4. Environmental bacteria
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
WHat is the predominant form of available nitrogen in aerobic soil
is nitrate (NO3-)
What is the predominant form of nitrogen in anaerobic soil?
Ammonium (NH4+)
Why is there no nitrate availabile in anaerobic soil?
Nitrifying bacteria are obligate aerobes
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
are capable of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonium (NH4+)
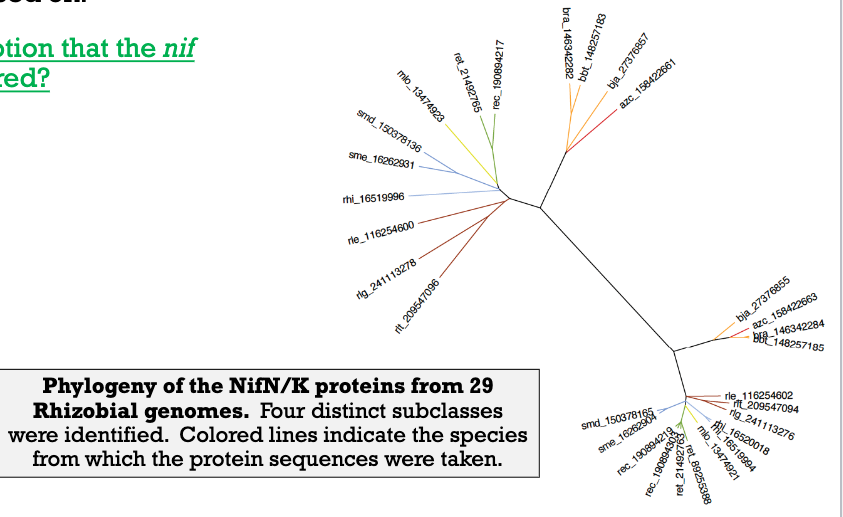
How does the figure support the nif genes are horizontally transferred
clustering pattern suggests that the nif genes have been transferred horizontally, as the proteins group together based on genetic similarities rather than the evolutionary relationships of the species
Strepomyces
Filamentous bacteria which are like fungi and play a key role in soil health by decomposing organic material and recycling nutrients.
Strepmyces mycelium (Hyphae) growth
DNA replication occurs without cell division because functional spores are being generated
First streptomyces genome to be sequnced
was that of the large linear chromosome of Streptomyces coelicolor in 2001
How was the S. coelcolor genome sequenced?
Heirarchical shotgun sequencing method using a cosmid library
Hassle with linear chromosome of S. coelicolor
Telomeres shorten with each round of cell division, potentially leading to genetic instability and loss of essential genes.
What is the benefit of S. coelicolor linear chromosomes
After recombination, functional spores can be produced, allowing for greater genetic diversity and adaptation.
Why is it difficult to make functional spores with a circular chromosome
hard to package chromosome cantameter
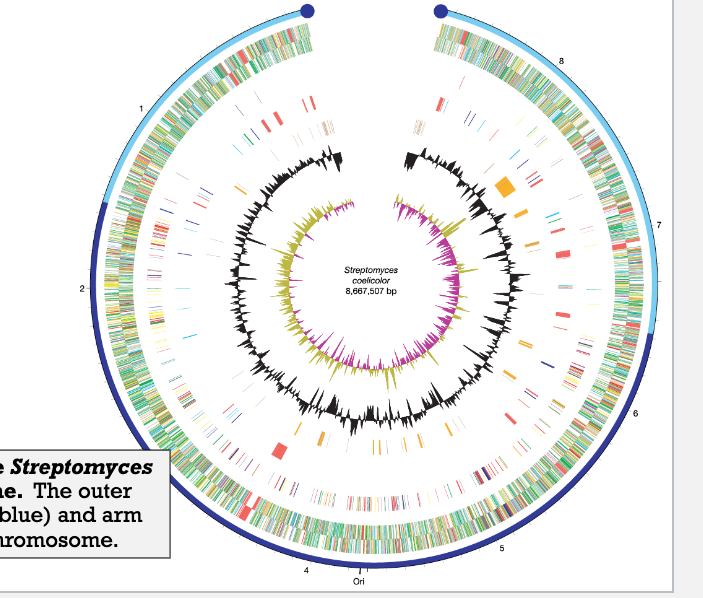
What is the dark blue on the graph
Central region of linear S. coelicolor chromosome, which contains essential genes
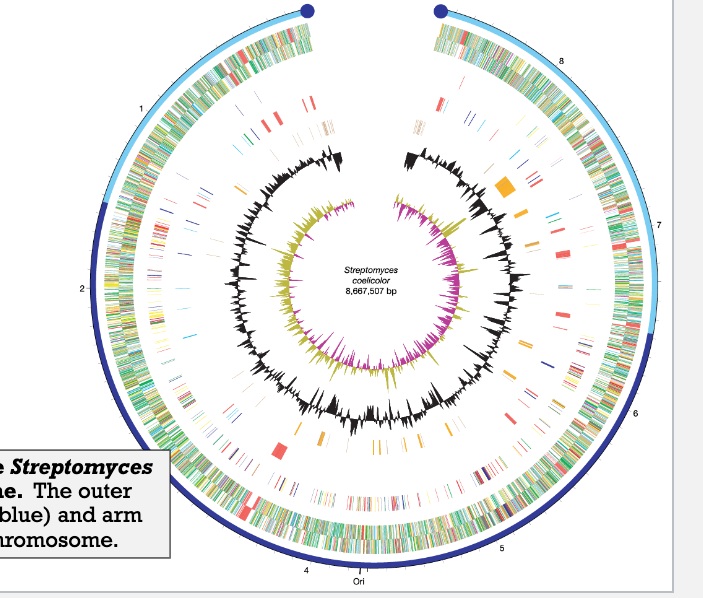
What is the light blue on the graph
Arms of the linear S. coelicolor chromosome, which may contain non-essential or adaptive genes.
Most Streptomyces isolates harbor a linear
chromosome. However, some lab isolates have
a circular chromosome that has been generated
following recombination between the two
“arms” of a linear chromosome (the light blue
regions of the outer scale in the figure). What
property of these “arms” enable such a process
to occur?
They only contain nonessential genes
PGL system of S. coelicolor
a defense mechanism against the temperate bacteriophage φC31 and its homoimmune relatives
How does the PGL system work?
PGL+ hosts to support an initial phage burst, but subsequent cycles are severely attenuated due to nonlethal modification
Will a phage that was released from a pgl+ host be able to subsequently live in a pgl- host?
Yes because the modification is nonlethal so they can efficiently infect a Pgl – host to give successive rounds of normal phage burst
glY and pglZ do not constitute the whole Pgl system....so where in the genome should we start looking for additional pgl genes?
Using the cosmids from shotgun sequencing, they looked nearby pglYZ and found pglWX
Why do Streptomyces species make antibiotics
to inhibit competing microbial species and secure resources in their environment.
How can we take advantage of the S. coelicolor clusters which encode secondary meltabolites (antibiotics)
creating new chemicals by splicing together genes from different biosynthetic clusters.
The S. coelicolor A3(2) genome sequence identified that genes
involved in the generation of secondary metabolites are grouped
together in clusters, each cluster making a different chemical. How
is information about the function of each gene in these clusters being
used to help synthesize novel compounds with unique properties?
genetic engineering is being used to mix and match genes from
different clusters, generating entirely new chemicals