TEST STUDY GUIDE BIO TEST DNA AND RNA
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
What is the name of the sugar found in the nucleotides of DNA?
Deoxyribose
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Are cytosine and thymine purines?
False
What type of structure do purines have?
Two rings
What is the backbone of the DNA molecule made of?
Sugar and phosphate molecules
Frederick Griffith conducted experiments on which type of bacteria?
Pneumonia-causing bacteria
What did Griffith call the process where harmless bacteria were transformed into harmful bacteria?
transformation
What type of biological molecule did Oswald Avery determine was responsible for transformation?
DNA
What did Hershey and Chase use to determine that DNA was the genetic material?
Radioactive sulfur and phosphorus
What significant rule did Erwin Chargaff discovered regarding the bases in DNA?
A alway equals T and G always equals C
Who was primarily responsible for producing the first image of DNA’s structure?
Rosalind Franklin
DNA structure adenine and thymine are connected by how many hydrogen bonds?
Two
Which model of DNA did Watson and Crick introduce in 1953?
A double-stranded helix
Which of the following is true?
RNA is usually single-stranded
Which type of RNA brings the information in the genetic code from the nucleus to other parts of the cell?
mRNA
Which molecules are involved in protein synthesis?
messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA
During eukaryotic transcription, an RNA molecule is formed that is
Complementary to part of one strand of DNA
How many RNA nucleotides are needed to specify four amino acids?
12
During translation, the type of amino acid that is added to he growing polypeptide depends on the
codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on the tRNA
RNA polymerase ______ a ______ to initiate transcription.
does not, primer
Amino acids are linked by __________ during translation
Peptide bonds
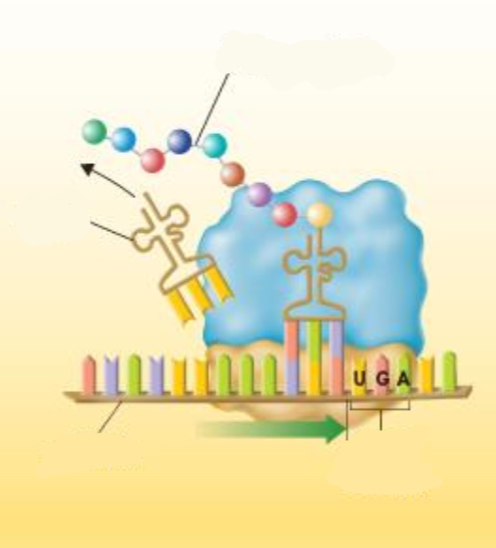
What signals the end of protein synthesis?
stop codon
Each _____ on mRNA corresponds to one ______.
codon, amino acid
What is the start codon for mRNA?
AUG/ methionine
When does mRNA translation occur?
the cytoplasm with ribosomes
What do you call the process described in these two chapters?
gene expression
The anticodon is a part of the _____ molecule.
mRNA
Hydrogen bond counts for nitrogenous bases:
2:AT/TA
3:GC/CG
Gene
The specific order of nitrogen bases located on a specific region of a chromosome (20,000 to 25,000)
The order of nitrogenous base pairs is a code for
A specific form of a gene
What does the gene do?
it instructs cells to synthesize certain proteins
What do proteins give organisms?
expressed physical traits
What happens before a cell divides
it duplicates its DNA in a process called replication
What does replication do?
It ensures that each cell that divides will have a complete set of DNA.
What do Watson and Crick’s models suggest?
DNA serves as a template during replication.
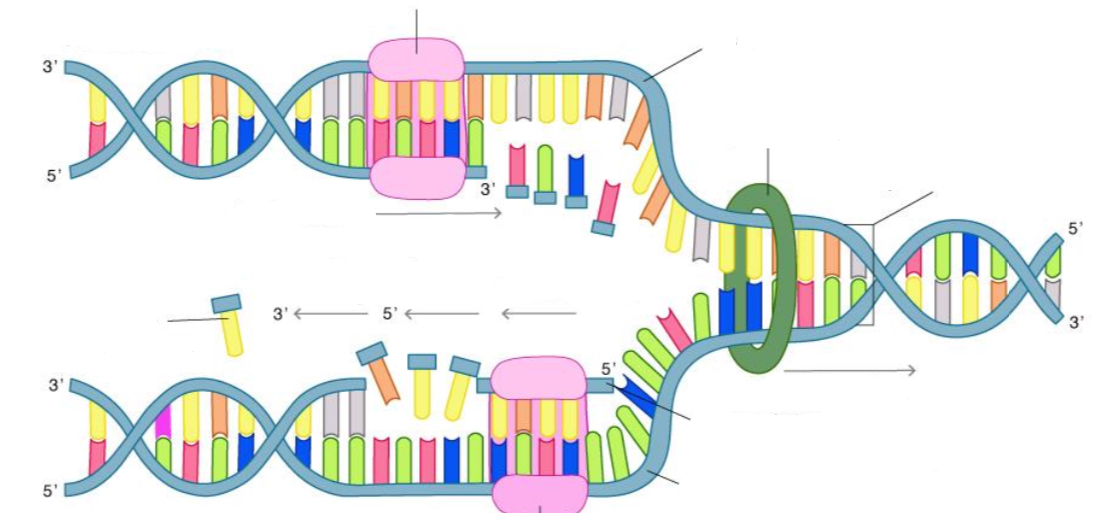
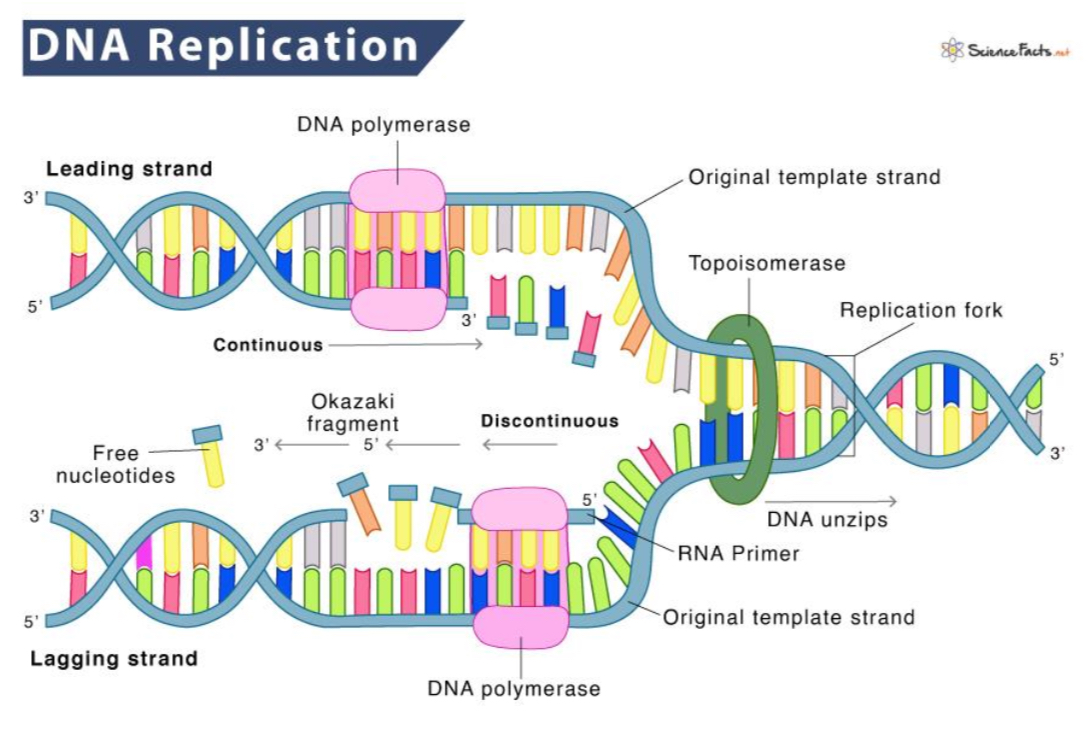
Describe DNA replication
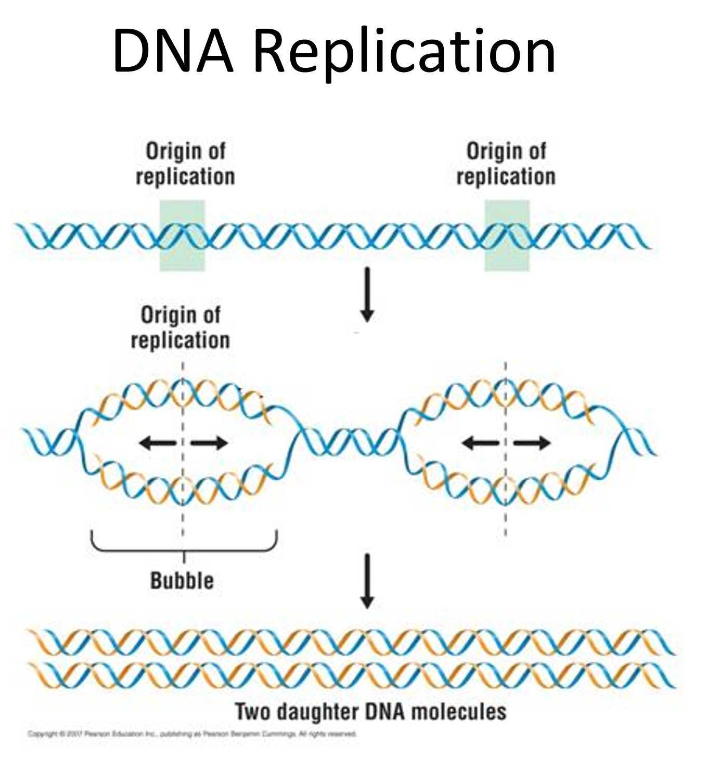
DNA synthesis always proceeds in a
5 to 3 direction vice versa
Where do you add nucleotides?
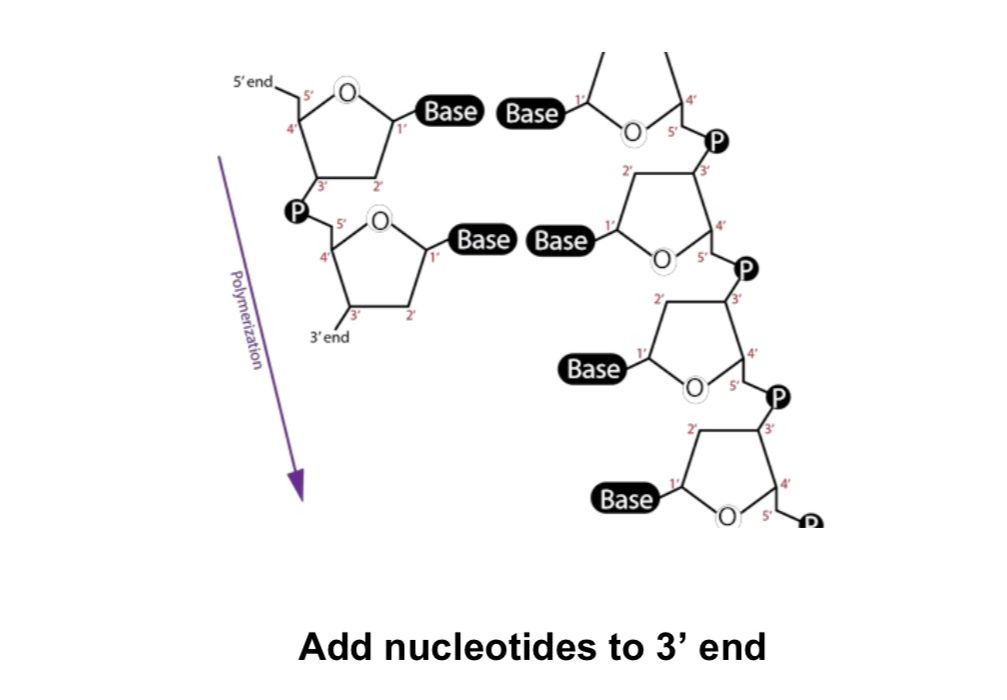
Helicase
enzyme that separates double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied
DNA polymerase
the enzyme that joins individual nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA.
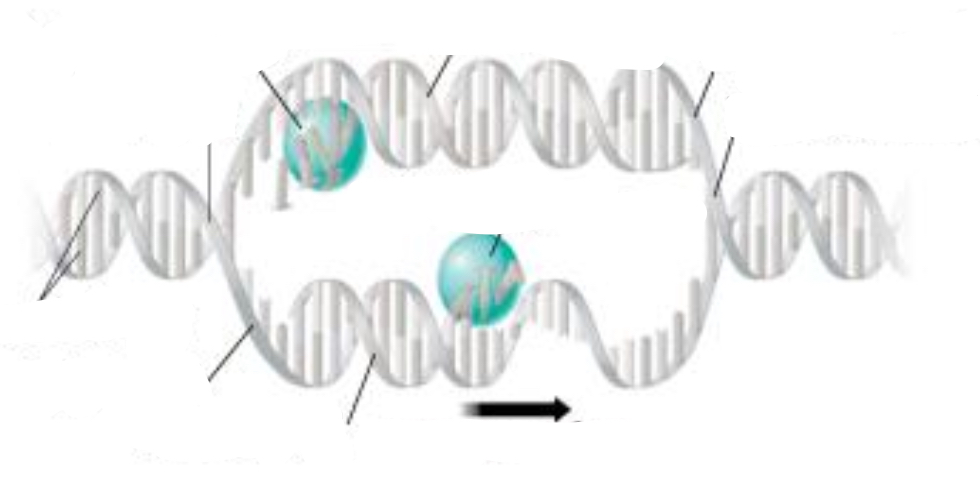
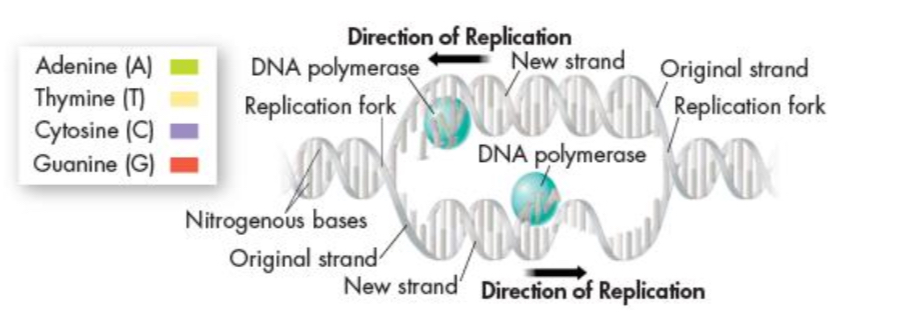
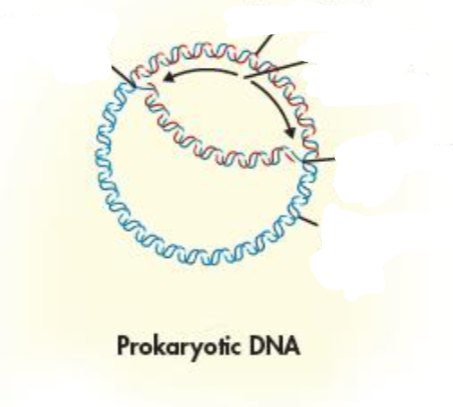
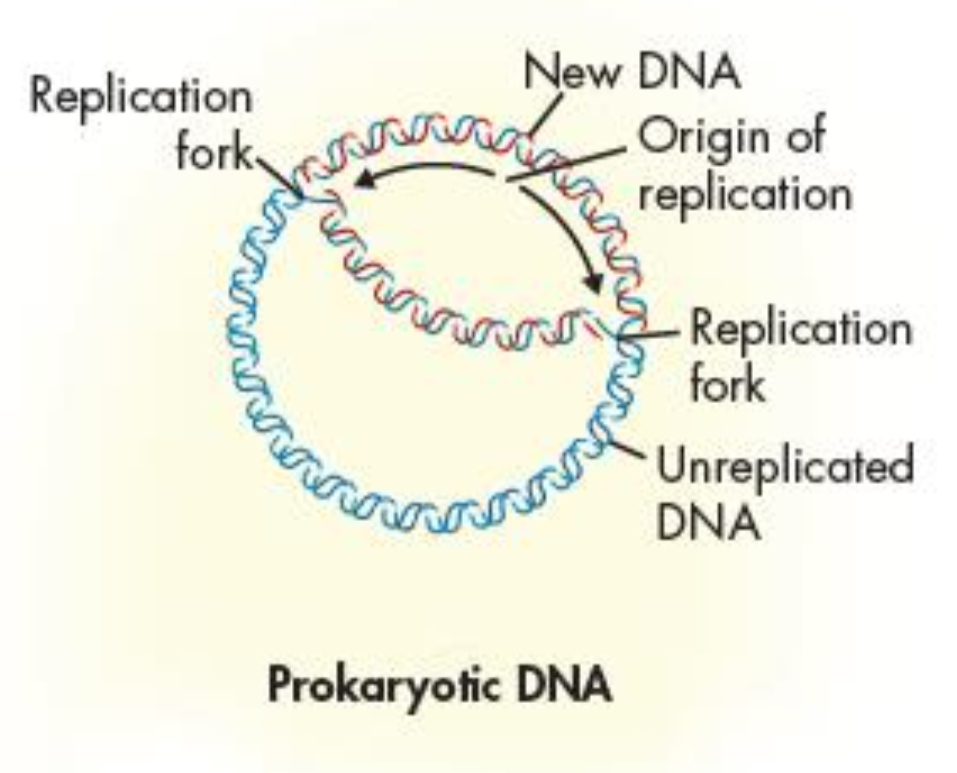
How is replication in Prokaryotic cells?
replication starts from a single point and then proceeds in two direction until the whole chromosome is copied
How many chromosomes do humans usually have
23 pairs 46 total
Mutation
heritable change in genetic information
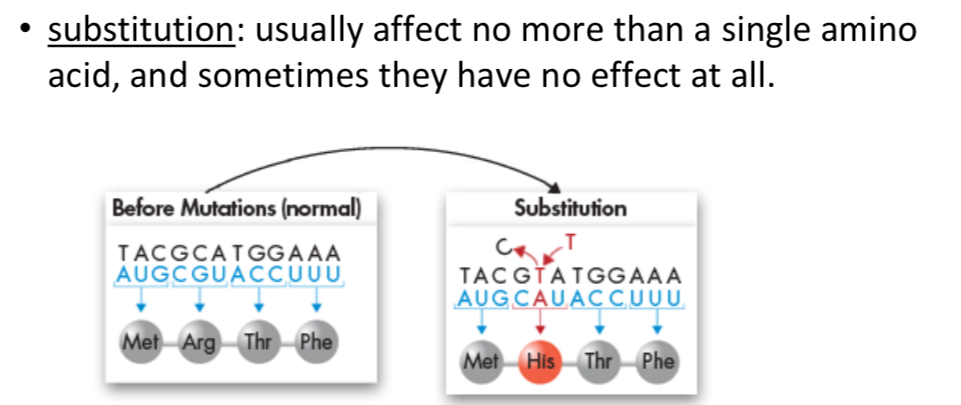
Gene mutation
changes in a single gene
Point mutation
occur at a single point in the DNA sequence, generally during replication
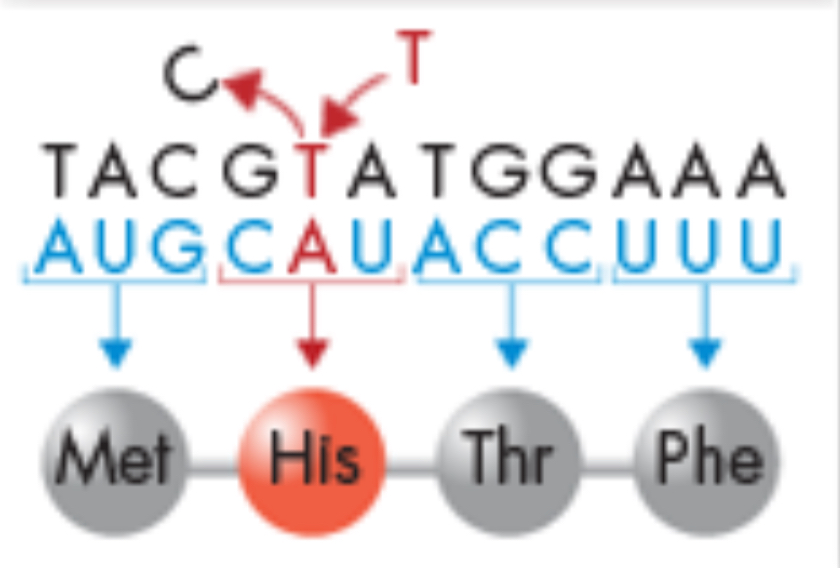
Guess and define
-Point mutation
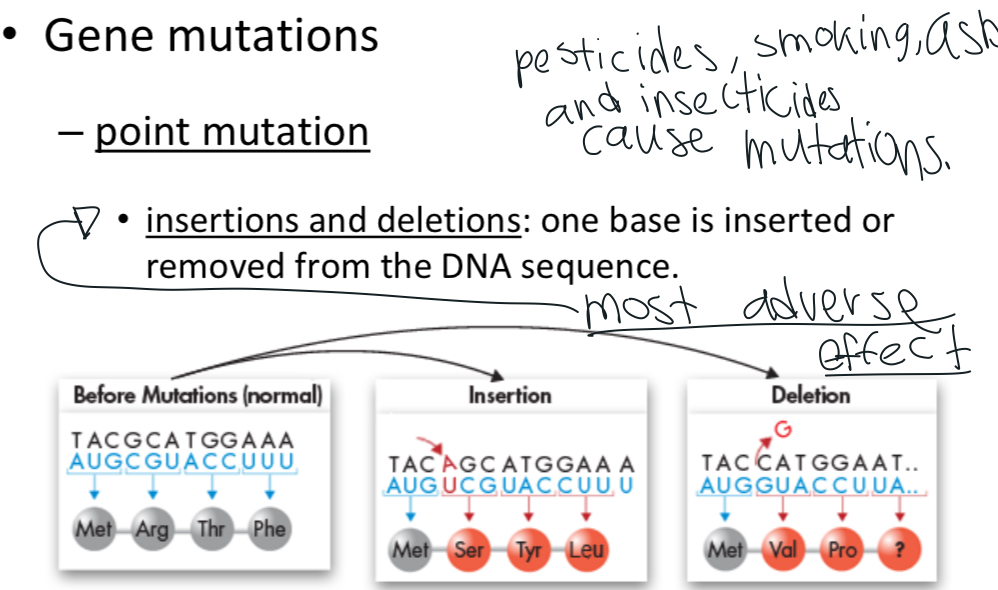
What genetic mutation has the most adverse effect?
Insertions and deletions
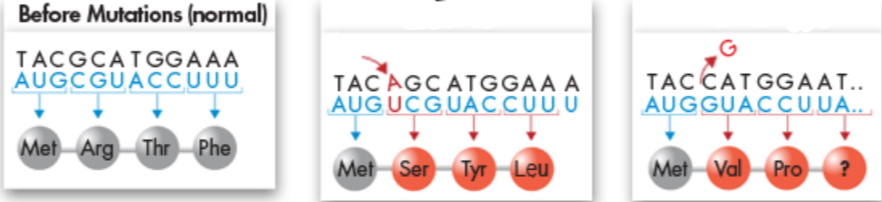
Guess and define
Chromosomal Mutation:
produce changes in the number or structure of chromosomes. Can change the location of genes on chromosomes and can even change the number of copies of some genes
Deletion
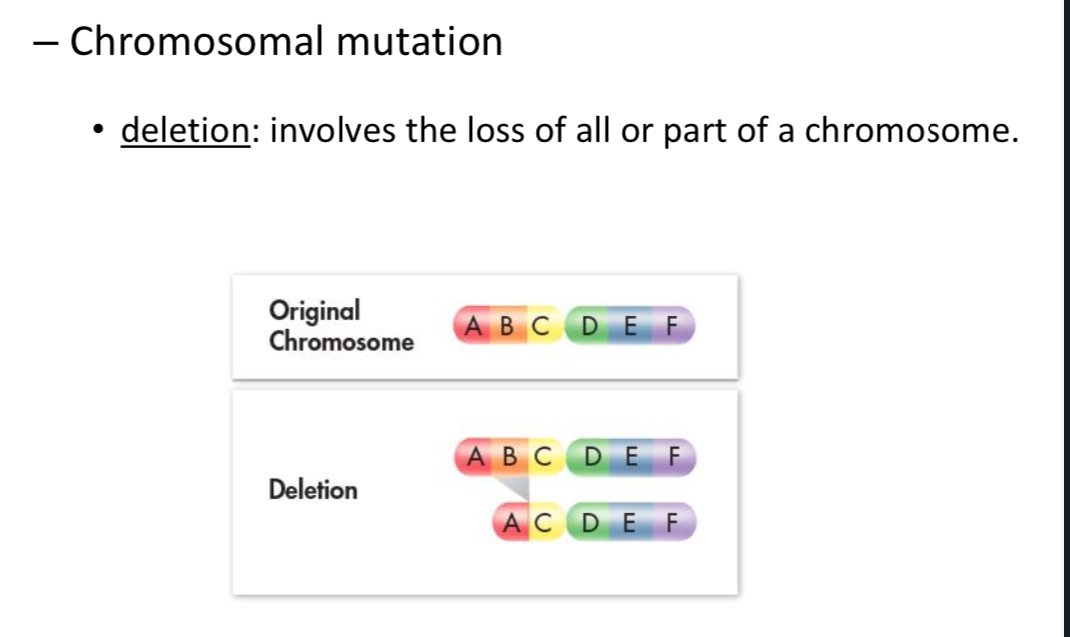
Duplication
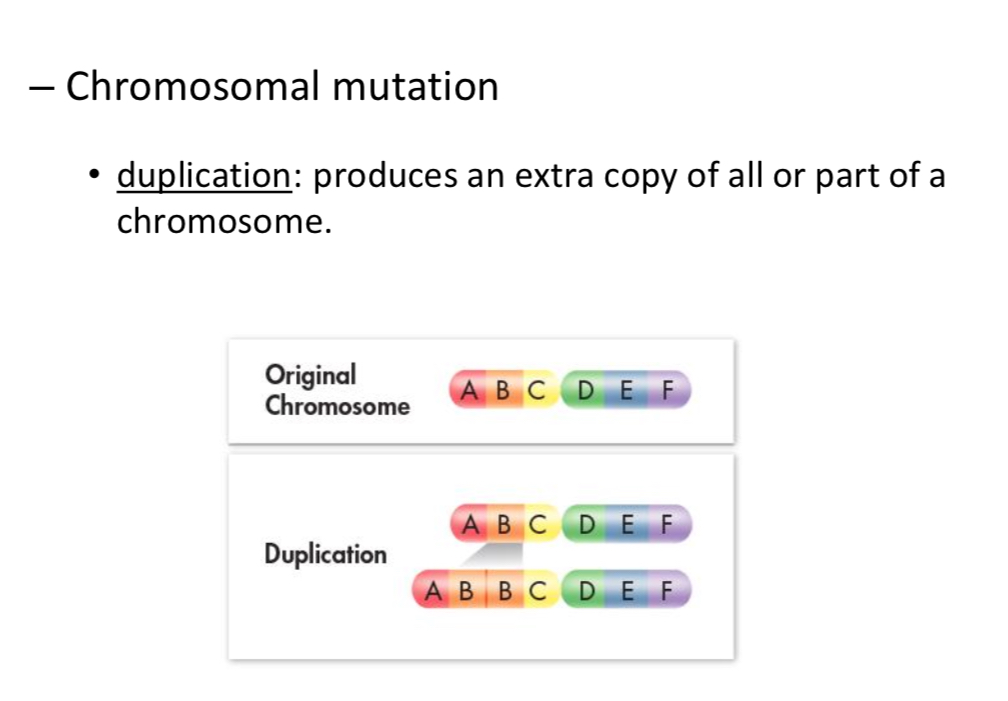
Inversion

Translocation
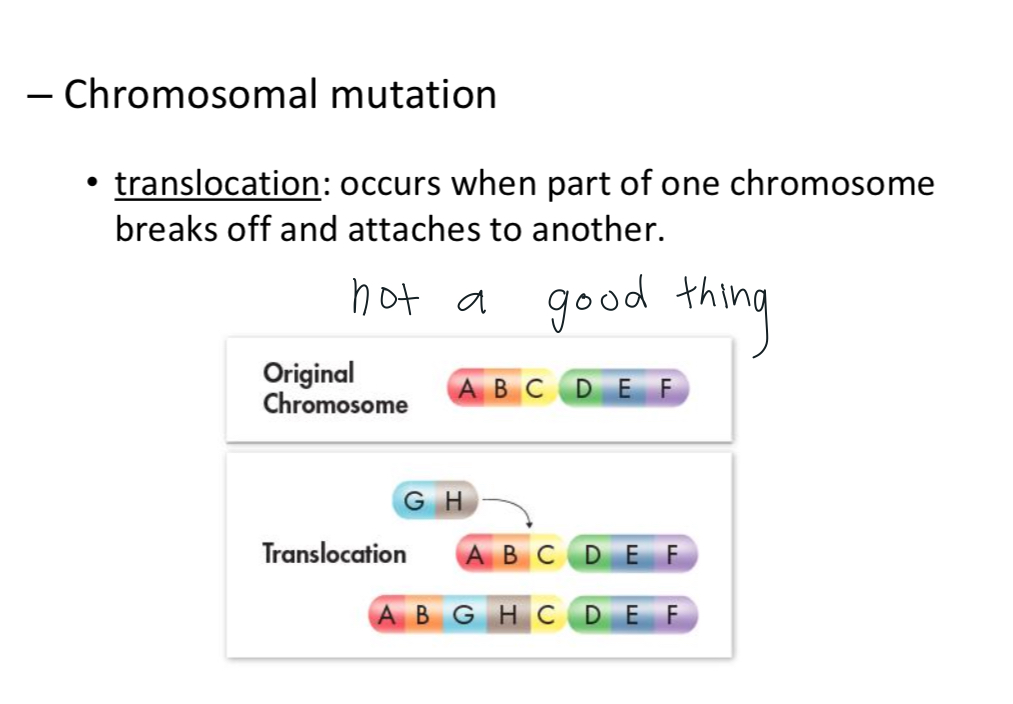
What are the two causes of mutation?
-errors in replication
-mutagens
Mutagens
chemical or physical agents in the environment
-pesticides, alkaloids, tobacco smoke, env. pollutants
-radiation like x-rays and UV light
What do cells do about mutation?
cells can sometimes repair the damage; but when they cannot, the DNA base sequence changes permanently
What are mutations the source of in a species?
genetic variability
What are three effects of mutations?
-no effect
-beneficial variations
-negative disruption of gene function
What is the most common disease from chromosome mutations?
Down syndrome
DNA contains the instructions to
make proteins
RNA controls
the assembly of amino acids into proteins
DNA to RNA process is known as
transcription
RNA to protein process is known as
translation
What is the central dogma
DNA→RNA→Protein
What is RNA
-a nucleic acid that consists of a long chain of nucleotides (Ribonucleic acid)
What are the three main differences between DNA and RNA
-the sugar in RNA is ribose
-RNA is single stranded
-nucleotides (monomers) (thymine v Uracil)
Which one is more liable?
RNA
mRNA
Carries copy of instructions for assembling amino acids into proteins
Transcription
Process where segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules (occurs in the nucleus)
RNA polymerase
-enzyme that separates the DNA strands and uses one strand of DNA as a template from which to assemble nucleotides into a complementary strand of RNA
-transcription
Promoter
sequence of DNA that shows RNA polymerase where to begin making RNA
Terminator
sequence of DNA that cause transcription to stop
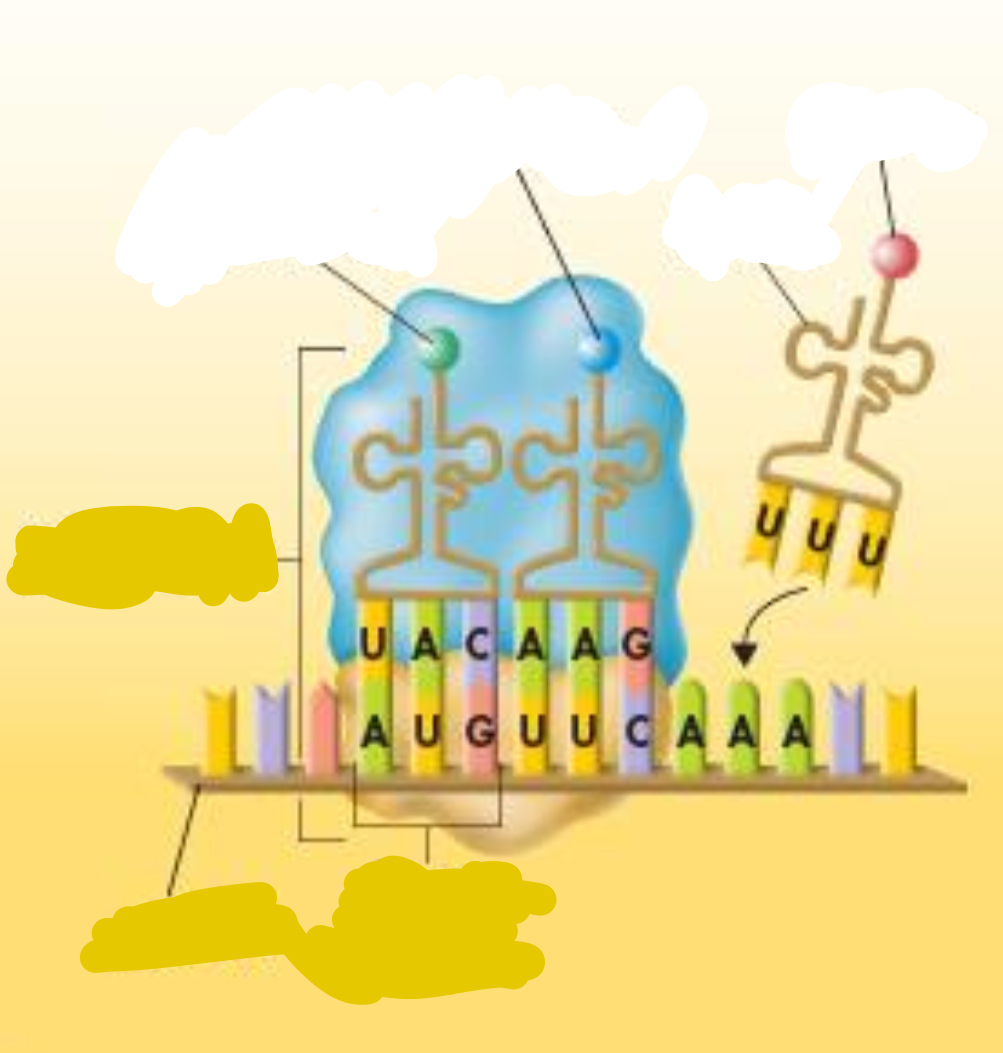
Picture describing transcription for description (try to recite)
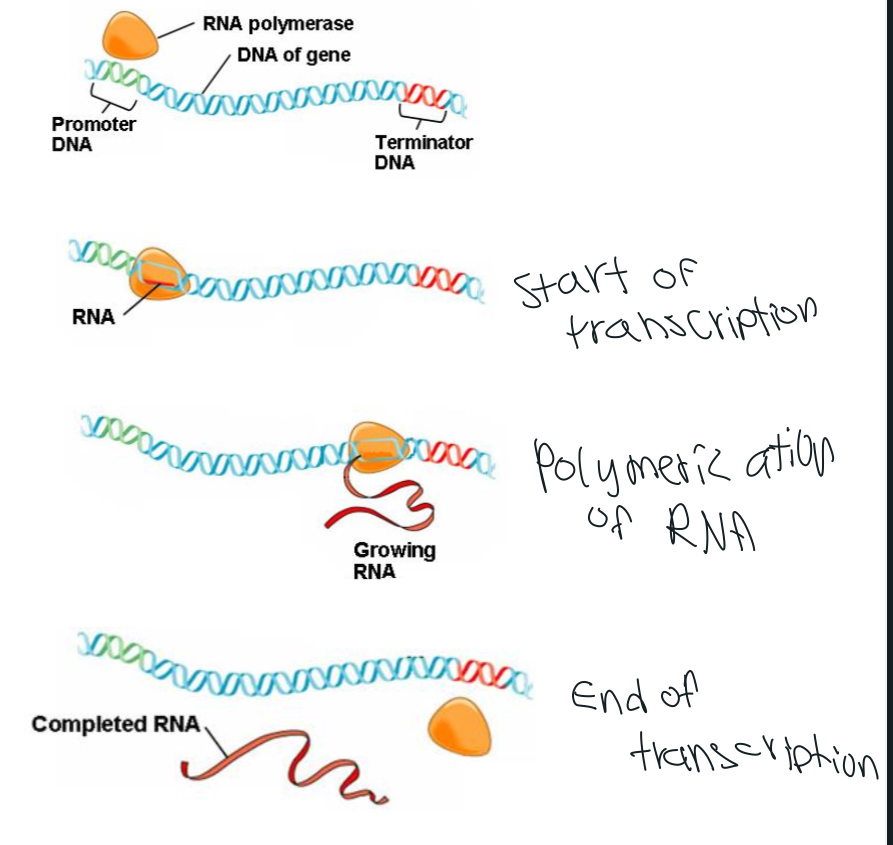
RNA Editing
includes introns and exons that transform Pre-mRNA into mRNA
Introns
portions that are cut out and discarded of pre-mRNA
Exons
Remaining pieces of RNA that are spliced back together to form the final mRNA
(Think of the gas station Exxon keeping only the best gas)
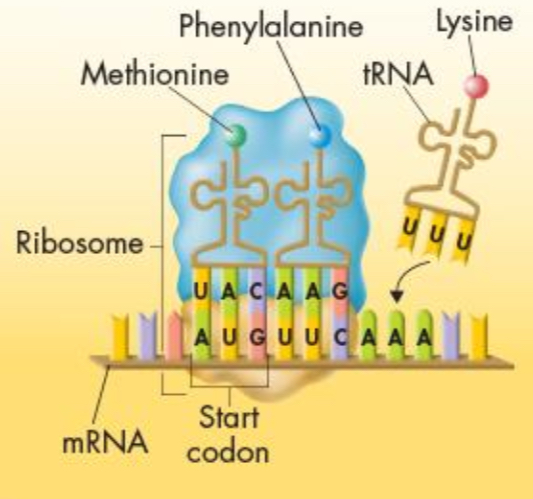
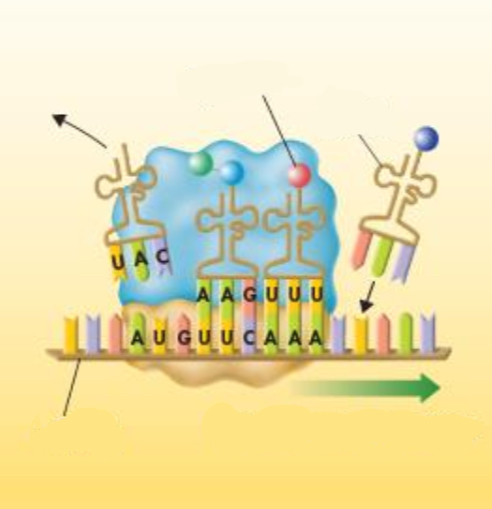
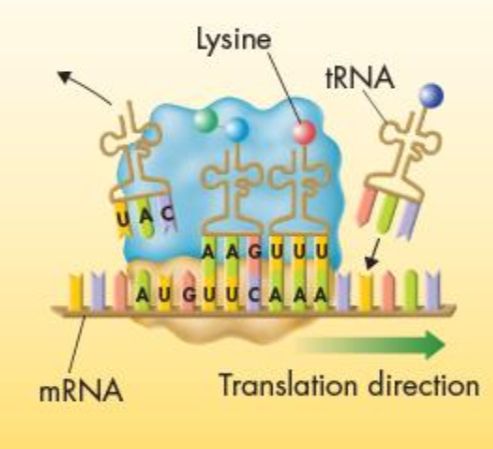
Translation
-The process of decoding of an mRNA message into a protein
-occurs in the cytoplasm (specifically ribosomes)
How are proteins made?
proteins are made by joining amino acid monomers together into long chains called polypeptides
How many amino acids does it take to create a protein?
20 minimum
What does the amino acid sequence mean?
the sequence influences the shape and function of the protein
Codon
consists of three consecutive RNA bases that specify a single amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain
Ribosomal RNA forms
subunits of ribosomes

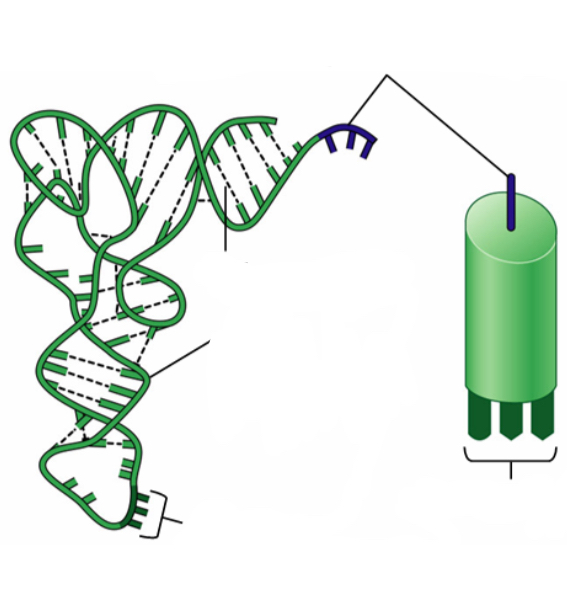
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
transfers each amino acid to the ribosome as it is specified by the coded messages in mRNA
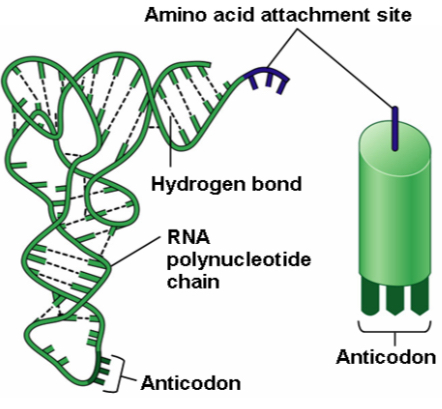
Peptide bond

Make this DNA strand a matching RNA strand: TAG CAT TTT ACA
AUC GUA AAA UGU
What is ribosomal RNA’s function
reading mRNA strands to be translated into a polypeptide chain
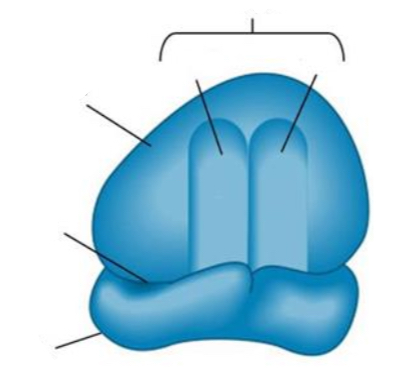
Large Subunit (LSU)
Catalyzes peptide bond formation
Small Subunit (SSU)
Binds to mRNA and endures correct codon-anticodon pairing
tRNA Binding Sites
The location where tRNA goes in the ribosomal RNA to lay down its anti codon (connects to codon) and amino acid
What turns another bacteria from non disease causing to disease causing
-another bacteria transferring chemical factor/ DNA
-process called transformation
-permanent
Experiment 1 vs 2
-1 used enzymes to destroy proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and RNA from heat killed bacteria (transformation)
-2 used enzymes to destroy DNA (no transformation)
What does DNA do?
Store, transmit, and copy genetic information (genes) in a cell.
Virus
nonliving particles that can infect living cells