Neuropsychology: Brain Development, Disorders, and Effects of Drugs
1/304
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
305 Terms
What is the significance of specialization in brain development?
Specialization is evident early in development, with some brain areas already specialized at birth.
How does brain specialization occur?
It takes two forms: brain regions become more focused during processing, shifting from general to specific stimuli.
What is an example of a specialized brain area?
The Fusiform face area, which becomes specific to faces and activates in response to recognizing them.
Do all brain systems specialize at the same rate?
No, different brain systems specialize at different rates and times.
What is required for successful brain specialization?
Stimulation from the environment is necessary for successful specialization.
What is experience-expectant growth?
Growth influenced by environmental input that is expected to be experienced, such as exposure to language.
What is experience-dependent growth?
Unique experiences over a lifetime that affect brain structure and organization, such as those of taxi cab drivers.
What is plasticity in the context of brain development?
The immature brain's ability to recover from damage or deprivation of experiences, allowing children to regain skills more easily than adults.
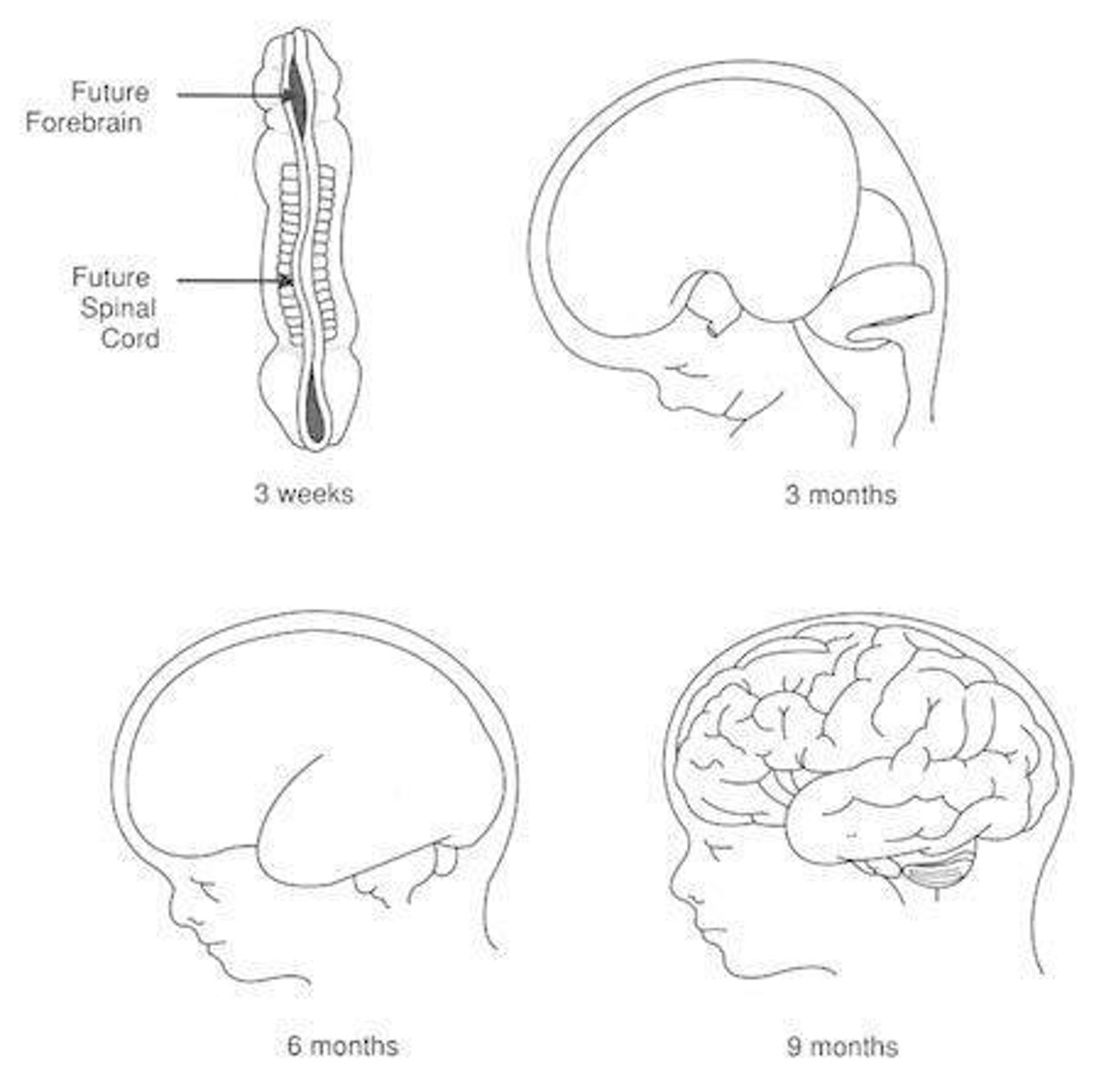
What are the key milestones in brain development from 3 weeks to 18 months?
3 weeks: neural tube forms; 3 months: brain multiplies; 6 months: cortex separates into lobes; 9 months: cortex wrinkles; 18 months: neuronal development finishes.
What happens during synaptic pruning?
The number of synapses grows rapidly, plateaus, and then rapidly decreases, with a loss of about 50% by age 2.
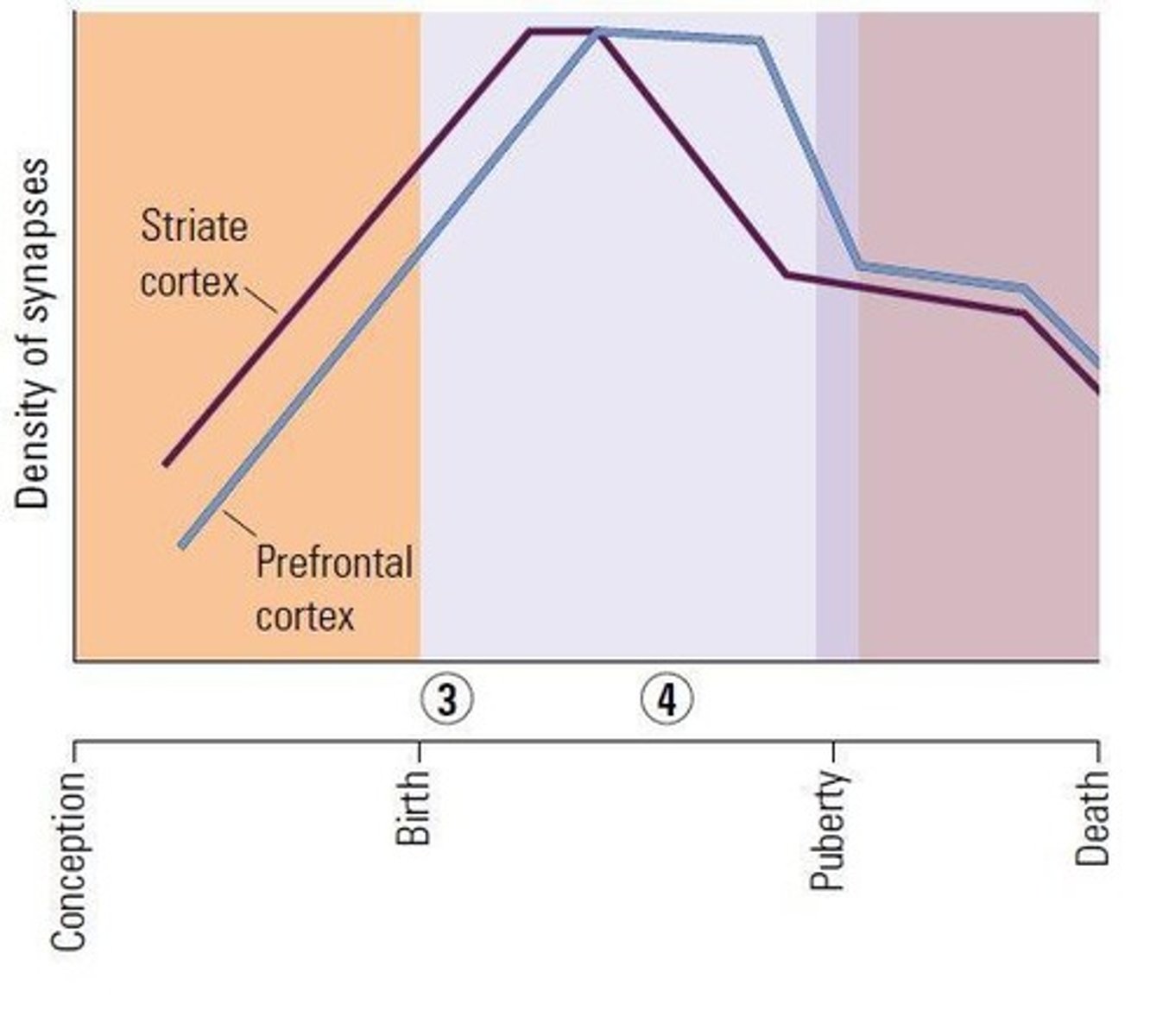
What is neuronal maturation?
After birth, neurons extend their axons and connect with other neurons.
When does total cerebral volume peak?
Total cerebral volume peaks just before puberty.
What is the role of the hippocampus in memory?
The hippocampus continues to develop throughout childhood and is crucial for encoding complex memories.
How does the prefrontal cortex develop in relation to the limbic system?
The limbic system develops first, controlling emotions and rewards, while the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions, develops later.
What are the functions of the limbic system?
The limbic system is responsible for rewards, pleasure, and emotions.
What are the responsibilities of the prefrontal cortex?
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for executive functions such as planning, impulse control, and decision-making.
What is the relationship between limbic and prefrontal regions in adolescents?
The limbic system is fully developed before the prefrontal cortex, leading to potential risk-taking behaviors due to limited self-control.
What emotional skills do children rely on?
Children's emotional skills are in early development stages, often relying on caregivers for appropriate responses.
What changes occur in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex during adolescence?
Connections between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex develop, often resulting in heightened emotions.
What is the trajectory of cortical maturation?
Cortical maturation continues until at least age 30, with primary areas maturing first.
What are the two types of intelligence in cognitive development?
Fluid intelligence, which declines in adulthood, and crystallized intelligence, which improves over time.
What is fluid intelligence?
Fluid intelligence refers to abilities that make us flexible, adaptable, and abstract thinkers.
What is crystallized intelligence?
Crystallized intelligence is the knowledge acquired throughout life, such as experiences and education.
What type of memory is key for recognizing faces and voices in infancy?
Sensory and motor memory
What memory improves during early childhood, allowing for explicit memories of events?
Working memory
What memory strategies develop during middle childhood?
Techniques to help remember lists, facts, and information
What is the primary cognitive development in adolescence regarding memory?
Improvement in working memory and memory strategies
What type of communication do infants primarily use?
Gestures, sounds, and expressions (pre-language communication)
At what age do children typically begin to speak their first words?
Around 18 months
What cognitive skill improves in middle childhood regarding language?
Comprehension and expression of complex sentences
What language skills are fine-tuned during adolescence?
Ability to use sarcasm, metaphor, and abstract reasoning
What are executive functions (EFs) and when do they begin to develop?
EFs help regulate attention, behavior, and emotions; they begin to develop in infancy and early childhood.
What improvements in executive functions occur during middle childhood?
Cognitive flexibility, problem solving, planning, time management, and organizational skills.
What cognitive abilities are enhanced in adolescence related to executive functions?
Abstract reasoning, critical thinking, and strategic planning.
What type of attention is reflexive in infancy?
Attention to novel high contrast stimuli.
What attention skills develop during early childhood?
Ability to focus for longer durations and develop selective attention.
How does attention change in middle childhood?
Improves in sustained attention and the ability to switch and divide attention.
What emotional developments occur in infancy?
Experience of basic emotions and reliance on body language to communicate feelings.
What emotional skills develop during middle childhood?
Recognition of others' emotions and labeling of their own emotions.
What is the difference between cross-sectional and longitudinal data in cognitive studies?
Cross-sectional compares different ages at one time, while longitudinal follows the same individuals over time.
What cognitive performance trends are observed in different cohorts?
Different cohorts show varying levels of cognitive performance, suggesting cohort effects.
What are crystallized abilities and how do they change with age?
Cumulative abilities like general knowledge that remain stable or improve with age.
What are fluid abilities and how do they change with age?
Abilities requiring cognitive flexibility that decline with age.
What happens to processing speed as individuals age?
It declines steeply starting in the 30s.
How does sustained attention change in older adults?
It is preserved with age.
What happens to selective and divided attention in older adults?
Both decline with age.
What is the status of long-term episodic memory in older adults?
Stable until about 55-60, then declines around 65.
How does semantic memory change with age?
Increases from ages 35-55, followed by a plateau and slight decline after 65.
What is the relationship between vocabulary and age?
Vocabulary remains stable and may improve over time.
What cognitive skills begin to develop during middle childhood?
Cognitive flexibility, problem solving, planning, time management, organizational skills, and the ability to consider other perspectives.
How do executive functions (EFs) improve during adolescence?
They contribute to abstract reasoning, critical thinking, strategic planning, self-regulation, goal setting, and management of complex tasks.
At what age does cognitive decline typically begin according to longitudinal studies?
Cognitive decline typically begins around age 55.
What is meant by 'experience-dependent brain growth'?
It refers to unique factors or experiences that create differences in our brain, driving group differences.
What is a common example of individual differences in brain structure?
London taxi drivers have increased gray matter in their hippocampus due to their navigational experience.
How does sustained practice in juggling affect brain structure?
It increases volume in the medial temporal area and left posterior intraparietal sulcus.
What significant difference was found in brain structure between Taiwanese and Western participants?
Westerners had increased gray matter in the frontal-parietal regions, while Taiwanese participants had increased gray matter in the temporal and occipital regions.
How do cultural differences affect cognitive performance?
European Americans tend to think analytically, while East Asians think holistically.
What impact does smoking have on brain structure and function?
Smoking is associated with decreased brain volume and reduced prefrontal activity, leading to cognitive deficits.
What role does sleep play in cognitive functioning?
Sleep is essential for memory consolidation, attention, emotional regulation, decision making, and problem solving.
What do twin studies suggest about brain volume and genetics?
Total brain gray and white matter volume is highly heritable, indicating genetics play a significant role in individual differences in cognition.
What are the three main categories of gene-environment correlation?
Passive, active, and evocative.
How do hormones influence physiological and behavioral activities?
Hormones regulate mood, metabolism, reproductive functions, hunger, sexual arousal, immune system activation, and circadian rhythms.
What are the average brain size differences between males and females?
Females generally have smaller brains than males, but the ratios of gray and white matter are similar.
What cognitive advantages do females typically have over males?
Females often have advantages in reading, while males tend to excel in mental rotation tasks.
What factors can influence individual differences in cognitive performance?
Biological/genetic, environmental, and cultural factors can all interact and influence brain structure, function, and cognition.
What is the significance of the hippocampus in cognitive aging?
Individuals with larger hippocampus volumes may experience less atrophy as they age.
What is the relationship between cannabis use and brain volume?
Cannabis abuse and genetic variants associated with schizophrenia can independently lead to decreases in white matter volumes.
What is the impact of environmental factors on brain structure?
Environmental factors like smoking, sleep, education, and diet can influence brain structure and cognitive performance.
What is the role of estrogen and testosterone in brain function?
Estrogen is associated with female reproductive systems, while testosterone is linked to male reproductive systems.
How do cultural stereotypes affect cognitive performance?
Stereotypes can influence educational opportunities and societal expectations, impacting cognitive performance across genders.
What is the take-home message regarding individual differences in cognition?
Biological, environmental, and cultural factors all influence brain structure, function, and cognitive performance, necessitating further research.
What is the relationship between poor sleep and risky behavior in adolescents?
Poor sleep leads to less recruitment in the dorsolateral PFC and greater unusual activation, resulting in decreased inhibition and increased activation of rewards, which can lead to risky behavior.
What are the implications of drug use on neurotransmitters?
Drugs can interfere with how neurons send, receive, and process signals, altering neurotransmitter function and potentially leading to addiction.
Which brain region is involved with motivation and pleasure and is affected by drug use?
The basal ganglia is involved with motivation, pleasure, and the formation of habits, and is overactivated by drugs, producing euphoria.
What happens to the brain's neurotransmitter production with repeated drug use?
The brain produces fewer of its own neurotransmitters in the reward circuit, leading to loss of motivation and inability to enjoy previously pleasurable activities.
What role does the extended amygdala play in substance use disorders?
The extended amygdala is involved in stress and withdrawal symptoms, becoming hypersensitive with increased drug use, which motivates individuals to seek drugs for relief.
How does the prefrontal cortex relate to drug use?
The prefrontal cortex is involved in decision making and self-control; drug use can impair these functions, leading to reduced impulse control and compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
What neurotransmitter is primarily associated with mood regulation and is influenced by drugs like ecstasy?
Serotonin is responsible for stabilizing moods and regulating emotions, and drugs like ecstasy can disrupt its function.
Which neurotransmitter is affected by marijuana and what are its effects?
Marijuana affects dopamine, causing euphoria but also impairing memory, motor skills, and cognitive functions.
What are the short-term effects of marijuana use?
Short-term effects include altered senses, mood changes, impaired body movement, difficulty thinking, and hallucinations.
What are the long-term effects of marijuana on the brain?
Long-term effects can impair brain connectivity related to learning, thinking, and memory, especially if used before the brain is fully developed.
What is the role of dopamine in drug addiction?
Dopamine regulates mood and pleasure; drugs can cause surges in dopamine, leading the brain to seek drugs over other goals.
What are the seven main categories of drugs?
The seven main categories are stimulants, depressants, opioids, psychedelics, cannabinoids, dissociatives, and empathogens.
What is the function of GABA in the brain?
GABA acts as a natural tranquilizer, mitigating stress responses, lowering anxiety, and slowing down CNS functions.
How do benzodiazepines influence GABA?
Benzodiazepines bind to GABA receptors, increasing the likelihood of GABA binding and enhancing its calming effects.
What is the impact of norepinephrine on the CNS?
Norepinephrine speeds up the CNS during the 'fight or flight' response, improving focus and attention.
What is the gene-environment correlation?
The gene-environment correlation suggests that individuals can elicit responses from their environment and seek out environments that fit their genetics.
Are all sex differences genetic in nature?
No, some sex differences are driven by environmental and social factors.
What is the effect of smoking on brain volume?
Smoking is associated with decreased brain volume.
What is the significance of environmental cues in drug addiction?
Environmental cues can trigger uncontrollable cravings for drugs, which can persist even after a person is drug-free.
What is the role of the limbic system in drug use?
The limbic system is involved in emotional responses and can drive individuals to seek drugs for relief from discomfort.
What is the effect of stimulants on dopamine?
Stimulants stop the reuptake of dopamine, leading to increased levels in the brain.
What are the implications of drug-induced changes in neurotransmitter levels?
Drugs can produce much higher levels of neurotransmitters than natural situations, leading to a decrease in the brain's own production and receptor sensitivity.
What is the relationship between drug use and the brain's reward system?
Drugs can hijack the brain's reward system, leading to compulsive drug-seeking behavior and diminished pleasure from natural rewards.
What is the association between adolescent cannabis use and IQ?
It is associated with lower IQ, but changes are reversible.
What are the short-term effects of heroin and opioids?
They block pain sensations and induce drowsiness.
What long-term effects do heroin and opioids have on the brain?
They cause reductions in brain's white matter, poor stress responses, and emotional regulation issues.
What is hypoxia in the context of opioid use?
It refers to a lack of oxygen in the brain, which can lead to coma, permanent damage, or death.
How does alcohol affect the brain?
It is a depressant that interferes with white matter tracts controlling balance, memory, speech, and judgment.
What are the short-term effects of alcohol consumption?
Changes in mood and behavior, reduced coordination, impaired thinking, blackouts, and reduced reaction time.