Herpetology Exam 1
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
The Gibbs reading talks about similarities and differences between amphibians and reptiles. One similarity is that amphibians and reptiles are _____
ectothermic
What are two of the outcomes of ectothermy that Gibbs covers and what is his rationale?
ectotherms can be smaller since they don’t rely on their surface area needing to be greater than their body volume, ectotherms also dont use as much energy
why would wake and koo be biased researchers?
they’re from temperate regions so they see temperate species'
Compare and contrast the global distribution of the three orders of amphibians.
anura- widespread, largest range
caudata- mainly north america
gymnophiones- south america, smallest range
the top threat to amphibians worldwide is?
habitat loss and degradation
what is herpetology
study of ectothermic tetrapods
compare ectothermy and endothermy in terms of food
they don’t need food to create energy for body heat
why could ectothermy not be as good as endothermy
restricts activity based on time of day/year
outcome of ectothermic energy savings- according to gibbs
increased biomass
4 reasons why amphibians and herps are grouped together
data deficient
small (most under 10 grams)
ectothermic
highly threatened
3 Orders of Amphibia
Anura Caudata Gymnophiona
what defines a clade
Group of organisms believed to have evolved from a common ancestor
science of classifying organisms
taxonomy
synapomorphies
synapomorphies are shared characteristics between ancestor and descendents
example of a diagram that can represent synapomorphies
phylogenic tree, cladogram
point at which common ancestor gives rise to 2 sister lineages or branches
node
region between 2 nodes
stem
clade definition
common ancestor and all its descendent taxa
all descendants and their ancestor
monophyly
some descendants and their ancestor
paraphyly
descendants and no ancestor
Polyphyly
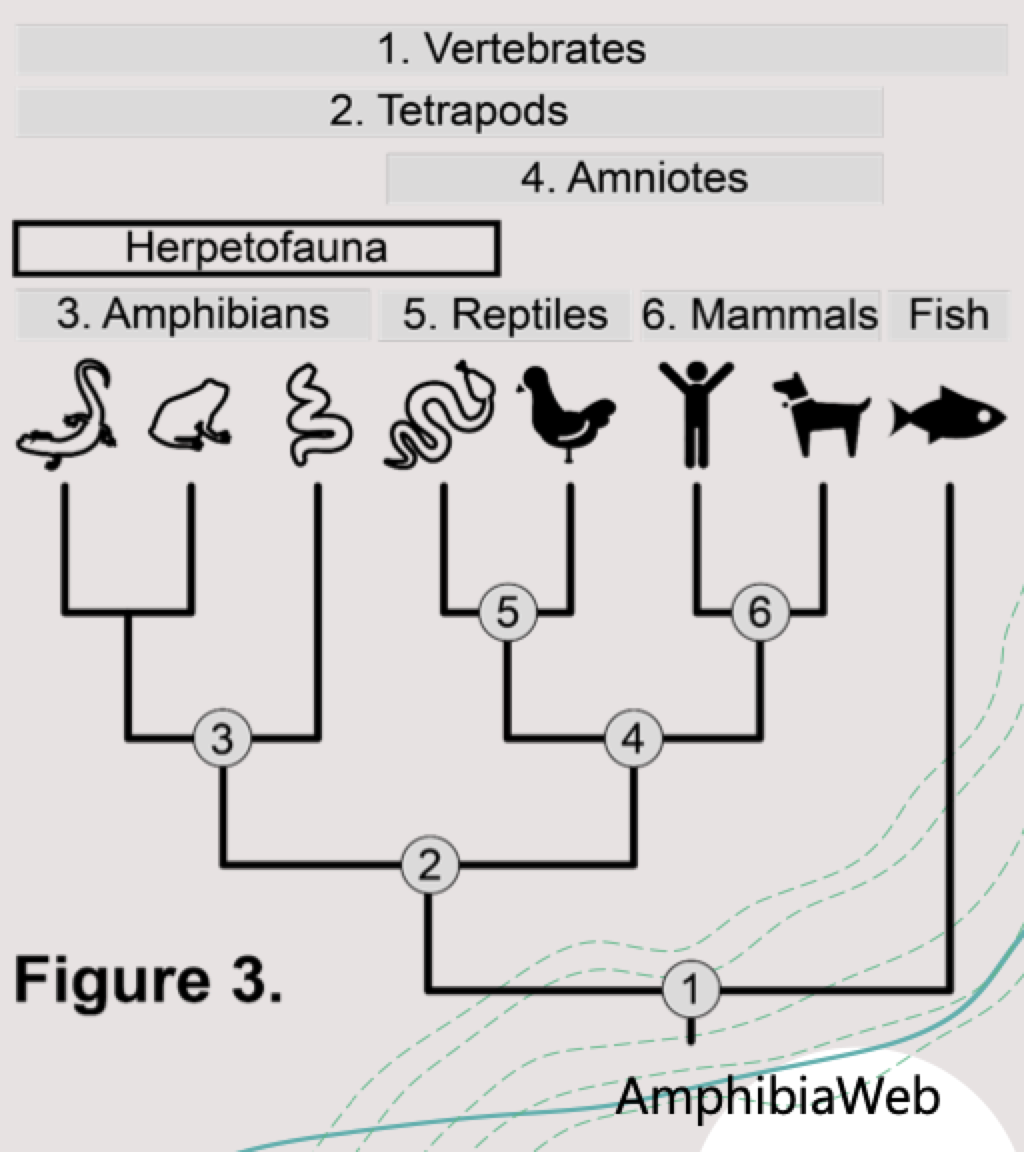
herpetofauna are what type of phyletic group
paraphyly
differences between reptiles and amphibians (at least 3)
amps have slimy permeable skin and lay eggs for moist environments that undergo metamorphosis, reptiles have dry scaly skin and usually lay eggs in dry areas like birds with “mini” adults that don’t need metamorphosis
why is the term “cold-blooded” not correct
ectotherms can be warmer than endotherms (warm-blooded) based on the environment’s heat
this order of amphibia is concentrated the most in Appalachia
Caudata- sals and newts
a symbol of fire and power
salamanders
1 main feature of caudata’s anatomy
extremely moist permeable skin that secretes toxins
this order of amphibia is extremely cryptic…if they’re not underground, they’re underwater
gymnophiona, caecillians
characteristics of gymnophiona anatomy
long vertebrate, blind, leg-less, skull, 2 rows of sharp teeth and an extremely powerful jaw, muscular
this order of amphibia uses electroreception in tentacles between their eyes and nostrils
gymnophiona
gymnophiona maternal contributions (not all caecilian species but some)
nutrient-rich outer layer of skin that offspring feeds from
most populated (88%) and most diverse order of amphibia
anura
which order of amphibia is the most studied? why?
caudata, they live where white guys live
pros/cons of caudata tail
predator defense and display of dominance, but it uses a lot of fat, is costly on locomotion and the immune system (more susceptile to disease)
caudata life history
4 limbs, elongate trunk and tail, mainly aquatic eggs that turn into aquatic larvae
amphibia usually have
3 chambered heart (2 atria, 1 ventricle), skin adaptations, complex life cycles
Unkenreflex
ability to show hidden bright colors while releasing poison from glands to warn preds
Transect sampling
walking in a line to search for herps
pigment for yellow, orange, red
xanthophores
types of searches
active, easy-passive, intensive-passing
active searching
visual encounter protocol
list 3 types of survey types
point survey, dip net survey, egg mass survey
paedomorphism
retains juvenile characteristics throughout life
vernal pool
non-permanent water body that amphibians like to lay eggs in
salamanders in larval stage vs post metamorphosis adult
larval- external gills and tail fin
adult- resorption of gills and closure of slits, reduction of tail fin, tooth maturation
salamanders are herbivores as larvae
false, they’re always carnivorous
how does water temp impact anura larval development
the warmer water means faster development
2 most dangerous time periods for frogs
when motionless as larvae, absorbing yolk sores (eyes and mouth start working, operculum covers gills)
metamorphosis when reducing tail makes it hard to swim but cant yet jump
amphibians with the most change to their digestive tract during metamorphosis
frogs
what are amphibians mostly made of
water
how frogs gain water
drink patch and good posture
brumation
moving from environment with temperatures too cold to live (moving underground, underwater, etc)
wood frog adaptability in winter
freeze tolerance by producing glucose-based antifreeze
aestivation
become inactive and reduce metabolism to prevent death by dehydration
using technology to monitor amphibians without trapping them
easy passive sampling
using tech to monitor amphibians with traps
intensive passive samplingsn
snout-vent length SVL
used to measure size for all amphibians
list 3 marking methods
toe clipping, photo id, pain