate activity of body systems, Defend the body against pathogens and disease, Contract muscles for movement, Stores nutrients inside animal eggs and seedlings
Amino Acids
About 20 Amino Acids are found in nature. All have an amino group, carboxyl group, and R group.
Proteins Organizational Levels
Primary: Sequence of Amino Acids, Secondary: Folding of Polypeptide Chain, Tertiary: 3-D Arrangement of Polypeptide Chain, Quaternary: Association of 2 or More Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Composed Of: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus - CHONP
Monomer of Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides - composed of 5-Carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen base.
Polymer of Nucleic Acids
Nucleic Acids
Function of Nucleic Acids
Store and Transmit Hereditary or Genetic Information - DNA & RNA
Components of Nucleic Acids
Monosaccharide: DNA- deoxyribose, RNA- ribose; Phosphate Group; Nitrogenous Base: DNA: cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine; RNA: cytosine, guanine, adenine, uracil