Intro to Economics (non micro/macro specific)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
economics
Social Science concerned with the efficient usage of scare resources to achieve economics wants
Categories of Economic resources
Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurial
Land
natural resource involved in production
Labor
Human effort involved in production
Capital
Man made object involved in production
entrepreneurial ability
innovative process of creation and risk taking
Scarcity & Choice
Resources are limited forcing individuals and firms to make choices
Utility
humans act in order to maximize satisfaction
self interest
assumption that individuals act to maximize their personal benefit
Marginal analysis
Marginal cost vs marginal benefit
Other things equal assumption (Ceteris paribus)
assumption that non focus factors remain constant
Microecnomics
Concerned with decision making of individuals, households, and firms
Macroecnomics
Examines the economy as a whole and aggregate variables.
Positive economics
Focused on facts and cause and effect relationships, establishes scientific statements
Normative economics
Incorporates value judgements about what economy should be like
Economizing Problem
The need to make choices, as wants exceed economics means
Budget Line
Graphical display of goods a consumer is able to purchase with a specific income
Production possibility curve
Combination of goods and services that can be produced with a given set of resources
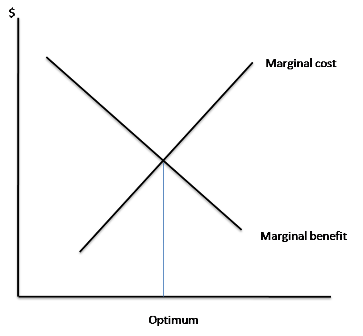
Optimal allocation
MB=MC
opportunity cost
the cost of forgoing a choice
Law of increasing opportunity cost
as more of one good is produced less of another can be produced.
Laissez-Fare capitalism
very limited government role
Command system
Government owns most resources. economic decision making set by central planning
The market system
Used by vast majority of world’s economy. Private ownership of resources. mixture of centralized and decentralized action.
Private property
ownership of private property plays a large role in market system. includes the right to negotiate contracts and use resources as seen fit.
Freedom of enterprise
Firms are free to use resources to produce their choice of goods in their chosen market.
Competition
2 or more buyers or sellers acting in a market with freedom to enter and exit market.
specialization
devoting resources to produce one or few goods to increase efficiency
division of labor
divide labor force to specialize and maximize outputs
Geographic specialization
production that optimally aligns with local geographic factors
5 fundamental questions
-What will be produces
-how will it be produced
-who will receive the output
-how will the system change
-how will the system promote technological advancement
The invisible hand
firms seeking to further their self interest in a competitive market will be guided in favor of public interest
Demise of command system
coordinating and incentive problem
circular flow model
the dynamic market creates a continuous and repetitive flow of goods, resources, and currency.
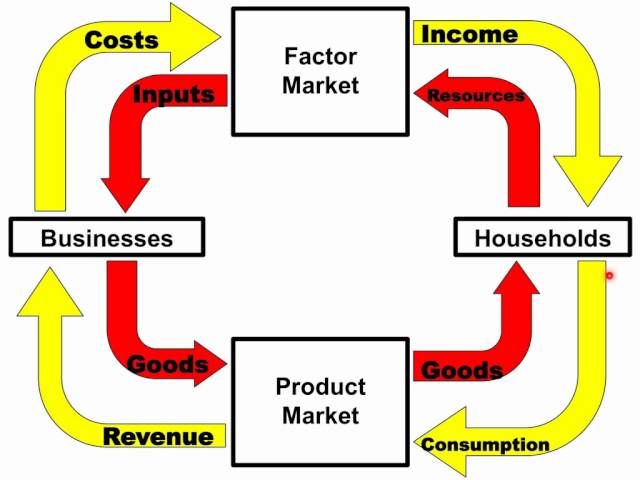
circular flow model (image)
households
buy goods and obtain income by selling resources
businesses
sell goods and services to obtain revenue. Purchase resources to produce goods.
Product market
households purchase goods and money spent goes to businesses.
Resource market
households sell resources to businesses in order to produce goods.
Risk
the market system creates risk. owners subject to risk and are residuals claimant.
Benefits of limiting risk
-attracting inputs
-focusing attention
creative destruction
new advanced products outcompete an outdated product
Optimal output graph
Future consideration
investing in future goods allows for the PPC to shift outwards
Absolute advantage
one group is better at producing a good (faster and more)
Comparative advantage
One group is relatively better at producing a good through lower opportunity cost
Benefit of trade
Through specialization there is net increase in total goods produced by all groups.
PPF shifted outwards
technology advancements, trade, capital formation
Demand
The amount of a product consumers are willing to purchase at a given price
Law of demand
other things equal, as price falls the quantity demanded rises, and as price rises demand falls.
Demand curve
represents the inverse relation between demand and price. Negative slope.
Determinants of demand
consumer preference, number of buyers, consumer income, price of related goods, consumer expectation
Movements along demand curve
change in product price
Demand curve shifts right
more demanded at every price
Demand curve shifts left
less demanded at every price
Supply
Amount of good producers are willing to make available at a series of prices
Law of supply
Positive relation as price rises, the quantity supplied increases.
Determinants of Supply
Resource prices, technology, taxes & subsidies, price of other goods, and number of sellers in market.
Equilibrium Price/quantity
the intentions of buyers and sellers align
Characteristics of a competitive market
many buyers and sellers and standard product
Network effect
Value increases with more users
Congestion effect
values decreases with greater use
Complimentary goods
goods used together, demand increases in tandem
Inferior Goods
demand decreases and income increases
Normal goods
demand increases as income increases
Substitute goods
goods that can replace eachother
Independent goods
vast majority of goods that are unrelated
Greatest effect on quantity supplies
price of good
Market clearing price
equilibrium price where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
Productive efficiency
producing goods at the lowest possible cost
allocative efficiency
producing the right mix of goods that the market demands
rationing function
buying and selling decisions are consistent
price ceiling
maximum legal price a seller may charge for a good
law of diminishing marginal utility
as a person consumes more of a good the satisfaction (utility) decreases with each additional good
Demand Increase, Supply constant
P increase + Q increase
Demand decrease, supply constant
P decrease + Q decrease
supply increase, demand constant
P decrease + Q increase
supply decrease, demand constant
P increase + Q decrease
Demand increase + supply increase
P ? + Q increase
Demand decrease + supply decrease
P ? + Q decrease
Demand increase + supply decrease
P increase + Q ?
Demand decrease + supply increase
P decrease + Q ?
determinants of demand
(1) Price of the product, (2) Income of the buyers, (3) Prices of related goods (substitutes/complements), (4) Tastes and preferences, and (5) Consumer expectations regarding future prices.
determinants of supply
1) Input costs (resource prices), 2) Technology advancements, 3) Government actions (taxes/subsidies), 4) Number of sellers, 5) Producer expectations of future prices, and 6) Prices of related goods.