Hearing Science: Inner Ear Anatomy
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Where are high frequency sounds received?
at the base of the cochlea
Where are low frequency sounds received?
at the apex of the cochlea
The cochlea turns around the...
modiolus
Where do the cochlear nerves connect?
the inner and outer hair cells
Where do the cochlear nerves go?
through the habenula perforata, and into the modiolus
What makes up the VIIIth nerve?
nerve fibers (when they come out of the modiolus, they are the VIIIth nerve)
What makes up the VIIIth nerve?
bipolar neurons
The VIIIth nerve is made up of bipolar neurons. Where does it start and end?
Base of hair cells, through the habenula perforata, into the modiolus (cell body is within/connects to cell body), becomes the VIIIth nerve, connects to cochlea nucleus
What happens to the nerve fibers?
the nerve fibers come out of base of hair cells, all go through habenula perforata, meet the cell bodies in the modiolus, forms the VIIIthe nerve, VIIIth nerve is connected to cochlea nucleus
What part of the cochlea is closest to the modiolus?
the medial aspect of the cochlea
Where is the tectorial membrane located?
on top of the stereocilia
What covers the tops of the hair cells?
reticular lamina (thin layer of connective tissue)
What is the modiolus closest to, inner or outer hair cells?
inner hair cells
Inner Hair Cell
-peak or flask shaped
-approx. 3,500
-single row
stereocilia not attached to the tectorial membrane
-stereocilia in cresent shape
-centralized nucleus
-organelles distributed throughout the cell body
More on the Inner Hair Cell
-95% of the afferent neurons
-many afferent neurons (inner radial fibers) connect to each IHC
-afferent neurons synapse with cell body, efferent neurons synapse with the afferent neurons
-no motility
Outer Hair Cell
-cylindrical shape
-approx. 12,000
-3 rows
-stereocilia attached under the tectorial membrane
-stereocilia in W or V shape
-nucleus found in base
-organelles found along the outer walls
More on the Outer Hair Cell
-5% of afferent neurons
-each afferent neuron (outer spiral fibers) connects to many OHCs
-efferent and afferent neurons synapse directly with cell body
-OHCs "stretch and shrink" this is called OHC motility
What is an afferent nerve fiber?
goes towards the brain
Afferent neurons synapse with...
inner hair cells
Efferent neurons synapse with...
afferent neurons
What synapses directly with the outer hair cells?
efferent and afferent neurons
What does each afferent neuron (outer spiral fibers) connect to?
many outer hair cells
Type I Fibers
associated with outer hair cells
-slow twitch
Type II Fibers
associated with inner hair cells
-fast twitch
Many Type I fibers synapse...
with one inner hair cell directly opposite their habenular opening
What makes the outer hair cells contract?
efferent nerve stimulation
Features of the Cochlea
-mechanical (vibratory motion)
-hydraulic (wave motion)
-chemo-electrical (nerve energy)
Membranous Labyrinth
filled with endolymph
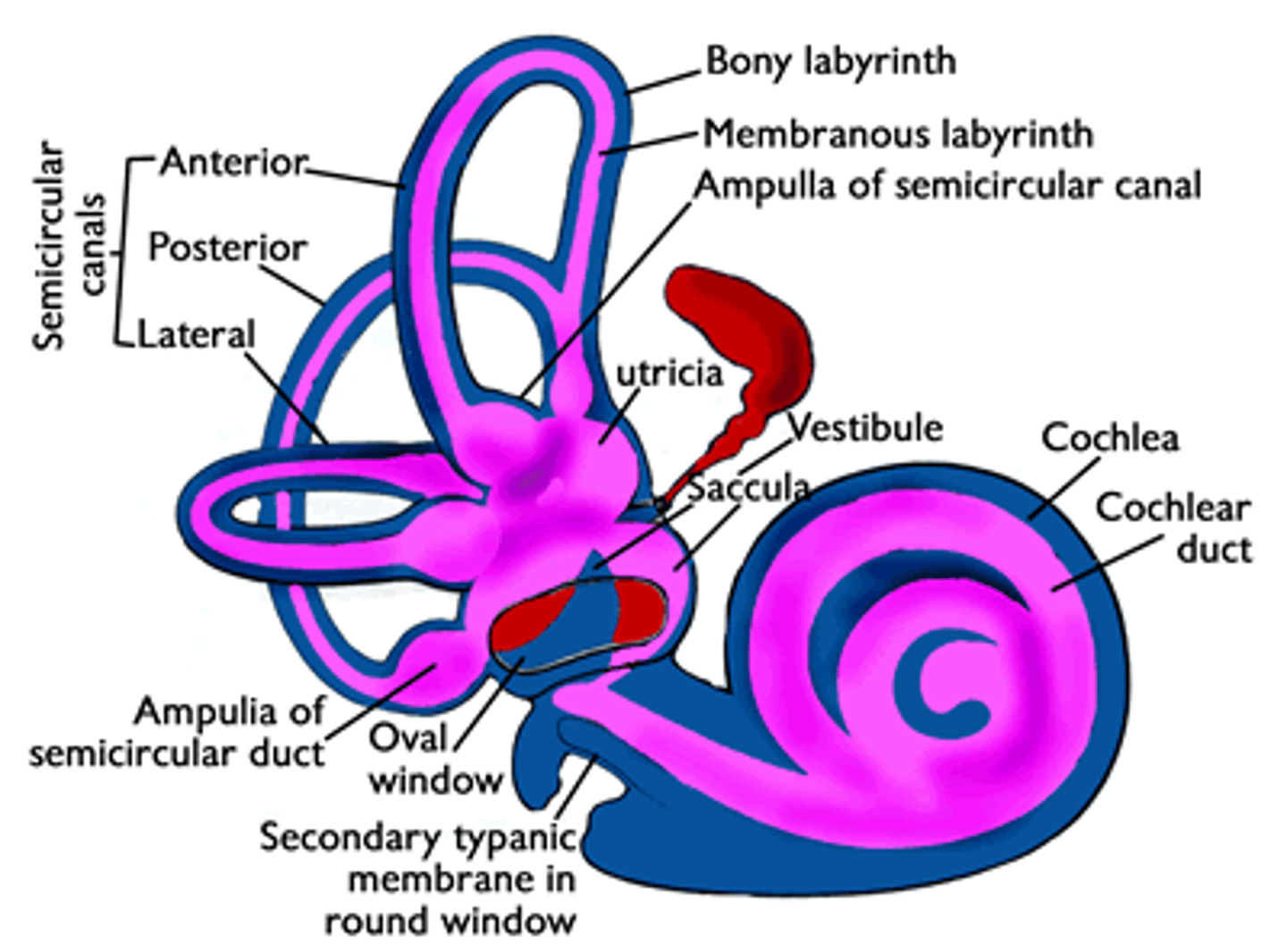
What are the three major anatomical components of the inner ear?
semi-circular canals
vestibule (saccule and utricle)
cochlea
Semi-Circular Canals
sense movement of the head, both speed and direction
-three fluid-filled tubes
How many semi-circular canals are there?
three
Vestibule
utricle and saccule are used to detect the orientation of the head
Cochlea
closed, labyrinthine (maze-like) capsule, filled with fluid
-most anterior structure
-two 5/8th turns, large bundle of nerve cells enters the center (auditory branch of the VIIIth nerve)
Modiolus of the Cochlea
bony center of cochlea
-the bony canal turns around the modiolus
-"continuous left turn" (spiral staircase)
-walls are solid bone
The auditory nerve fibers from the hair cells...
enter the modiolus
Labyrinth of the Cochlea
-2 5/8th turns
-35 mm length base to apex
-ends at the helicotrema in the apex
Where is the base of the cochlea?
near the stapes footplate
Where is the apex of the cochlea?
other end of the bony labyrinth
Story through the Cochlea
-stapes footplate removed, you see oval window
-through oval window, you would be in the Scala vestibuli
-go through Scala vestibuli, you are in the helicotrema (at apex)
Helicotrema = where the scala vestibuli and scala tympani
-past helicotrema, you are now in lower level (scala tympani)
-down spiral staircase, to round window (the base)
Osseous Spiral Lamina
bony extension of the medial wall of the bony labyrinth
-runs continuously along the medial wall
-gets skinnier as it goes from the base to the apex
The width of the osseous spiral lamina _________ between the base and the apex of the cochlea.
decreases
Why is the change in width necessary?
-basilar membrane is narrow at the base because it is responsible for detecting high frequencies
-basilar membrane is wider at apex because it is responsible for detecting low frequencies
By the time the cochlea reaches its third turn, the osseous spiral lamina has nearly ___________.
disappeared
What are the three sections of the scala?
scala vestibuli
scala tympani
scala media
Scala Vestibuli
-bounded inferiorly by Reissner's membrane
-ends at helicotrema
-contains perilymph
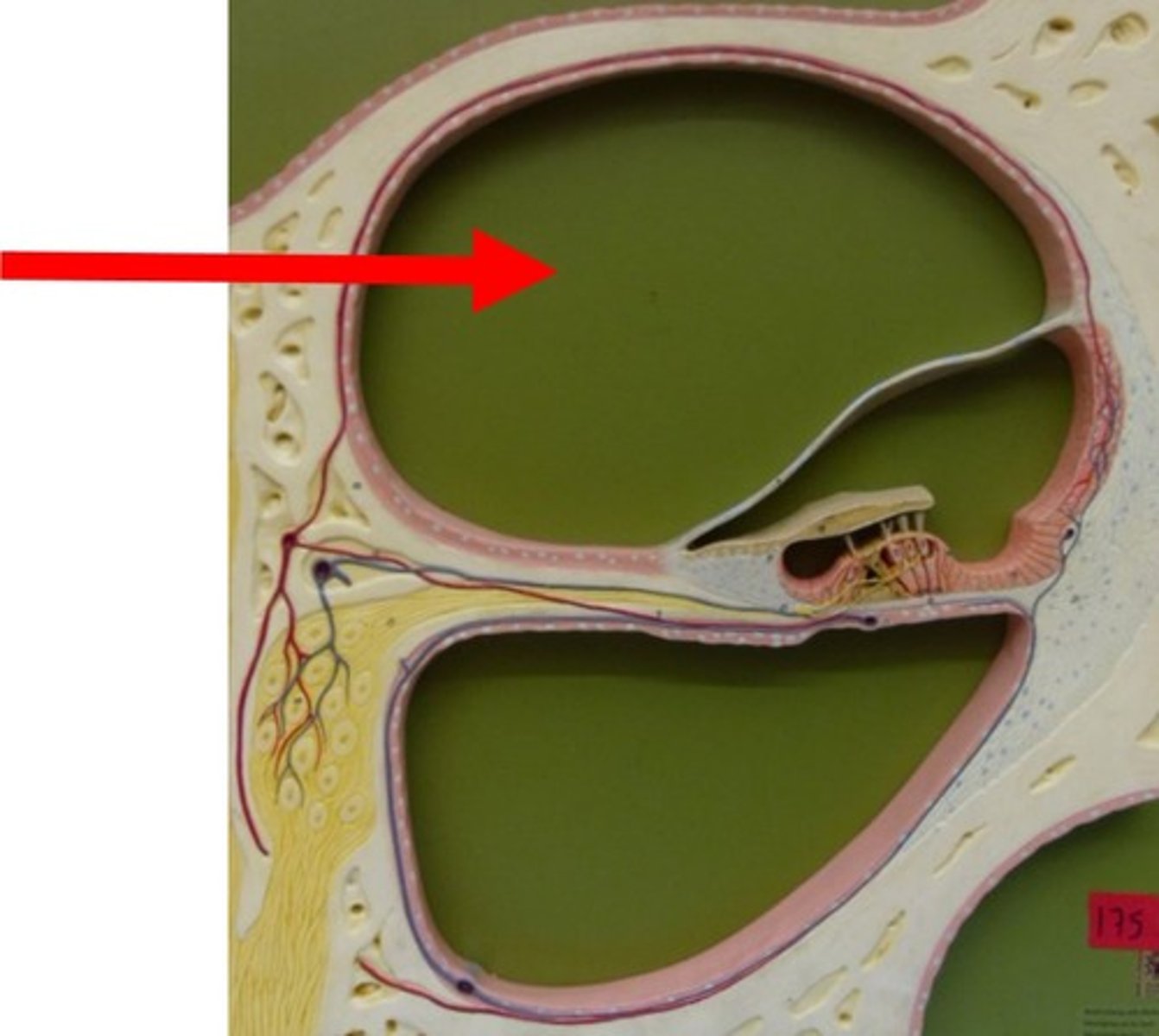
Reissner's Membrane
-floor of scala vestibuli
-roof of scala media
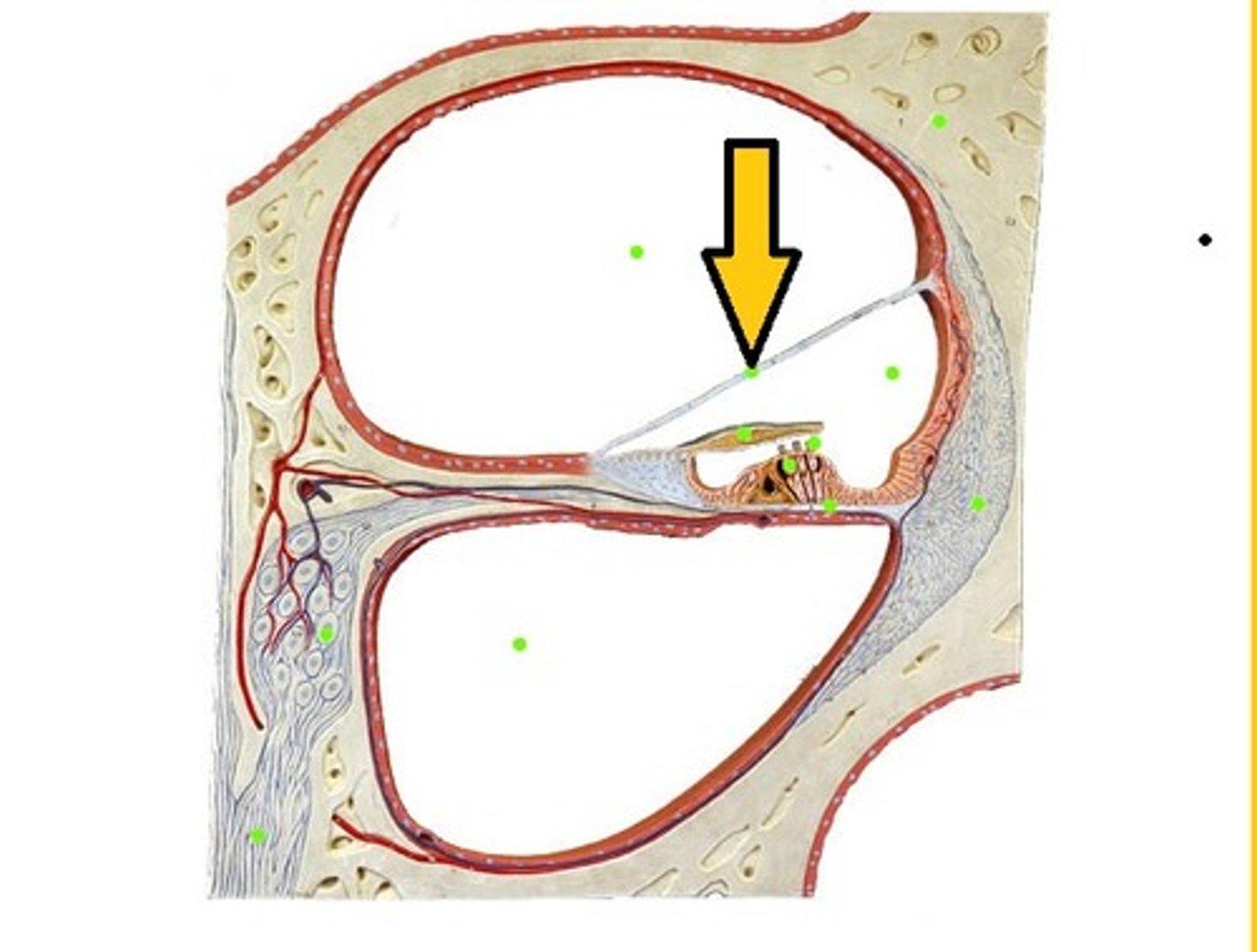
Perilymph
fluid around scala media (fills scala vestibuli and scala tympani)
The scala vestibuli is bounded inferiorly by...
Reissner's membrane
Scala Tympani
-bounded superiorly by the basilar membrane
-ends at helicotrema
-contains perilymph
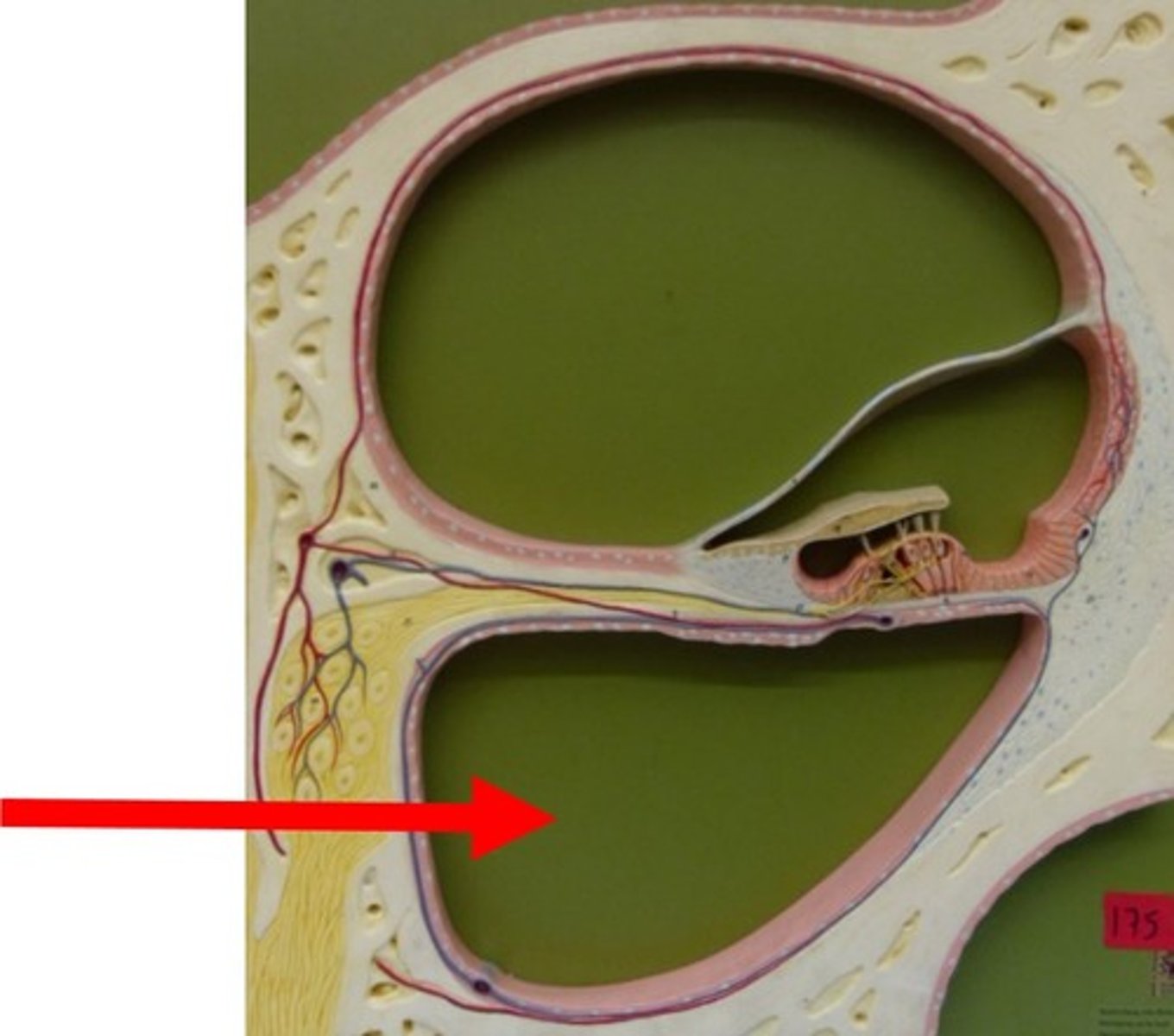
The width of the basilar membrane ___________ between base and apex of cochlea.
increases
Tonotopic
pertains to the way in which the primary auditory cortex is organized so that neurons that respond to particular frequencies are grouped together
The scala tympani is bounded superiorly by the...
basilar membrane
Scala Media
-bounded superiorly by Reissner's membrane
-bounded inferiorly by basilar membrane
-contains Organ of Corti
-contains endolymph
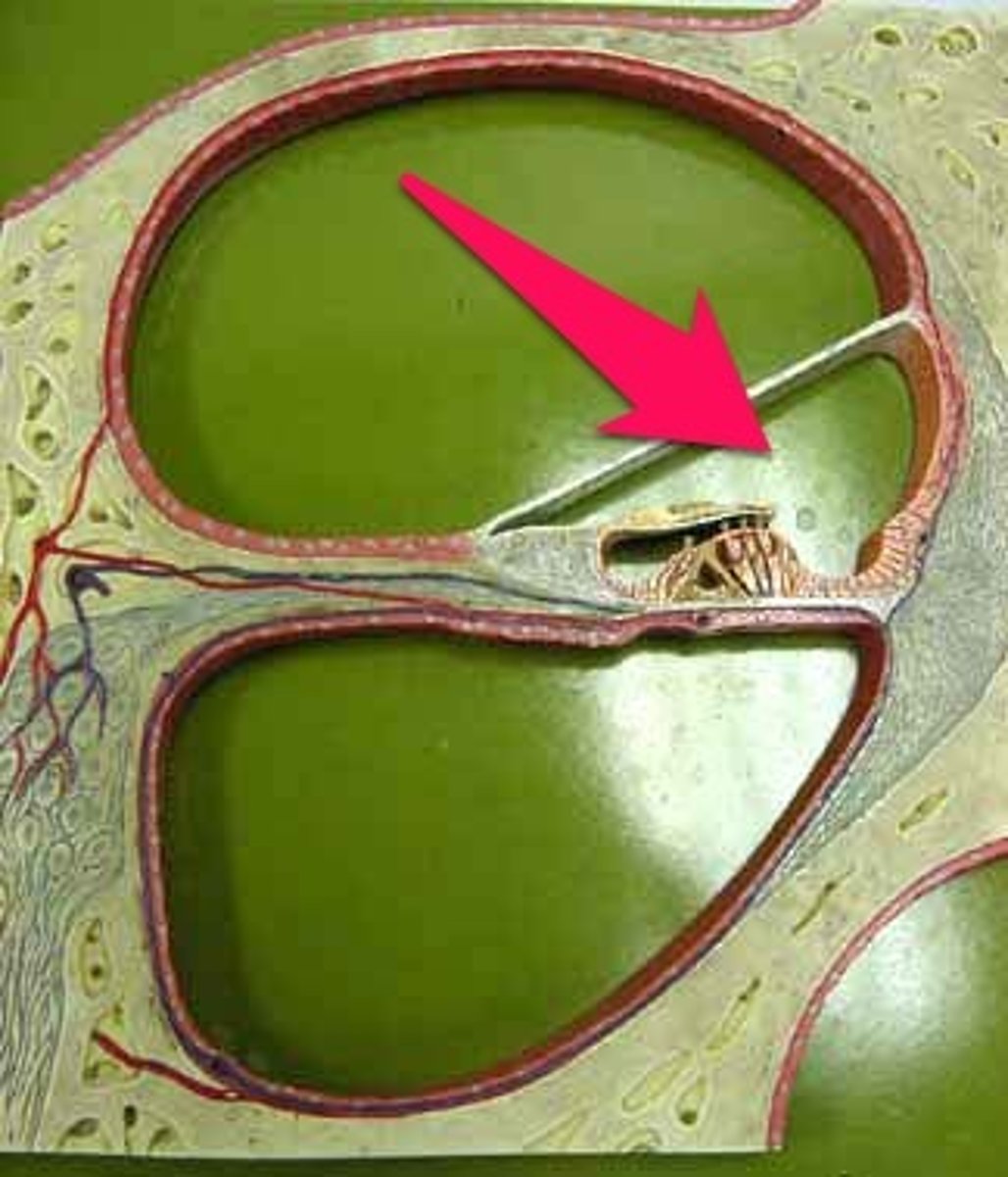
The scala media is bounded superiorly by...
Reissner's membrane
How do the scala vestibuli and scala tympani share perilymph?
at the helicotrema
What keeps the endolymph in the scala media?
reissner's membrane and basilar membrane
Gross Anatomy of Scala Media
-Reissner's Membrane
-Basilar Membrane
-Osseous Spiral Lamina
-Spiral Limbus
-Tectoral Membrane
-Organ of Corti
-Stria Vascularis
What are the attachment points for the basilar membrane?
lateral side: spiral ligament
medial side: osseoud spiral lamina
What kind of cells are on top of the osseous spiral lamina?
fibrous cells
Stria Vascularis
-occupies most of the lateral surface of the scala media
-major source of blood supply to all the structures of the scala media
-source of endolymph
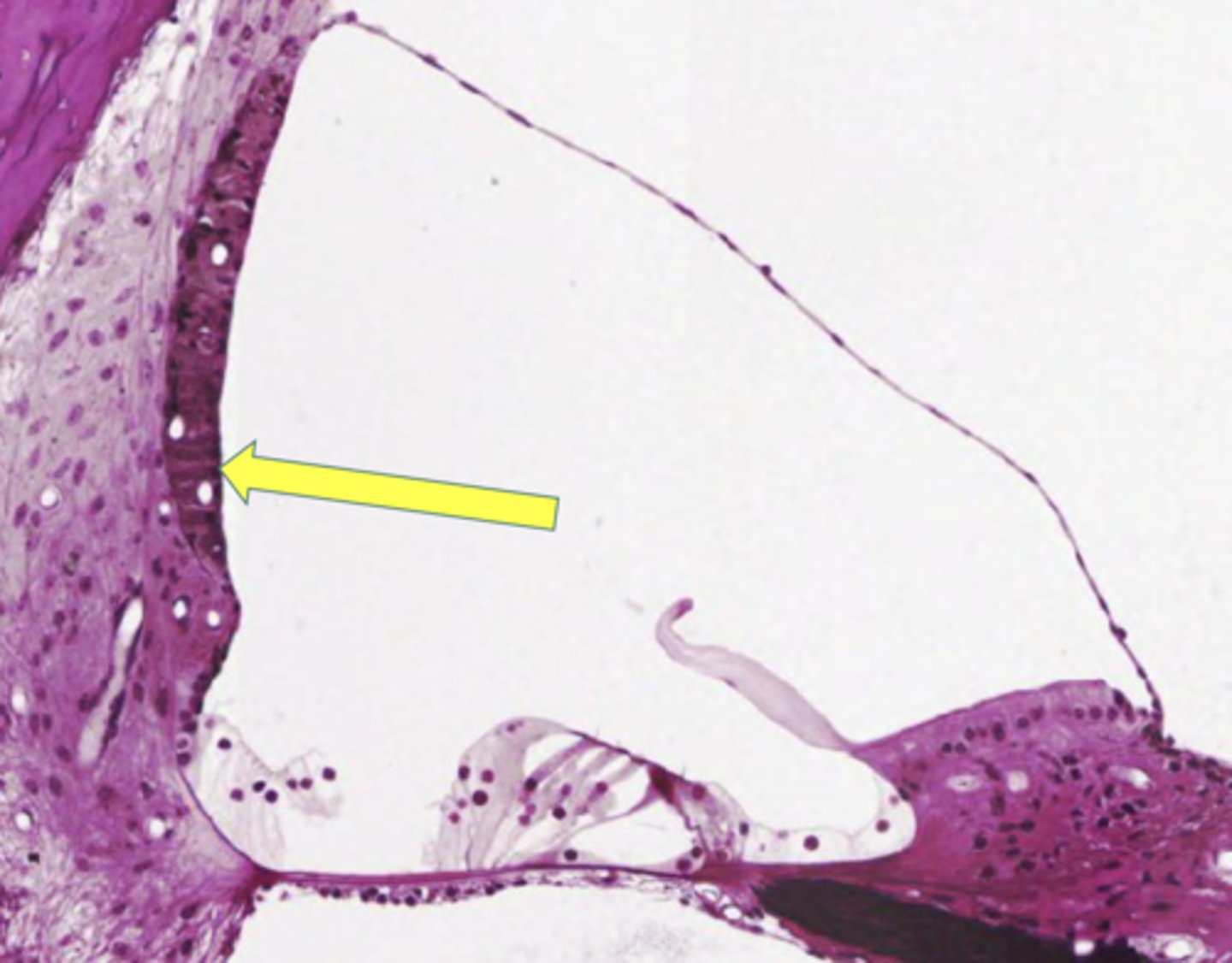
What is another name for the stria vascularis?
endolymphatic pump
Exhausted Endolymph
chemical content changes and you need a fresh supply of ions for the nerve impulse
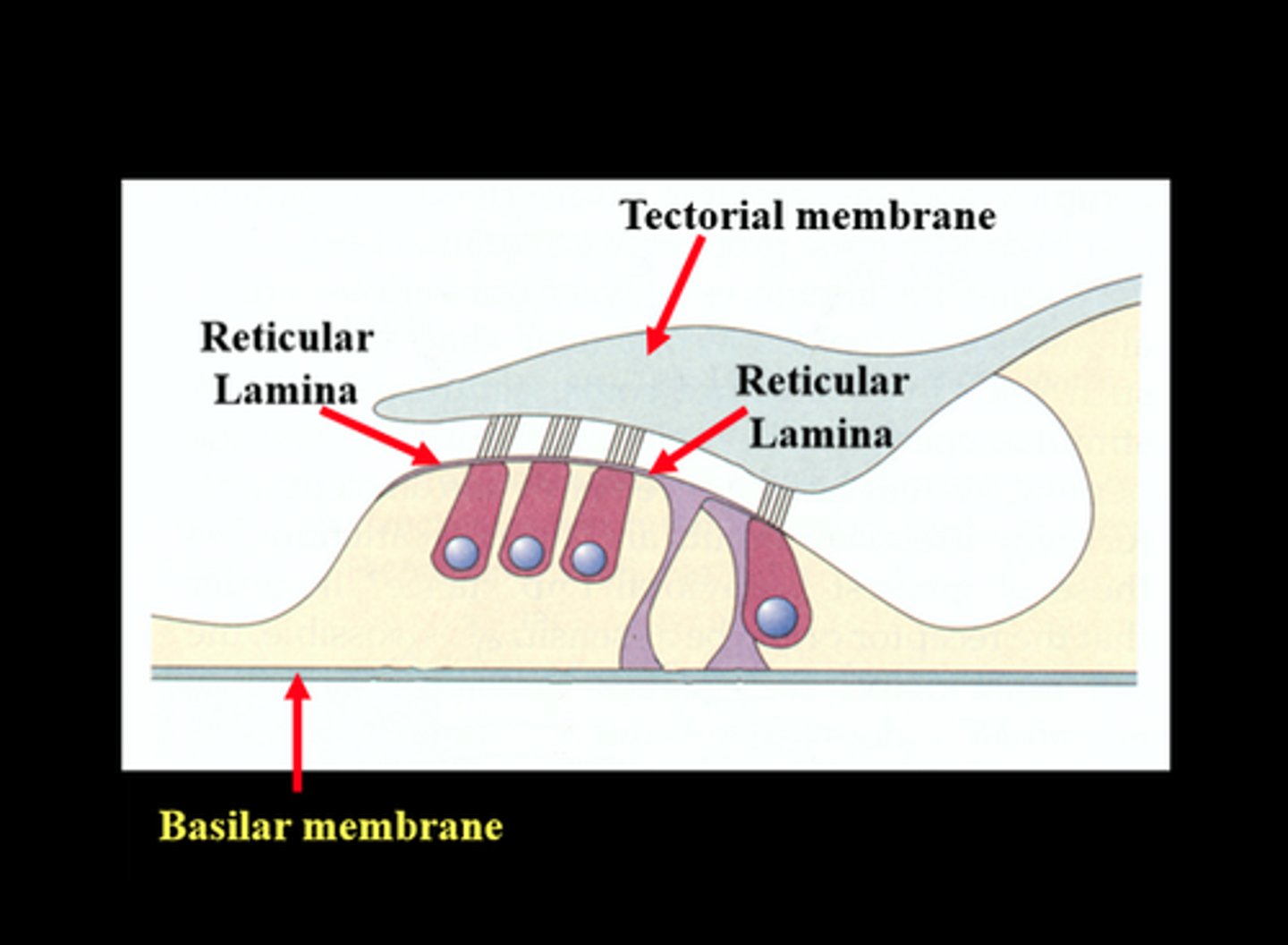
Tectorial Membrane
comprised mostly of water
-lighter density than endolymph
-seeks to float in a more salty endolymph environment
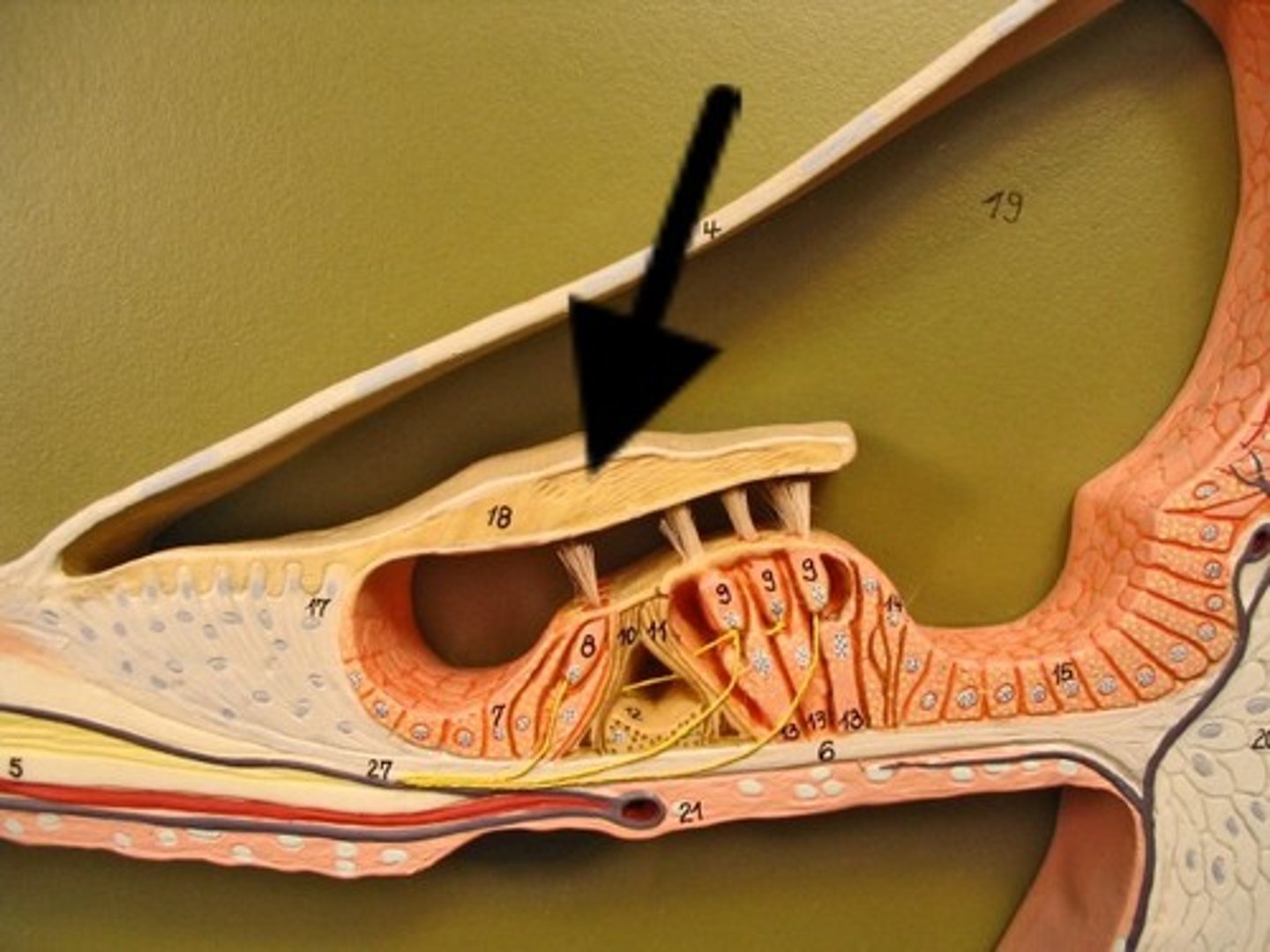
What ties down the tectorial membrane?
it is tied down at its medial (spiral limbus) and lateral (Hensen's cells) edges
Fine Features of the Scala Media
-inner sulcus supporting cells
-inner hair cells
-rods of corti
-deiter cells
-outer hair cells
-Hensen's cells
-cells of clause
Inner Sulcus Supporting Cells
support for organ of corti from medial side
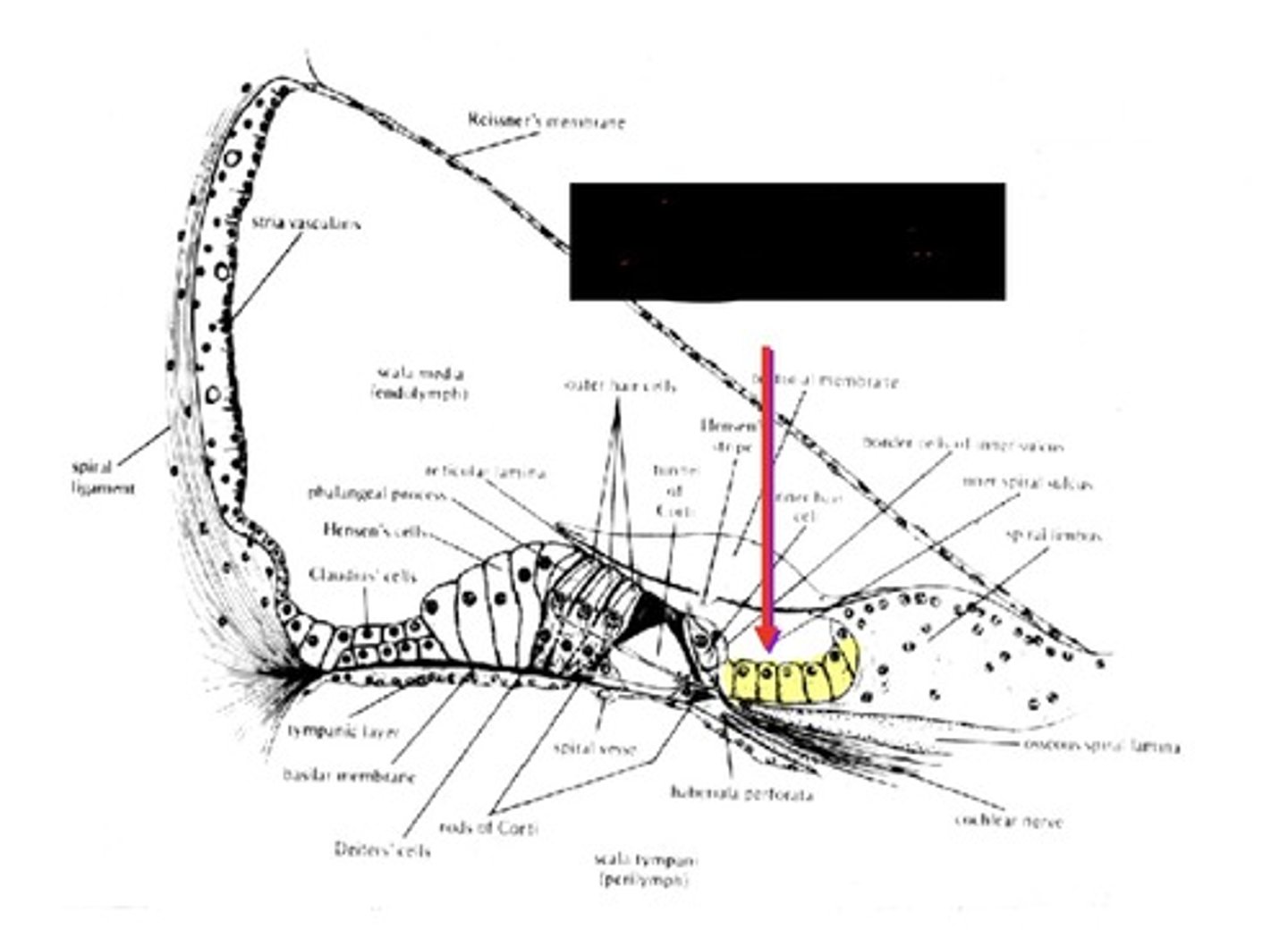
Corti's Tunnel
gaps between pillar cells permit free circulation of liquids throughout the interior of organ of Corti
What liquids are present in the scala media?
endolymph
cortilymph
Endolymph
fluid within the labyrinth of the inner ear
-source; stria vascularis
-high concentration of K+
-relatively low concentration of Na+
-found: superior to reticular lamina
Cortilymph
the thick fluid located within the organ of Corti
-source: may be from perilymph, diffused through the basilar membrane
-similar in composition to perilymph
-found: interior of corti's organ
Who discovered Corti's Organ?
Alfonso Corti
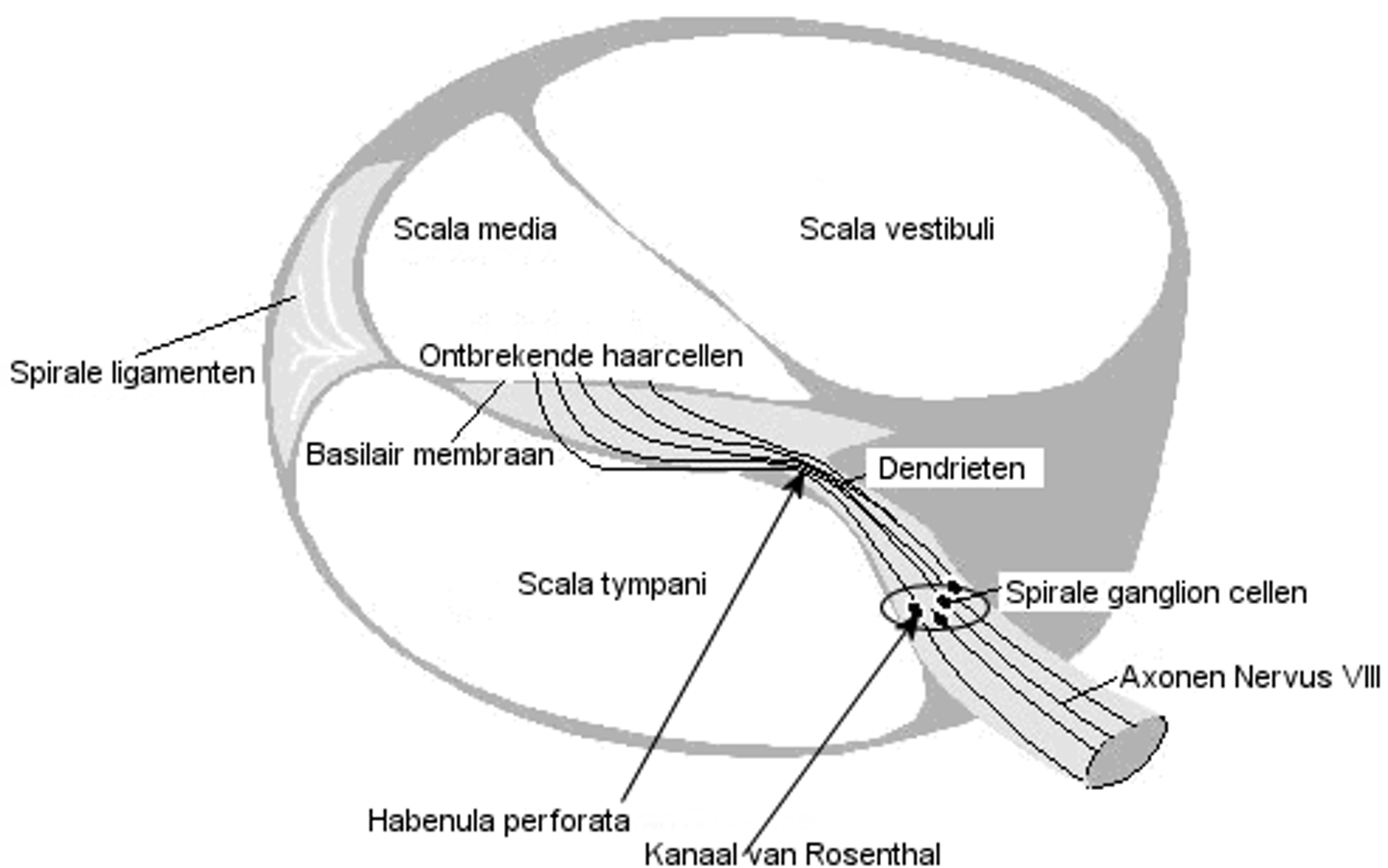
Habenula Perforata
holes in the osseous spiral lamina where the nerve fibers enter the Organ of Corti
Reticular Lamina
under the tectoral membrane
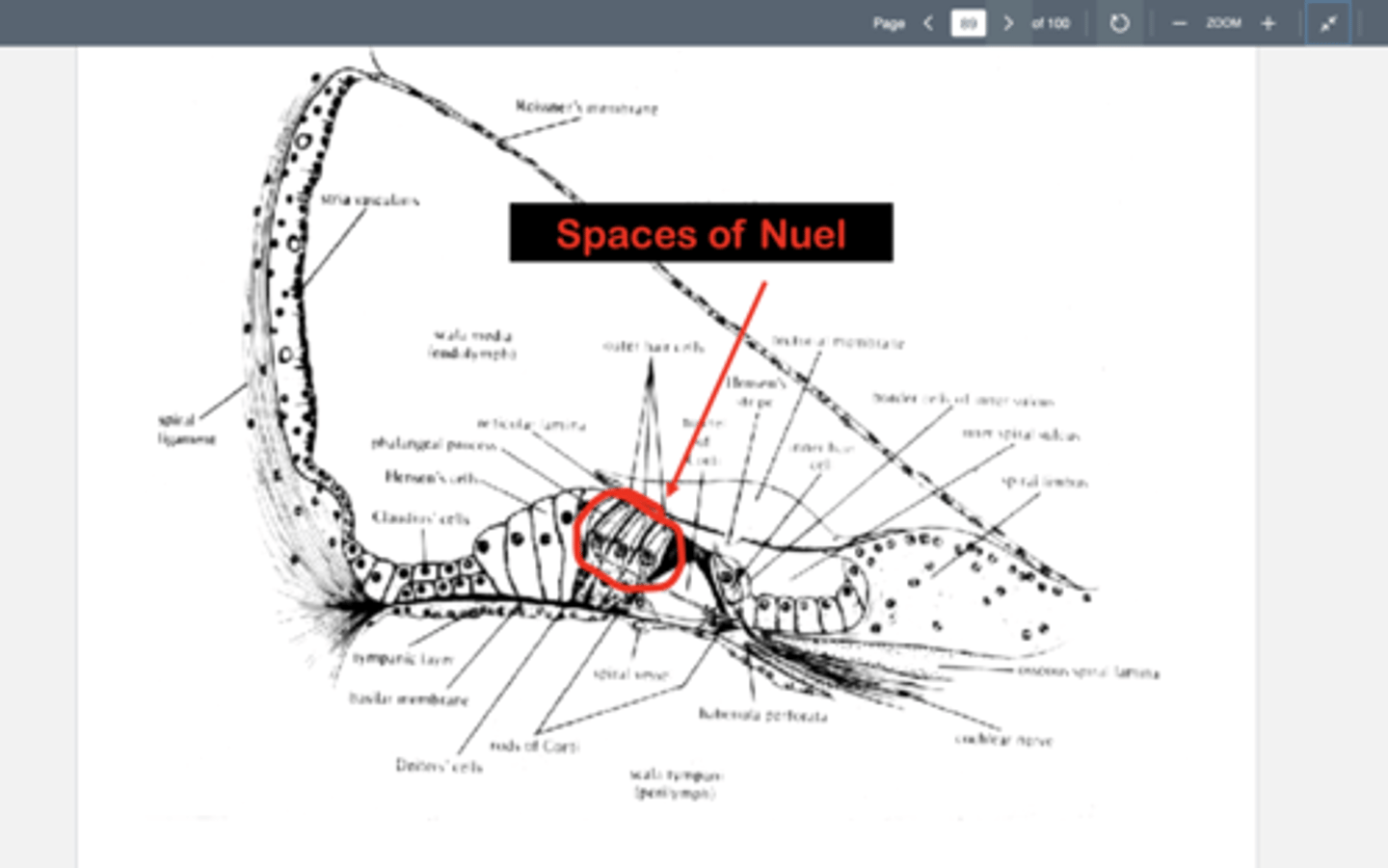
Spaces of Nuel
spaces betwenn outer hair cells
Where are the phalanges of deiter cells found?
in the 2nd and 3rd row of deiter cells
Reticular lamina with...
outer hair cell cilia extending above the surface
Basilar membrane with...
bases of Deiter cells resting on it
The first row of Deiter cells do not have...
phalanges
-instead they have bulges that look like cotton balls stuck on their sides
-bulges are located near the pocket of Deiter cells where they hold the OHCs
Hair Cell Cilia
"hair"- extensions of cell membrane
Stereocilia
many per cell
-fine, feathery, paddle-like appearance
-highly organized in patterns
-rigid, interconnected with tip-links
-deep roots within hair cells
What are the light-grey colored areas between cilia?
tip-link inter-connectors
What happens when the cilia move?
the tip-link inter-connectors are stretched or shorten
-when stretched they open tiny
conduits for electron flow
What does the tapered handle-like appearance at the base of each cilia do?
acts as a hinge so that the cilia can swing back and forth
What acts as a support for sensory cells?
- Inner sulcus (medial side)
- Hansen's cells (lateral side)
- Reticular lamina (superior)
- Dieter cells (inferior to the outer hair cells)
- Corti's rods (between the IHCs and the OHCs)
Blood Supply to the Cochlea
-Arterial Course
-Venous Course
Arterial Course in the Scala Media
-the internal auditory artery arises from the meatal loop of the middle cerebral artery which usually sits on the cochlear nerve in the internal auditory canal.
-arteries penetrate into the cochlea via the modiolus.
-the spiral modiolar artery gives off radial branches to the lateral cochlear wall, including the stria vascularis
Venous Course in the Scala Media
-venous drainage of the cochlea occurs via the modiolus
-most mammals have a spiral modiolar vein
-no main vein is visible among the nerves in the internal auditory canal in humans
-the venous blood empties either directly into the inferior petrosal sinus or the internal jugular vein or travels through other venous sinuses
The inner ear is innervated by the...
VIIIth cranial nerve (auditory nerve)
What are the two branches of the VIIIth Cranial Nerve
auditory branch
vestibular branch
Auditory Branch
-nerve fibers connected to hair cells in the cochlea are routed through the habenula perforate to the modiolus
-the cell bodies of these nerve cells are called the spiral ganglion
Where are the auditory and vestibulaar branch found?
in the internal auditory canal (or meatus)
Ganglion
mass of nerve cell bodies
Afferent Nerve Fibers
send information from the hair cells (mostly the inner hair cells) to the brainstem and then to the brain
Efferent Nerve Fibers
send information from the brainstem and the brain to the
hair cells(mostly the outer hair cells)
Axons of both types of nerves reach the cochlea via the...
habenula perforata
How many neurons are in the afferent division of the auditory branch of the VIIIth nerve?
30,000
Radical Fibers (Type I)
-90 to 95 % of afferent nerve fibers
-about 20 of these fibers connect to a single inner hair cell
-bipolar neurons
-myelinated fibers with Nodes of Ranvier
-the neural spike jumps from node to node for fast conduction time
Spiral Nerve Fibers (Type II)
-about 5% of afferent nerve fibers
-connect to outer hair cells
-each nerve fiber connect to as many as 10 different outer hair cells
-pseudo-monopolar neurons
-not myelinated (slower conduction time)
The VIIIth nerve leaves the internal auditory canal and enters the brainstem at the...
cerebellopontine angle (where the
cerebellum and the pons meet)
Cerebellum
involved in the coordination of movement