QCAA Unit 3 and 4 Physics Definitions from Syllabus
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Define the term normal force.
A force acting perpendicular to the surface.
Describe uniform circular motion.
Uniform circular motion describes the motion of an object travelling at a constant speed in a circle. The force acting on the object constantly either pushes or pulls it towards the centre of motion and is perpendicular to the velocity of the object.
Define the concept of average speed.
the rate of change of distance calculated by the formula, average speed = distance/time.
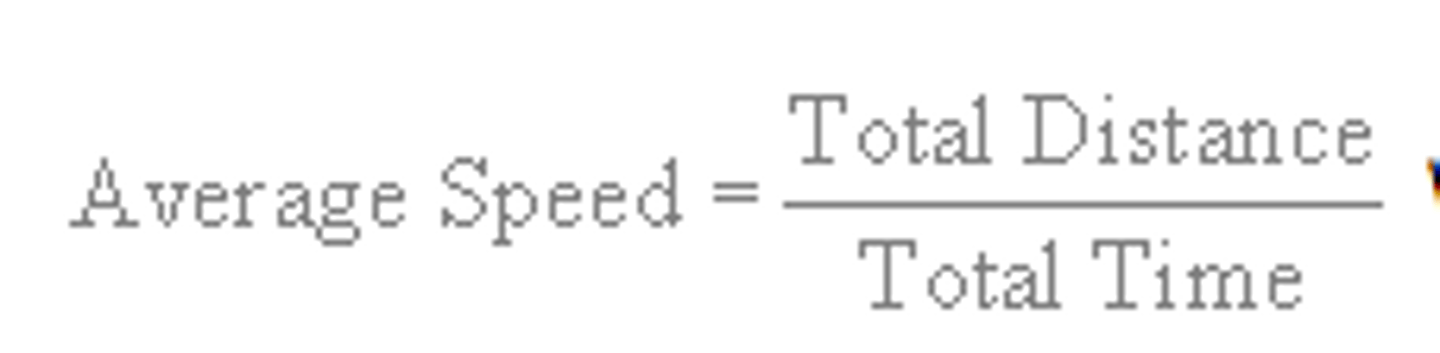
Define the concept of period.
The amount of time one cycle or one event takes to occur.
In waves, the period is the length of time taken for one wavelength to pass a given point. In circular motion the period refers to the time taken to complete one revolution (symbol, 𝑇; SI unit, s)
Define the term centripetal acceleration.
The acceleration experienced by an object moving in a circle, which is directed towards the centre of motion (symbol, 𝑎; SI unit is m/s² ).
Define the term centripetal force.
The force acting on an object moving in a circle that constantly either pulls or pushes the object towards the centre of motion (symbol, 𝐹ₙₑₜ ; SI unit is N)
Recall Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation.
A law stating that the force of attraction between each pair of particles is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
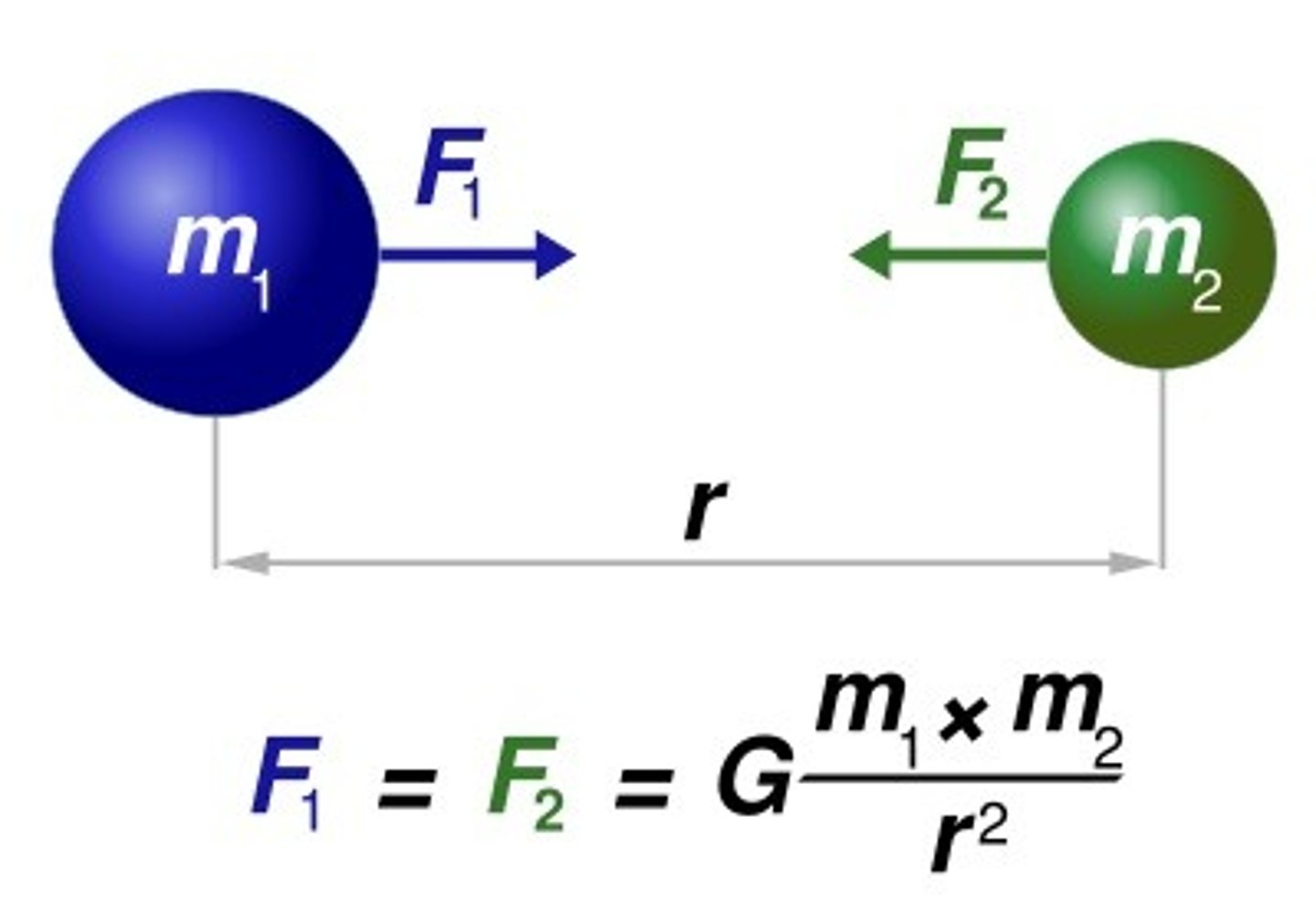
Define the term gravitational fields.
The region of space surrounding a body in which another body experiences a force of gravitational attraction.
Recall Kepler's laws of planetary motion.
The first law states that all planets travel around the Sun in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus.
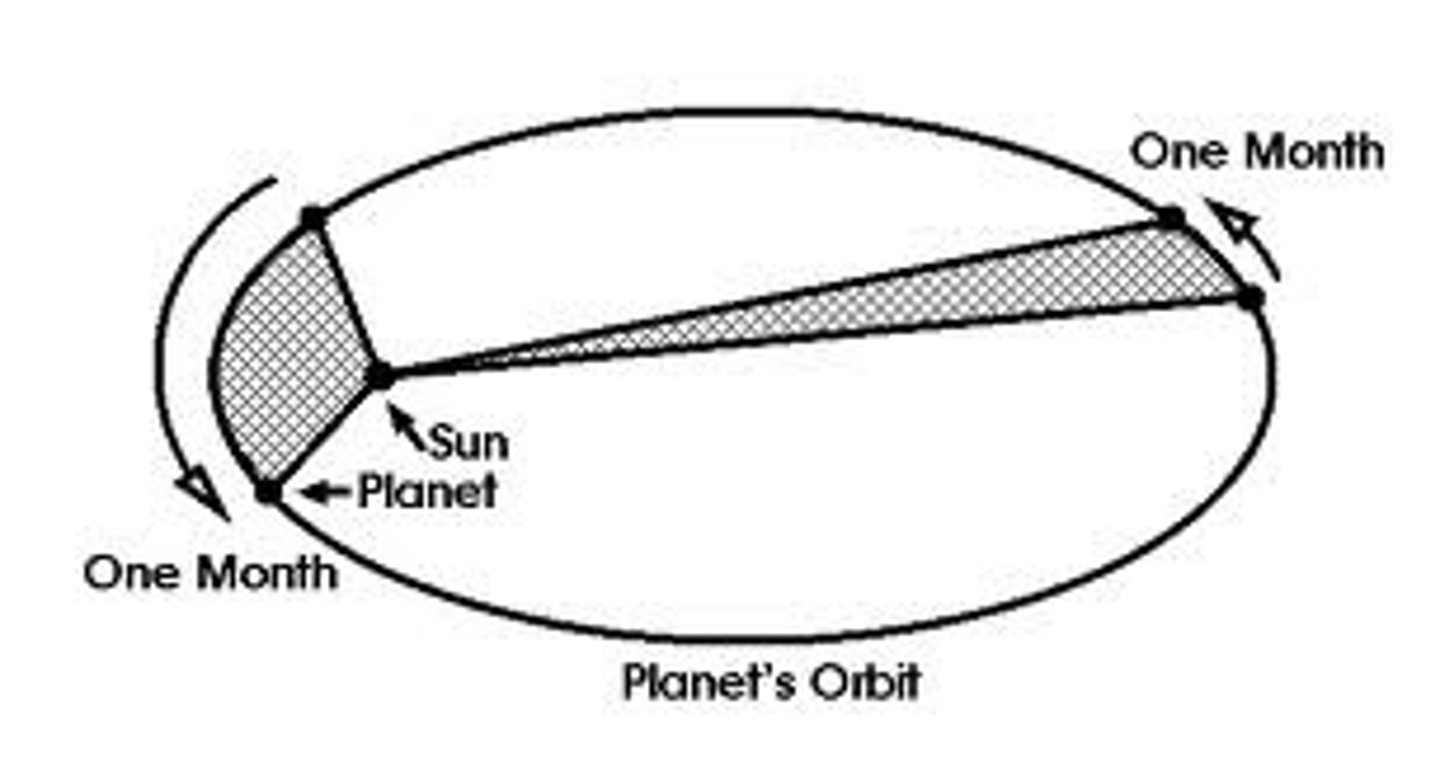
The second law states that a line from any planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal lengths of time.
The third law states that the squares of the sidereal periods of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of their mean distance from the Sun.
Derive Kepler's third law.
Using the relationship between Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation and uniform circular motion.

Define Coulomb's Law.
Coulomb's Law describes the force exerted by electrostatically charged objects on other electrostatically charged objects. It states that like electric charges repel and opposite electric charges attract, with a force proportional to the product of the electric charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, expressed by the formula:
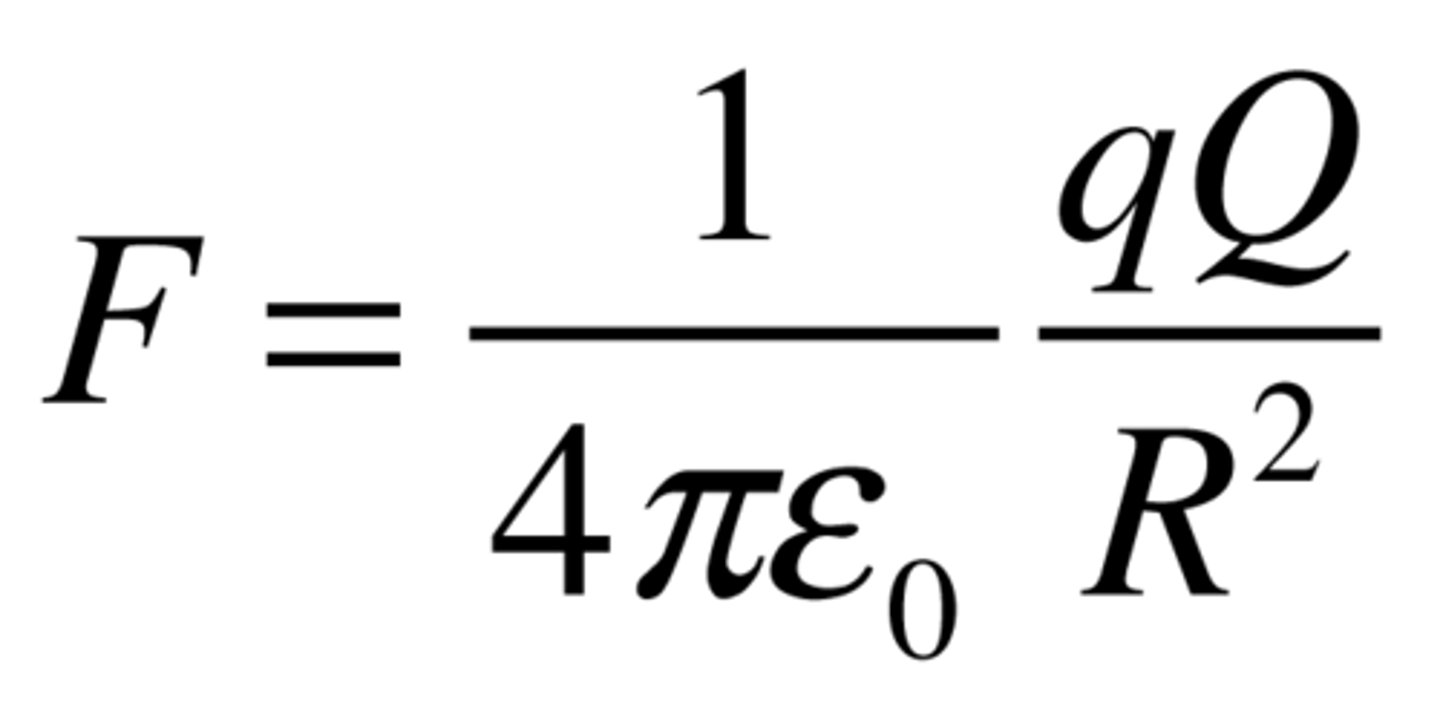
Define the term electric fields.
The region of space surrounding an electrically charged particle or object in which another electrically charged particle or object experiences a force.
Define the term electric field strength.
The intensity of an electric field at a particular location (measured in N/C)
Define the term electrical potential energy.
The capacity of electric charge carriers to do work due to their position in an electric circuit.
Define the term magnetic field.
The region of space surrounding a magnet, electric current or moving electrically charged particle in which another magnet, electric current or moving electrically charged particle experiences a magnetic force (SI unit; T).
Define the term magnetic flux.
A measurement of the total magnetic field that passes through a given area (symbol, 𝜙; SI unit, Wb)
The angle is between the perpendicular to the loop and the field.
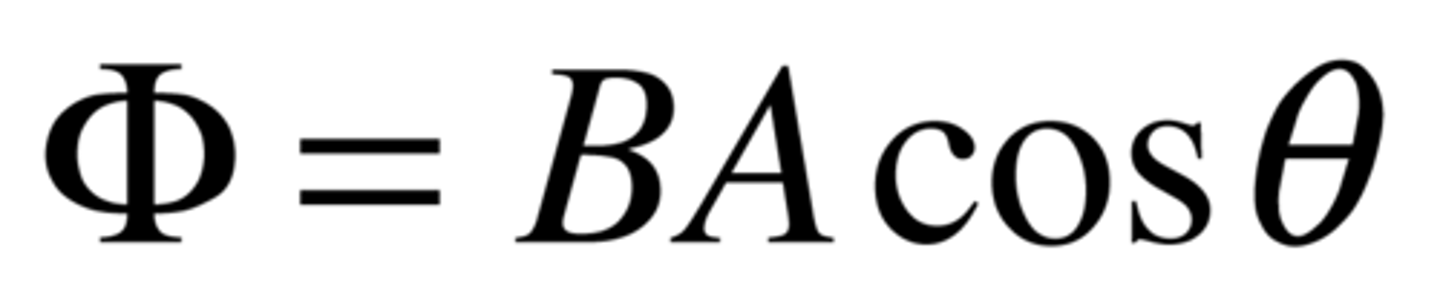
Define the term magnetic flux density.
The strength of a magnetic field per unit area (symbol, 𝐵; SI unit, Wb/m² or T).
Define the term electromagnetic induction.
The production of a voltage or EMF across an electrical conductor due to its dynamic interaction with a magnetic field.
Define the term electromotive force (EMF).
A difference in potential that tends to give rise to an electric current, also written as EMF (measured in V)
Define the term Faraday's Law.
A law stating that change in magnetic flux induces an electromotive force in a circuit, which is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux. This creates a current.
Define the term Lenz's law.
A law stating that the direction of induced current will be such that the change in magnetic flux is opposed by the induced magnetic field.
Define and explain electromagnetic radiation in terms of electric fields and magnetic fields.
Electromagnetic radiation is energy made up of synchronised oscillating electric and magnetic fields propagated at the speed of light in a vacuum.
Define the term frame of reference.
The abstract coordinate system that defines location of the observer
Define the term inertial frame of reference.
A non-accelerating frame of reference in which Newton's laws of motion hold.
Define the term time dilation.
the difference of elapsed time between two events as measured by observers moving relative to each other.
Define the term proper time interval.
The time interval measured in the frame of reference in which the object is at rest.
Define the term relativistic time interval.
The time interval measured in the frame of reference in which the object is in motion.
Define the term length contraction.
An observer at rest relative to a moving object would observe the moving object to be shorter along the dimension of motion.
Define the term proper length.
The length of an object measured in the frame of reference in which the object is at rest.
Define the term relativistic length.
The length of an object measured in the frame of reference in which the object is in motion.
Define the term rest mass.
The mass of an object measured in the frame of reference in which the object is at rest.
Define the term relativistic momentum.
The momentum of an object measured in the frame of reference in which the object is in motion
Define the term threshold frequency.
The minimum frequency of a photon required to eject an electron from a surface.
Define the term Plank's constant.
A fundamental constant used in quantum mechanics
Define the term work function.
The minimum energy required to eject an electron from a solid.
Define the concept of an elementary particle.
a particle whose substructure is unknown.
Define the concept of an antiparticle.
A particle with the same mass and opposite charge and/or spin to a corresponding particle.
Define the term baryon.
A subatomic particle made up of three quarks.
Define the term meson.
A subatomic particle made up of one quark and one antiquark.
Define the concept of lepton number.
A conserved quantum number representing the difference between the number of leptons and anti-leptons.
Define the concept of baryon number.
A conserved quantum number representing one third of the difference between the number of quarks and anti-quarks.
What are the four gauge bosons and what forces are they responsible for?
The strong nuclear force is mediated by the gluon
The electromagnetic force is mediated by the photon
The weak nuclear force is mediated by the W and Z bosons