MGMT 300 Midterm
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Louise K UW
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Organizational Behavior
The field of study dedicated to understanding, explaining, and improving the attitudes and behaviors of individuals and groups in organizations to maximize job performance and organizational commitment
Theory
A collection of assertions that specify how and why variables are related, as well as the conditions in which they should (and should not) be related
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation
Correlation
Perfect positive relationship: 1
Perfect Negative relationship: -1
More compact = stronger correlation; less compact = weaker correlation
The Rule of 1/8
½ of organizations don’t believe the connection between how they manage their people and profits they earn
½ of organizations who do see the connections will try to make a single change and do not realize that this requires a more comprehensive system
of the organizations that make comprehensive changes, ½ will persist their practices long enough to actually derive economic benefits
Human Resource Management
Takes the theories and principles studied in OB and explores the “nuts-and-bolts” applications of those principles in organizations.
Strategic Management
Focuses on the corporate tactics and industry characteristics that affect an organization’s profitability
Methods of Knowledge
Methods of experience, method of intuition, method of authority, method of science
Job Performance
The value of the set of behaviors that contribute, either positively or negatively, to organizational goal accomplishment
Task Performance
The behaviors directly involved in transforming organizational resources into the goods or services an organization produces (i.e the behaviors included in one’s job description)
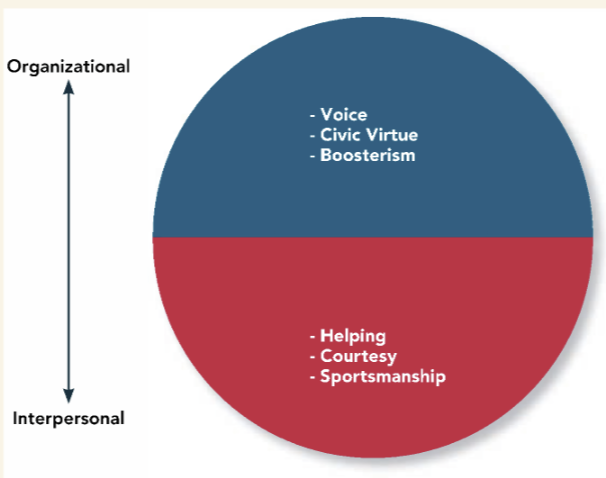
Citizenship Behavior
Voluntary activities that may or may not be rewarded but that contribute to the organization by improving the quality of the setting where work occurs
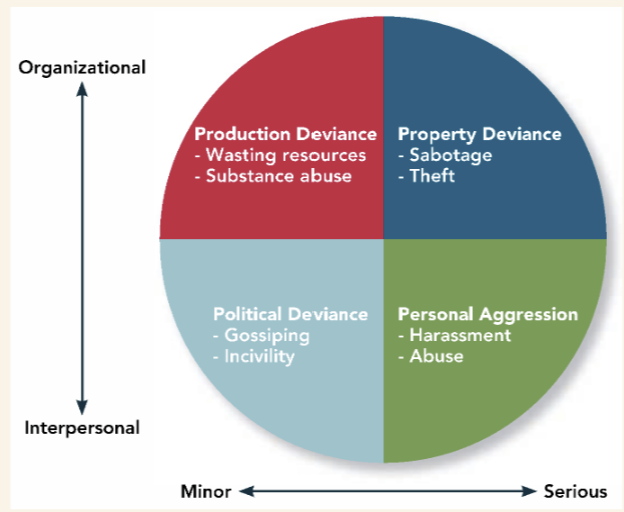
Counterproductive Behavior
Employee behaviors that intentionally hinder organizational goal accomplishment
Types of Performance Management
MBO: performance goals
Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales: job performance behaviors
360 degree feedback: feedback from multiple people directly involved
forced ranking: ranking employees into top 20, the vital 70, bottom 10
social networking systems: anonymous ranking
Routine Task Performance
well-known responses to demands that occur in a normal, routine, or otherwise predictable way
Adaptive Task Performance
involves employee responses to task demands that are novel, unusual, or, at the very least, unpredictable.
Creative Task Performance
Refers to the degree to which individuals develop ideas or physical outcomes that are both novel and useful.
Boosterism
means representing the organization in a positive way when out in public, away from the office, and away from work.
Knowledge Work
Cognitive work, applying theoretical and analytical knowledge acquired through education and continuous learning
Service Work
Work that provides nontangible goods to customers through direct electronic, verbal, or physical interaction
Job Satisfaction
A pleasurable emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one’s job or experience
Value-Percept Theory
Does your job provide what you value? (Dissatisfaction = (Vwant-Vhave) * Vimportance
Job Characteristics theory
Jobs are more intrinsically enjoyable when work tasks are challenging and fulfilling
Five Core Characteristics
Variety, Identity, Significance, Autonomy, Feedback
Affective Events Theory
Specific Workplace Events trigger affective reactions during the day which influence work attitudes and behaviors
Organizational commitment
desire to remain a member of an organization
affective commitment
emotional attachment to an organization
continuance commitment
staying due to perceived cost of leaving
normative commitment
staying because of obligation
withdrawal behavior
actions employees take to avoid work
Social influence model
If you have linkage with leavers, you will leave as well
Stars
High Task Performance, High Organizational Commitment
Citizens
Low Task Performance, High Organizational Commitment
Lone Wolves
High Task performance, low organizational commitment
Apathetics
low task performance, low organizational commitment
psychological withdrawal
mental escape from work
physical withdrawal
physical escape from work