Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:15 PM on 9/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
1
New cards
objective of course part 1
explore answers to the question “what is emotion?” from several perspectives: historical, evolutionary, biological, cultural, and psychological
2
New cards
3 emotion families
* anxiety
* shame
* positive emotions
* shame
* positive emotions
3
New cards
important functions of positive emotions
social function
4
New cards
essentialism beliefs
* hard wired
* essence/essential
* fixed traits
* biological determinism
* WHO you are
* essence/essential
* fixed traits
* biological determinism
* WHO you are
5
New cards
constructivism
* context matters
* dependent on experience
* construction/building
* learning and adaptation
* HOW you become
* dependent on experience
* construction/building
* learning and adaptation
* HOW you become
6
New cards
motivation defintion
energy that is directed toward achieving some goal
7
New cards
energy from motivation manifests into…
* activation (getting mobilized)
* persistance (how long you keep at it)
* persistance (how long you keep at it)
8
New cards
intrinsic motivation
motivation that springs naturally from internal forces
9
New cards
why are intrinsic motivations rewarding
they fulfill basic human psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness
10
New cards
why are we intrinsically motivated to do certain tasks
bc we enjoy them, they feel good, and/or bc they are inherently fulfilling or meaningful
11
New cards
extrinsic motivation
motivation that reflects external pressures
12
New cards
why are we extrinsically motivated
we do them because they have a downstream effect that we want, such as avoiding cavities or continuing to get paid
13
New cards
continuum of motivation
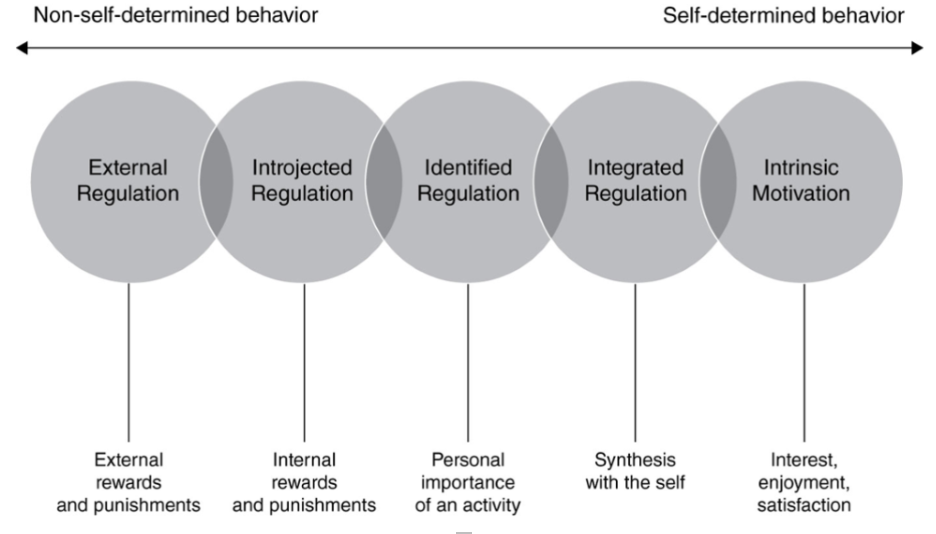
14
New cards
identified regulation (continuum)
motivation based on behavior feeling like its part of ones identity
15
New cards
integrated regulation (continuum)
motivation that began with rewards and punishments but is transitioning to a more internalized appreciation of this behavior
16
New cards
introjected regulation
motivation based on awareness of societal norms regarding this behavior and wish to avoid internal feelings of shame or embarassment that might arise if you didnt behave in concordance with these norms
17
New cards
regulatory focus theory
argues that in addition to understanding how human beings approach and avoid certain situations and outcomes, we would do well to also consider whether these motivations are focused on achieving gains or avoiding losses
18
New cards
the 3 psychological needs emphasizes in self-determination theory
* autonomy
* competence
* relatedness
* competence
* relatedness
19
New cards
self-determination theory
motivation theory suggesting that people can become self-determined when their needs for competence, relatedness, and autonomy are fulfilled
20
New cards
autonomy (motivation)
ability to choose your own path and behaviors
21
New cards
competence (motivation)
succeeding at existing tasks and mastering new skills
22
New cards
relatedness (motivation)
connecting with social others
23
New cards
promotion goals
work to reach (or promote) a desired end state
24
New cards
prevention goals
work to stop (or prevent) an undesired end state
25
New cards
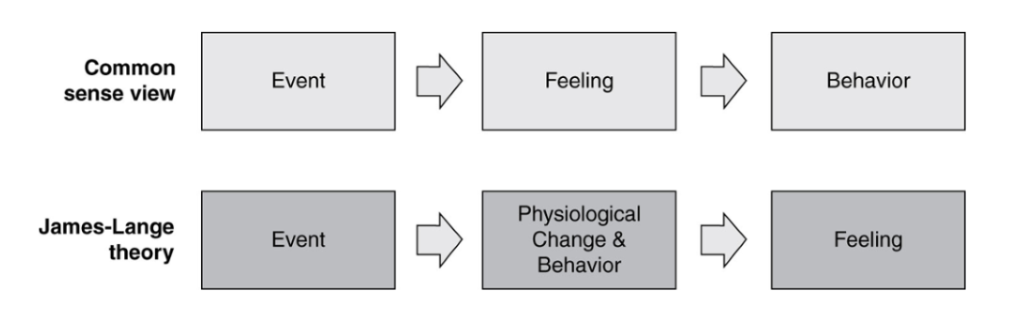
James-Lange theory of emotion
emotional feelings are based on body’s instinctive reaction to certain kinds of situations. feedback from physical experiences produce emotions
the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the the situation, and our feeling of the same changes as they occur IS the emotion
sensation from the muscles and/or the internal organs is necessary for the full experience of emotion
every “shade of emotion” might be associated with a unique profile of changes throughout the body
the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the the situation, and our feeling of the same changes as they occur IS the emotion
sensation from the muscles and/or the internal organs is necessary for the full experience of emotion
every “shade of emotion” might be associated with a unique profile of changes throughout the body
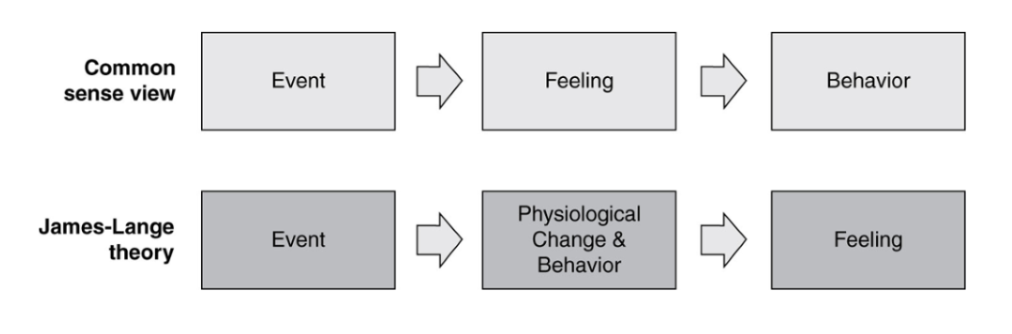
26
New cards
common sense view of emotion
event occurs, feeling occurs, resulting in behavior
e.g. you feel angry and therefore you attach
e.g. you feel angry and therefore you attach
27
New cards
Plutchik’s defintion of emotion
an inferred complex sequence of reactions to a stimulus \[including\] cognitive evaluations, subjective changes, autonomic and neural arousal, impulses to action, and behavior designed to have an effect upon the stimulus that initiated the complex sequence
28
New cards
Plutchik’s 4 aspects of emotion
* congitive eval./appraisal of what the stimulus means for our goals/concerns/well-being
* feelings
* physiological changes
* behavior
* feelings
* physiological changes
* behavior
29
New cards
Russell’s circumplex model
emotional feelings form a circle defined by the dimensions of pleasantness and arousal
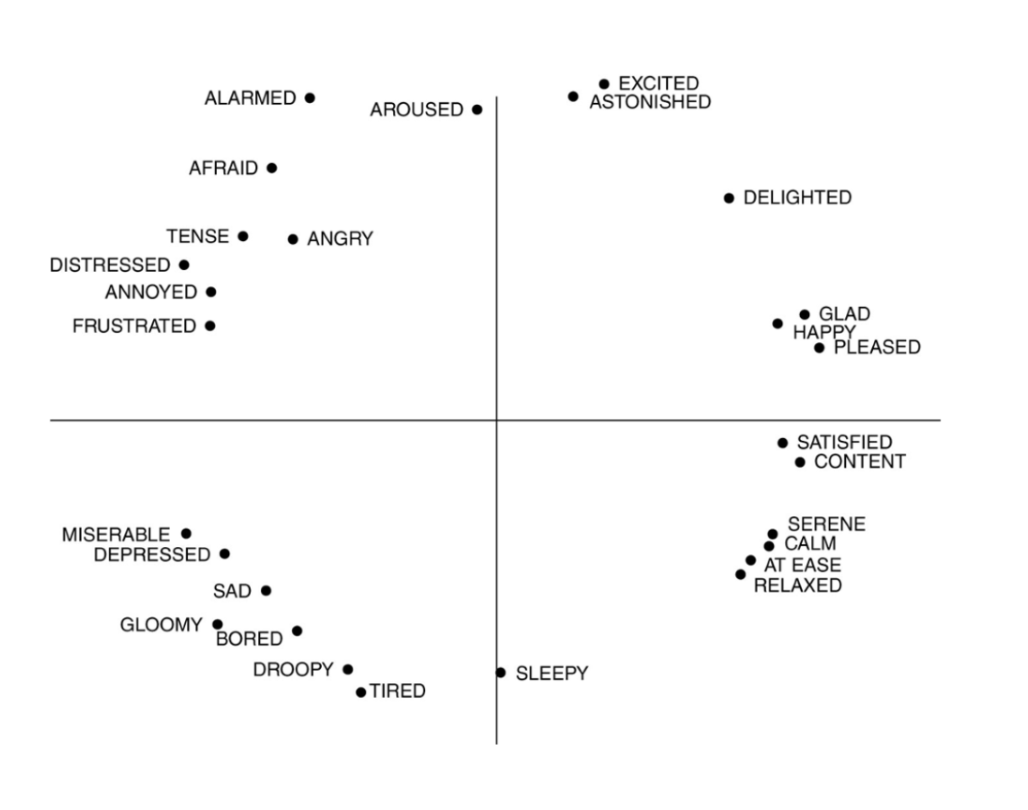
30
New cards
core affect (Russel, circumplex)
the feeling aspect of emotion in terms of pleasantness and arousal
31
New cards
differences between emotion and mood
* time; emotions are short lived, whereas moods can linger over hours/days/etc
* cause; emotions are linked to an easily identified internal or external trigger while there may be multiple, diffuse reasons for moods
* action; emotions are tied to specific behaviors (at least in theory), moods are less obviously connected with specific actions
* cause; emotions are linked to an easily identified internal or external trigger while there may be multiple, diffuse reasons for moods
* action; emotions are tied to specific behaviors (at least in theory), moods are less obviously connected with specific actions
32
New cards
propositions of basic/discrete emotion theory
* each emotion is thought to serve a distinct adaptive function
* basic emotions serve to coordinate the individual aspects of emotion, producing a coherent package of responses that should help you respond effectively to the situation at hand
* some of the conceptual categories people have for their emotions reflect distinctions among real, naturally occurring categories of human psychological experience, at least to some extent
* basic emotions serve to coordinate the individual aspects of emotion, producing a coherent package of responses that should help you respond effectively to the situation at hand
* some of the conceptual categories people have for their emotions reflect distinctions among real, naturally occurring categories of human psychological experience, at least to some extent
33
New cards
basic/discrete emotions def.
complex psychobiological reactions that evolved in response to prototypical threats and challenges in the environment of our early human ancestors (e.g. happiness, sadness, fear)
34
New cards
component process model
proposes that emotions are responses to events in the environment, that they reflect our evolutionary heritage, and that they include multiple aspects that tend to hang together in similar ways across cultures
35
New cards
explain how the structure of appraisal differs between basic/discrete emotion theory and the component process model
* basic/discrete = appraisal is needed for an emotional response to occur, and determines which emotion is activated, appraisals are thought to be categorical
* component process model = dimensional, with the same set of dimensions used to evaluate the significance of every event we experience
* component process model = dimensional, with the same set of dimensions used to evaluate the significance of every event we experience
36
New cards
reliability
reflects the consistency or repeatability of its scores
37
New cards
validity
an assessment of whether scores on some measure represent what the researcher claims they represent
38
New cards
face validity
the content of the measure should match the intended construct in a reasonably obvious way
39
New cards
content validity
a measure is supposed to capture some construct, it needs to cover the whole of that construct without being influenced by a bunch of stuff beyond the intended construct
40
New cards
convergent validity
different measures of the same general thing should correlate positively with one another
41
New cards
predictive validity
scores on the measure should accurately predict some theoretically relevant outcome
42
New cards
ways to measure emotion
* self-reports
* biological measurements
* behaviors
* biological measurements
* behaviors
43
New cards
self-reports
participants descriptions of their own feelings, thoughts, beliefs, goals, and other aspects of emotion and motivation
44
New cards
biological measurements
includes measures of heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, and other variables that fluctuate during emotional arousal, as well as brain activity and hormones
45
New cards
behaviors (measurements)
actions we can observe, such as facial and vocal expressions, speech, task performance, and real-world action
46
New cards
Aristotle (384-322 BCE) beliefs
* “All human actions have one or more of these seven causes: chance, nature, compulsions, habit, reason, passion and desire.”
* emotions essential to virtue
* functionalist, trying to figure out the functions of emotion
* emotions essential to virtue
* functionalist, trying to figure out the functions of emotion
47
New cards
Rene Descartes (1596-1650)
* existentialist
* “"I doubt, therefore I think; I think, therefore I am"
* our doubt propels us forward into our existence
* mind body dualism
* “"I doubt, therefore I think; I think, therefore I am"
* our doubt propels us forward into our existence
* mind body dualism
48
New cards
mind body dualism
* associated with Descartes
* the mind is the unknowable (psychology), the body is the earth and what is knowable (biology)
* the mind is the unknowable (psychology), the body is the earth and what is knowable (biology)
49
New cards
Charles Darwin (1809-1882)
* published and wrote the expression of the emotions in man and animals (1872)
* believed in universal discrete emotions via facial expressions
* believed in universal discrete emotions via facial expressions
50
New cards
main ideas of Darwin’s “the expression of the emotions in man and animals (1872)”
* sets of facial behaviors = expression, expressions can function to display information to others
* emotions are automatic – emotions are habits/reflexes; occur without conscious intent
* evolutionary link between humans and animals are emotions
* emotions are automatic – emotions are habits/reflexes; occur without conscious intent
* evolutionary link between humans and animals are emotions
51
New cards
Darwin believed that emotions are evolutionary ____,__ we have them but do not neccasarily *them. they are* __
left-overs; need; vestigal
52
New cards
ID (Freud)
animalistic natured
53
New cards
super ego (Freud)
more rational and logical
54
New cards
combonation of the ID and the super ego create the…
EGO that is outer facing and that outsiders see
55
New cards
Watson beliefs
* behaviorism
* pairing unconditioned stimuli with unconditioned responses is building block of habits we call emotions
* pairing unconditioned stimuli with unconditioned responses is building block of habits we call emotions
56
New cards
old ass views
* aristole
* darwin
* descartes
* watson
* darwin
* descartes
* watson
57
New cards
early 20th century views
* James-Lange
* Cannon-Bard
* Cannon-Bard
58
New cards
Cannon-Bard beliefs
components of emotion occur independently
59
New cards
mid 20th century perspectives
Schachter-Singer two-factor theory
60
New cards
Schachter-Singer two-factor theory:
* physiological arousal determines intensity but not specific emotional state
* people use context and other cues to differentiate which emotional state they are experiencing
* people use context and other cues to differentiate which emotional state they are experiencing
61
New cards
emotion as a latent process
emotion CAUSES physio, expression, and cognition outputs
62
New cards
emotion as an emergent process
emotion EMERGES from the combination of physio, expression, and cognition
63
New cards
natural selection
process by which random genetic mutations that happen to be problematic are removed from the population (because they cause the individuals who have them to die or underproduce)
individuals that survive to reproduce will pass along their characteristics to their offspring
individuals that survive to reproduce will pass along their characteristics to their offspring
64
New cards
evolution
any change in the heritable traits within a population across generations
65
New cards
adaptation
beneficial characteristics that spread as a result of natural selection
66
New cards
mutation
when the gene-copying process goes awry, and the copy is off, just by chance
only a new mutation that happens to improve on the previous version will replace what’s already there, and even that will spread through the population very, very slowly in most cases
only a new mutation that happens to improve on the previous version will replace what’s already there, and even that will spread through the population very, very slowly in most cases
67
New cards
three criteria for calling a gene-based characteristic “functional” in the evolutionary sense
* the characteristic increases the probability that you will survive long enough to reproduce
* the characteristic increases the probability that you will have more offspring than your neighbor who lacks the characteristic, and these offspring survive and reproduce
* the characteristic increases the probability that your relatives will survive and have more offspring
* the characteristic increases the probability that you will have more offspring than your neighbor who lacks the characteristic, and these offspring survive and reproduce
* the characteristic increases the probability that your relatives will survive and have more offspring
68
New cards
environment of evolutionary adaptedness (EEA)
the ancestral environment to which a species is adapted
the time and place in the past when that characteristic spread throughout the population as a result of natural selection
“statistical composite of selection pressures that caused the genes underlying the design of an adaptation to increase in frequency until they became species-typical or stably persistent”
the time and place in the past when that characteristic spread throughout the population as a result of natural selection
“statistical composite of selection pressures that caused the genes underlying the design of an adaptation to increase in frequency until they became species-typical or stably persistent”
69
New cards
adaptive significance
the adaptiveness of a trait depends on how well it solves an evolutionary problem, or struggle
70
New cards
instinct theory
belief that instincts govern complex behaviors and drive the majority of our behavior
environmental cues trigger instincts which elicit emotions, which then pushes the organism toward a certain behavior
environmental cues trigger instincts which elicit emotions, which then pushes the organism toward a certain behavior
71
New cards
each emotion has a ____ function
evolutionary
72
New cards
major brain regions
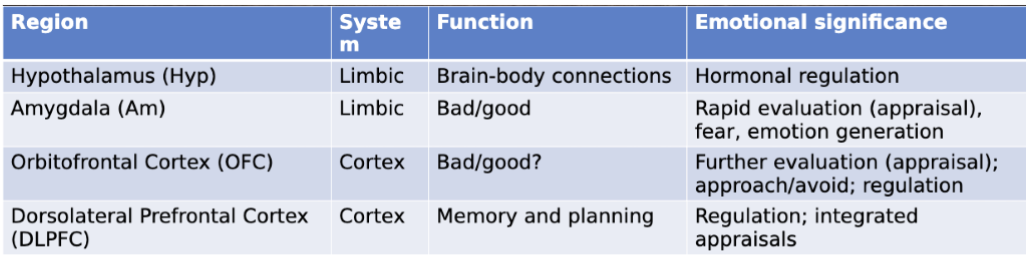
73
New cards
critiques of instinct theory
circular and untestable (everything is listed as an instinct)
74
New cards
75
New cards
drive
an urgent basic need pressing for satisfaction, usually rooted in some physiological tension, deficiency, or imbalance impelling the organism to action
76
New cards
____ theory replaced (blank) theory
drive; instinct
77
New cards
homeostasis
process of detecting a biological deficiency and activating motivated behavior to re-establish a stable internal state
78
New cards
explain how drives relate to the concept of homeostasis
individuals are motivated to engage in behaviors that reduce or satisfy their biological needs (drives) to achieve a state of homeostasis
79
New cards
Freud’s theory of human motivation
argued that that drives such as hunger, aggression, and sex were constantly fluctuating between need and satiety
deficits in fulfilling these needs built up, they led to an uncomfortable excess of energy in the nervous system that was experienced by the individual as anxiety, or some other discomforting mental health symptom
desire to reduce anxiety then motivated the person to satiate the drive, thereby releasing the energy and bringing relief
deficits in fulfilling these needs built up, they led to an uncomfortable excess of energy in the nervous system that was experienced by the individual as anxiety, or some other discomforting mental health symptom
desire to reduce anxiety then motivated the person to satiate the drive, thereby releasing the energy and bringing relief
80
New cards
Clark Hull’s drive theory of motivation
saw all bodily needs as summing to a sort of pooled energy, which he called drive, and which he thought related to the energy component of motivation
when needs were unfulfilled, the organism would become energized to satiate the need
Behavior = Drive x Habit
when needs were unfulfilled, the organism would become energized to satiate the need
Behavior = Drive x Habit
81
New cards
Henry Murray’s theory
described psychological needs as “predispositions to act” in certain ways, given certain circumstances
the physiological needs described above as well as needs linked to intrinsic psychological experiences, such as independence, power, and ambition
the physiological needs described above as well as needs linked to intrinsic psychological experiences, such as independence, power, and ambition
82
New cards
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
argued that psychological needs are not equal in terms of importance and priority, but are organized in a hierarchical structure
more fundamental needs must be fulfilled before you can really be concerned about the ones further up the hierarchy
some needs take priority over others, and fulfilling these needs provides a foundation that can then support attention to “higher” needs
more fundamental needs must be fulfilled before you can really be concerned about the ones further up the hierarchy
some needs take priority over others, and fulfilling these needs provides a foundation that can then support attention to “higher” needs
83
New cards
criticisms of Maslow’s theory
* may have been strongly influenced by his time working with indigenous people of the Blackfoot Nation
* Maslow’s hierarchy has not generated much in the way of empirical research
* Maslow’s hierarchy has not generated much in the way of empirical research
84
New cards
how did Kenrick expand on Maslow’s theory
revitalized the proposal for a hierarchy of human needs, however, based on a synthesis of contemporary behavioral science data and evolutionary theory
85
New cards
Kenrick’s pyramid
fulfilling basic physiological needs and protecting oneself from harm are at the bottom of the pyramid
the next two levels—affiliation and status—also correspond to levels of Maslow’s hierarchy and recognize the crucial role that relationships with groups and communities play in human life
the next two levels—affiliation and status—also correspond to levels of Maslow’s hierarchy and recognize the crucial role that relationships with groups and communities play in human life
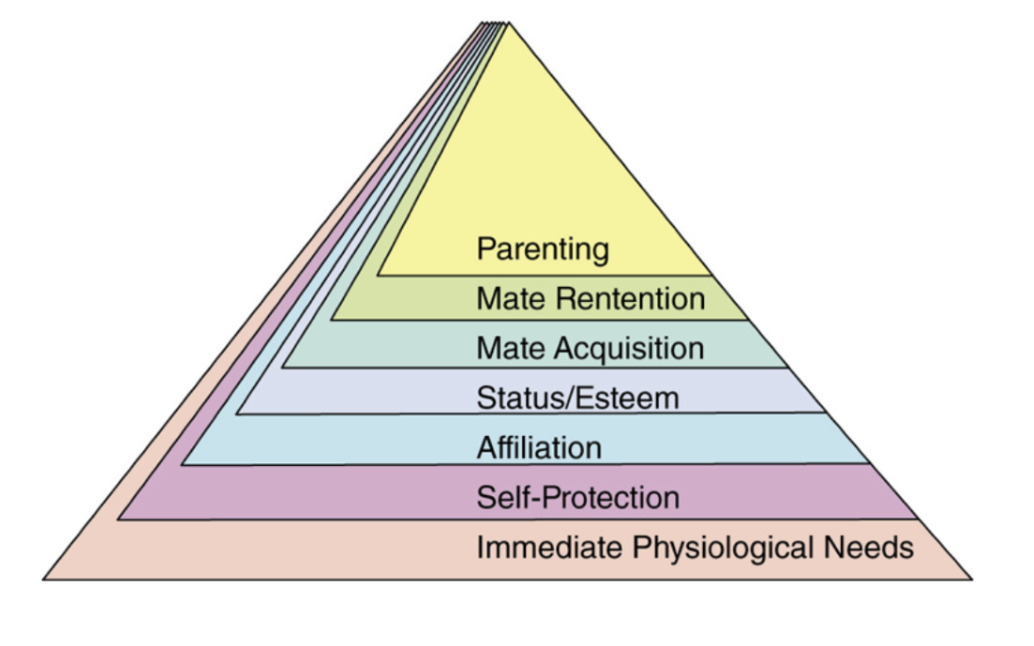
86
New cards
self-determination theory
proposed by Richard Ryan and Edward Deci, argues that human beings possess innate psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness
87
New cards
adaptation process of emotions
individuals with emotions had more offspring than individuals without emotions, and/or took better care of their genetic relatives in such a way that their relatives had more offspring
bc of this process of natural selection, the genes supporting emotions spread through later generations to become typical of the human species
bc of this process of natural selection, the genes supporting emotions spread through later generations to become typical of the human species
88
New cards
intrapersonal functions of emotions
directly benefits the individual experiencing the emotion
e.g. fear helps save the life of the frightened person, facilitating that person’s escape from a predator or some other physical threat
e.g. fear helps save the life of the frightened person, facilitating that person’s escape from a predator or some other physical threat
89
New cards
interpersonal function of emotion
support the committed, interdependent, and complex relationships among people that in turn, help us to survive and pass on our genes
e.g. love, humans feel strong emotions toward the people they depend on and who depend on them—families, romantic partners, children, and close friends
e.g. love, humans feel strong emotions toward the people they depend on and who depend on them—families, romantic partners, children, and close friends
90
New cards
affect infusion model
modern theory of emotion stating that emotional feelings influence our judgments and decisions in a variety of important ways
e.g. happy mood tells us that we are safe, things are going well, and we should be on the lookout for opportunities
e.g. distressed mood tells us something has gone wrong; we need to slow down, find the problem that is making us feel bad, and either avoid it or take steps to correct it
e.g. happy mood tells us that we are safe, things are going well, and we should be on the lookout for opportunities
e.g. distressed mood tells us something has gone wrong; we need to slow down, find the problem that is making us feel bad, and either avoid it or take steps to correct it
91
New cards
superordinate neural program
researchers define emotions as ____ activated in certain kinds of situations with serious implications for fitness
job of these is to activate any little programs (we’ll call them subroutines) that will help resolve the situation, and to inhibit any subroutines that would interfere with resolving the situation
job of these is to activate any little programs (we’ll call them subroutines) that will help resolve the situation, and to inhibit any subroutines that would interfere with resolving the situation
92
New cards
emotional response coherence
the extent to which self-reports of emotion predict physiological changes and simple behaviors like facial expressions
93
New cards
phylogeny of emotions
description of relationships among different emotion in terms of shared evolutionary history and branching from a common ancestor
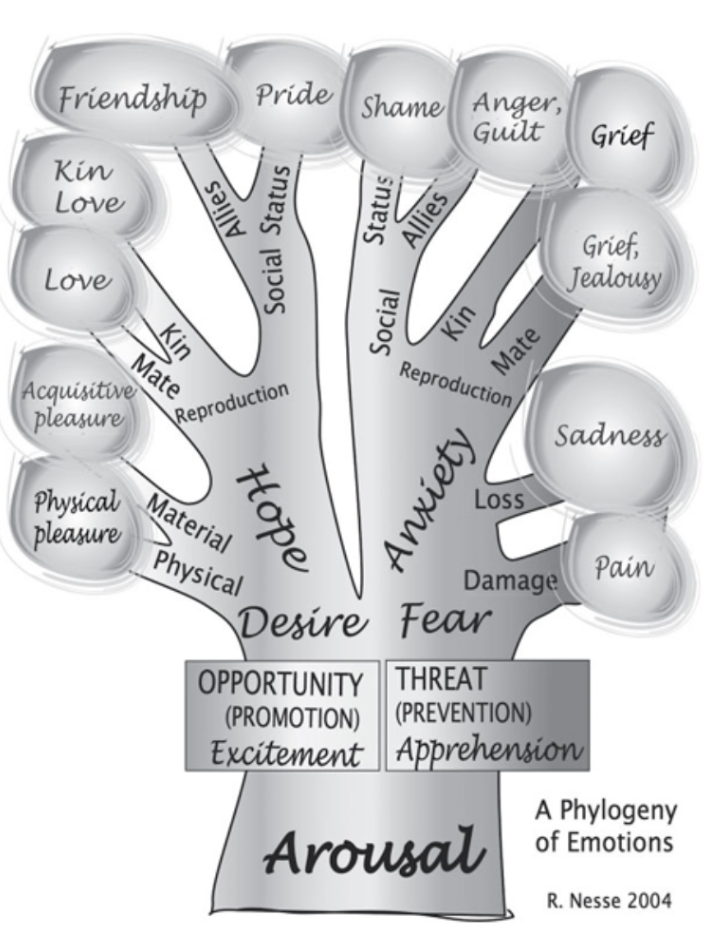
94
New cards
central nervous systems
the brain and the spinal cord
95
New cards
limbic system
a set of neural structures originally proposed by Paul MacLean (1952) as the emotion network of the brain
96
New cards
triune brain model
divided the brain into three regions
* a central “reptilian” area
* a “mammalian” area
* neocortex
* a central “reptilian” area
* a “mammalian” area
* neocortex
97
New cards
central “reptilian” area (TBM)
controlled sensory, survival, and reflex actions
98
New cards
a “mammalian” area (TBM)
also called the limbic system, surrounded the reptilian area and controlled emotion
99
New cards
neocortex (TBM)
surronding both reptile and mammalian areas, responsible for complex cognition and reasoning in humans and other primates
100
New cards
tools for investigating emotion and motivation at the level of the brain
* brain damage
* electroencephalography (EEG)
* functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
* neurochemistry techniques
* electroencephalography (EEG)
* functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
* neurochemistry techniques
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
Foundations of govt, British history, DOI, Articles of Confederation
Updated 881d ago