Bio Characteristics of living organisms
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
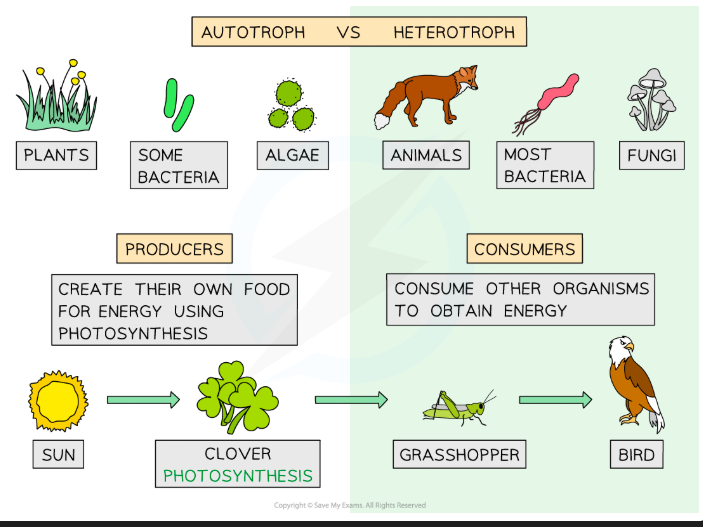
Qualifications of something to be considered “Living”
Movement
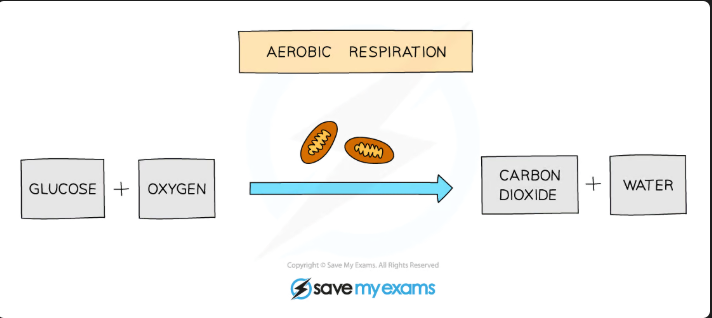
Respiration
Sensitivity
Control
Growth
Reproduction
Excretion
Nutrition
Definition of Nutrition
food obtained by organisms to provide Energy.
Definition of Respiration
A chemical reaction carried out in all living organisms, Energy is released from glucose either in the presence of oxygen(aerobic respiration) or the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration)
Definition of Excretion
The removal of toxic materials and substances from living organisms.
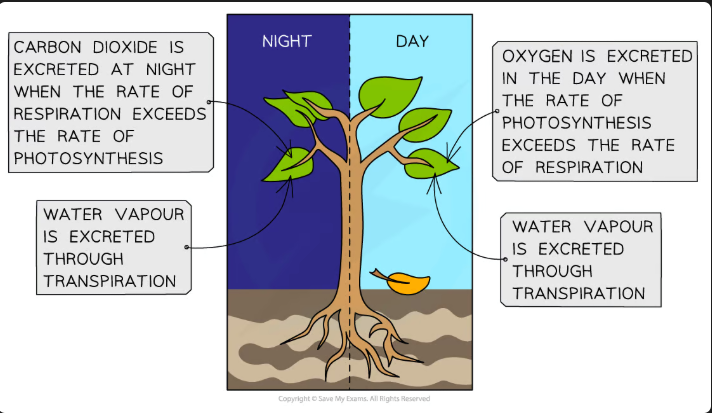
Excretion in plants
Waste products excreted by plants include:
Oxygen from photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide from respiration
Water from respiration and other chemical reactions
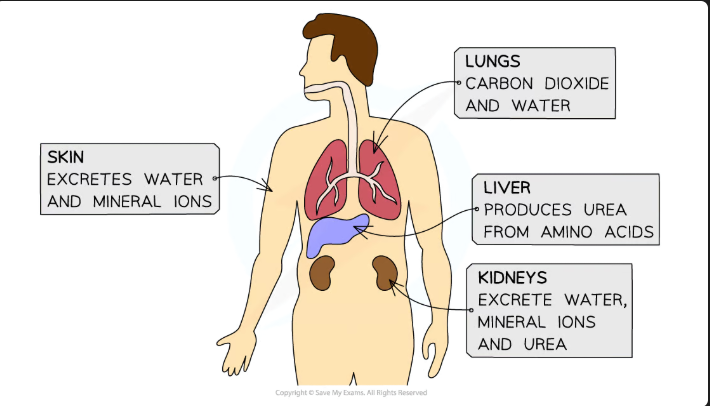
Excretion in animals
Waste products excreted by animals include:
Carbon dioxide from respiration
Water from respiration and other chemical reactions
Urea which contains nitrogen resulting from the breakdown of proteins
Definition of Sensitivity
The ability to detect and respond to stimuli in its surroundings.
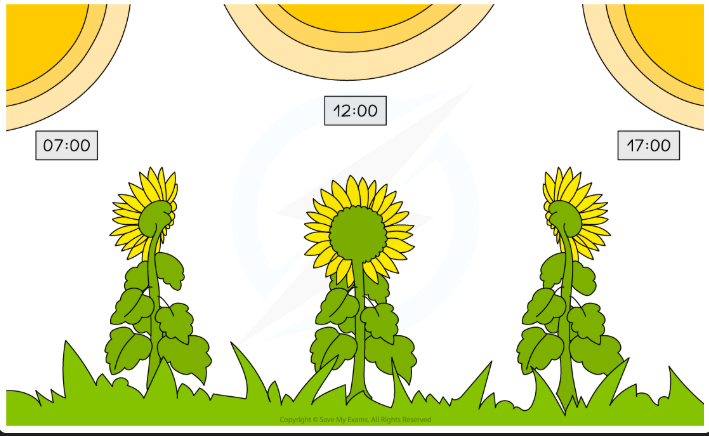
Definition of Movement
An action by an organism causing a change of position or place. For example, sunflowers track the sun and so change their orientation throughout the day
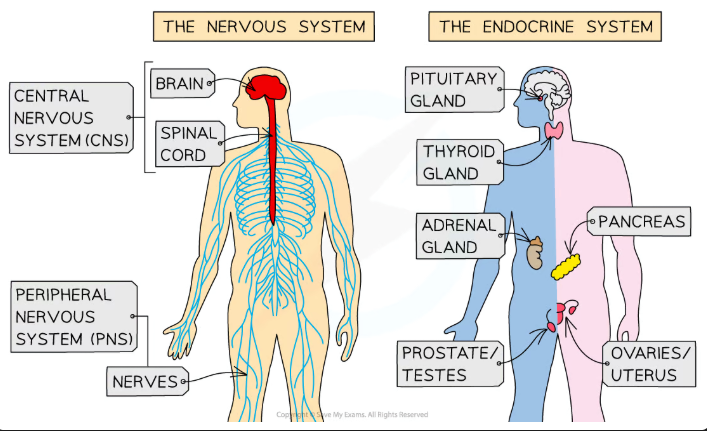
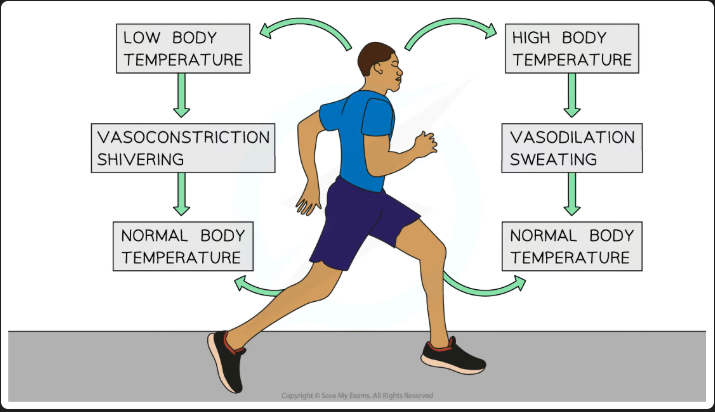
Definition of Homeostasis
The control of the internal environment in order to keep conditions within required limits. The optimum human body temp is 37°C
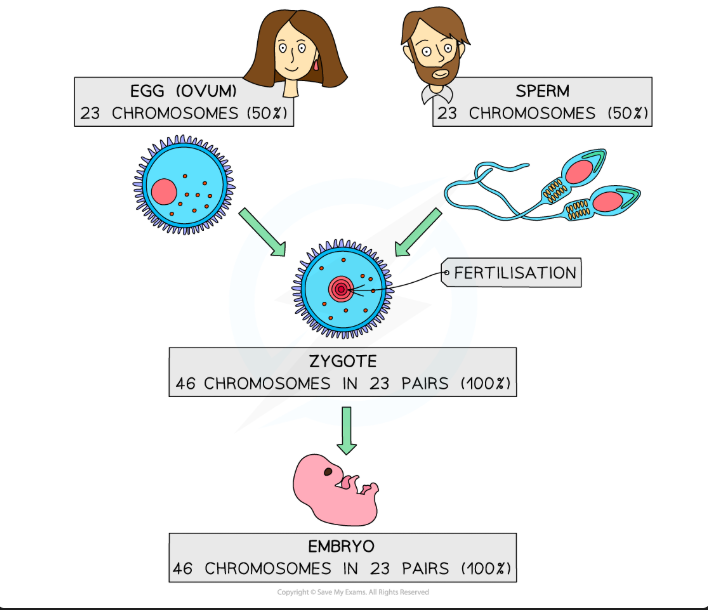
Definition of Reproduction
The process that leads to the production of more of the same kind of organism. It is fundamental to the survival of a species.
Definition of Growth
A permanent increase in size. in animals, an individual grows larger between the zygote and adult stage. In plants, an individual grows larger throughout their whole life with new shoots, leaves, branches etc…
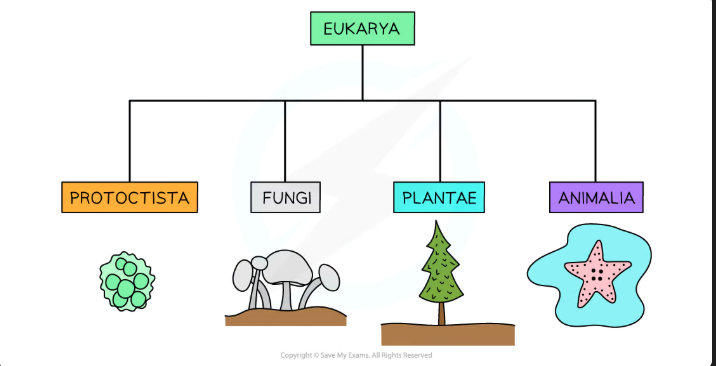
Five kingdoms of Living organisms
Animals
Plants
Fungi
Protoctists
Prokaryotes
Definition of Eukaryotes
Multicellular or single-celled and are made up of a nucleus with a distinct membrane.
Animals
Main features of Animals:
Multicellular
Their cells contain a nucleus
They do NOT have cell walls
They often store carbohydrates as glycogen
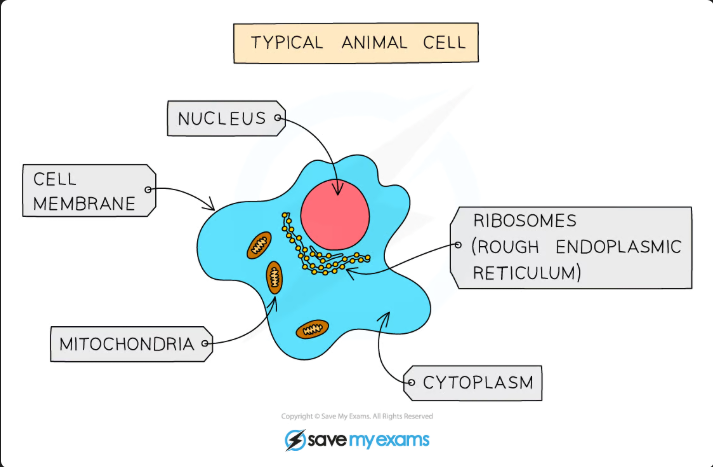
Cell structures found in both Animals and Plants
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Ribosomes
Mitochondria

Plants
Main features of plants:
Multicellular
Their cells contain a nucleus
They DO have cell walls
They contain Chloroplasts
They feed by Photosynthesis
They store carbohydrates as Starch or sucrose
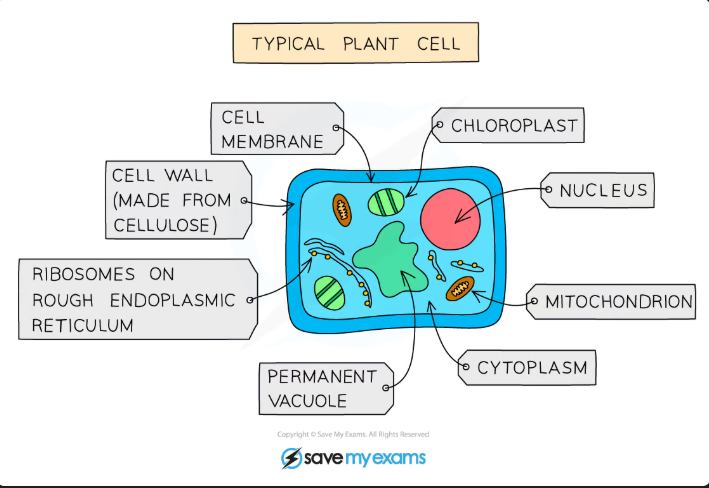
Cell structures found only in plants
Cell wall
Chloroplasts
Permanent vacuole

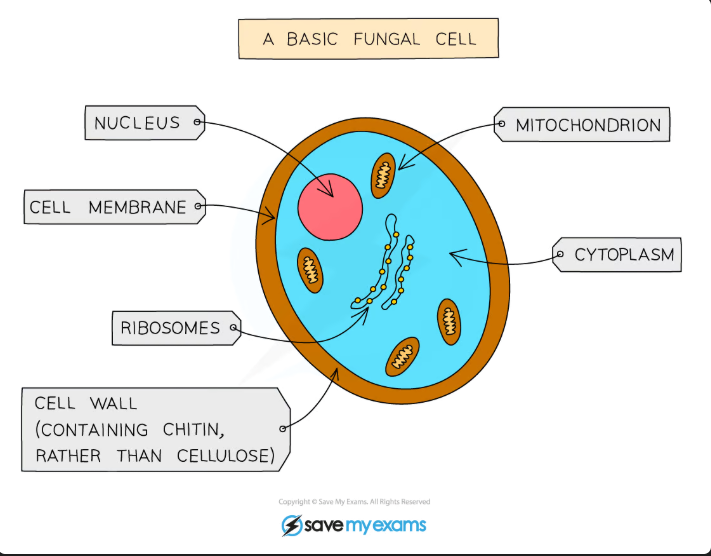
Fungi
Main features of fungi:
Usually multicellular, but some are single-celled
They contain a nucleus
They have Cell walls made of Chitin
They store carbohydrates as glycogen
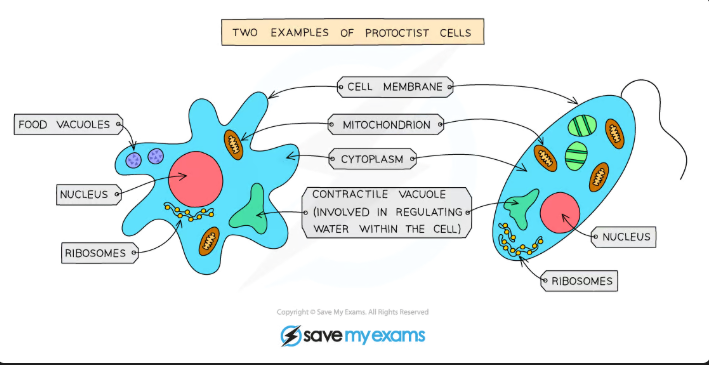
Protoctists
Main features of Protoctists:
They are very diverse and dont really belong in any of the other eukaryotic kingdoms(animals, plants, and fungi)
They are mainly single-celled, but some can form together into larger forms
They contain a nucleus
Some have features making them more like animal cells(e.g, Chlorella)
This means some protoctists can photosynthesise and some feed on other substances
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are different from the other four kingdoms, which are eukaryotes. Features of prokaryotes include:
single-celled
They have NO nucleus
The nuclear material is found in the cytoplasm
Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms
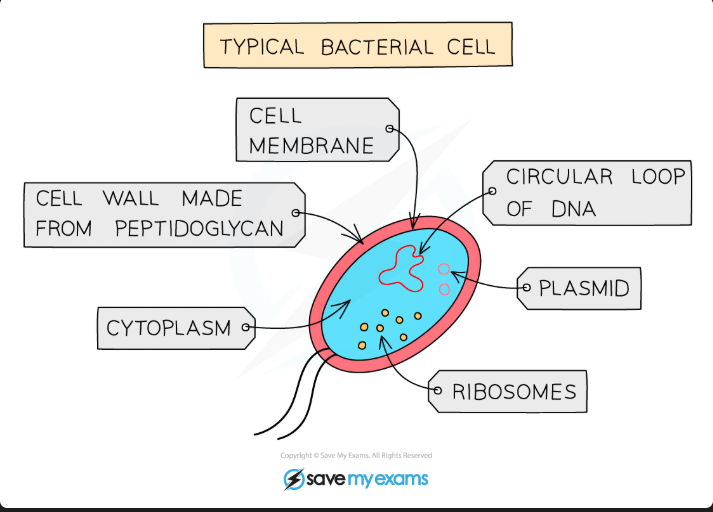
Bacteria
Bacteria are:
Single-celled organisms
They have a cell wall, cell membrane cytoplasm AND plasmids
They lack a nucleus but contain circular DNA
They lack Mitochondria and have NO membrane bound organelles
Examples of Bacteria
Lactobacillus
A rod-shaped bacterium used in the production of yoghurt from milk
Pneumococcus
A spherical bacterium that acts as the pathogen causing pneumonia
How bacteria feeds
SOME Bacteria can carry out photosynthesis despite having no chloroplasts, this is due to them possessing chlorophyll
Most feed on other living or dead organisms, if they feed on dead organic matter then they are known as decomposers.