Histo Lab- Integumentary System (Aughey)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
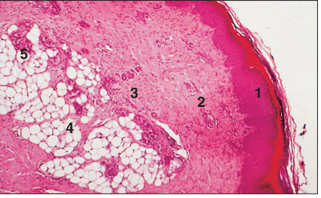
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Digital pad (cat). (1) Epidermis: stratified squamous keratinized epithelium. (2) Dermis: connective tissue. (3) Hypodermis: loose connective tissue. (4) Adipose tissue. (5) Sweat glands. H & E. ×20.
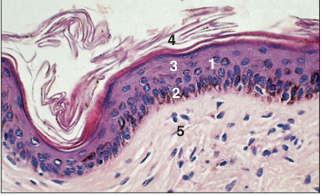
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Thin hairless skin (horse). (1) The epidermis is three layers deep. The basal germinal layer (2) has melanocytes and clear cells; the middle layer (3) is hexagonal keratocytes; and the surface layer (4) is dead squames in the process of being shed. (5) Dermis: vascular connective tissue. H & E. ×125.
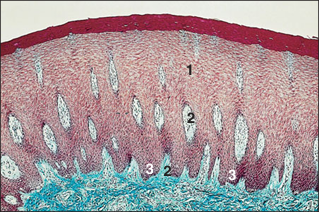
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Dental pad– thick skin (ox). (1) The epidermis is at least 20 cells deep. (2) Dermal papillae project into the epidermis, necessary for the nutrition of the epidermal cells. (3) Equivalent epidermal pegs. Masson’s trichrome. ×62.5.
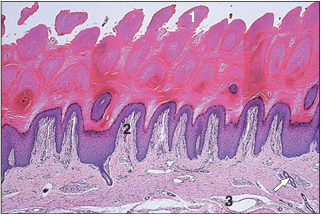
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Digital pad– thick skin (dog). (1) The epidermis is heavily keratinized. (2) Dermal papillae project into the epidermis. (3) Hypodermis: loose connective tissue with sweat glands (arrowed). H & E. ×62.5.
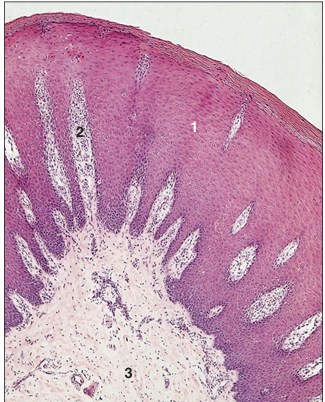
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Planum nasale– thick skin (ox). (1) The epidermis is at least 20 layers of cells; the surface cells are keratinized. (2) Deep vascular dermal papillae project into the epidermis. (3) Hypodermis. H & E. ×62.5.
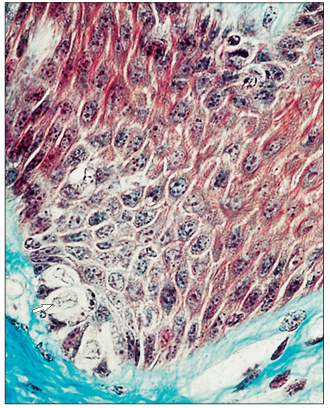
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Epidermis– stratum germinativum (basale; ox). Clear cells (arrowed) lie in the basal germinal layer of columnar keratocytes. Masson’s trichrome. ×250.
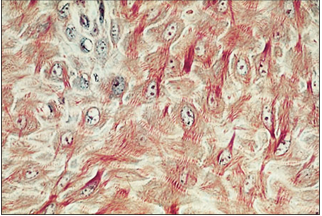
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Epidermis– stratum spinosum (prickle cell layer; ox). The hexagonal keratocytes have a large clear nucleus. The cytoplasm has extensive spines or prickles around the circumference. Masson’s trichrome. ×250.
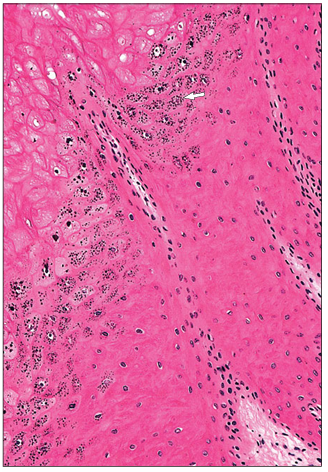
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Epidermis– stratum granulosum. Hoof (horse). The keratocytes have distinctive deep blue granules in the cytoplasm (arrowed). H & E. ×125.
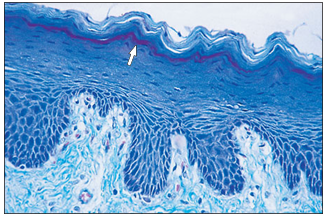
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Epidermis– stratum lucidum (dog). Digital pad. The bright thin line (arrowed) marks the clear layer of thick skin. Gomori’s trichrome. ×100.
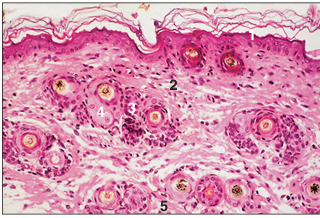
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Thin skin (cat). (1) Epidermis with two layers of keratocytes. The free surface shows desquamating dead cornified cells. (2) Dermis. (3) Groups of hair follicles. (4) Sebaceous glands. (5) Smooth muscle. H & E. ×62.5.
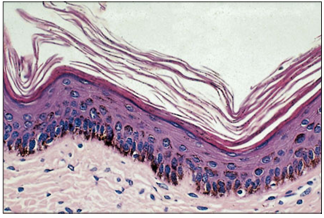
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Pigmented skin (cat). The epidermis is four cells thick; melanocytes with brown pigment granules are present in the basal layer, the stratum germinativum. H&E. ×125.
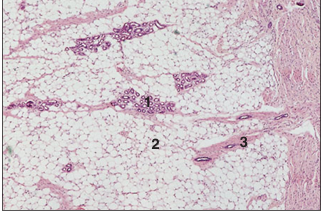
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Digital pad– hypodermis (dog). (1) Sweat glands. (2) Fat cells. (3) Connective tissue. H & E. ×62.5.
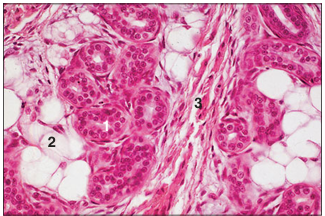
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Digital pad– hypodermis (cat). (1) Sweat glands. (2) Fat cells. (3) Connective tissue with blood vessels. H & E. ×125.
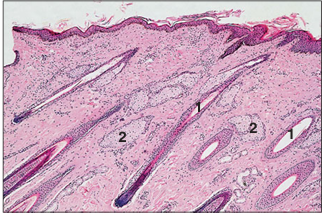
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Skin (horse). (1) Single hair follicles are present in the dermis. (2) Sebaceous glands. H & E. ×62.5.
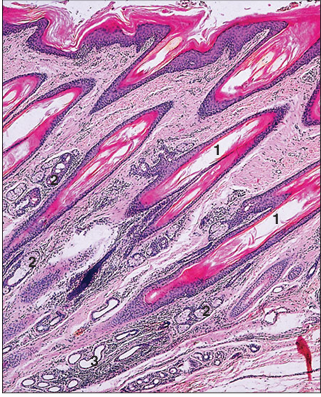
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Skin (dog). (1) Single hair follicles are present in the dermis of the digital pad. (2) Sebaceous glands. (3) Sweat glands. H & E. ×125.
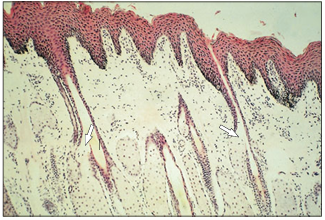
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Flank skin (horse). The sebaceous glands are numerous, associated with the hair follicles, often opening directly into the follicle (arrowed). H & E. ×25.
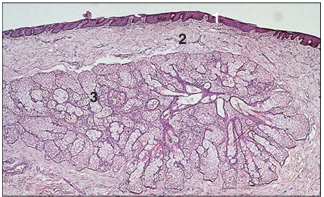
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Eyelid (horse). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Tarsal gland, sebaceous secretion. H & E. ×62.5.
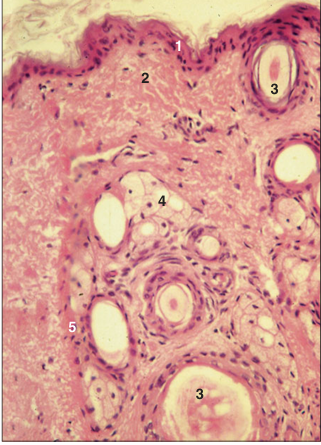
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Skin (sheep). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Hair follicle. (4) Sebaceous glands. (5) Arrector pili muscle; contraction assists expression of the sebum. H & E. ×160.
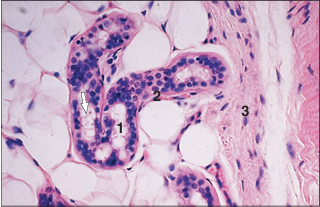
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Apocrine sweat gland (dog). (1) Gland tubule lined by a simple columnar epithelium; secretory blebs are arrowed. (2) The myoepithelial cells lie between the secretory cell and the basement membrane. (3) Dermal connective tissue. H & E. ×160.
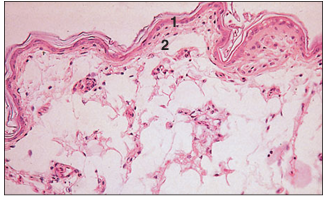
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Skin (bird). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. H & E. ×25.
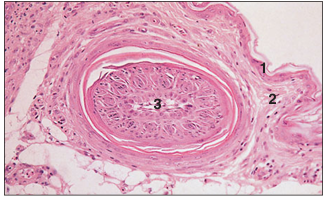
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Skin (bird). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Developing feather follicle. H & E. ×62.5.
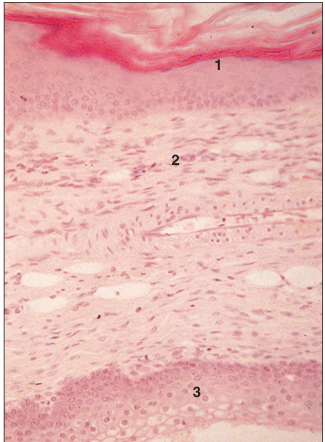
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Uropygial gland (bird). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Lobar duct lined by stratified epithelium. H & E. ×62.5.
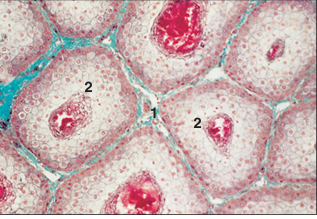
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Uropygial gland (bird). (1) Connective tissue. (2) Secretory glands units. Masson’s trichrome. ×100.
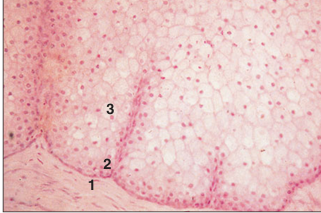
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Uropygial gland (bird). (1) Connective tissue. (2) Basal layer of the secretory epithelium. (3) Superficial layers of fat filled cells. H& E. ×250.
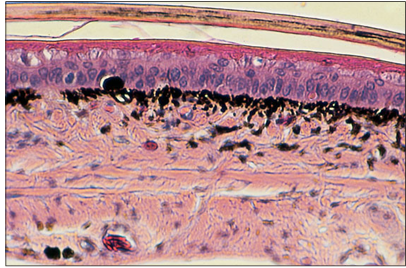
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Section of pre-ecdysis integument of a mountain kingsnake (Lampropeltis zonata). The uppermost keratinized, lightly pigmented, pale pink layer is disengaged from the lightly cornified eosinophilic epithelium that lies immediately above the stratified squamous layer. Numerous black melanophages are present in the upper dermis. H & E. ×125.
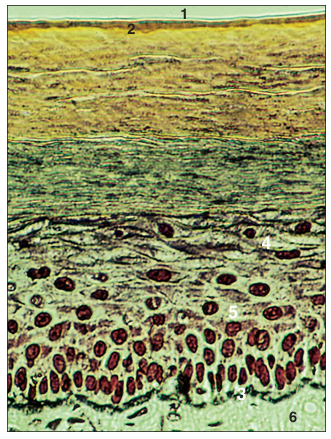
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__ 6.__
Stain used:
Immediately beneath the squamous epithelium of the section in 16.33are dendritic neurons that, when treated with silver-containing dyes, stain black. (1) Senescent stratum corneum. (2) Current stratum corneum. (3) Stratum basale. (4) Stratum granulosum. (5) Stratum spinosum. (6) Dermis. Bodian’s silver. ×125
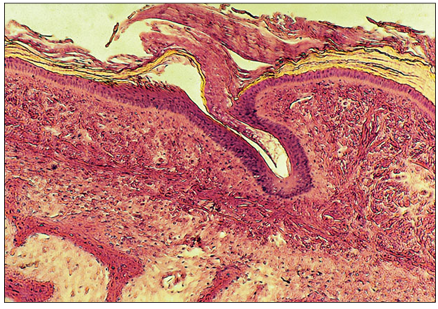
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Rattle of a small Mexican rattlesnake (Crotalus enyo). This keratinized structure forms as a button-like protruberance to which a loosely interlocking segment is added each time the snake moults its integument. The most cranial segment retains a living core of dermis, whereas the tissues of the distal segments are no longer living. H & E. ×12.5.

name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
The carapacial shell of a red eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans), is covered by a layer of horn-like keratin (1) and a variable thickness of stratified squamous epithelium (2). The dermis is variable in thickness, depending upon the size and species of the turtle. It covers multiple layers of membranous compact and cancellous bone in which bone marrow fills the cancellous spaces. H & E. ×62.5.
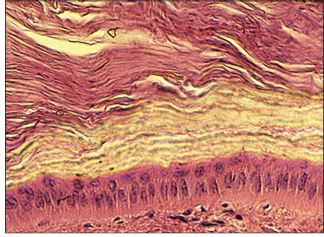
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Section of the most superficial layers of the keratinized carapace of a terrestrial tortoise (Xerobates agassizi). Most terrestrial tortoises possess a much thicker carapacial and plastral shell than aquatic turtles or terrapins of the same size. H & E. ×100.
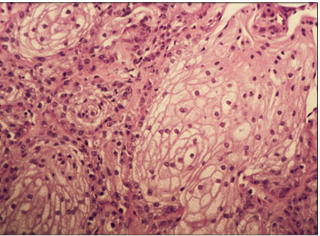
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Mental gland from a desert tortoise. This modified sebaceous glandular structure is believed to produce a pheromone-rich secretion that initiates and at least partly mediates premating courtship behaviour. H & E. ×100.
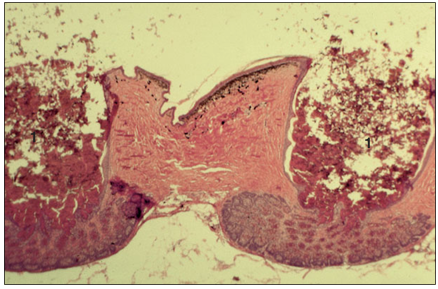
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
A cross-section of the skin of the ventral thigh of a sexually mature male green iguana (Iguana iguana), containing two femoral pores (1). The eosinophilic holocrine secretion from these glands is exuded as a waxy substance. H & E. ×12.5.
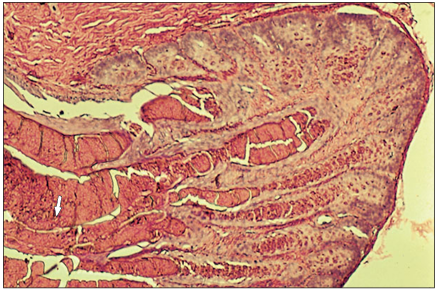
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Medium-power magnification of a femoral pore from a male iguana. Note the eosinophilic secretion and cellular debris being extruded into the ductal system that empties its contents onto the epidermal surface (arrow). H & E. ×100.
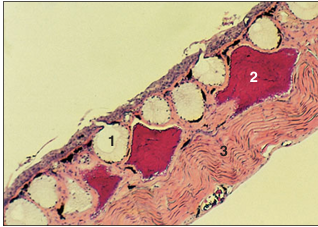
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Full thickness section of the skin of an African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis). The integument contains two types of glandular structures: (1) clear-staining mucus-secreting glands and (2) highly eosinophilic poison glands. The secretory products of both are carried to the skin surface via short ducts. (3) Much of the thickness of the subepithelial tissue is comprised of skeletal muscle fibres. H & E. ×12.5.
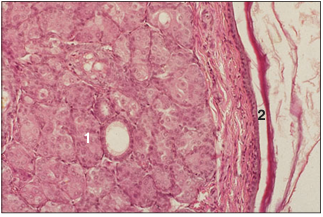
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Anal gland (cat). (1) Tubular, saccular sweat glands in the circumanal connective tissue. (2) Anus lined by stratified squamous keratinized epithelium. H & E. ×100.
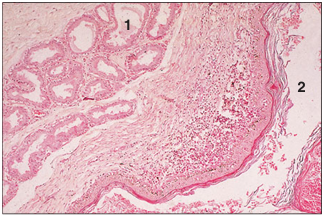
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Anal sac (dog). (1) Apocrine tubular glands. (2) Anal sac. H & E. ×62.5.
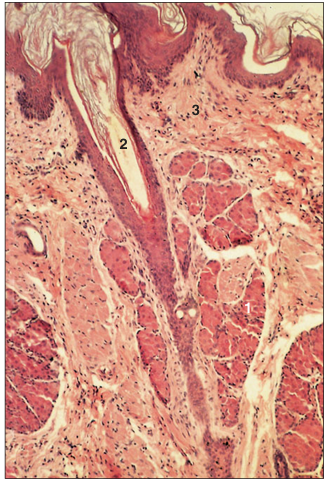
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Perianal sinus (dog). (1) The glands are a mixture of sebaceous and sweat glands. (2) Hair follicle. (3) Dermal connective tissue. H & E. ×125.
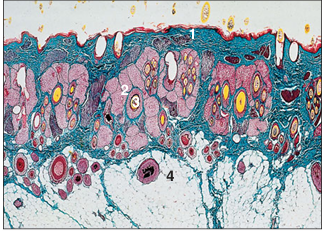
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Supracaudal organ (cat). The supracaudal organ or tail gland is an area of sebaceous secretory units in the tail region; the secretion is used in grooming. (1) Epidermis. (2) Sebaceous glands. (3) Hair follicles. (4) Hypodermis. Sacpic staining method. ×12.5.
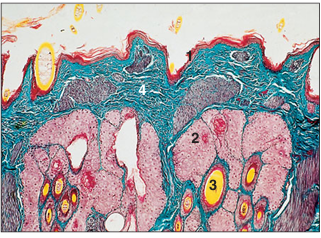
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Supracaudal organ (cat). (1) Epidermis. (2) Sebaceous glands. (3) Hair follicles. (4) Dermis. Sacpic staining method. ×100.
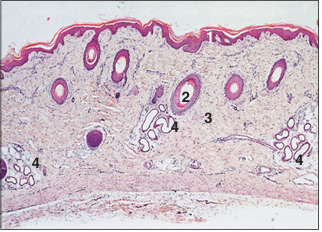
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Carpal skin (pig). (1) Epidermis. (2) Hair follicles are distributed singly. (3) Dermis. (4) Merocrine carpal sweat glands. H & E. ×12.5
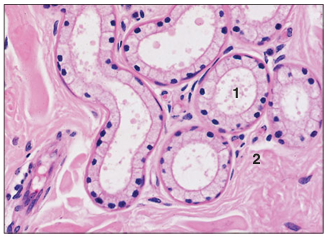
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Carpal skin (pig). (1) Merocrine sweat glands are lined by a cuboidal epithelium. (2) Dermis. H&E. ×125.
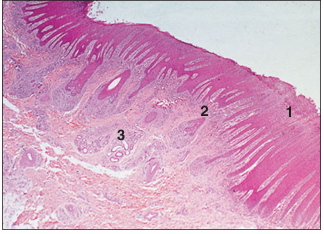
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Interdigital skin (sheep). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Sebaceous and sweat glands. H & E. ×12.5.
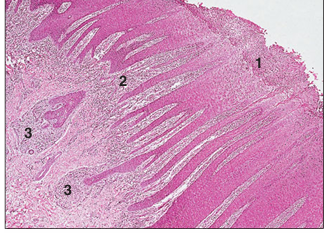
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Interdigital skin (sheep). (1) Epidermis with epidermal pegs. (2) Dermis with deep dermal papillae. (3) Glandular region of the dermis. H&E. ×125.
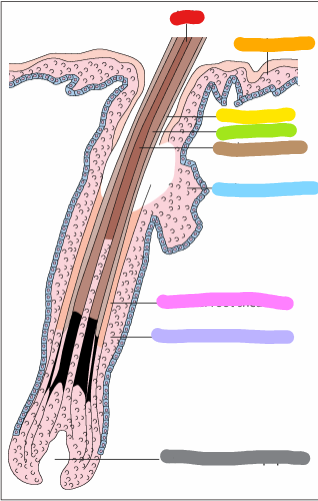
red:
orange:
yellow:
green:
brown:
blue:
pink:
lilac:
gray:
red: hair
orange: epidermis
yellow: hair cuticle
green: hair cortex
brown: hair medulla
blue: sebaceous gland
pink: internal root sheath
lilac: external root sheath
gray: connective tissue papilla
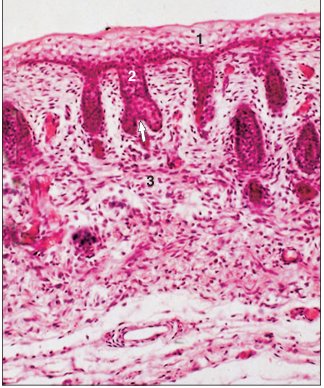
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Skin. Cat embryo. (1) Ectoderm. (2) The ectodermal cylinder with the invaginated papilla (arrowed) forms the primordium of the hair follicle. (3) Mesoderm. H & E. ×125.
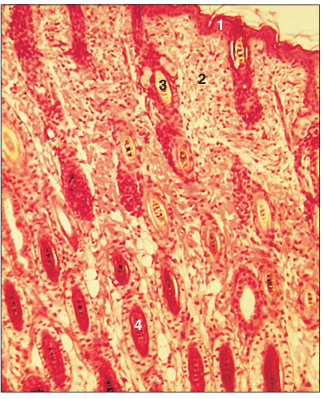
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Neonatal skin (cat). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Hair shaft. (4) Root sheath. H & E. ×125.
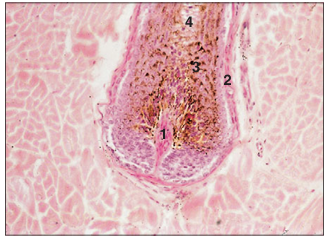
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Bulb region of the hair follicle. Horse (skin). (1) Dermal papilla. (2) Dermal root sheath. (3) Epidermal root sheath: (a) outer sheath, (b) inner sheath. (4) Hair. Note the melanin pigment in the epidermal sheath. H & E. ×125.
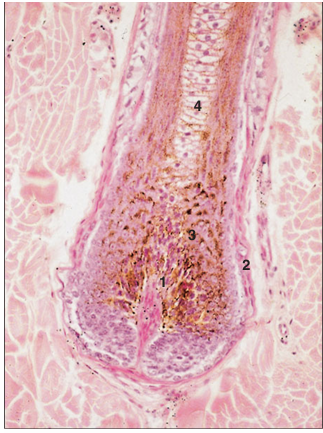
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Hair follicle. Skin (horse). (1) Dermal papilla. (2) Dermal root sheath. (3) Epidermal root sheath with (a) outer sheath and (b) inner sheath. (4) Hair. Note pigmentation. H& E. ×250.
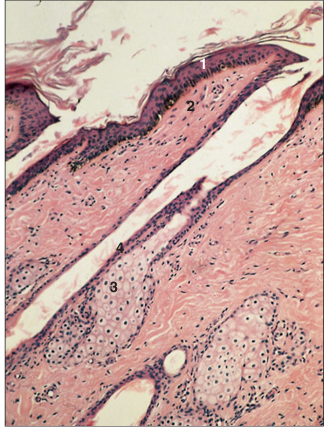
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Skin (horse). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Sebaceous gland opening into the hair follicle. (4) Epidermal root sheath is reduced to two layers of cells; the inner layer is thin horny scales. Note the oblique set of the hair follicle. H & E. ×125.
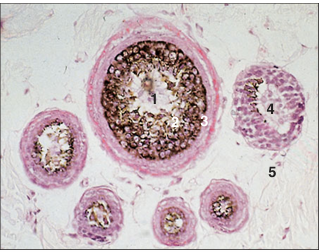
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Skin. Compound hair follicles (cat). (1) Large cover hair cut in cross-section: (2) epidermal sheath and (3) hair. (4) Fine wool/lanugo hairs. (5) Dermis. H & E. ×25.
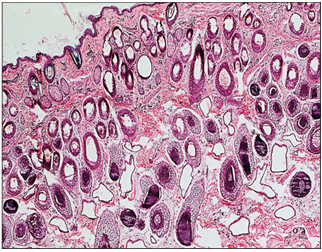
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Woolly skin. Flank (sheep). The hair follicles are all of the smaller wool/lanugo type, set individually in the dermis and lying vertically. H & E. ×12.5.
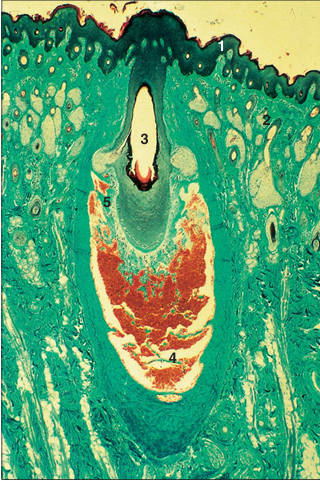
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Sinus/tactile hair (horse). (1) Epidermis. (2) Dermis. (3) Hair follicle. (4) Blood sinus in the dermal sheath. (5) Connective tissue trabeculae of the dermal sheath. Masson’s trichrome. ×12.5.
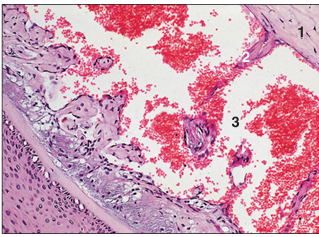
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Sinus/tactile hair (horse). (1) Dermal sheath. (2) Connective tissue trabeculae of the dermal sheath. (3) Blood sinus. H & E. ×125.
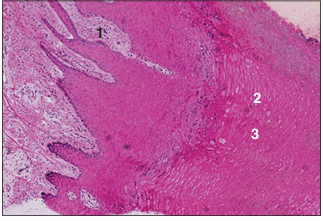
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Hoof (calf). (1) Deep dermal papillae. Stratified squamous epithelium with (2) tubular and (3) intertubular horn. H & E. ×12.5.
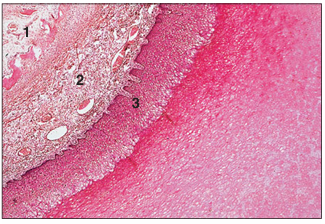
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Hoof (foal). (1) Developing bone. (2) Vascular dermis. (3) Stratified squamous epithelium. H&E. ×12.5.
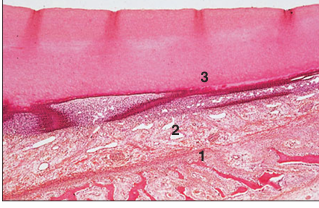
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Hoof (foal). (1) Phalangeal bone. (2) Vascular dermis. (3) Epidermis with a thick stratum corneum. H & E. ×12.5.
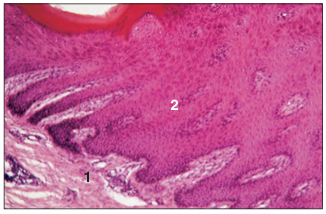
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Hoof (goat). (1) Dermis. (2) Stratified squamous epidermal epithelium, with a thick stratum corneum. H & E. ×125.
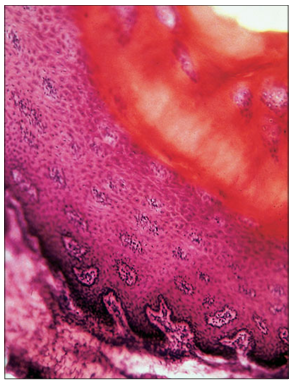
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Hoof (goat). The epidermis clearly shows all the layers of a stratified squamous epithelium; note the stratum corneum. H & E. ×250.
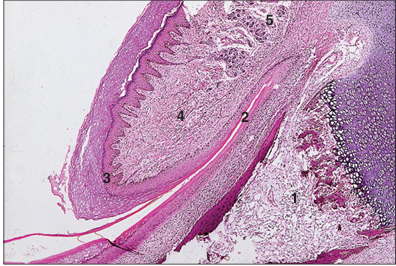
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Claw (dog). (1) Third phalanx. (2) Claw fold. (3) Stratified squamous epithelium. (4) Dermis. (5) Digital pad. H& E. ×12.5.
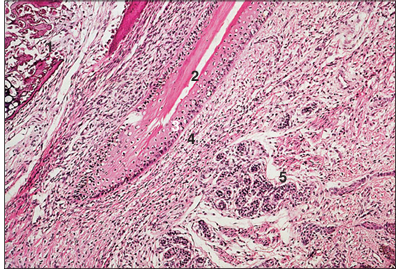
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Claw (dog). (1) Third phalanx. (2) Claw fold. (3) Stratified squamous epithelium. (4) Dermis. (5) Digital pad. H & E. ×62.5.
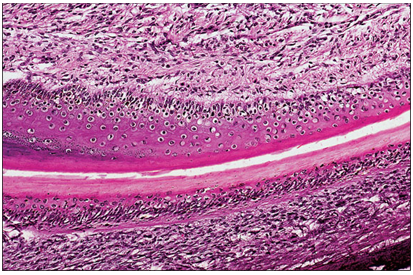
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Claw (dog). The superficial clear area of the stratified squamous epithelium is the developing claw (equivalent to the human nail). H & E. ×125.
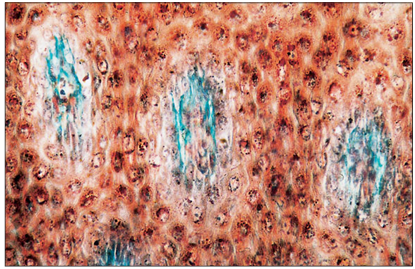
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Horn (goat). The deep dermal papillae are stained green and surrounded by epidermal cells in columns, the horn tubules. Masson’s trichrome.×250.
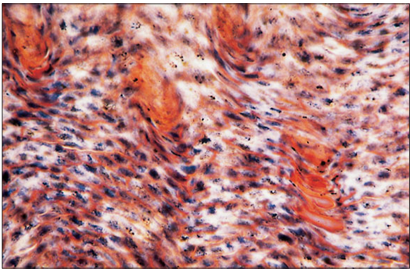
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Horn (goat). The undulating effect is caused by the alternating tubular and intertubular arrangement of the developing horn. Masson’s trichrome. ×250