BIOL 2050 - Transcription, RNA Postprocessing, Translation, and Gene Regulation
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
transcription
process in which a DNA message (a segment of DNA that codes for specific proteins) is converted into an RNA molecule
translation
the process in which a RNA molecule is used to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide
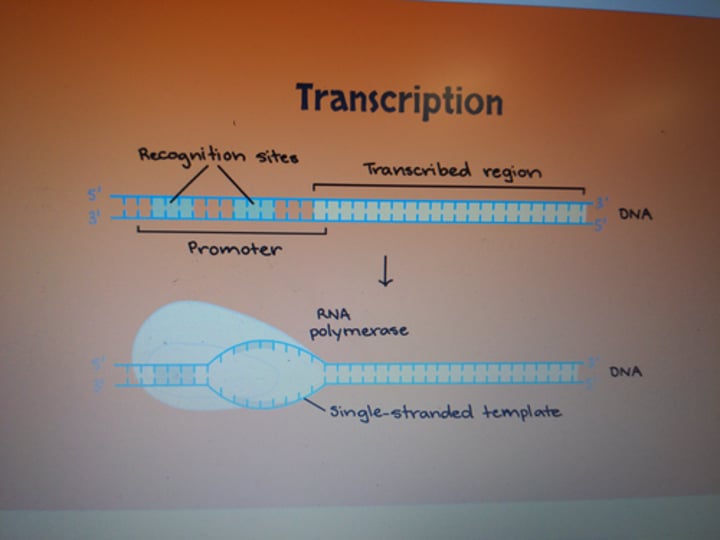
transcription initiation
the first step of transcription where RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region containing a recognition site. Separates the strands of DNA
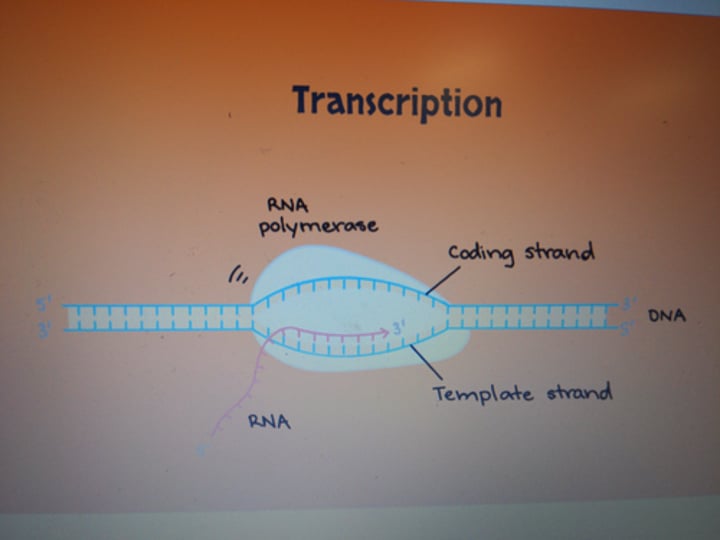
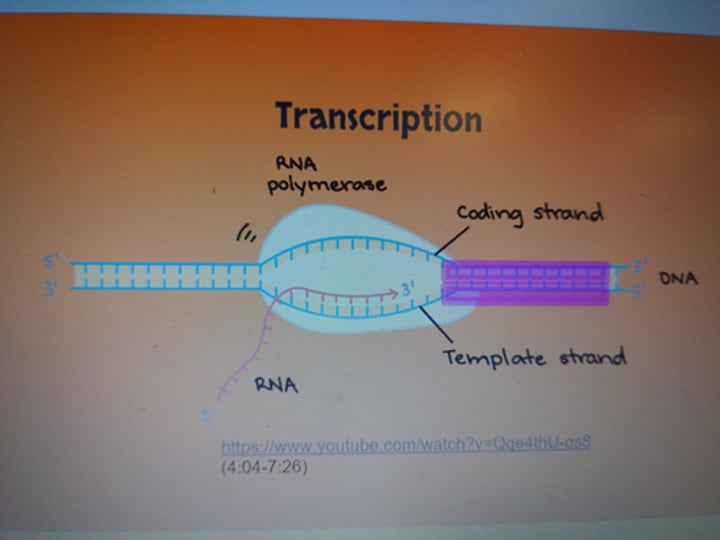
transcription elongation
second step of transcription where RNA polymerase moves along the template strand in 3' to 5' direction. RNA polymerase zips the DNA up as it moves forward. The mRNA is made in 5' to 3' direction
transcription termination
the third phase of transcription where RNA polymerase hits the terminator sequence and transcription stops
mRNA
type of RNA that carries genetic information from DNA into the nucleus to direct protein synthesis in the cytoplasm
intron
noncoding sequences that are transcribed from the DNA and are removed in post processing
exon
sections of the DNA that are transcribed and code for proteins
post processing
following transcription, introns are removed from mRNA and exons are spliced back together. A 5' cap is made of guanine and phosphate. A 3' poly-A tail is made of 50-250 adenines. These both facilitate the export of mRNA from the nucleus and protect it from degradation in the cytoplasm
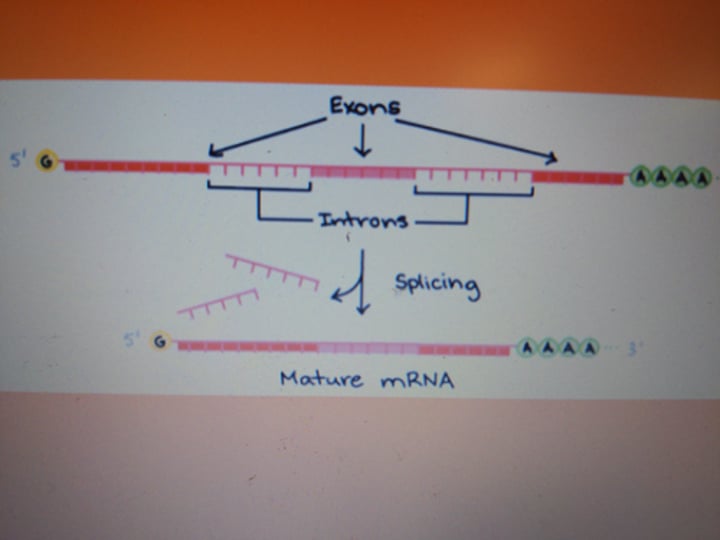
RNA splicing
the removal of introns in the mRNA by the spliceosome
codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid in translation. Multiple can code for the same amino acid.
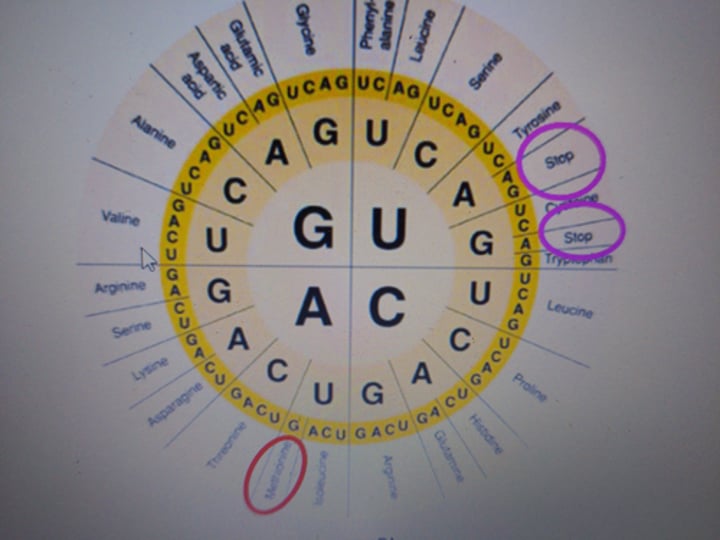
reading frame
on an mRNA, the start and stop codon defines which codons will be transcribed, specifying which amino acids will be created

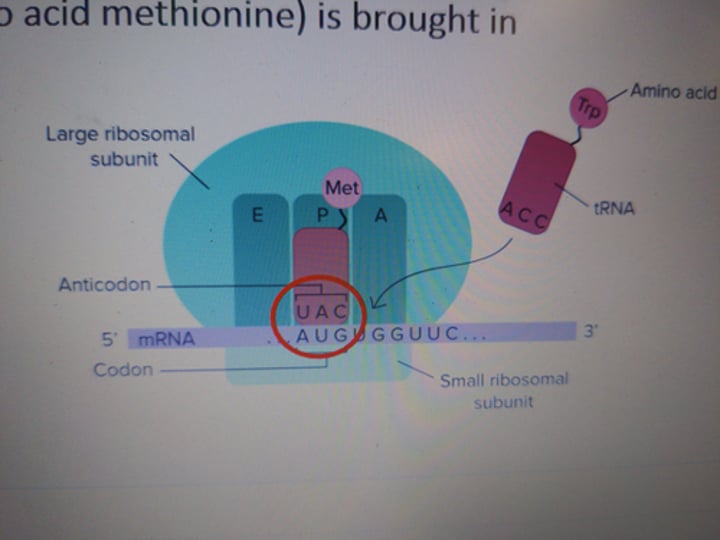
ribosome
cell organelles made of rRNA and proteins which slot where mRNA can be read and tRNA can deliver amino acids
tRNA
RNA molecules that use complimentary anticodons to match specific codons on the mRNA and deliver amino acids
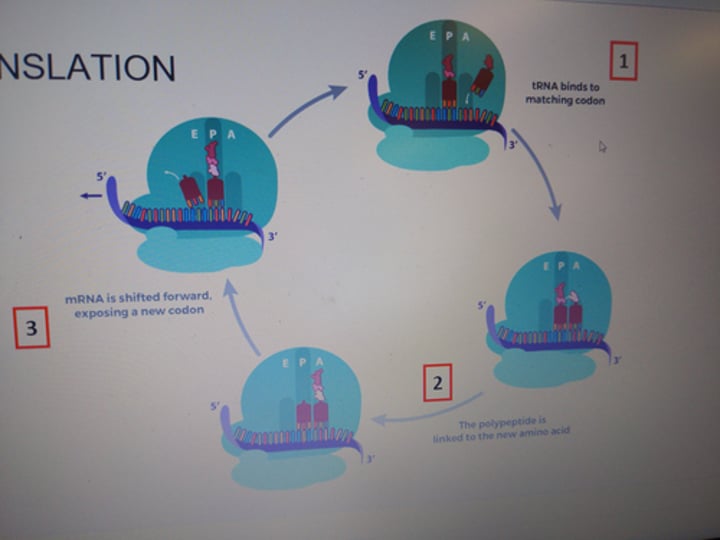
translation initiation
first step of translation where the ribosome assembles around the mRNA to be read. The first tRNA is brought in.
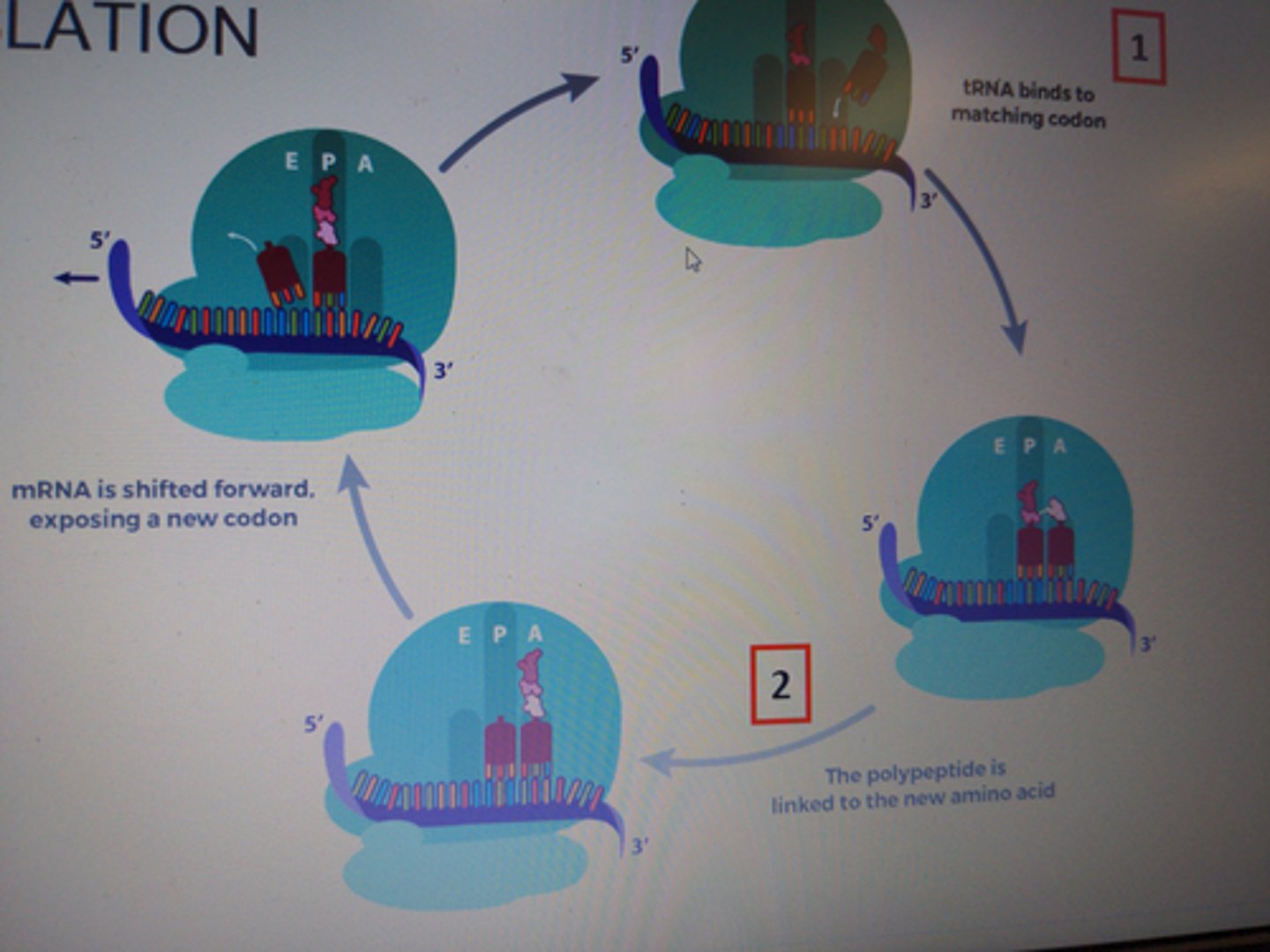
translation elongation
second step of translation where the mRNA is read one codon at a time, and the amino acid matching each codon is added to the growing protein chain
translation termination
third step of translation where a stop codon enters the reading frame and release factors bind to the stop codon at the A site, releasing the polypeptide chain
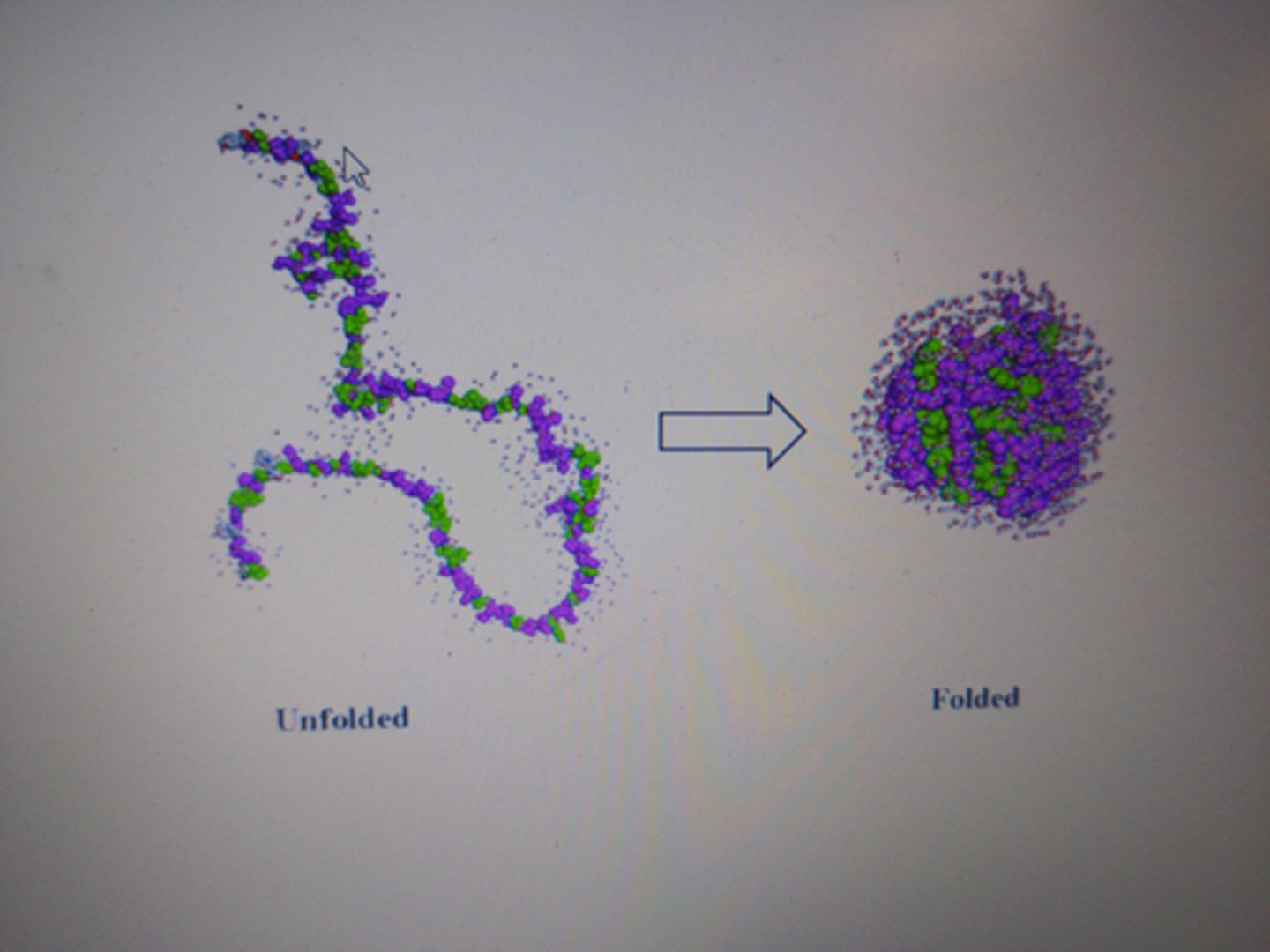
post-translational modifications
after translation, phosphates, carbohydrates, and lipids are added to the new polypeptide chain which is then folded
constitutive genes
genes that are always expressed, having essentially constant levels of expression
gene regulation
cells have the ability to control their level of gene expression. This ensures proteins are produced at the correct time and amount. This is necessary to respond to differences in the environment.
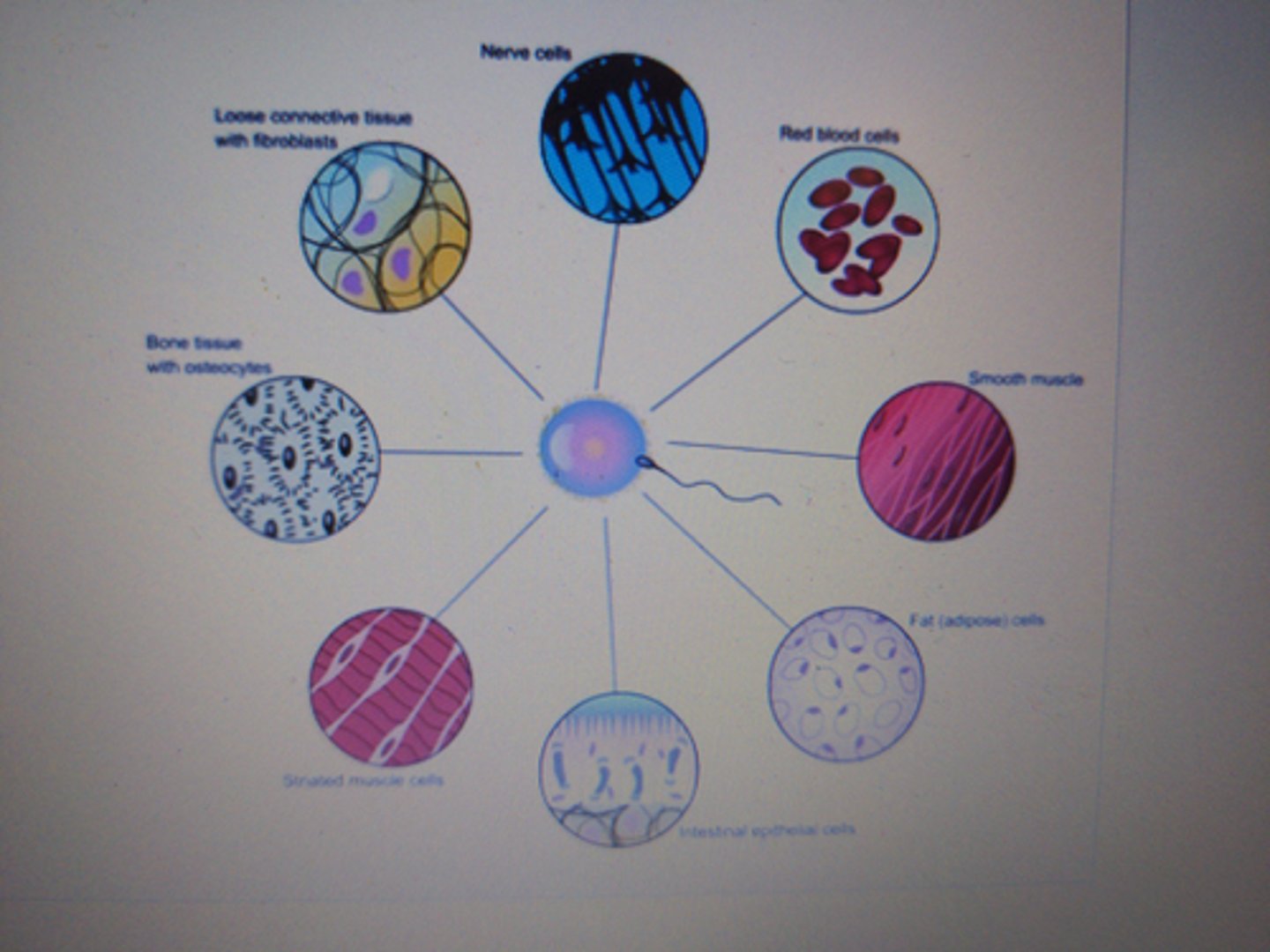
cell differentiation
for eukaryotes, different cell types with different proteomes are created from the same genome through gene regulation, allowing cells to perform specific tasks
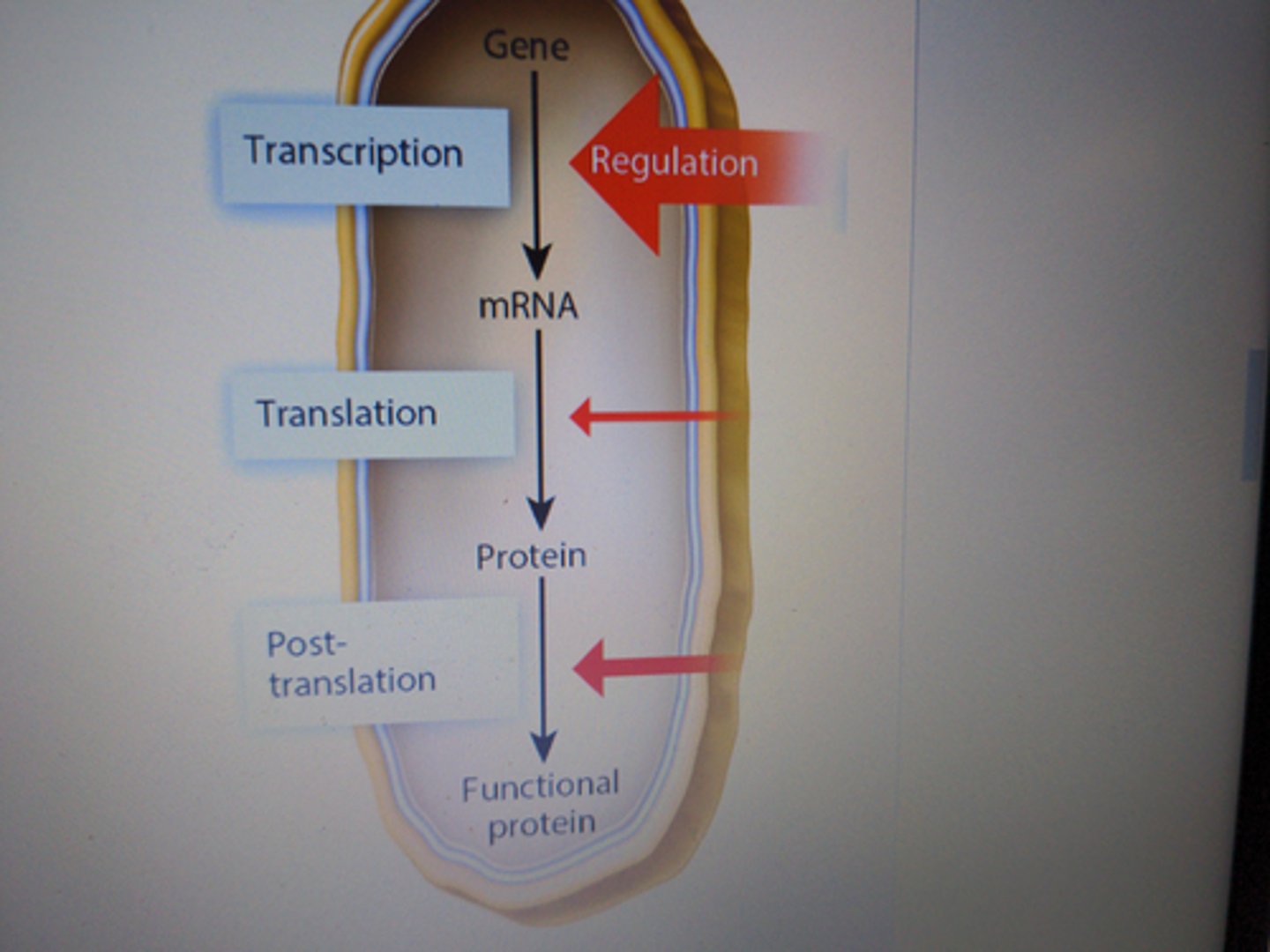
bacteria gene regulation
gene regulation that mostly occurs at the level of transcription and can be regulated at the protein or post-translational level
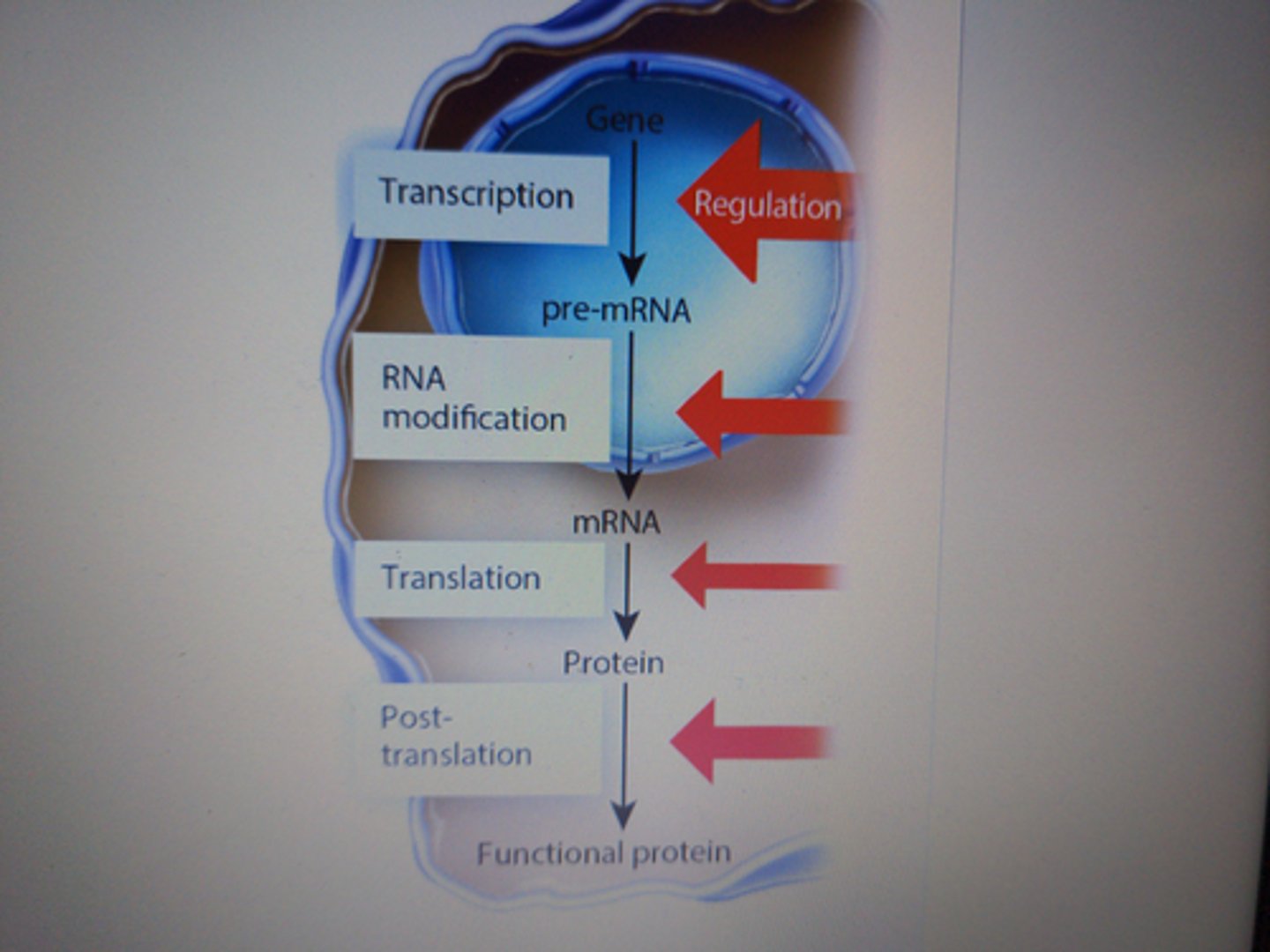
eukaryote gene regulation
gene regulation is most common at transcription, but, gene regulation is still common at other levels of protein synthesis
repressors
proteins that inhibit transcription (negative control)
activators
proteins that increase the rate of transcription (positive control)
small effector molecules
molecules that bind to activators and repressors to cause confrontational change. Similar to an on/off switch for transcription factors
operons
in bacteria, a cluster of genes under transcriptional control of one promoter
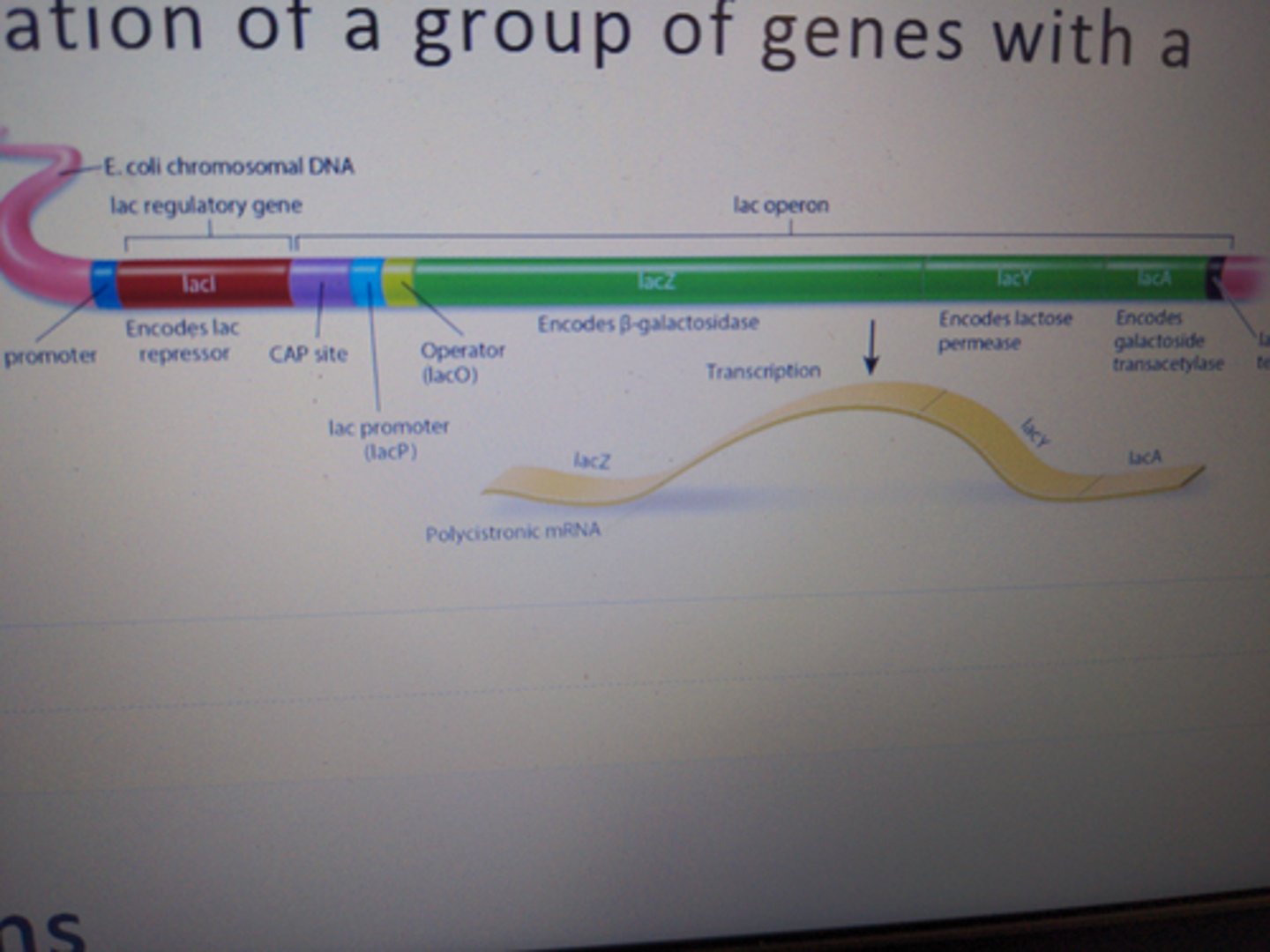
lac operon
a common operon that codes for transport and metabolism of lactose. Lac repressor binds to its operator in absence of a small effector molecule. Inducible, meaning genes are turned off until necessary
trp operon
a common operon that codes for the enzymes to produce tryptophan. Trp repressor binds to its operator in the presence of its small receptor molecule. Repressible, when enough tryptophan enzyme is present, genes are turned off to prevent overproduction