A level Bio 2.3 Transport across Membranes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
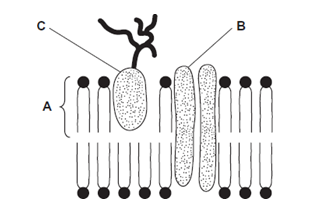
The diagram shows the structure of the cell-surface membrane of a cell.
Name A and B. (2)
A phospholipid (layer) (1)
B pore/channel/transport protein (1)
Describe how phospholipids are arranged in a plasma membrane. (2)
Bilayer (1)
Polar / phosphate group / hydrophilic (head) to outside (1)
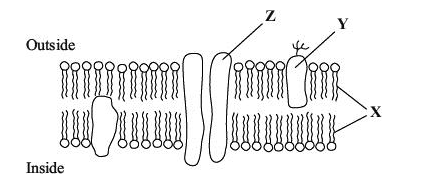
Describe two functions of the structure made from the parts labelled X.(2)
form(water) impermeable barrier to water-soluble substances/allows non-polar molecules to pass through (1)
allows cell to maintain different concentrations either side (1)
The structure of a plasma membrane is described as fluid mosaic. Explain why (2)
Fluid = molecules move around (1)
Mosaic = proteins floating among phospholipids (1)
Cholesterol increases the stability of plasma membranes. Cholesterol does this by making membranes less flexible.
Suggest one advantage of the different percentage of cholesterol in red blood cells compared with cells lining the ileum (1)
Red blood cells are free in blood so cholesterol helps to maintain shape (1)
Explain how three features of a plasma membrane adapt it for its functions.(6)
phospholipid bilayer (as a barrier) (1)
forms a barrier to water soluble / charged substances (1)
glycoproteins / glycolipids (1)
responsible for cell recognition (1)
cholesterol (1)
regulates fluidity (1)
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of increasing methanol concentration on the permeability of beetroot cell membranes.
Give two things that should be done with the colorimeter before it is used to measure the absorbance of liquid samples (2)
It should be set up so it's using the correct (blue) filter (1)
It should be calibrated to zero (using a cuvette containing distilled water). (1)
Temperature also affects membrane permeability.
Temperatures that are too high can denature proteins in the membrane , increasing permeability
How could temperature below 0 degree Celsius affect membrane permeability (3)
Channel and carrier proteins can denature (1)
Ice crystals can also form and pierce the membrane (1)
Makes the membrane more permeable(1)
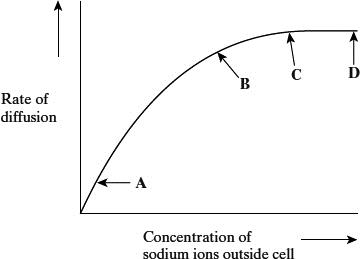
What limits the diffusion of sodium ions across the membrane between A and B on the graph?
Give the evidence for your answer (2)
Limiting factor- concentration of sodium ions outside cell (1)
Evidence- As concentration variable increases, the rate of diffusion increases (1)
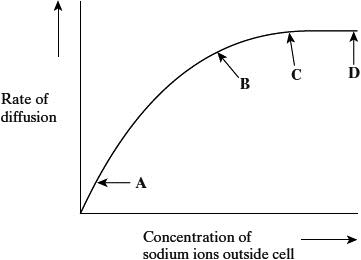
Explain the shape of the curve between C and D (2)
Sodium ions are passing through the channels (1)
Rate is limited by the number of sodium channels (1)
Before the cell was examined using the electron microscope, it was stained. This stain caused parts of the structure of the cell-surface membrane to appear as two dark lines.
Suggest an explanation for the appearance of the cell-surface membrane as two dark lines.(3)
Membrane has phospholipid bilayer (1)
Stain binds to phosphate/glycerol (1)
On inside and outside of membrane (1)
The image below shows the cell-surface membrane of a red blood cell seen with a transmission electron microscope.
No organelles are visible in the cytoplasm of this red blood cell.
Suggest why. (1)
Cytoplasm of red blood cell filled with haemoglobin. (1)
(lose organelles for them!)
Describe how substances move across cell-surface membranes by facilitated diffusion (3)
Carrier / channel protein (1)
(Protein) specific / complementary to substance (1)
Substance moves down concentration gradient (1)
Explain why molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are able to diffuse across membranes (2)
small, non-polar molecules (1)
so can pass through down a concentration gradient (1)
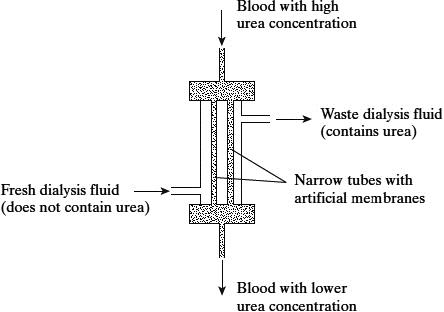
A dialysis machine contains artificial membranes which enable urea to be removed from the blood of a person with kidney failure. The diagram shows a dialysis machine.
Suggest two reasons for keeping the fluid in the dialysis machine at 40 °C rather than room temperature.(2)
high rate of exchange/diffusion (1)
prevents cooling of the blood (1)
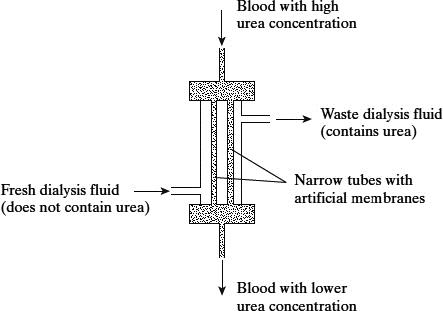
A dialysis machine contains artificial membranes which enable urea to be removed from the blood of a person with kidney failure. The diagram shows a dialysis machine.
The blood and the dialysis fluid flow in opposite directions in the dialysis machine. Explain the advantage of this. (2)
concentration gradient maintained (1)
blood always meets fluid with lower concentration of urea (1)
Draw a peptide bond showing how the COOH group of one amino acid joins to the NH2 group of another (1)
gains 1 mark
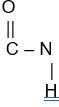
Experiments have shown that valinomycin is unable to transport potassium ions across a membrane when it is cooled. Gramicidin A continues to facilitate the movement of potassium ions at these low temperatures. Explain these results. (3)
Action of valinomycin depends on fluidity of membrane (1)
Fluidity reduced / not fluid at low temperatures (1)
Pore formed by gramicidin A remains in place / permanent (1)
Oxygen and chloride ions can diffuse across cell-surface membranes. The diffusion of chloride ions involves a membrane protein. The diffusion of oxygen does not involve a membrane protein.
Explain why the diffusion of chloride ions involves a membrane protein and the diffusion of oxygen does not.(5)
Chloride ions water soluble/charged/polar (1)
Cannot cross (lipid) bilayer (of membrane) (1)
Chloride ions transported by facilitated diffusion OR diffusion involving channel/carrier protein (1)
Oxygen not charged/non-polar (1)
(Oxygen) soluble in/can diffuse across (lipid) bilayer (1)
Give two similarities in the movement of substances by diffusion and by osmosis (2)
movement down a concentration gradient (1)
They are both passive processes (1)
Explain how sodium ions are transported through the membranes (2)
Active transport (1)
by specific carrier proteins (1)
There is a higher concentration gradient between cytoplasm and the vacuole than between cytoplasm and the intercellular fluid. Suggest how the vacuole membrane maintains this higher concentration gradient (2)
more sodium ions are transported into vacuole (than to outside) (1)
vacuole membrane less permeable to sodium ions (1)
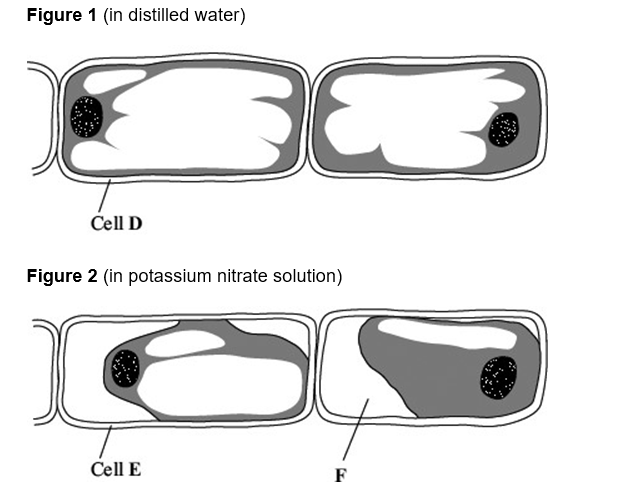
Tradescantia is a house plant. There are small hairs on its flowers. These hairs are made of cells.
Figure 1 shows the appearance of cells from one of these hairs after 20 minutes in distilled water.
Figure 2 shows cells from another hair after 20 minutes in a solution of potassium nitrate.
What does Figure 2 suggest about the permeability of the plasma membranes surrounding these cells? (3)
partially permeable membrane (1)
allows water to pass through but not potassium nitrate (1)
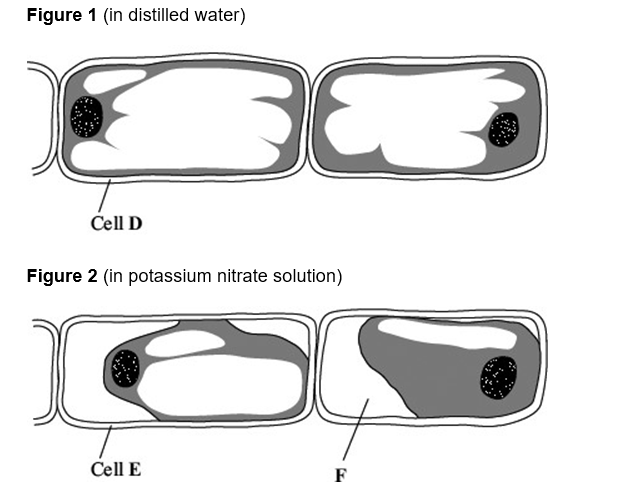
Tradescantia is a house plant. There are small hairs on its flowers. These hairs are made of cells.
Figure 1 shows the appearance of cells from one of these hairs after 20 minutes in distilled water.
Figure 2 shows cells from another hair after 20 minutes in a solution of potassium nitrate.
How would the water potential of the sap in the vacuole of cell E differ from the water potential of the sap in the vacuole of cell D? Explain your answer. (3)
water potential more negative in cell E (1)
Water removed via osmosis (1)
greater sap concentration in cell (1)
Describe the processes of facilitated diffusion and active transport. (3)
Facilitated diffusion - (movement of) polar/charged molecules (1)
movement down a concentration gradient via carrier/channel protein (1)
(Active transport) movement against a concentration gradient via carrier protein using ATP (1)
What are microvilli? (1)
(Highly) folded cell(-surface) membrane (1)
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble substance.
Micelles are involved in the process of vitamin A absorption.
Describe the process of vitamin A absorption into cells lining the ileum. (3)
Combine/mix/join with bile salts (1)
Make (more) soluble (in water) (1)
Diffuses (into cells/ileum) (1)
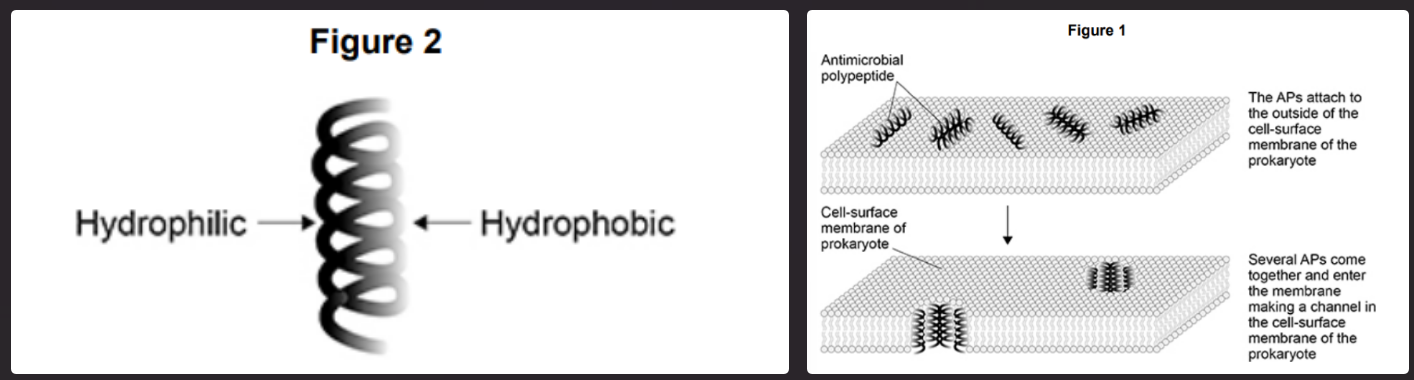
Many multicellular organisms produce antimicrobial polypeptides (APs) that protect them against prokaryotes. Figure 1 shows how one type of AP acts on the cell-surface membrane of prokaryotes.
The amino acids on one side of each AP helix have hydrophobic properties. The amino acids on the opposite side of each helix have hydrophilic properties. Figure 2 shows this.
Suggest how these properties of the APs allow them to become positioned across the membrane (as shown in Figure 1) and make a channel through which ions can pass (2)
Hydrophobic side next to/in/face hydrophobic (part of) phospholipid/bilayer (1)
Hydrophilic sides allow ion movement through membrane (1)
The APs damage prokaryotic cells but do not damage the eukaryotic cells in the organisms that produce them. Prokaryotic cell membranes do not contain cholesterol.
Assess why the APs do not damage the eukaryotic cells of the organisms that produce them. (2)
Cholesterol restricts the movement of molecules/phospholipids/fatty acid (tails) (making up the membrane) (1)
(So) APs cannot enter the (eukaryotic) membrane (1)
Scientists observed these APs on prokaryotes using a transmission electron microscope.
They stained the APs using a monoclonal antibody with gold attached to it.
Suggest how these techniques allowed observation of APs on prokaryotes (3)
Antibody binds to AP (1)
(As antibody/tertiary structure is) complementary (to AP) (1)
Gold interacts with electrons (in TEM) (1)
Name and describe five ways substances can move across the cell-surface membrane into a cell (5)
(Simple) diffusion of small/non-polar molecules down a concentration gradient (1)
Facilitated diffusion down a concentration gradient via protein carrier/channel (1)
Osmosis of water down a water potential gradient (1)
Active transport against a concentration gradient via protein carrier using ATP (1)
Co-transport of 2 different substances using a carrier protein (accept a correct example) (1)
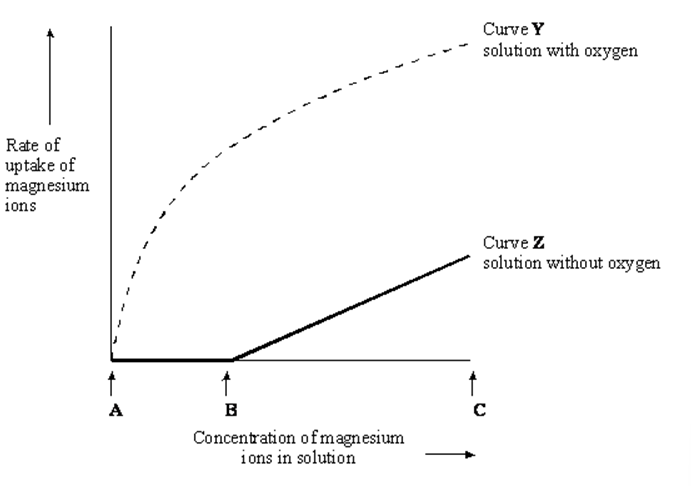
The graph shows the effect of concentration on the rate of uptake of magnesium ions by root hair cells.
In the solution without oxygen, explain why no magnesium ions are taken up between concentrations A and B. (1)
concentration inside cells higher than surrounding solution (1)
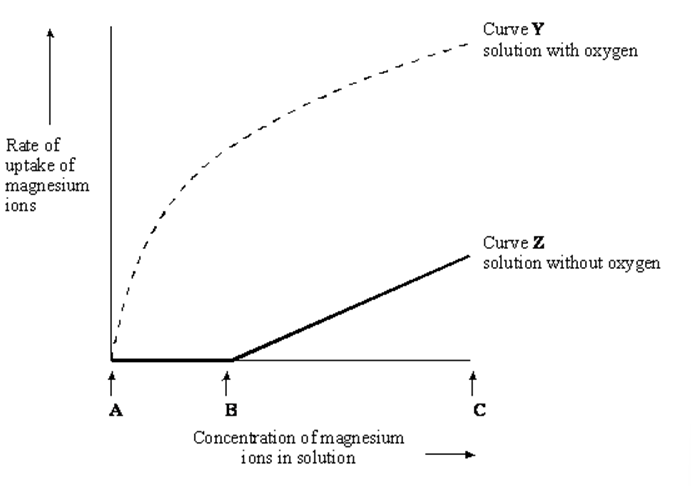
The graph shows the effect of concentration on the rate of uptake of magnesium ions by root hair cells.
For curve Z explain why the rate of uptake increases between B and C (1)
diffusion is proportional to the concentration gradient (1)
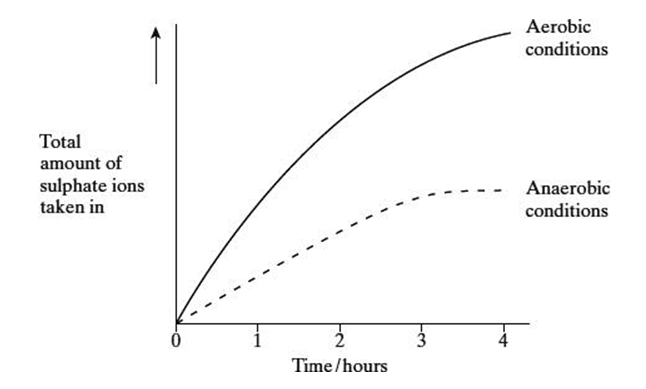
An investigation was carried out to compare the uptake of sulphate ions by barley roots in aerobic and in anaerobic conditions. The results are shown in the graph.
Suggest why the uptake of sulphate ions by the roots in anaerobic conditions stopped after 3 hours (1)
no net movement of ions (1)
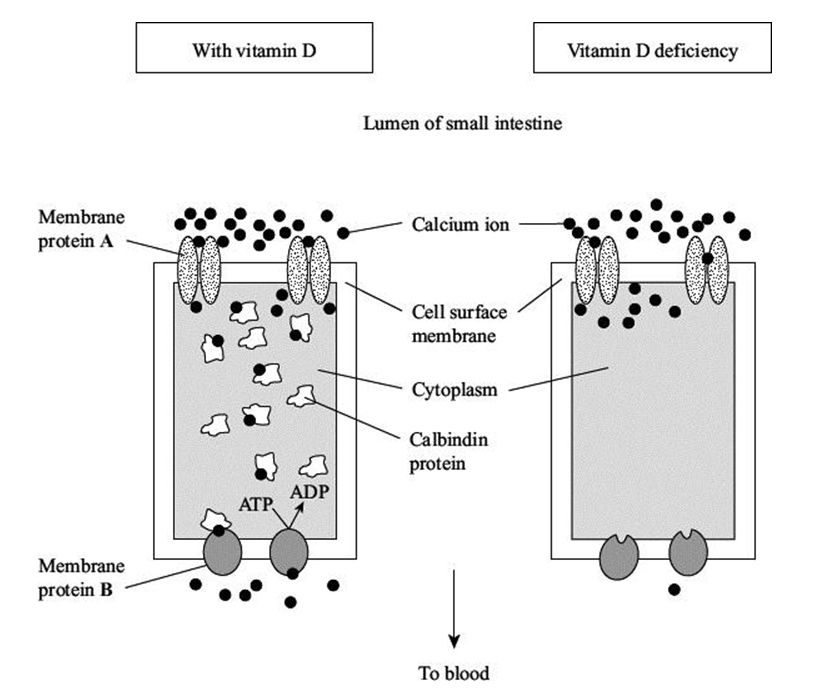
Vitamin D deficiency reduces the uptake of calcium ions by epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The diagrams show how calcium ions are transported through normal epithelial cells and those deficient in vitamin D.
Use the information in the diagrams to explain how vitamin D deficiency reduces calcium ion uptake through gut epithelial cells. (2)
No/less calbindin protein is produced (1)
calcium not transported (across the cytoplasm) ()
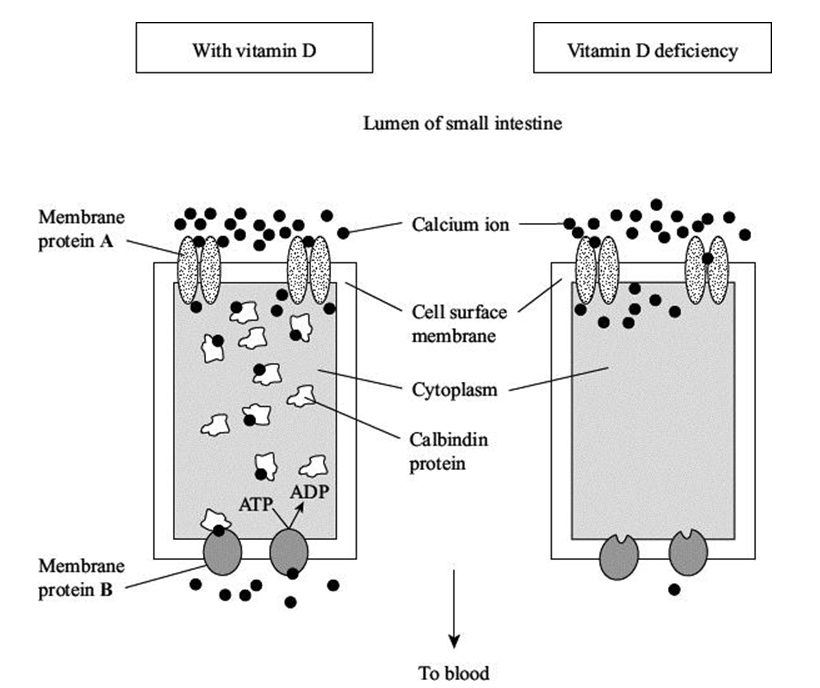
Use the information in the diagrams to explain how vitamin D deficiency reduces calcium ion uptake through gut epithelial cells.
Membrane proteins A and B transport calcium ions through cell surface membranes. Explain how each type of membrane protein transports calcium ions. (4)
Protein A - Channel/pore protein (for calcium ions) (1)
Passage by facilitated diffusion down a concentration gradient (1)
Protein B - Carrier protein (for calcium ions) (1)
Passage by active transport against a concentration gradient (1)
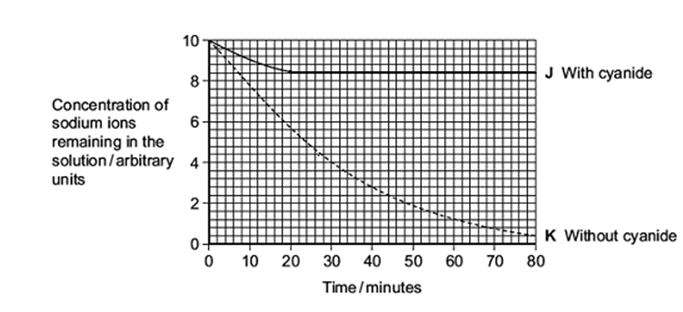
A scientist investigated the effect of cyanide on the uptake of sodium ions by animal tissue.
He set up two beakers, J and K.
He put equal volumes of a solution containing sodium ions and equal masses of an animal tissue in each beaker.
• He added cyanide to beaker J.
• He did not add cyanide to beaker K.
He measured the concentration of sodium ions remaining in the solution in each beaker, for 80 minutes. The graph shows his results.
Cyanide is a substance which affects respiration.
Use information in the question to explain the effect of cyanide on the uptake of sodium ions by the tissue. (3)
Inhibits respiration (1)
No ATP is produced (1)
ATP is needed for active transport (1)
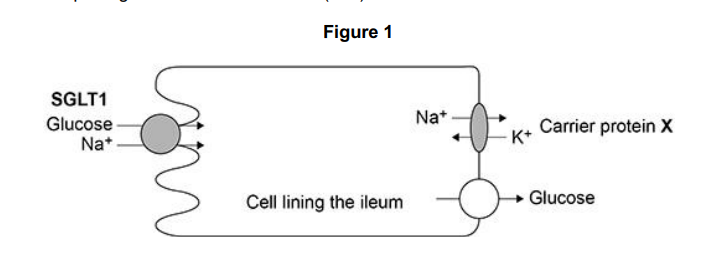
Figure 1 shows a cell from the lining of the ileum specialised for absorption of products of digestion.
SGLT1 is a carrier protein found in the cell-surface membrane of this cell, it transports glucose and sodium ions (Na+ ) into the cell.
The action of the carrier protein X in Figure 1 is linked to a membrane-bound ATP hydrolase enzyme. Explain the function of this ATP hydrolase. (2)
(ATP to ADP + Pi ) Releases energy (1)
(energy) allows active transport of ions (1)
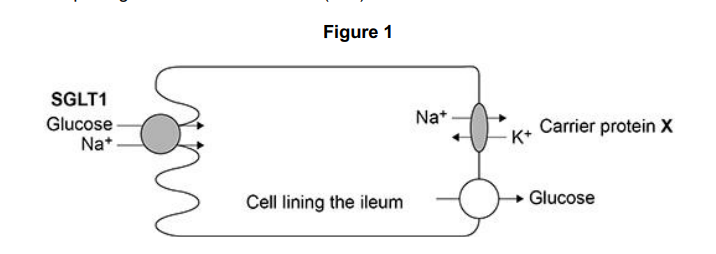
The movement of Na+ out of the cell allows the absorption of glucose into the cell lining the ileum. Explain how. (2)
(Maintains/generates) a concentration/diffusion gradient for Na+ (from ileum into cell) (1)
Na+ moving (in) by co-transport, brings glucose with it (1)
Describe and explain three features you would expect to find in a cell specialised for absorption. (3)
Folded membrane/microvilli so large surface area (for absorption) (1)
Large number of mitochondria so make (more) ATP (by respiration) (1)
Large number of co-transport/carrier/channel proteins so fast rate (of absorption) (1)
The movement of substances across cell membranes is affected by membrane structure. Describe how. (5)
Phospholipid (bilayer) allows movement/diffusion of nonpolar/lipid-soluble substances (1)
(Membrane) proteins allow polar/charged substances to cross the membrane/bilayer (1)
Carrier proteins allow active transport (1)
Membrane surface area determines how much diffusion/movement (1)
Cholesterol affects fluidity/rigidity/permeability (1)
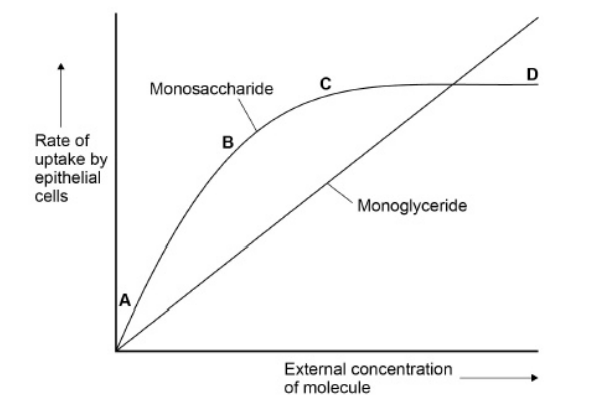
A scientist measured the rate of uptake of a monoglyceride and a monosaccharide by epithelial cells of the small intestine of mice.
A monoglyceride is a molecule of glycerol with one fatty acid attached. She did this for different concentrations of monoglyceride and monosaccharide.
Her results are shown in the graph.
Use your knowledge of transport across membranes to explain the shape of the curve in the graph for uptake of monosaccharides between concentrations: (3)
Facilitated diffusion between A and B (1)
Rate of uptake proportional to (external) concentration (1)
Between C and D
All channel / carrier proteins in use (1)
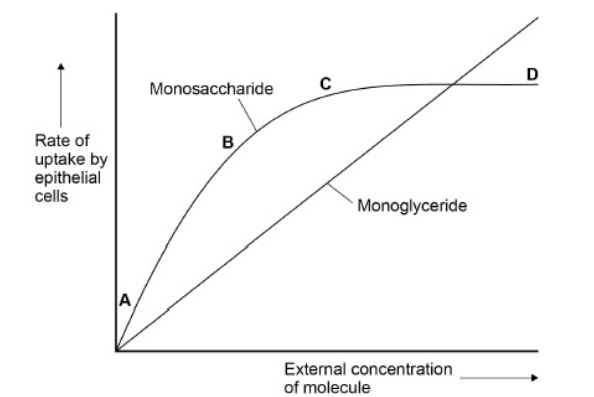
A scientist measured the rate of uptake of a monoglyceride and a monosaccharide by epithelial cells of the small intestine of mice.
A monoglyceride is a molecule of glycerol with one fatty acid attached. She did this for different concentrations of monoglyceride and monosaccharide.
The graph is evidence for monoglycerides being lipid-soluble molecules. Suggest how. (2)
Rate of uptake is proportional (so diffusion occuring) (1)
(Lipid-soluble molecules) diffuse through (1)
The cells of beetroot contain a red pigment. A student investigated the effect of temperature on the loss of red pigment from beetroot. He put discs cut from beetroot into tubes containing water. He maintained each tube at a different temperature. After 25 minutes, he measured the percentage of light passing through the water in each tube.
The student put the same volume of water in each tube.
Explain why it was important that he controlled this experimental variable.(2)
(If) too much water the concentration of pigment (in solution) will be lower / solution will appear lighter / more light passes through (than expected) (1)
So results (from different temperatures) are comparable (1)
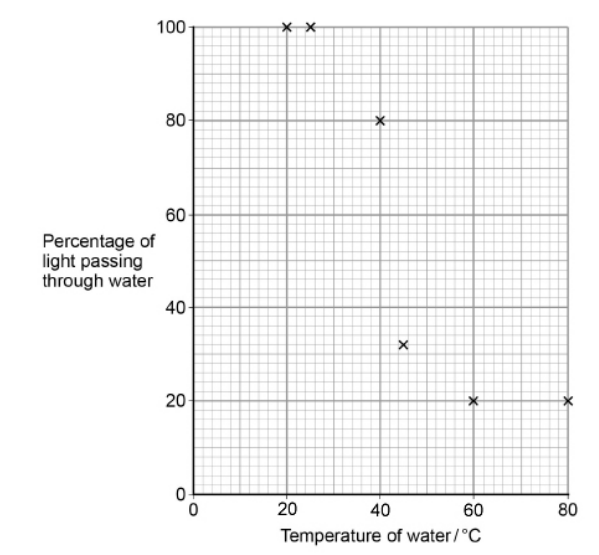
The decrease in the percentage of light passing through the water between 25 °C and 60 °C is caused by the release of the red pigment from cells of the beetroot. Suggest how the increase in temperature of the water caused the release of the red pigment.(3)
Damage to (cell surface) membrane (1)
(membrane) proteins denature (1)
Increased fluidity / damage to the phospholipid bilayer (1)
Sodium ions from salt (sodium chloride) are absorbed by cells lining the
gut. Some of these cells have membranes with a carrier protein called NHE3.
NHE3 actively transports one sodium ion into the cell in exchange for one
proton (hydrogen ion) out of the cell.
Use your knowledge of transport across cell membranes to suggest how
NHE3 does this. (3)
Co-transport (1)
Uses (hydrolysis of) ATP (1)
Sodium ion and proton bind to the protein (1)
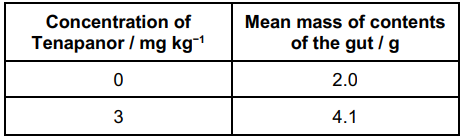
Scientists investigated the use of a drug called Tenapanor to reduce salt absorption in the gut. Tenapanor inhibits the carrier protein, NHE3.
The scientists fed a diet containing a high concentration of salt to two groups of rats, A and B.
• The rats in Group A were not given Tenapanor (0 mg kg−1).
• The rats in Group B were given 3 mg kg−1 Tenapanor.
One hour after treatment, the scientists removed the gut contents of the
rats and immediately weighed them.
Their results are shown in the table.
The scientists carried out a statistical test to see whether the difference in the means was significant. They calculated a P value of less than 0.05.
They concluded that Tenapanor did reduce salt absorption in the gut. Use all the information provided and your knowledge of water potential to explain how they reached this conclusion.(4)
Tenapanor / (Group)B drug causes a significant increase (1)
There is a less than 0.05 probability that the difference is due to chance (1)
(More salt in gut) reduces water potential in gut (contents) (1)
(so) less water absorbed out of gut (contents) by osmosis (1)
High absorption of salt from the diet can result in a higher than normal concentration of salt in the blood plasma entering capillaries. This can lead to a build-up of tissue fluid. Explain how. (2)
(Higher salt) results in lower water potential of tissue fluid (1)
(So) less water returns to capillary by osmosis (at venule end) (1)
Strawberries may be dehydrated by removing most of the water they contain. Dehydrated strawberries have many different uses in the food industry.
Food scientists investigated the effect of using osmosis to dehydrate strawberries.
In this investigation, the scientists cut the strawberries into slices (step 1).
Explain the advantage of this. (2)
Increase surface area (1)
producing water loss (1)
Strawberries may be dehydrated by removing most of the water they contain. Dehydrated strawberries have many different uses in the food industry.
Food scientists investigated the effect of using osmosis to dehydrate strawberries.
In the second column of the table, the percentage loss in mass for one of the values has been recorded as not applicable. Explain why. (1)
Length of time in | Percentage loss in mass | Texture / arbitrary units |
0 | Not applicable | 1.2 |
1 | 15.96 | 0.9 |
2 | 22.88 | 0.7 |
4 | 32.36 | 0.7 |
6 | 38.78 | 0.7 |
the time is too short for osmosis (1)
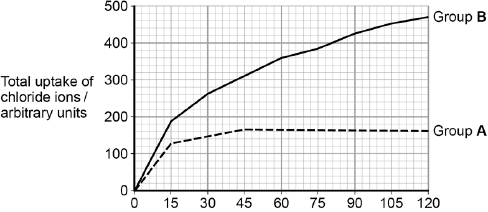
Students investigated the uptake of chloride ions in barley plants. They divided the plants into two groups and placed their roots in solutions containing radioactive chloride ions.
• Group A plants had a substance that inhibited respiration added to the solution.
• Group B plants did not have the substance added to the solution.
The students calculated the total amount of chloride ions absorbed by the plants every 15 minutes. Their results are shown in the figure below.
Explain the results shown in figure 4 (4)
Group A – initial uptake slower because by diffusion (only) (1)
Group A – levels off because same concentrations inside cells and outside cells / reached equilibrium (1)
Group B – uptake faster because by diffusion plus active transport (1)
Group B fails to level off because uptake against gradient / no equilibrium to be reached (1)
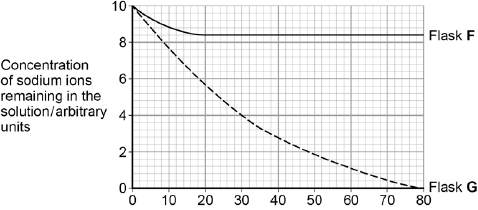
A scientist investigated the uptake of sodium ions by animal tissue.
To do this, he:
• used two flasks, F and G
• put equal masses of animal tissue into each flask
• added equal volumes of a solution containing sodium ions to each flask
• added to flask F a solution of a substance that prevents the formation of ATP by cells
• measured the concentration of sodium ions remaining in the solution in each flask.
The graph below shows his results.
The scientist concluded that the cells in flask G took up sodium ions by active transport. Explain how the information given supports this conclusion. (4)
Uptake in flask G much greater than in flask F (1)
Showing use of ATP in flask G (1)
Sodium ion concentration in flask G falls to zero(1)
Showing uptake against a concentration gradient.(1)
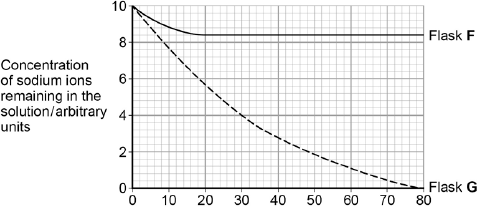
A scientist investigated the uptake of sodium ions by animal tissue.
To do this, he:
• used two flasks, F and G
• put equal masses of animal tissue into each flask
• added equal volumes of a solution containing sodium ions to each flask
• added to flask F a solution of a substance that prevents the formation of ATP by cells
• measured the concentration of sodium ions remaining in the solution in each flask.
The graph below shows his results.
The curve for flask F levelled off after 20 minutes. Explain why. (2)
(Uptake of sodium ions occurring by) facilitated diffusion (1)
Equilibrium reached / sodium ion concentrations in solution and in cells the same. (1)