Joints and Their Classification
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A series of flashcards covering key concepts about joints, their classifications, structures, and related diseases.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a joint?
A joint is a connection in the skeleton between any of its rigid component parts, whether bones or cartilages.
What are the three structural classifications of joints?
Fibrous joints, Cartilaginous joints, Synovial joints.
What are three classification based on degree of mobility of joint?
Immovable (synarthrodial) joint - fibrous joints
Partially movable (amphiarthrodial) joint - cartilaginous joints
Freely movable (diarthrodial) joint - synovial joints
Define Immovable (synarthrodial) joint exp: fibrous joints.
Joints between two bones of intra-membranous.
What are the three (four) types of fibrous joints?
Sutures, Syndesmosis, Gomphosis. (Synotoses)
What is a suture?
immovable (synarthrodial) joint (fibrous joints) 1. Sutures
A type of fibrous joint found between the bones of the skull,
providing a minimal degree of movement during childbirth. (Foetal skull)
After birth, rigid and no movement
Define Syndesmosis.
immovable (synarthrodial) joint (fibrous joints) 2. Syndesmosis
A type of fibrous joints in which the bony components are further apart and united by a fibrous interosseus membrane.
Example: Joint between radius and ulna/Joint between tibia and fibula
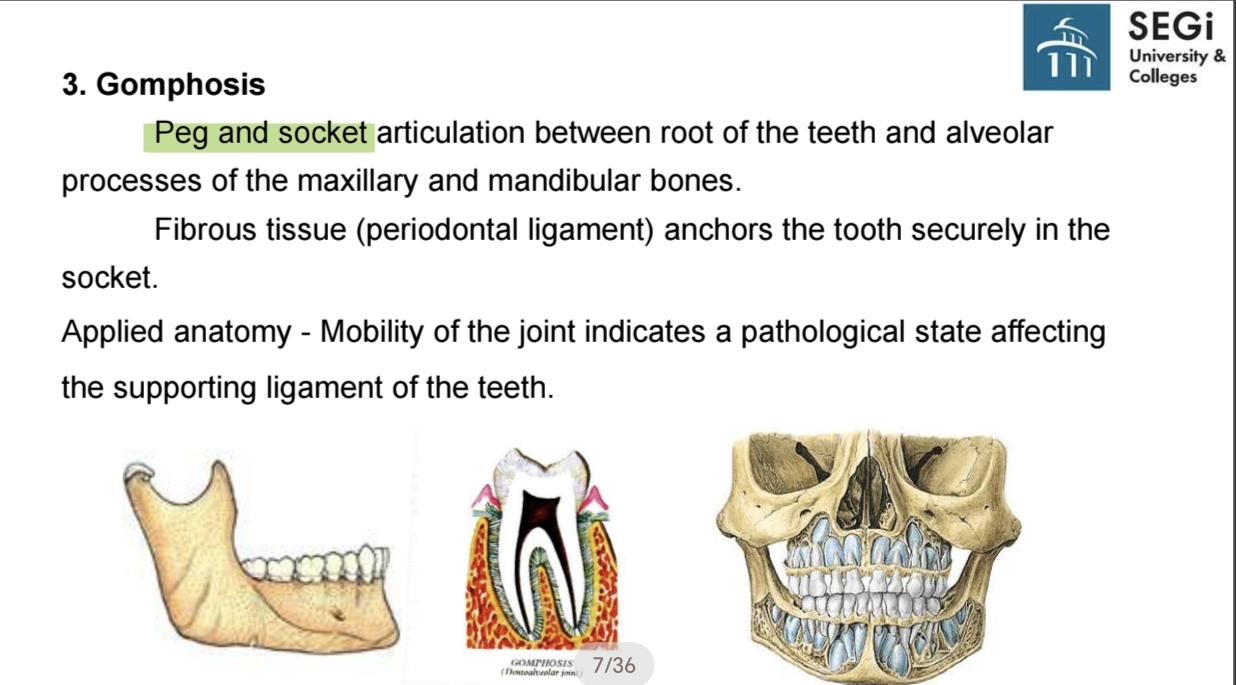
Describe a gomphosis joint.
Immovable (synarthrodial) joints (fibrous joint) 3. Gomphosis
A peg and socket articulation between the root of the teeth and the alveolar processes of the jaw.
Define and identify the two types of cartilaginous joints?
Partially movable (amphiarthrodial) joint (cartilaginous).
Cartilaginous: bones are united by hyaline or fibrocartilage.
Primary cartilaginous joints (synchondrosis) and Secondary cartilaginous joints (symphysis).
What is the distinguishing feature of primary cartilaginous joints (synchondrosis).
Partially movable (amphiarthrodial) joint (cartilaginous) 1. Primary cartilaginous joint (synchondrosis)
They are temporary unions develop between the bones of endochondral origin, replaced by bone when growth ceases.
Example: between epiphysis and diaphysis of long bone/ between ribs and costal cartilage
What characterizes secondary cartilaginous joints?
Partially movable (amphiarthrodial) joints (cartilaginous) 2. Secondary cartilaginous joint (symphysis)
Permanent joint where opposing surface are covered with cartilage but separated by fibrocartilage.
Example: (midline of body): symphysis pubis, between vertebral bodies, manubrio-sternal joint (strenum).
What are the characteristics of synovial joints?
Freely movable joints (diarthrodial) , features:
1. articular surfaces,
joint cavity,
capsular ligament,
synovial membrane,
and sometimes discs.
Examples: almost all joints of upper and lower limbs
In synovial joints, the articular surface’s features (3)
Coated by hyaline cartilage
Avascular, no nerves and alymphatic
Nourished by adjacent bone and synovial fluid within synovial joint
What is the joint cavity of synovial joint?
A space exist between the articular surfaces of the opposing bones, containing the synovial fluid
Define capsular ligament.
Ligaments of joint that cover the synovial joint like a fibrous sleeve and attach to the circumference of both bones to completely enclosed the joint cavity.
What is the role of the synovial membrane in a synovial joint?
It lines the inner aspect of capsular ligament and bone within the joint cavity (but not the articular cartilage).
It secretes a lubricating fluid (synovial fluid) into the joint cavity.
Identify the three classifications of synovial joints based on the number of articulating surfaces.
Simple- one pair of a.s. (fingers joints)
Compound- more than one pair of a.s. (elbow joints)
and Complex- joints cavity that is partially or completely divided by disc/meniscus. (Temporo-,amdibular j/ knee joint)
Identify the seven classifications of synovial joints based on the shape of the articulating surfaces.
Plane, Hinge, Pivot, Ellipsoidal, Saddle, Ball and Socket joints, Condyloid joint.
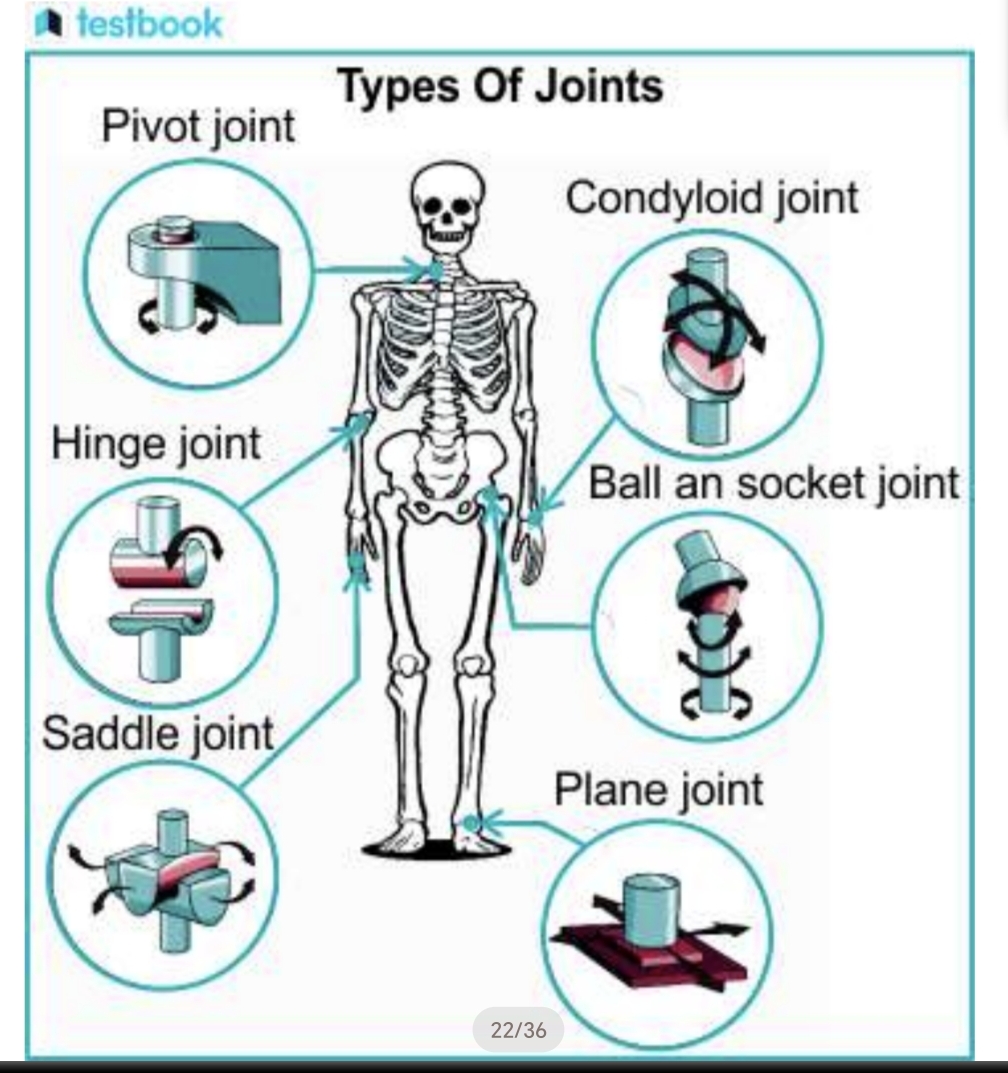
What type of synovial joint is characterized by rotational movement around a vertical axis?
Pivot joint.
Stability of joints (3-5 features)
Shape of a.s.
Muscles (more stable if surround with muscles)
Ligament (more stable if ligament presents)
Degree of movement (increased of degree cause lose contact easily)
Posture (at some posture cause unstable of joint)
What is the significance of Hilton's Law in joint anatomy?
It states that the same trunk of nerve supplying the muscles moving a joint also supplies the overlying skin and the interior of the joint itself.
List some common joint diseases.
Osteoarthritis, gout, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis.
What is osteoarthritis?
A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of joint tissues over time.
Most common type of arthritis (common in elders)
Most common sites: knees, hips, spine, hands.
What does a dislocation involve?
A dislocation is the separation of two bones where they meet at a joint.
Most common site: shoulder
What connective tissue anchors a tooth in the gomphosis joint?
Periodontal ligament.
How does mobility relate to the stability of synovial joints?
Stability is generally inversely related to mobility; increased mobility may lead to decreased stability.