Body Composition and Weight Management
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
State of the Nation
Obesity trends up
first time, life expectancy down
73.6% Americans overweight or obese
Thermodynamics
Cal. density:
fat 9 cal per g
protein/carbs 4 cal per g
alcohol 7 cal per g
RMR: 55-75% (all vital functions)
Exercise: 10-40%
Feeding: 5-15% (digestion)
Body Fat
Stored in adipose cells
men: 3% essential, 12% non
women: 12% essential, 12% non
Nonessential:
subcutaneous “below-skin”
Visceral “around viscera”
Fat. dist. types:
Gynoid: pear-shape, subcutaneous fat (hips and thighs), low risk chronic disease
Android: apple-shape, abdomen and visceral fat, higher disease risk
Normal Weight Obesity: low muscle mass high fat mass, but within BMI recommendations (doesn’t appear overweight)
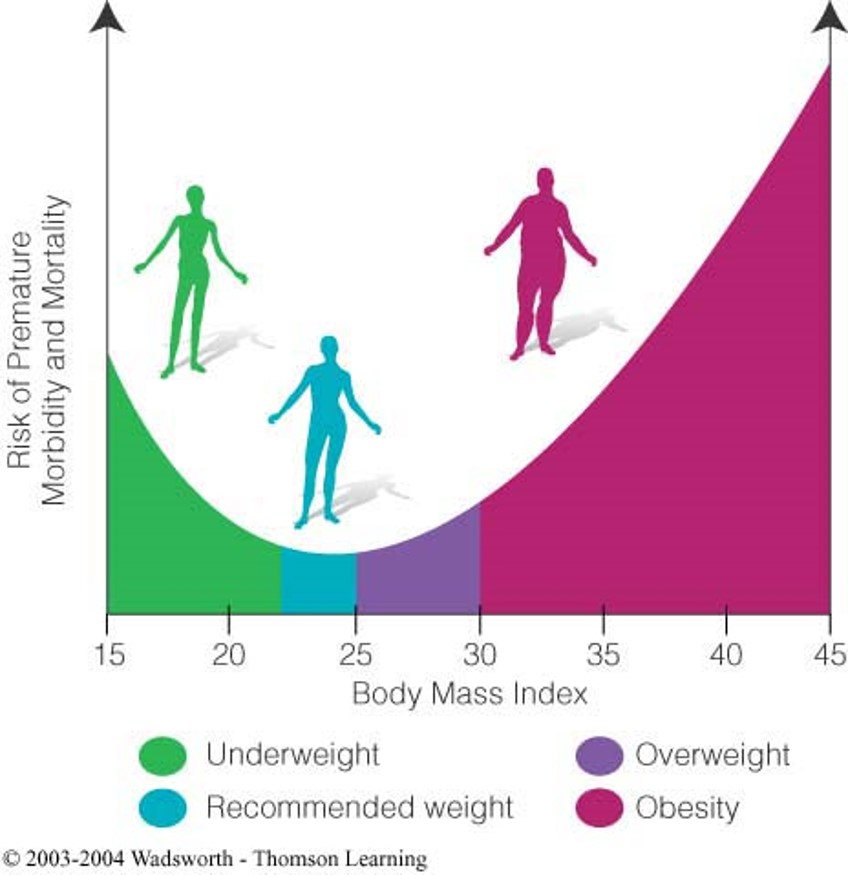
Weight vs Health
Body Mass Index: BMI
<18 under
18.5-25 healthy
25-30 over
>30 obese
Average trends, more risk for causes of low or high weight than the weight itself
IE: smoking or drug use, or fat consumption and sedentary
Blood Regulation
homeostasis between insulin and glucagon ~100mg/dL
insulin lowers Blood Glucose (into cells)
Glucagon raises blood Glucose (from liver)
Diabetes: disorder of B. Glucose levels
Type 1: insulin dependent, low insulin production
Type 2: insulin independent, low insulin sensitivity
Diabetes symptoms: thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, hunger, weakness, blurry vision, weight loss, numbness in extremities, infections or skin sores
Diabetes decreases adiponectin (hormone coenzyme for insulin reception) (adiponectin is released by adipose cells)
Body Composition Assessments
Height Weight Tables
BMI: weight (kg) / hieght² (m²)
not accurate for women, children, or very muscley
Abdominal Circumference: estimates visceral fat
<40” men, <35” women
Bioelectrical impedance:
highly dependent on hydration
Skinfolds
men: chest, abdomen, thigh
women: tricep, hip, thigh
Underwater weighing
Bod Pod
Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
Set Point Theory: there is an ideal body weight that a body tends to with healthy lifestyle, body will resist change from this value
Diets Do Not Work!
Promoting Health
diet, activity, sleep, relationships, function in school/work, emotionally healthy
Obesity Treatment: Focus on health over weight
Body types are different:
mesomorph: muscly
ectomorph: tall and thin
endomorph: round and heavy
Ideal body weight is one attained through healthy lifestyle
Factors of Obesity and Health
Genetic Predisposition: does not determine fully
Satiety Cues: Appetite vs Hunger, clean-your-plate mentality, don’t trust portion sizes, trust your stomach
Convenience: most likely to eat food when it is convenient
Meal size/frequency: more smaller meals prevents binge eating
Physical Activity: sedentary is bad, “latch-key” syndrome
Childhood Influences: breast-fed, childhood weight, Hyperplasia (low/high cal leads to excess fat storage)
Sugar-Sweetened Beverages: sweet tooth and low satiety
Weight Management Guidelines
Focus on healthful behaviors not numbers
loss of 5-10% of bodyweight for clinical improvements
No more than .5-2lbs loss per week
1lb fat=3500 cals
minimum 1200cal/day women, 1500 cal/day men
Diet and activity together
Strategies for promoting Healthful Habits and Weight Management
Appetite vs Hunger: Hunger is physical, listen to that
Manage Hunger: low Blood Glucose and empty stomach cause it
Eat low calorie density foods, focus on fiber fruits, vegs., water
replace less healthful food with vegs. or fruit
Eat regular, balanced meals: energy released over time
increase variety of fruits and vegs
make healthful choices convenient, and less healthful choices inconvenient
shoot for unsweetened beverages
make vegs half of your plate vegs/fruit, shoot for healthier options for other food
look for in-balance icon at Dining Hall
Eating Disorders
Anorexia Nervosa: self starvation, overexercise, compulsive cal counting: Osteoporosis, iron-def. anemia, fatigue, fainting, heart/brain/muscle atrophy
Electrolyte imbalance
arrythmia (irregular heartbeat)
cardiac arrest
kidney failure
cold intolerance
fine-hair growth (Lanugo)
Amenorrhea: lack of menstration
primary: late start
secondary: infrequent or nonexistent
Bulimia Nervosa: Binge and Purge: healthy/overweight, erosion of teeth and esophagus, sores on hands from vomiting, Electrolyte imbalance
Binge Eating Disorder: Binge only