Variations in economic activity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
aggregate demand (AD)
The total value of all goods and services consumers are willing and able to purchase in an economy over particular time period, at different possible price levels
calculated using expenditure approach
if AD increases, economic growth has happened
AD curve
average price level on y-axis, real GDP on x-axis
downward sloping
changes in average price = movement along AD curve
increase in AP = contraction
decrease in AP = expansion
movement along AD curve
changes in average price = movement along AD curve
shifts of entire AD curve
causes by change in non price determinant of AD
increase in non price determinant = shift right
decrease in non price determinant = shift left
factors influencing consumption
consumer confidence
the stronger the economy, the higher the consumer confidence
consumption increases and saving decreases
interest rates
increased interest rates = greater incentive to save
hence less consumption
wealth
consumer wealth increases = consumption increase
income taxes
taxes increase = disposable income decrease
hence less consumption
expectation of future price level
if it’s believed prices will rise in future, consumers incentivised to spend now
indebtedness of household
higher debt = less disposable income for consumption
factors affecting investment
interest rates
decreased interest rates = higher investment
business confidence
longer period of economic growth = higher business confidence
technology
when firm identifies new technology which reduces costs and raises output, they’re incentivised to invest
business taxes
higher taxes = less profit = less money for investment
corporate indebtedness
higher debt = less money available for investment
factors influencing gov spending
political priorities
some parties believe the state should provide more goods and spending increases, others believe role of gov in society should be small
economic priorities
depends on fiscal policy
expenditure related to gov’s objectives
factors influencing net exports
income of trading partners
household income of trading partners increases = foreigners purchase more products, exports increase
exchange rates
when domestic currency value rises, consumers money can buy more abroad - imports increase
exports are also more expensive for foreigners - exports decrease
trade policies
if import tariffs increase, decreased demand for imports
aggregate supply
total quantity of goods and services produced in an economy over a particular time period, at different price levels
short run = period which wages and other factors are inflexible
long run = period in which there is full wage and factor price flexibility
SRAS curve
upward sloping
AS is the combined supply of all individual supply curves
as real GDP increases, firms must spend more to increase production
increase in AP = expansion of real GDP (Y)
decrease in AP = contraction of real GDP (Y)
shifts of SRAS curve
decrease in cost/increase in productivity shifts the SRAS curve right
increase in cost/decrease in productivity shifts SRAS curve left
changes to costs of raw materials - impact on SRAS
as price of raw materials increase, fewer goods can be made with the same amnt of money
SRAS shifts left
as price of raw materials decrease, more goods can be made with same amnt of money
SRAS shifts right
change in indirect taxes - impact on SRAS
decrease in taxes = decrease in costs = more output
SRAS shifts right
increase in taxes = increase in costs = less output
SRAS shifts left
neo classical LRAS
LRAS is perfectly inelastic at a point of YFe of all available resources
believe that LRAS will always return to FE, all changes in the LR will be at AP
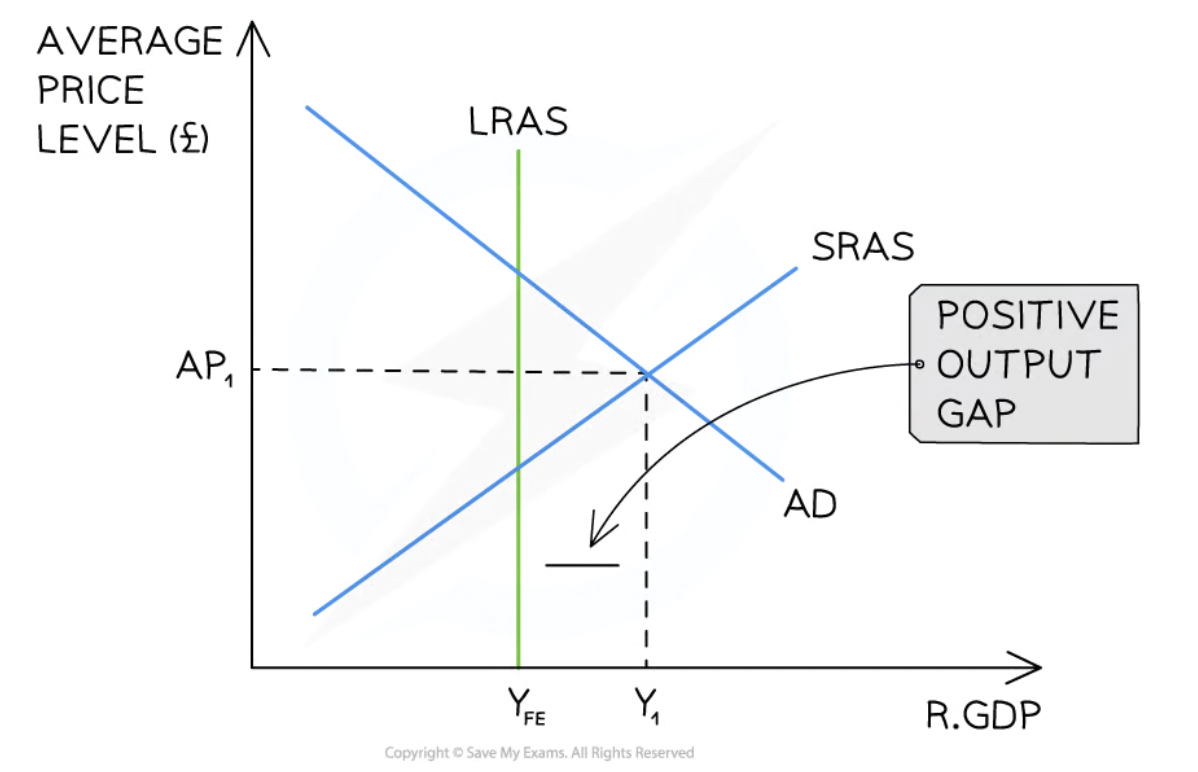
during extreme periods of growth, there can be inflationary gap
will self correct and return to LR level, but at higher AP
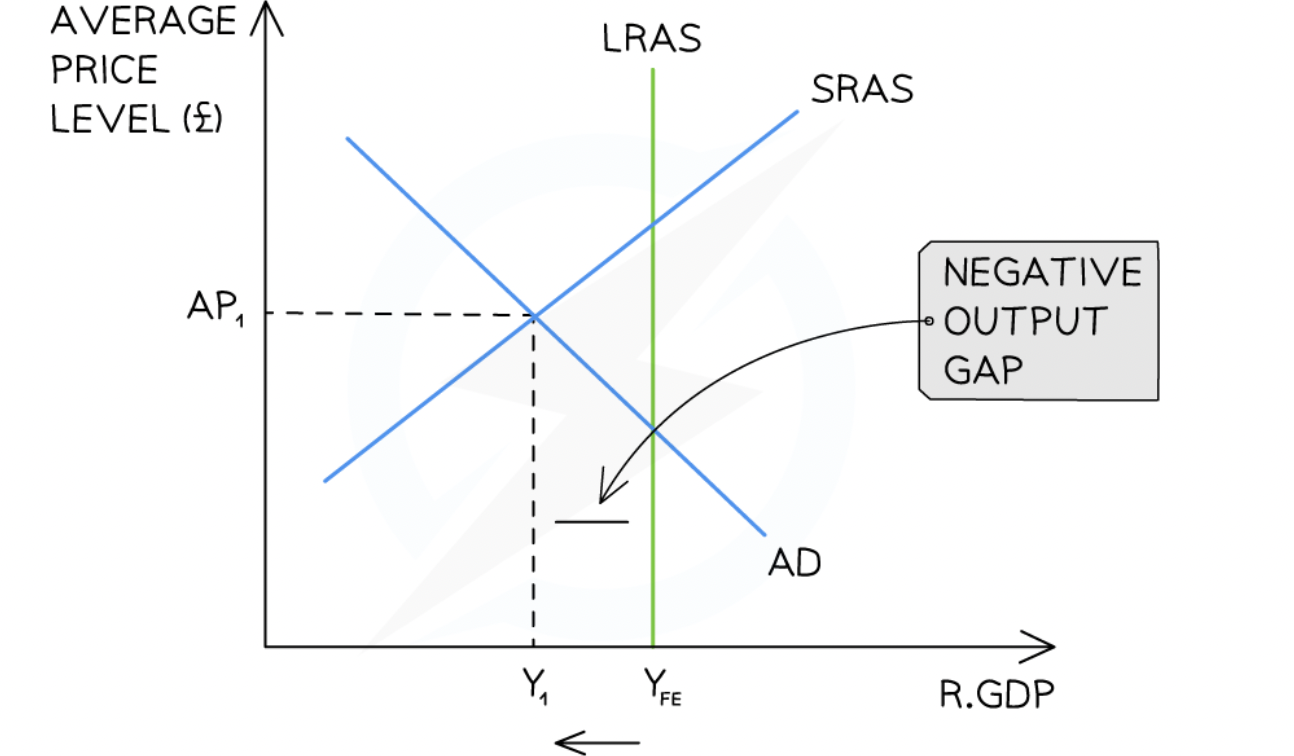
during recessions , can be recessionary gap
will self correct and return to LR level but at lower AP
inflationary/recessionary gaps
inflationary: when real GDP is greater than potential real GDP
deflationary: when real GDP is less than potential real GDP
deflationary gap neo classical
inflationary gap neo classical
factors that shift LRAS
changes in quality/quantity of FOP
increase in this causes increase in production possibilities (outward shift of PPC
technology advances
efficiency improvements
changes in institution
e.g implementation of new legislations, increasing financial institutions
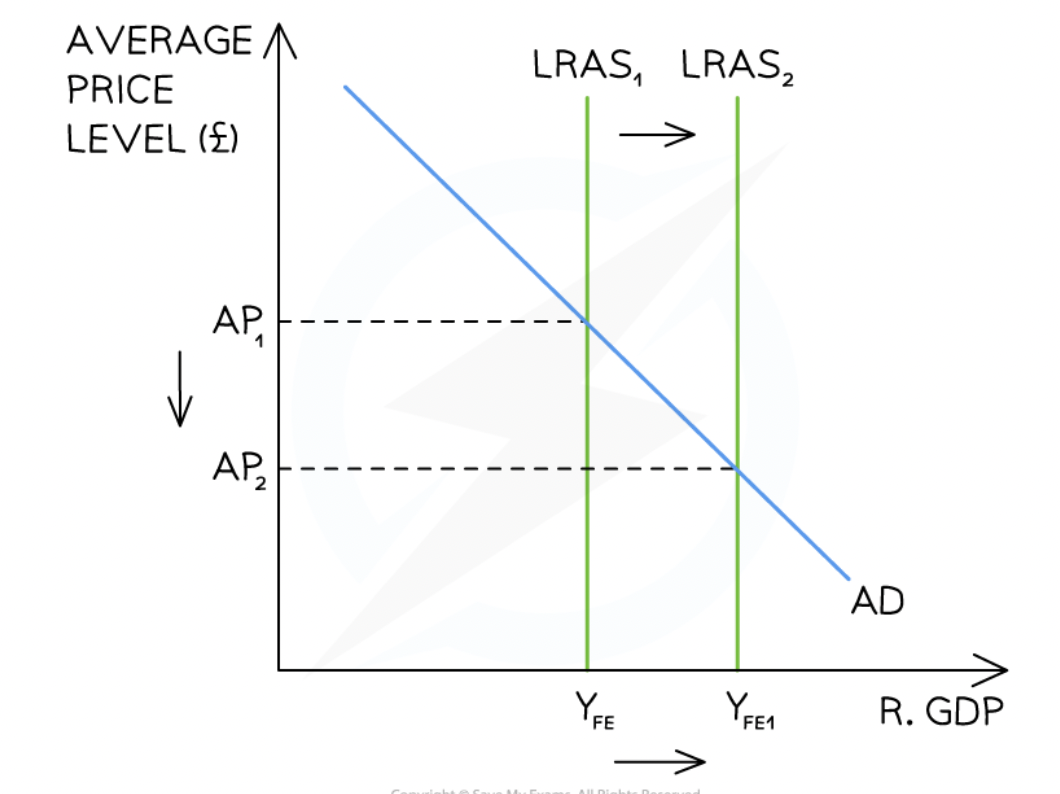
classical LRAS model
initial equilibrium at A1Yfe
increase in quality of labour causes LRAS to shift right
extra supply in economy allows prices to fall and output to increase
new equilibrium at A2Yfe1