ch 8- environmental science
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Biodiversity
the variety of life across all levels of biological organization (genes through ecosystems)
species
a set of organisms that share unique characteristics and can breed and produce fertile offspring
Species diversity
describes the number or variety of species found in a region
Species richness describes the number of species.
Evenness or relative abundance describes how much the species differ from each other in numbers of individuals.
Genetic diversity
ncludes differences in DNA composition among individuals
Populations with little genetic diversity are more likely to suffer inbreeding depression and be vulnerable to environmental change, as they lack the variation needed to help adapt to new conditions.
Ecosystem diversity
the number and variety of ecosystems, communities, or habitats.
Species richness generally increases near equator, due to:
Greater geographic area.
More solar energy.
Stability of tropical climates.
Lack of disruptive glaciation events.
Biodiversity provides many free benefits, including:
Food, fuel, fiber, and shelter
Air and water purification
Waste decomposition
Climate stabilization
Pollination of plants
Controlling pests and diseases
Maintaining genetic diversity for crop varieties and livestock
Cultural and aesthetic benefits
biophilia
human beings share an instinctive love for nature and feel an emotional bond with other living things.
Extirpation
the loss of a species from one area, but not the entire world.
– The black rhino
background extinction rate
the pace at which organisms independently go extinct.
Based on the fossil record, scientists estimate this rate at an average of 1 out of every 1–10 million mammal and marine animals going extinct each year
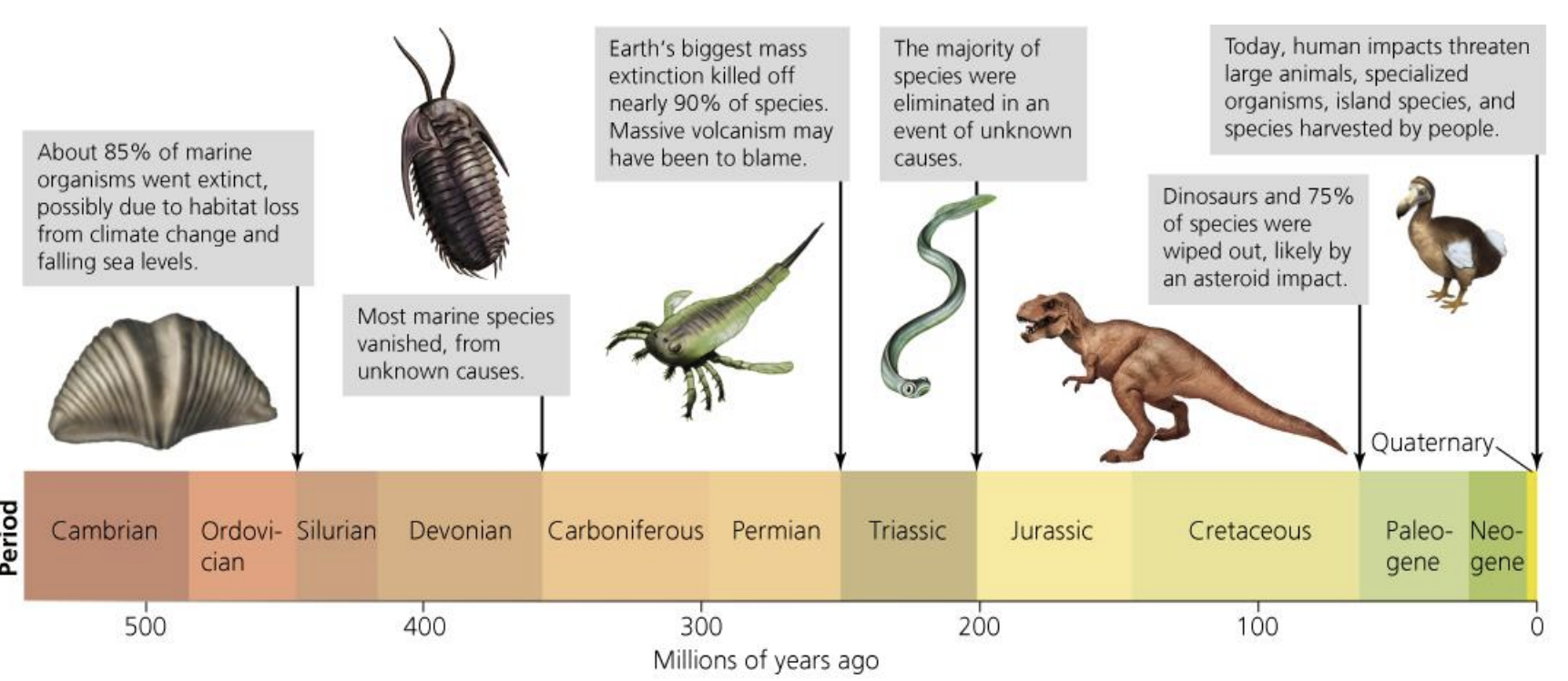
Mass extinction events
Red List
a list of all species at high risk of extinction.
The 2017 Red List reported that the following animals were threatened with extinction:
21% of mammal species
13% of bird species
20% of reptile species
32% of amphibian species
14% of fish species
the greatest threat to biodiversity today.
Habitat loss
habitat fragmentation.
This makes habitats smaller, and prevents movement of organisms between habitats.
Habitat loss %
the primary source of population decline in more than 80% of threatened birds and mammals.
Pollution harms organisms in many ways.
Air pollution degrades forests and affects the atmosphere and climate.
Noise and light pollution affect the behavior and habitat use of animals.
Water pollution directly harms fish and amphibians.
Agricultural runoff affects the food webs of aquatic ecosystems.
Persistent pollutants like heavy metals directly poison people and wildlife.
Plastic in the ocean can strangle, drown, or choke marine animals.
Poaching
the illegal killing of wildlife for meat or body parts.
Invasive species
non-native species introduced to new environments, can proliferate and displace native species.
Monarch butterflies
are in decline because of the loss of milkweeds due to herbicide use and habitat loss in their overwintering forests in Mexico.
worldwide collapse of amphibians
due to a “perfect storm” of factors, including habitat destruction, chemical pollution, invasive species, climate change, and disease.
Conservation biology
a study that seeks to understand the loss, protection, and restoration of biological diversity.
minimum viable population size
how small a population can become and how much genetic variation it can lose before encountering inbreeding depression.
By determining this size, they can help wildlife managers make plans for increasing the size of a population.
Endangered Species Act (ESA) of 1973
offers protection to species that fall within two categories:
Endangered, or in danger of becoming extinct in the near future.
Threatened, likely to become endangered soon.
Habitat conservation plans
allow the landowner to harm some individuals of a species if the overall habitat is improved.
Harbor agreement
promise that the government will not pursue additional action if the landowner pursues actions that assist in the species’ recovery
The 1973 Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)
bans the international transport of the body parts of rare species.
Convention on Biological Diversity
a treaty that provides funding and incentives for conservation in developing countries.
Successes include promoting ecotourism at the Serengeti National Park, promoting sustainable crops like shade-grown coffee, and discouraging the use of pesticide-intensive farming
captive breeding
where endangered individuals such as black rhinos are bred and raised with the intention of reintroducing their progeny into the wild.
65 plant and animal species now exist only in captivity
Biodiversity hotspots
regions that support a large number of species that are found nowhere else.
Defined as harboring at least 1500 endemic plant species and having already lost 70% of habitat area.
community-based conservation
actively engages local people.