Exam 6 UC cohort 2027 physio endo (59 ppts)
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Hypothalamus Hormones named
TRH
Dopamine
Growth hormone release hormone
Somatostatin
Gonadotropin relase hormone
oxytocin
vasopressin
Pineal gland hormone
Melatonin
Anterior pituitatry hormone
GH
TSH
ACTH
FSH
LH
Prolactin
Posterior Pituitary Hormone
ADH
OXYTOVIN
VASOPRESIN
Thymus hormone
Thymopoeitin
Liver Hormone
IGF ,THPO
Stomach
Gastrin
grehlin
Histamine
Somatostatin
Neuropeptide Hormone
Adrenal hormone
Androgens
glucocorticoids
Adrenaline
Noradrenaline
Kidney Hormone
EPO
Calcitrol
Renin
Testes Hormones
Testosterone inhibin
Estradiol
Pancreas hormone
Insulin
Somatostain
glucagon
Uterus hormones
Relaxin
Prolactin
How do endocrine gland respond to specific signals?
by synthesizing and releasing hormones into the circulation
Endocrine gland are capable of ?
of synthesizing and releasing hormones (special chemical messengers).
Endocrine system functions
–Differentiation of the reproductive and central nervous systems in the developing fetus
–Stimulation of sequential growth and development during childhood and adolescence
–Coordination of the male and female reproductive systems
–Maintenance of an optimal internal environment
–Initiation of corrective and adaptive responses when emergency demands occur
•Chemical messengers that are released by glands
Hormones are
Autocrine
Within cells
Paracrine
Nearby cells
Endocrine communication
Between remote cells
Hormone release is regulated by
–Chemical factors (blood glucose or calcium levels)
–Endocrine factors (a hormone from one gland controlling another endocrine gland)
–Neural control (stress-induced release of catecholamines from adrenal medulla)
blood glucose or calcium levels
Chemical factors
a hormone from one gland controlling another endocrine gland
Endocrine factors
stress-induced release of catecholamines from adrenal medulla
Neural control
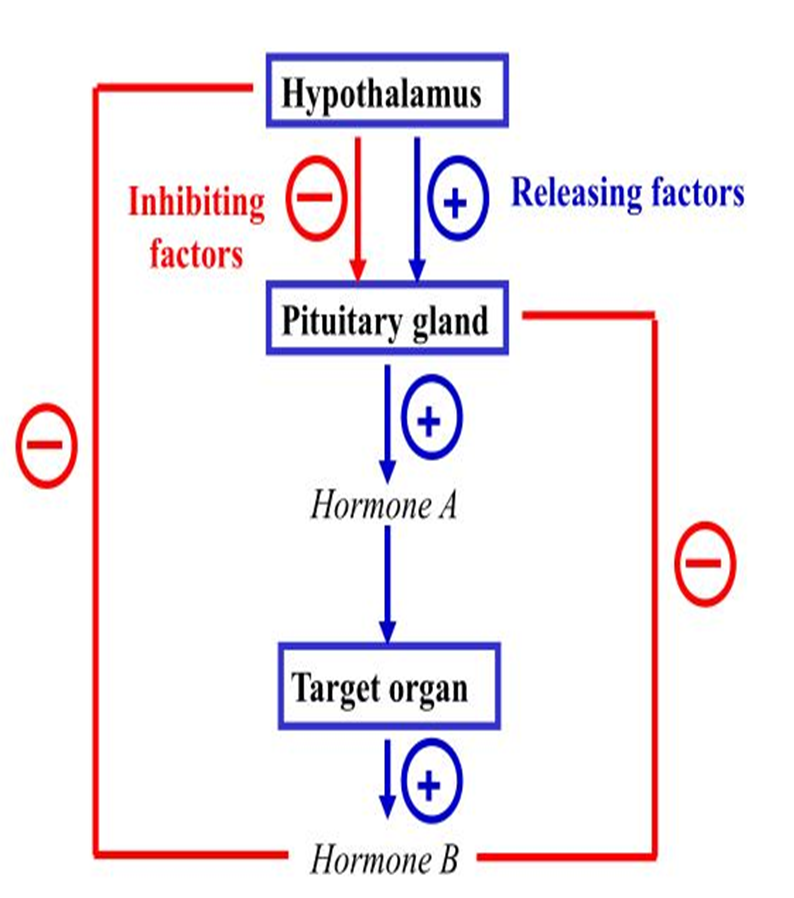
–Maintains an optimal internal environment (homeostasis) : positive feedback or negative feedback
•Products of a cycle act upon its gland of origin to shut off secretion (as a means to prevent excess secretion)
Negative Feedback Loops
hormones that have other endocrine glands as their target
Trophic hormone
At which levels negatives feedback is possible
ultrashort (target cells)
short (anterior pituitary gland)
long(hypothalamus)
–Recognize and bind with a high affinity to hormones.
–Initiate a signal transduction into the cell nucleus
Target cells
The more receptors
more sensitive is the cell
True or false : •Hormones Affect Only Cells With Appropriate Receptors
True
Mechanism of hormones
•Act on Cells to Initiate Specific Cell Functions
True or false : Hormones are Chemical Messengers
True
–hormones circulate in free, unbound forms (insulin 3-4 min half-life)
Water-Soluble hormone
–hormones are primarily transported bound to a carrier or transport protein. (half-life of hours to days)
Lipid soluble
Hormones differ by solubility name those class of hormones
Polypeptides (not lipid soluble,bind to receptors on surface of target cells): Secretin
Amino Acids (Epinephrine) : most not lipid soluble bind to receptors on surface of the target cells
steroids(Cortisol) lipids soluble often bind to receptors inside target cells
Steroid and sterols
Pepetides and glycoproteins
Monoamines
Others classification of Hormones
Monoamines hormones
Dopamine
Epinephrine
Melatonin
Norepinephrine
Hormone Receptors: Location
Plasma membrane or in the intracellular compartment of the target cell. May be G protein–linked, ion channels, or enzyme linked.
–Have a high molecular weight.
–Cannot diffuse across the plasma membrane.
•Water-soluble hormones
–Easily diffuse across the plasma membrane and bind to cytosolic or nuclear receptors.
•Lipid-soluble hormones
•Up-regulation
–Low concentrations of hormones increase the # of receptors per cell
–High concentrations of hormones decrease the # of receptors.
•Down-regulation
Specific Rates and Rhythms of Secretion
–(1) Circadian or diurnal patterns - MELATONIN
–(2) Pulsatile and cyclic patterns – secreted in bursts (GH)
–(3) Patterns that depend on circulating substrates (calcium, potassium, or hormones themselves) – CORTISOL
Circadian or diurnal patterns
Melatonin (pineal gland )
Pulsatile and cyclic patterns
Secretes in bursts (GH)
Patterns that depend on circulating substrates
Cortisol
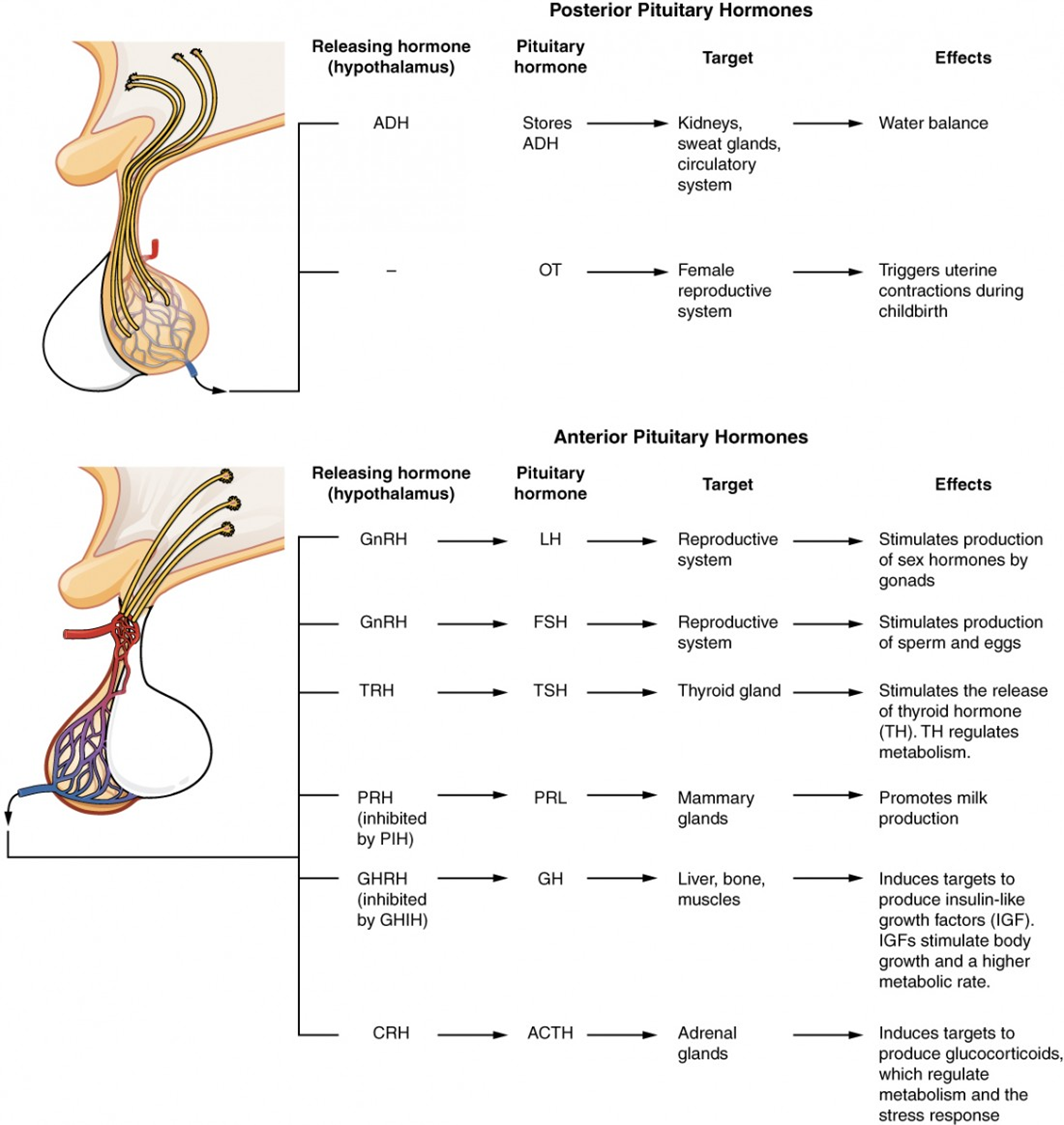
Identify each hormone and their effects on the target cells
•First Messenger
•Hormone that carries the message to the target cell
•Process by which this message is communicated into the target cell
•Involves several steps
•Signal Transduction
Transduction steps
1- Hormone is the first messenger that is secreted into the blood stream
2- Receptors activation of a hormone to its receptor
3- activation of G proteins (Transducer) and membrane associated enzyme (effector enzyme)
4- Production of second messenger
5- Activator of intracellular enzyme such as protein Kinase A or C
6- Alternation in gene transcription and the the resulting target cell response to the hormone
catabolized by circulating enzymes and eliminated in the feces or urine
Peptide hormones are
Metabolized (conjugated) by the liver which inactivates them and renders the hormone more water soluble for renal excretion
Steroid Hormone
Excreted directly by the kidneys
Steroid Hormone
1.Act on preexisting channel forming proteins to alter membrane channel permeability
2- Activating preexisting proteins through a second messenger system
3- Activating genes to cause protein synthesis
Binding of hormones initiates 3 types of effect
1.Direct-changes in cell function
2.Permissive-less obvious hormone changes that affect cell function (insulin increases glucose transport into skeletal muscle cells)
General effects of hormones on target cells:
located at the base of the brain.
Hypothalamus
is located at the sella turcica, a saddle-shaped depression on the surface of the sphenoid bone
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus Divided into several nuclei and nuclear areas which are :
Supraoptic
Paraventricular
median eminence
How Hypothalamus communicate with the pituitary gland
Via the 03 nucleus (Supraoptic-paraventricular-median eminence)
By which tract The hypothalamus is connected to the posterior pituitary
supraopticohypophysial
The hypothalamus is connected to the anterior pituitary
Blood vessels
•Controlled by the hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
known as the “master gland”
Pituitary gland
–Releasing hormones stimulate the pituitary to produce tropic hormones (hormones that have other endocrine glands as their target)
–Controls many of the other glands of the endocrine system
Pituitary gland
Pituitary Gland Division
Anterior Pituitary
Posterior Pituitary
The basis for central integration of neurologic and endocrine systems
the neuroendocrine system.
Hormones that affect diverse body function
Tropic hormones
•It secretes releasing and inhibiting hormones
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis
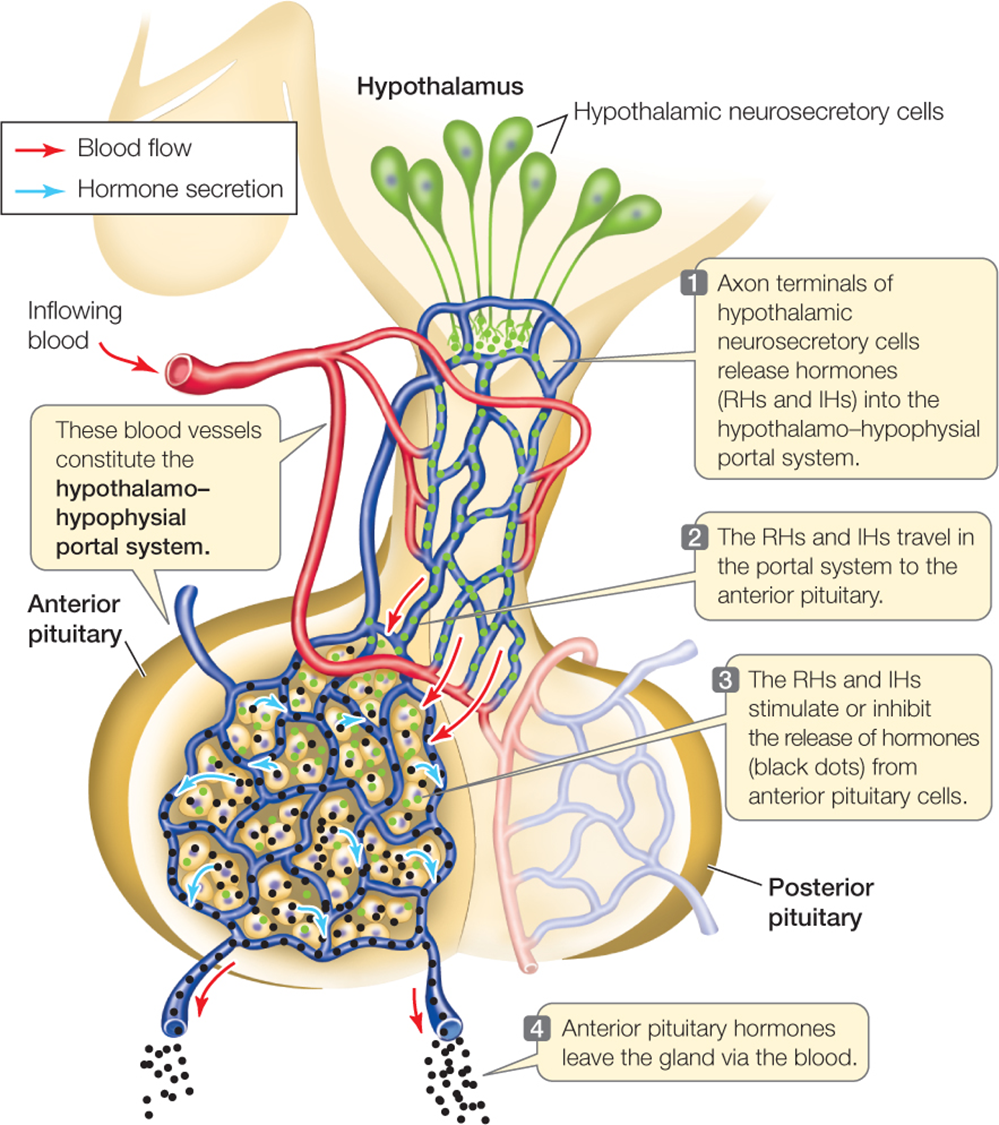
Actions of tropic hormones
In response of the HPA the pituitary releases
____ into general circulation to control activities of other endocrine glands.
Inhibting hormones actions
•Inhibitory hormones suppress pituitary secretions by:
•Inhibiting the pituitary gland
•Inhibiting the hypothalamus
•Inhibitory hormones are a negative feedback mechanism secreted by:
•Target endocrine hormones (ex thyroid)
•Hypothalamus
Secretion of posterior pituitary hormones is controlled by
Nerves reflexes
Not glandular
Posterior pituitary gland
Serves as a site for the secretion of hormones directly into the blood
Neurohypothesis
–Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, arginine vasopressin)
•Controls plasma osmolality.
•Causes water reabsorption in the kidneys.
•Is released when plasma osmolality is increased or intravascular volume is decreased.
•Causes uterine contractions and milk ejection (let-down) in lactating women.
Reduces the brain’s responsiveness to stressful stimuli, especially in pregnant and postpartum states
–Oxytocin
example of positive feedback.
Oxytocin
Example of hormones control by negative feedback
Thyroid
•Induces milk production during pregnancy and lactation.
Has effects on reproductive and immune functions
Prolactin and Oxytocin
–Melatonin regulates circadian rhythms and reproductive systems, including secretion of GnRH and the onset of puberty.
–Plays an important role in immune regulation.
–Possibly affects the aging process.
Pineal Gland
•Is located within the brain itself.
•Is made up of photoreceptive (light and dark) cells that secrete melatonin.
Pineal Gland