Investment Banking Concepts
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
193 Terms
What is accrual accounting and how is that different from cash accounting?
Recognize revenue and expenses when you receive or provide a product or service. Cash accounting tracks spending when cash is received or spent.
What does an income statement show?
Shows revenues, expenses, and profits (net income)
Go line-by-line through an income statement
Revenue
-COGS (Direct Costs - would not exist if product was not being made)
Gross Profit
-Operating Expenses (SG&A) (Indirect Costs - not directly traceable to product)
EBITDA
-Depreciation & Ammortization
EBIT
-Interest Expense
-Other
Pre-Tax Income (EBT)
-Taxes
Net Income
What does a cash flow statement show us?
Our change in cash by bridging net income to cash
What does a cash flow statement look like?
Net Income
+ Depreciation & Amortization
- Gain on Sale
+Loss on sale
- Increase in NWC (Current Assets & Liabilities)
CFO
- Capex
+Proceeds from Sale
CFI
+ Borrowings
- Repayments
- Dividends
+ Issuances
- Buybacks
CFF
If an asset account increases balance, what happens on the cash flow statement?
It gets subtracted from net income in the cash flow from operations section
If a liability or shareholder’s equity increases in balance, what happens to that line on the cash flow statement?
It gets added
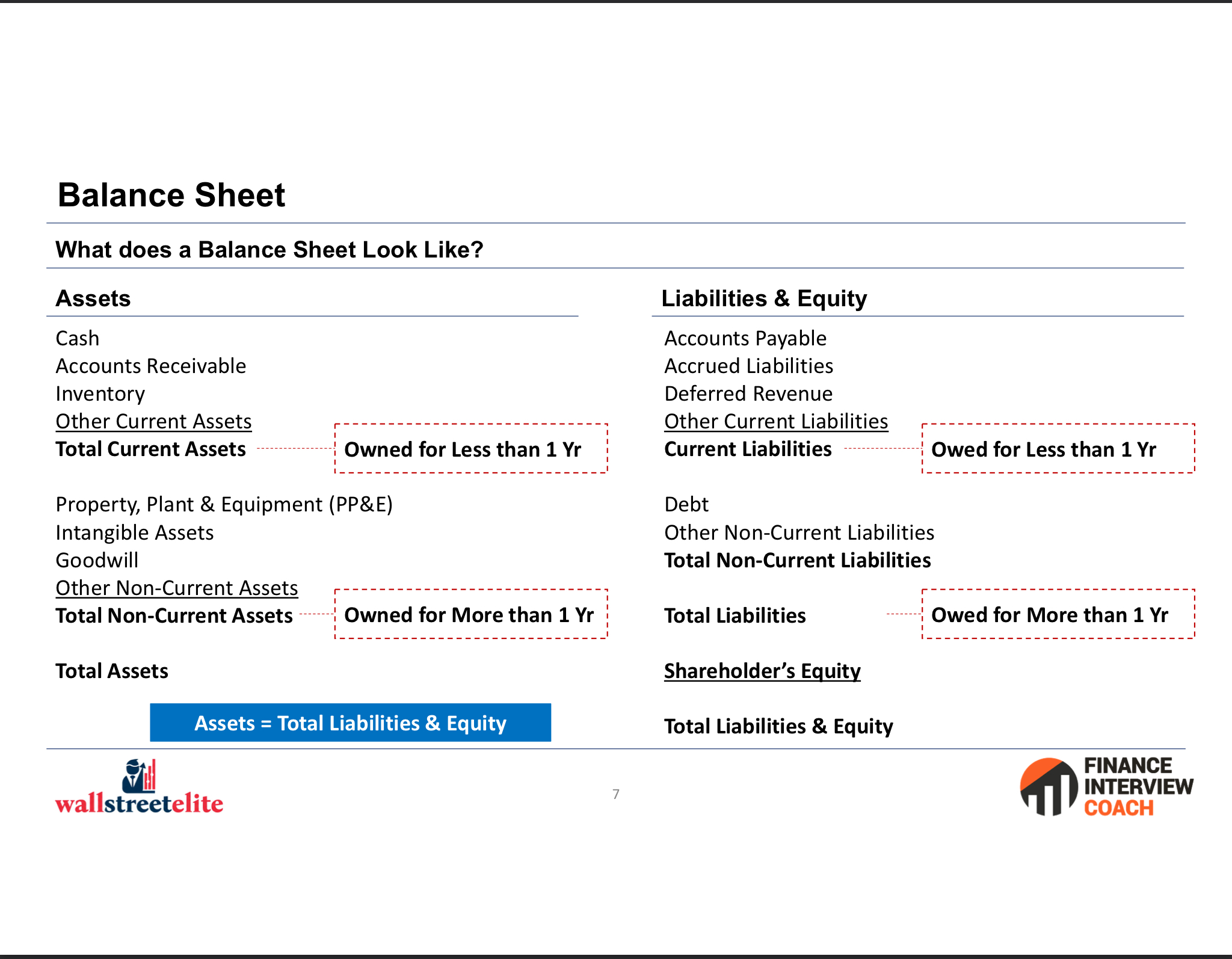
What is a balance sheet?
shows us the stuff we have (assets) vs. how we finance those assets (liabilities and shareholder’s equity)
What is the balance sheet formula?
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholder’s Equity
What does a balance sheet look like?
How do the 3 statements flow into each other?
Income statement ends with net income
Net income from the income statement flows to the first line of the cash flow statement and ends with cash
Cash from the cash flow statement flows to the balance sheet and ends with shareholder’s equity (which is net income from the income statement)
If you could look at 1 financial statement to analyze an investment, what would it be and why?
The Cash Flow Statement
Shows cash flows
Shows net income
Shows Net Working Capital Items
If you could only look at 2 financial statements to analyze an investment, which would they be and why?
The Income Statement and Balance Sheet
The income statement and the Balance sheet can create the Cash Flow Statement
Each line from the Balance Sheet flow to line items in the cash flow statement
What is the inventory equation?
Ending Inventory = Beginning Inventory + Purchases - COGS
Describe the difference between FIFO and LIFO?
FIFO
COGS is calculated with inventory we purchased first
LIFO
COGS is calculated with inventory purchased last
If costs are rising, does FIFO or LIFO provide the lowest COGS?
FIFO, because the earlier inventory is cheaper
What happens when a company buys PPE through the 3 statements in Year 0?
Income Statement
Nothing happens in year 0
Cash Flow Statement
Subtract Capex in CFI
Add any debt used for the transaction
Balance Sheet
Cash from CFS
PPE increase for transaction amount
(If debt is used, there should be a line item increasing debt)
What happens when a company buys PPE through the 3 statements in Year 1?
Income Statement
Depreciation Expense on Income Statement
(If debt is used, interest expense as well)
Cash Flow Statement
Add back depreciation in CFO
Subtract Interest Expense in CFF (Repayment)
Balance Sheet
Cash from CFS
Decrease PPE by Depreciation
Decrease Debt by Interest Expense (if funded by debt)
Net income from Income Statement = Shareholder’s Equity
When there is a write-down of PPE, what happens on the three statements?
Income Statement
Subtract the book value of PPE
Add back book value of debt (if applicable)
Cash Flow Statement
Add back book value of PPE (CFO)
Subtract Debt (CFF)
Balance Sheet
Cash from CFS
Decrease PPE by Book Value
Decrease Debt by Book Value
Bring over Net Income for Shareholder’s Equity
What happens to the 3 financial statements when there is a sale of PPE (gain)?
Income Statement
Gain on sale gets added before taxes are taken out
Cash Flow Statement
Subtract your gain on sale from Net Income
Add your proceeds from your sale (sale price)
Subtract your book value of debt
Balance Sheet
Cash from CFS
Decrease PPE by Book Value
Decrease Debt by Book Value
Bring over Net Income for Shareholder’s Equity
What is Net Working Capital?
The cash tied up in the daily operation of your business
When you buy inventory in Y0 with cash, what happens to your financial statements? How does that change when you buy on credit?
Income Statement
Nothing because nothing has been sold yet and cannot be transferred to COGS
Cash Flow Statement
Since Inventory is an Asset, and the balance is increasing, it gets subtracted from Net Income on the CFS
Balance Sheet
Cash from CFS
Increase inventory by amount purchased
When You Buy on Credit
The only thing that changes is on your cash flow statement, your accounts payable increases, and since it is a liability, it will be added to Net Income on the CFS (subtract inventory still)
On your balance sheet, instead of having a cash line item with inventory purchase amount, you will have a liability
What Assets and Liabilities are considered Net Working Capital?
Assets
Accounts Receivable
Inventory
Prepaid Expenses
Other Current Assets
Liabilities
Accounts Payable
Accrued Liabilities
Deferred Revenue
Other Current Liabilities
What is deferred revenue?
received revenue upfront, but the services or product have not yet been delivered
What are prepaid assets?
pay for an expense upfront, but have not yet received the product or service
What are accrued expenses?
Expenses which have not been paid for or do not have na invoice
EX: wages payable
What is shareholder’s equity and how is this different than market cap?
Your original cost plus cumulative net income
Market cap is the current value of the cost in the market today
What is the formula for market value / market cap?
#shares X share price
What is the formula for calculating shareholder’s equity?
Beginning SE + Net Income - Dividends + SBC + Issuances - Buybacks
Why doesn’t dividends impact the income statement?
Because dividends are a decision AFTER net income, we do not realize it on the income statement
What is the impact of stock based compensation on the 3 financial statements?
Income Statement
Subtracted before Pre-Tax Income
Cash Flow Statement
Add back SBC to Net Income
Balance Sheet
Line item for Cash from CFS
Line item for SBC (SE)
Line item for Retained Earnings (NI)
What is the concept of the time value of money?
Money today is more valuable than money tomorrow
What is the present value of a perpetuity?
Perpetuity Cash Flow / (1 + discount rate)
What is a discounted cash flow?
about finding how much future cash flows are worth in today’s money
Walk me through a DCF
Make assumptions
Project out future cash flows (5-10 years)
Calculate the terminal value
Exit Multiple: find mature comparables of EV / EBITDA and take the median to multiply it by the last year’s EBITDA
Perpetuity Growth Method: take the last year’s FCF and multiply it by 1+g and divide it by WACC - g
Discount the projected cash flows back using the discount rate (WACC) to find the PV
Add all the FCF together to find the enterprise value
Do a sensitivity analysis
What is an unlevered free cash flow? What is the formula?
An unlevered free cash flow does not include debt
UFCF = EBIT(1-tax rate)+D&A-Change in NWC - Capex
Who does UFCF belong to and why?
It belongs to both debt and equity holders because debt has not yet been paid out
Why do we use UFCF in a DCF? Why?
When debt is not core to the business
Including debt in calculations make it complicated and adds potential for error
What does free cash flow represent?
how much cash the core business is making in its day to day operations
Why don’t we include items from CFF in our calculation of UFCF?
Because we are looking at cash flows BEFORE we pay out capital holders
Why doesn’t NOPAT and UFCF not include interest tax shield?
The tax shield represents how much tax you save by deducting interest first
Why do we subtract D&A to get EBIT and add it back later?
We subtract D&A to decrease our EBIT and therefore our taxes, we add it back later because it is a non-cash expense
Who does levered free cash flow belong to?
It belongs to equity holders because debt holders have been paid
When would we use levered free cash flows in a DCF?
When debt is core to the business
EX: Banks and Insurance Companies
What is the formula for calculating levered free cash flows?
LFCF = Net Income + D&A - Increase in NWC - Capex - Mandatory Debt Repayments
Does levered free cash flows include the interest tax shield?
Yes, because it uses net income instead of EBIT (1- tax rate), it already deducts interest expense before calculating taxes
How do you go from UFCF to LFCF?
LFCF = UFCF - interest expense X (1-tax rate) - mandatory debt repayment
What do we discount UFCF by?
The Weighted Average Cost of Capital
What would we discount LFCF by?
The Cost of Equity
How do you calculate the WACC?
Cost of Equity (Weight of Equity) + (Cost of Debt)*(1- Tax Rate)*(Weight of Debt)
How do you calculate your cost of equity?
CAPM formula
= risk free rate + beta(average stock market return - risk free rate)
Equity Risk Premium / Market Risk Premium
= (average stock market return - risk free rate)
What are preferred shares?
Classified as equity, but they get paid out first like debt holders (not tax deductible)
How do we incorporate preferred shared into the WACC formula?
WACC = (% equity)*(cost of equity) + (%debt)(after-tax cost of debt)+(% of preferred shares)*(cost of preferred shares)
What is the cost of equity?
Investors need to be compensated for the risk of investing in the stock market, so it represents the return that investors needs to compensate them for the risk of investing in market
What do we use as the risk free rate and why?
Government bonds 10yr rate because governments in developed countries are not likely to default, making them somewhat risk free
They are also the most liquid and it aligns with a 5-10 year forecast
What does the equity risk premium represent?
Excess return above the risk free rate to compensate investors for the risk of the stock market
What does Beta represent?
the market risk; it shows how sensitive a company’s stock price is to the market
How do we find beta for a private company?
Use public comps
Is a Beta that you find online for a public company levered or unlevered?
Levered
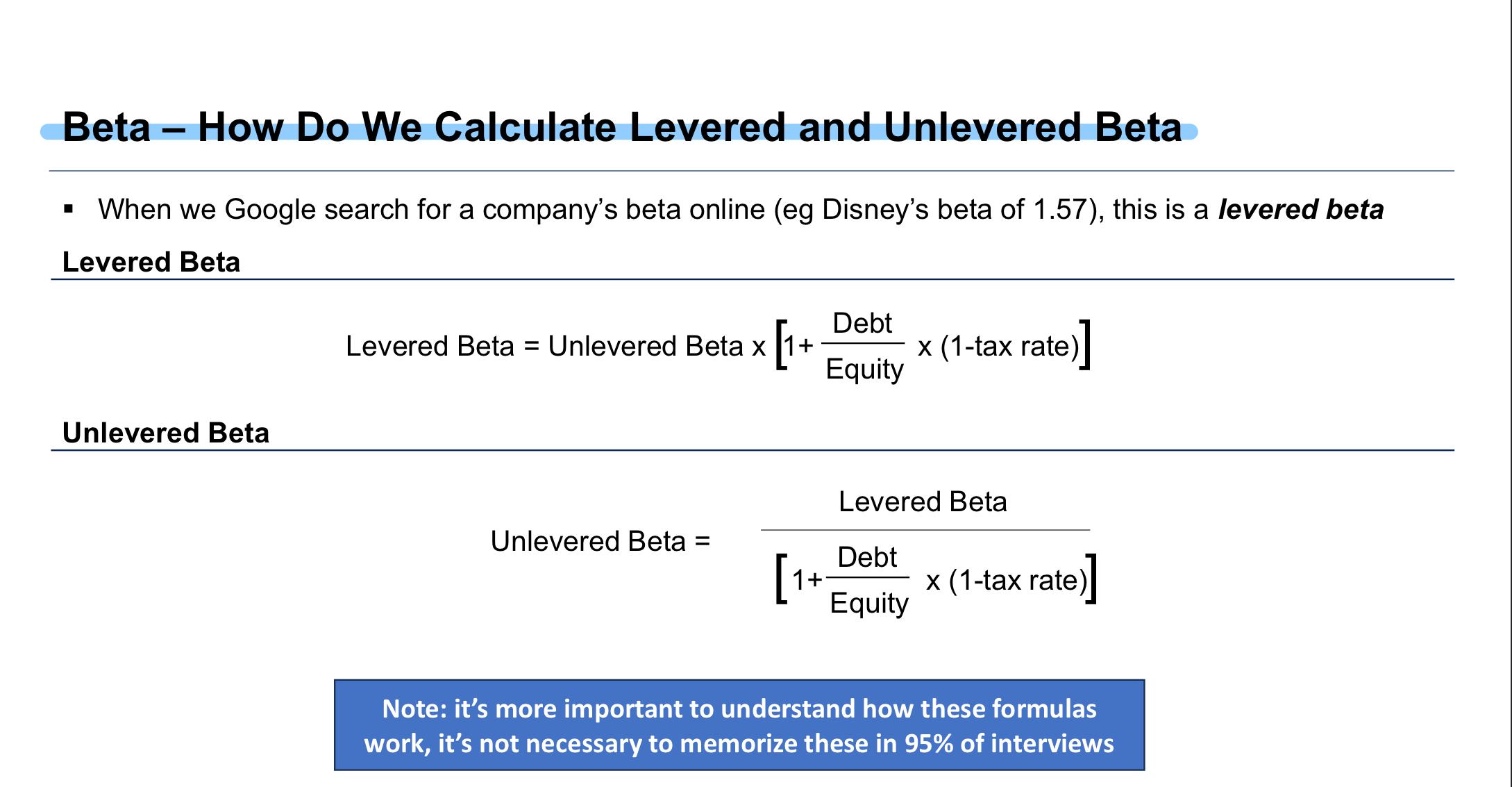
Why do we need to unlever the beta when using comps for a private company?
If debt increases risk, then different companies with different debt levels will hae different risk levels therefore the betas are not comparable
What is the formula to unlever Beta?
What are the steps for Beta Comps?
Find Betas of Comps
Unlever Betas and Find Median
Relever to Target Company’s Capital Structure
Do we use marginal cost of debt or existing cost of debt when calculating WACC?
Marginal cost of debt because it is the cost of debt TODAY, whereas the existing cost of debt is the cost of debt in the PAST
How to find cost of Debt?
10k filings (look at notes)
Yield of most recently issued bonds
Bond yields of comparable companies
Apply a spread to a benchmark rate based on company credit rating
Can the cost of equity ever be less than the cost of debt?
No! Because equity holders take on more risk than debt holders. Debt holders are paid out first and they are tax deductible
How does increasing debt impact WACC?
If you borrow too much, lenders get worried you won’t pay it back, so equity holders demand more return to compensate for higher risk
What should terminal value be with a 5 year and 10 year projection period as a percent of enterprise value?
5 Year
60% - 80% of enterprise value
10 Year
50% of enterprise value
If terminal value is too high as a percent of EV, what should we do?
Extend the projection period
What happens to EV when you increase the tax rate?
Lower Free Cash Flows → Lower EV
Increased taxes means lower free cash flows
Lower After Tax Cost of Debt → Higher EV
Increase of Tax Shield → Decrease After Tax Cost of Debt → Decrease WACC → Increase EV
Lower Cost of Equity → Higher EV
Increase Tax Shield → Decrease Levered Beta → Decrease Cost of Equity → Decrease WACC → Increase EV
Do you get the same EV using UFCF and LFCF?
UFCF will get us EV, LFCF will get us equity value
What is an LBO?
buying a company using debt and equity, but usually more debt using the cash flows from the company to pay down the debt, selling within 5-10 years
Why do PE firms use debt in an LBO?
Allows diversification (investing in other companies)
Debt increases returns because you don’t have to put in as much equity
What Makes A Good LBO Candidate?
Stable Revenue Growth
Stable, Healthy Margins
Strong market position and exit opportunities
Low Capital Intensity
Synergies with Existing Portfolio Companies
Large Tangible Asset Base
Walk me through an LBO
Make Assumptions:
Entry / Exit Multiple
Financing Structure
Create Sources and Uses:
calculates initial required equity
Project 3 Financial Statements without the effects of debt
adjust balance sheet for the transaction
Build Debt Schedule
use LFCF to determine debt repayments, then link interest and repayments to 3 statements
Determine the IRR and MoM
Perform Sensitivity Analysis:
finding IRR by sensitizing exit, entry, and leverage multiple
What is a paper LBO?
A simplified version of an LBO used in interviews
How do you calculate the MoM (Money on Money)?
Ending Equity / Beginning Equity
What are the other terms for MoM?
Multiple of Invested Capital (MoM)
Multiple of Capital (MoC)
Cash on Cash (CoC)
What are the rules for the IRR using MoM?
2x | 72 | |
3x | 114 | |
4x | 144 |
How do you find IRR for a paper LBO?
Your rule as a percent / number of years in hold period
What does the IRR represent?
How much the equity investment has grown per year
Why do we use IRR to measure returns in an LBO?
It accounts for the impact of time
Walk me through a paper LBO
Year 0
LTM EBITDA and Purchase Price
Find Enterprise Value using EBITDA and entry multiple
Debt & Equity
Find the Equity Value
Enterprise Value - Debt
Interim Years
Find LFCF
Forecast every year or find average LFCF
Find Total Cash Accumulated
Sum up all LFCF in all years
Exit Year
Exit Enterprise Value
Last year EBITDA multiplied by the exit multiple
Exit Equity Value
Exit Enterprise Value - Debt
Debt = Entry Debt - Sum of LFCF
Find MoM and IRR
How do you know cash flows are linear for a paper LBO?
Revenue increases by the same $ amount each year
COGS and SG&A are the same % of revenue
D&A, NWC, and Capex are constant over the term of the cash flows
When cash flows are linear in a paper LBO, how do you find your cash flows to subtract from debt in your exit?
Take the midpoint of your holding period (in the case of 5 years, Y3 should be your midpoint)
Find the EBITDA and calculate your LFCF
5 Year IRRs to Memorize
2x | 72 | 15% |
3x | 114 | 23% |
4x | 144 | 29% |
What are the sources of financing an LBO?
Senior Debt
Revolver
Term Loan A (TLA)
Term Loan B (TLB)
Junior Debt
Unsecured or Subordinated Debt
High Yield Bonds
Mezzanine or Convertible Bonds
Equity
Preferred Stock
What is PIK interest?
Interest compounding on debt balance before being paid at sale
How does $100 of PIK debt issuance affect the 3 financial statements in Y0?
Income Statement
None
Cash Flow Statement
Add $100 of borrowing to NI
Cash = 100
BS
Cash = 100
Debt = 100
How does $100 of PIK Debt Issuance Affect the 3 financial statements in Y1? 10% Interest, 40% tax rate
Income Statement
Interest Expense (10)
Tax Shield 4
Net Income = (6)
CFS
Net Income (6)
Interest Expense - PIK 10
Cash = 4
Note: Interest Expense gets added because PIK is a non-cash expense
BS
Cash: 4
Debt: 10
RE / SE: (6)
What is a dividend recap?
A PE portfolio company borrows money and pays the investors a dividends to help increase returns
What happens in Y0 with a $100 dividend recap?
Income Statement
None
Cash Flow Statement
Add $100 of borrowing to NI
Subtract $100 of dividends from NI
Cash = 0
BS
Cash = 0
Debt = 100
SE = (100) ← Paying out dividends
What are Maintenance Covenants?
Requires the borrower to maintain a certain ratio or metric at all times
Think of it similar to the reserve ratio in economics
What are the common maintenance covenants?
Senior Debt Leverage Ratio: Senior Debt to EBITDA
Leverage Ratio: Total Debt to EBITDA
Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (Interest Coverage Ratio)
EBITDA / Interest Expense
(EBITDA - Capex) / (Cash Interest Expense + Mandatory Amortization of Debt)
What is an incurrence covenant?
restrictions or requirements on specific actions
Why are LBOs monthly models?
Covenants are tested monthly
What are 9 drivers of IRR?
Using more debt to finance the deal
Lower interest rates → paying lower interest expense
Add on acquisitions → increased revenue
Price Increases → increased revenue
Synergies with existing portfolio companies
Applying best practices to reduce costs
Pay lower price or entry multiple
Exit at higher multiple
Dividend recap
What is enterprise value?
the total value of a business regardless of how it is financed
What is equity value?
the value of what you own excluding debt
How do you calculate enterprise value (simple)?
Equity Value + Net Debt
How do you calculate Net Debt?
Debt - Cash