Biology Edexcel Topic 9 (Nutrient cycles and decomposers)
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the three types of nutrient cycle
Carbon cycle, water cycle and nitrogen cycle
Why are the nutrient cycles important
Carbon, water and nitrogen are essential to life, and there is a fixed amount of nutrients on Earth which must be constantly recycled
Describe how materials cycle through the living and non-living components of an ecosystem
Organisms take in elements from their surroundings (e.g. soil and air), these elements are converted into complex molecules which becomes biomass, and are transferred along food chains - the elements are then returned to the environment during excretion and decomposition of dead organisms
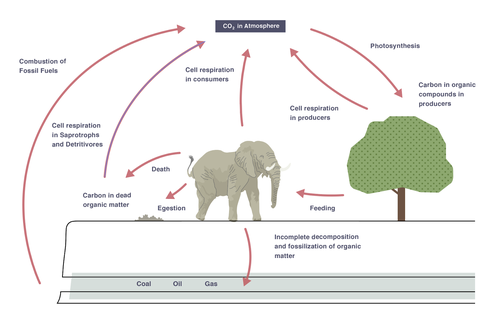
Describe the stages of the carbon cycle
Photosynthesising plants remove CO2 from the atmosphere
Eating passes carbon compounds along a food chain
Respiration in plants and animals returns CO2 to the atmosphere
Organisms die and decompose - decomposers (bacteria and fungi) break down dead material and release CO2 via respiration into the atmosphere
Combustion of materials (e.g. wood, fossil fuels) releases CO2 into the atmosphere
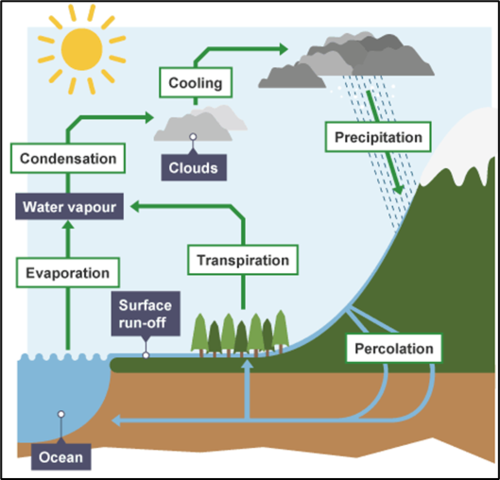
Describe the stages of the water cycle
- Energy from the sun evaporates water from sources such as lakes and oceans - transpiration also releases water vapour
- Water vapour rises, cools and condenses, forming clouds
- Precipitation occurs
- Water is absorbed by the soil and taken up by roots - some is used in photosynthesis or becomes part of the plant, entering the food chain
- Excretion returns water to the soil
- Surface runoff returns to streams, rivers and eventually the sea
What is potable water
Drinking water
How can potable water be prepared
Desalination
What is desalination
A process that removes salts from saline water
Name two methods of desalination
Thermal desalination and reverse osmosis
Describe thermal desalination
Salt water is boiled, evaporating water, which rises then condenses into a pipe, separating pure water from salts
Describe reverse osmosis
Saline water pumped into a vessel containing a partially permeable membrane at high pressure, which forces water molecules to move from an area of low water concentration (high salt concentration) to an area of high water concentration (low salt concentration), which separated pure water from salts
What do plants use to make protein
Nitrates from soil
Why can't nitrogen be used directly by plants to form proteins
Nitrogen is unreactive - it has strong triple bonds between the nitrogen atoms which are hard to break apart so it is hard to get the nitrogen atoms
Name the four types of bacteria involved in the nitrogen cycle
Decomposers, nitrogen fixing bacteria, nitrifying bacteria, and denitrifying bacteria
What is the role of decomposers in the nitrogen cycle
They break down proteins and urea into ammonia, which dissolves in solution, forming ammonium ions
What is the role of nitrogen fixing bacteria in the nitrogen cycle
They convert nitrogen gas into ammonia, which dissolves in solution, forming ammonium ions
Where are nitrogen fixing bacteria found
In the soil and in the root nodules of legumes
What type of relationship is exhibited between nitrogen fixing bacteria and legumes
A mutualistic relationship - the plants receive ammonium ions from the bacteria that they can use to form proteins, and bacteria gain sugars from the plant
What is the role of nitrifying bacteria in the nitrogen cycle
They convert ammonium ions into nitrites and convert nitrites into nitrates
What is the role of denitrifying bacteria in the nitrogen cycle
They convert nitrates into nitrogen gas
Where are denitrifying bacteria commonly found
Waterlogged soil
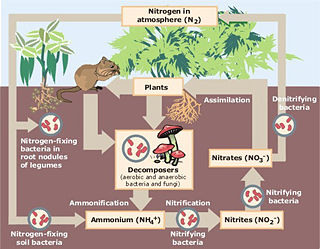
Describe the stages of the nitrogen cycle
- Lightning and nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas to ammonia, which dissolves to form ammonium ions
- Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonium ions to nitrate ions which are taken up by plants and used to build proteins
- Eating passes nitrogen through the food chain
- Organisms die and decompose - decomposers break down proteins and urea to form ammonia which dissolves to form ammonium ions
- Denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates in the soil back to nitrogen gas
How can the amount of nitrates in the soil be increased
Using fertilisers and a crop rotation (replenishes nitrates that may have been depleted by the previous crop by planting a nitrogen fixing crop such as legumes)
What is meant by decomposition
The breakdown of dead materials into simpler organic matter
How do decomposers break down dead matter
Decomposers release enzymes which catalyse the breakdown of dead material into smaller molecules
What factors affect the rate of decomposition
Oxygen availability, temperature and water content
Why is oxygen required for decomposition
Most decomposers require oxygen for aerobic respiration
How does the availability of oxygen affect the rate of decomposition
Oxygen levels increase, rate of decomposition increases
(and vice versa)
Why can decomposition still occur in the absence of oxygen
Some decomposers respire anaerobically (the rate of decomposition is slower as anaerobic respiration produces less energy)
How does temperature affect the rate of decomposition
The optimum temperature of the enzymes that decomposers release is 50^C - lower temperatures, enzymes work too slowly so rate decreases - higher temperatures, enzymes denature so decomposition stops
How does soil water content affect the rate of decomposition
Decomposers require water to survive so in moist conditions, the rate of decomposition is high (but in waterlogged soil, there is little oxygen for respiration so the rate decreases)
What conditions are required to make compost
Conditions that produce a high rate of decomposition (e.g. lots of oxygen, warm, moist, etc.)
Describe the methods of food storage used to slow down the rate of decomposition
Stored in a fridge/freezer to slow the activity of microbes, stored in airtight cans to prevent entry of microorganisms, using high temperatures to sterilise cans, destroying any bacteria, adding salt or sugar to kill the microbes (they lose water by osmosis), and keeping it dry which reduces the ability of microorganisms to survive
What is an indicator species
A species whose presence or absence in an environment provides indication of environmental conditions (e.g. pollution levels)
What indicator species can be used to identify polluted water
Bloodworms/sludgeworms, which are adapted to live in polluted water
What indicator species can be used to identify clean water
Freshwater shrimps and stonefly, which are sensitive to oxygen concentrations so can only survive in clean water
What indicator species can be used to identify clean air
Blackspot fungus found on rose leaves, which is sensitive to sulfur dioxide concentrations so can only survive in clean air
What are lichens used for
To monitor air pollution
How can lichens indicate air pollution
They are sensitive to the concentration of sulphur dioxide, different types of lichens grow in different levels of air pollution (e.g. bushy lichens grow in cleaner air than crusty lichens), and the abundance and distribution of lichens can indicate levels of pollution
Evaluate the use of indicator species as a measure of pollution
It is cheap and simple and can be used to monitor pollution levels over long periods of time, however, it is less accurate than non-living indicators (e.g. electronic meters) and it does not provide a definitive figure for pollution levels in an area