Mod 8 & 9: Lymphatic System and Human Development
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What are lymphatic capillaries?
vessels where interstitial fluid enters the lymphatic system to become lymph fluid. More permeable than blood capillaries. Made of simple squamous endothelial cells. It is interlaced with blood capillaries, arteries, and venules of CVD. They have collegen fibers that anchor them.
What are lymphatic vessels?
where lymphatic capillaries empty into, similar to veins. have overlapping endothelial cells that allow passage of large materials.
what are lymphatic trunks?
where the superficial and deep lymphatics merge to form larger lymphatic vessels called trunks
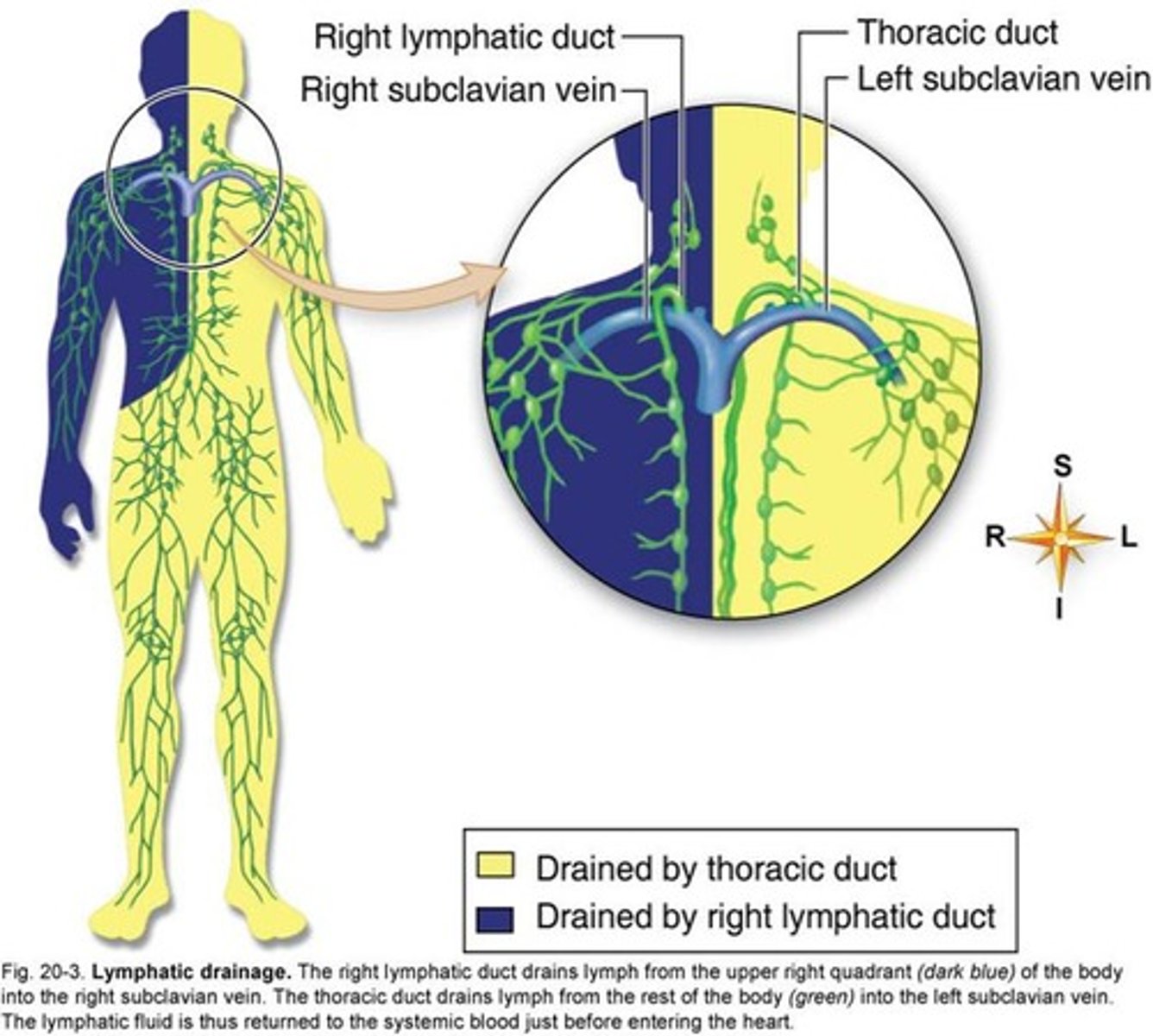
Right lymphatic duct
only the right side of the body, right side of head, thorax, and upper limb
thoracic duct
left side of body and remaining portions of body. both sides of body inferior to diaphram
What are plasma cells?
mature B cells that has differentiated in response to antigen binding and has gained ability to secrete soluble antibodies
What are T cells
do not secrete antibodies but secrete soluble fibers that communicate with other cells or destroy cells infected with intracellular pathogens. They are produced and mature in the THYMUS
Where is the thymus gland located?
between sternum and heart
What is the purpose of lymph nodes?
remove debris and pathogens from the lymph
Rank the ducts, vessels, trunk, and capillaries in smallest to largest diameter
capillaries-vessels-trunks-ducts
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
1. maintain normal blood volume and interstitial fluid composition
2. provide alternative routes for hormones, nutrients, and wastes
3. lymphocyte production, maturation, and distribution
4. pivotal role in bodies immune responses
What is lymph
fluid that is sucked up into lymphatic capillaries
it includes:
-interstitial fluid
-lymphocytes
-macrophages
-cellular debris
what are lymphatic vessels?
pass through lymphatic tissue and organs and clensing along the way
they deliver lymph to venous circulation
What are the primary lymphatic structures?
-thymys (T cells mature here)
-red bone marrow (B cells and T cells produced here, B cells mature here)
*in general, these are the places where lymphocytes are produced and mature
what are the secondary lymphatic structures?
-lymph nodes
-spleen
-lymphoid nodules
-tonsils
-MALT
-appendix
-aggregated nodules (peyer's patches)
They are considered to be part of the "front line" of defense. they are sites where lymphocytes encounter pathogens and mount immune responses
where are the places that need the most defense located in the body?
by the openings of the body, mouth, reproductive tract, liver etc
anatomy of lymphatic capillaries
-close ended tubes interspersed around blood capillary beds and they recieve fluid from interstitial fluid in CT
-highly variable and permeable
-overlapping endothelial cells act as one-way valves. If the capillaries are only getting a little bit of fluid leaving vessels and entering interstitial fluid, then the valves will close up and not allow as much fluid in.
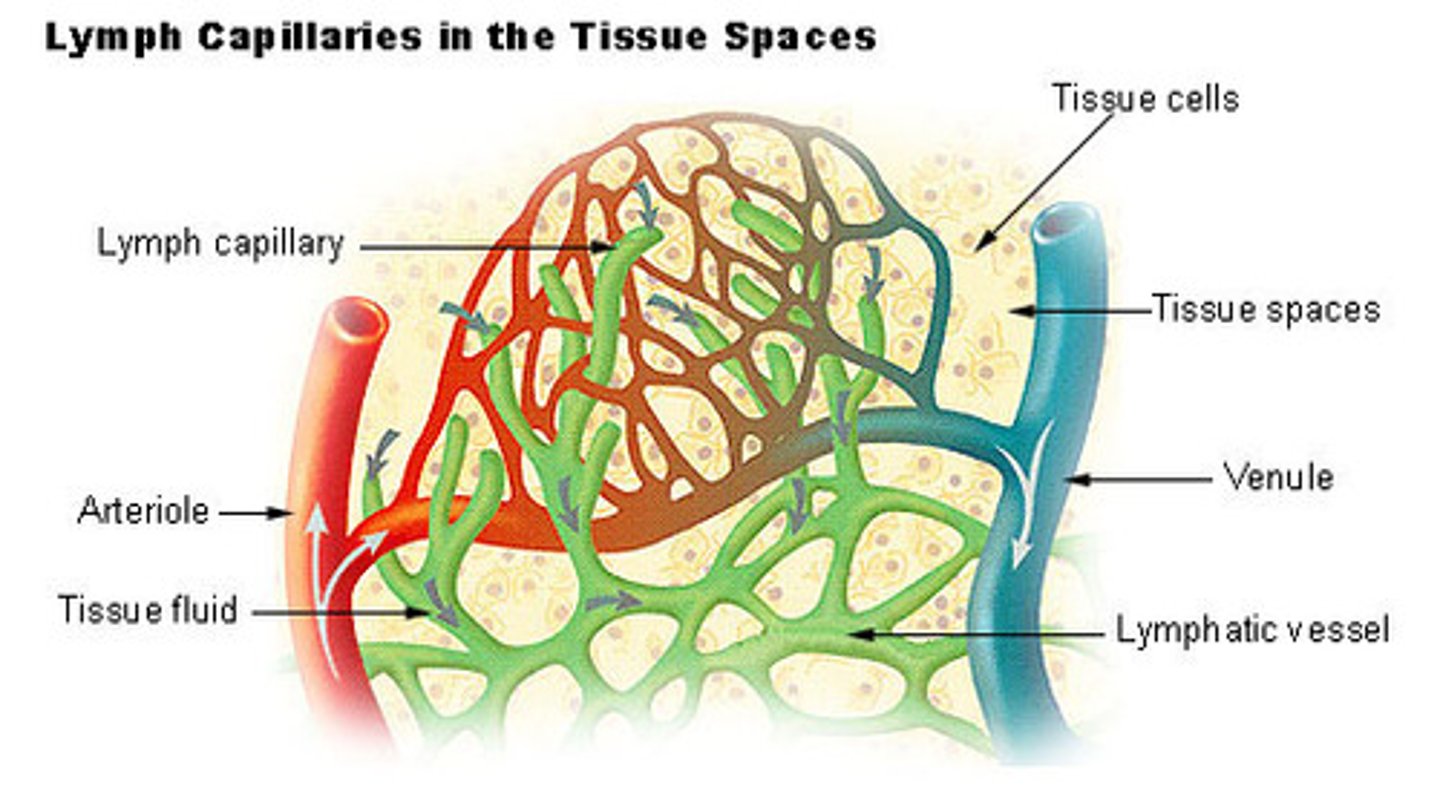
How does lymph move?
1. Lymphatic capillaries are first to recieve lymph. they collect tissue fluid from loose CT tissue and return it to the bloodstream
2. lymphatic vessels (larger than capillaries) collect lymph from lymphatic capillaries and accompany blood vessels
3. lymph trunks collect lymph from lymphatic vessels
4. lymph ducts empty into veins of the neck
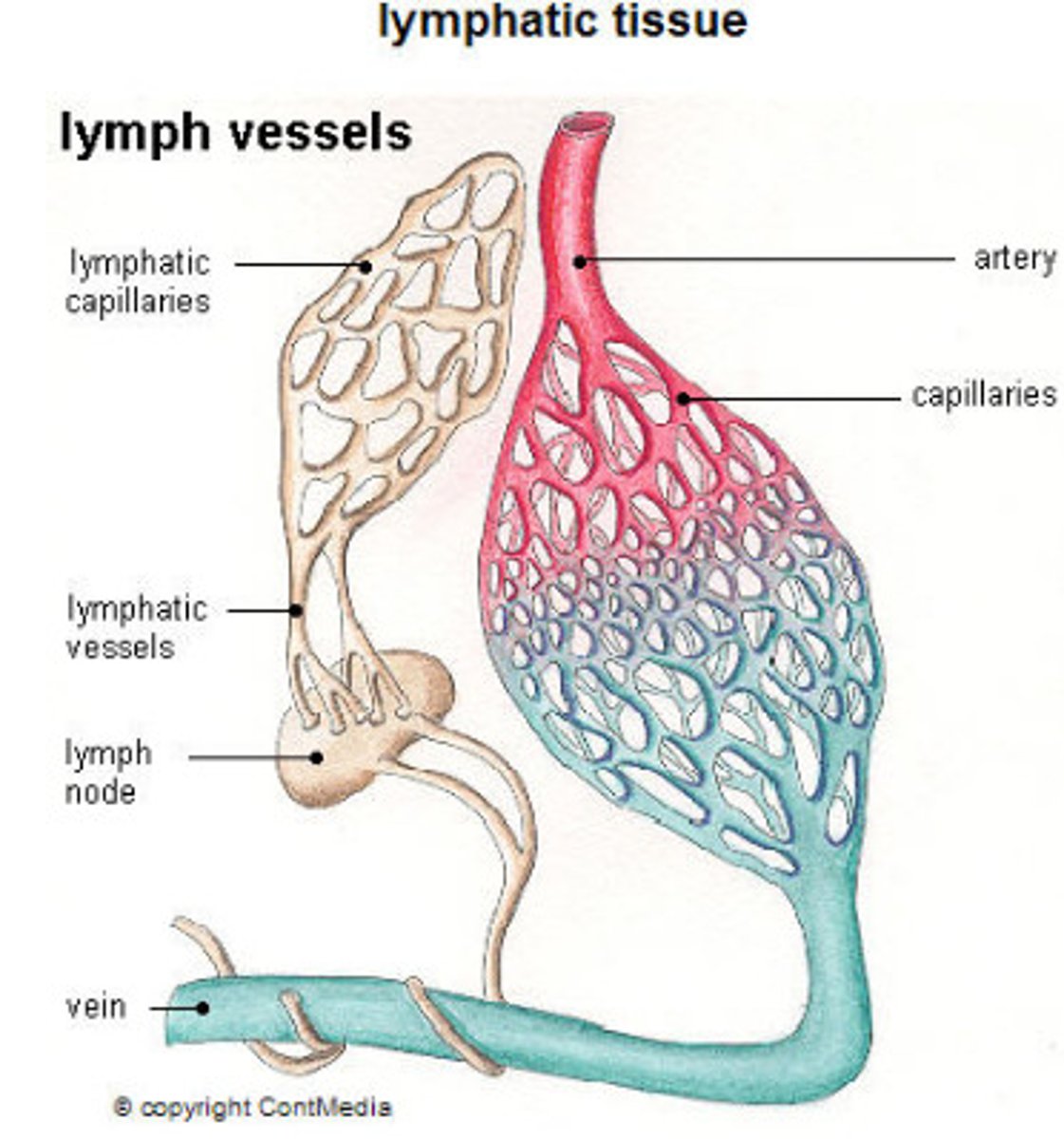
What are the differences between lymphatic capillaries and vascular capillaries?
Lymphatic capillaries: are wider, thinner, more permeable
vascular capillaries: more regular appearance, narrow, thin, and not as permeable as lymphatic capillaries
What are the differences between lymphatic vessels and veins?
lymphatic vessels: all three tunics are difficult to distinguish, widest, thinnest, and contain more valves than veins do because have less pressure than veins do
veins: all three tunics are distinguishable, wide, thinner, contain valves
What is the diameter rankings between arteries veins and lymphatic vessels
lymphatic vessels> veins>arteries
What are the two lymphatic ducts?
Right: deep to right clavicle, returns lymph from right side of head and upper body
thoracic: inferior to diaphram. begins as a saclike structure called the cisterna chyli which is the merging of many trunks and vessels. it collects lymph from most of the body
What are the type of lymphocytes
T cells (thymus-dependent): cell mediated immunity ie kill infected cells
B cells (bone marrow-derived): antibody mediated immunity ie produce antibodies, mature into plasma cells
NK cells(natural killers): viruses and cancer
What are the two types of lymphatic tissue?
Diffuse lymphatic tissue: all over the place. Lymphocytes are loosely aggregated within CT
lymphocyte nodules: lymphocytes aggregated within a supporting framework of reticular fibers. have a germinal center with contains lymphocytes.
what are the types of nodules?
-tonsils which are aggregated lymphoid nodules
-MALT
-within epithelia of GI tract, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems
-aggregates lymphoid nodules (peyers patches)
-appendix which allows recolonization of bacteria to large intestine if needed
What are lymphatic organs?
-seperated from surrounding tissue by a fibrous capsule
-include: lymph nodes, thymyus gland, spleen
What is the function of a lymph node and what are the two different types?
to "cleanse" lymph
afferent: carrying unfiltered lymph into the lymph node
efferent: carrying filtered lymph away from lymph node, exit at hilum
What is the fibroud capsule function
ensures that no pathogens make it out
What is the importance of a thymuys?
functions strictly in T-cell maturation ie knowing self from non-self cells
located just superior to the heart, just deep to sternum
What is the importance of s sleen?
-highly vascularized
-located URL
What makes up the spleen?
red pulp: 80% contains mostly erythrocytes, platelets, macrophages, and some plasma cells
functions in filtration of blood
white pulp: around arterioles of lymphoid tissues, lymphocytes, and macrophages
functions heavily in adaptive immunity
What is lymphedema?
an accumulation of interstitial fluid
-vascular capillaries depositing more fluid than lymphatic capillaries are sucking up
-caused by damage to lymphatic capillaries
Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and metastasis problems
-the anatomy of lymphatic capillaries allows large cells to enter them...including cancer cells
-cancer cells can become lodged within lymph nodes
-important to know lymphatic drainage patterns to check for metastases
Is it possible to live without lymphatic structures?
No, you need the cells and their activation sites
What is the embryonic period?
from fertalization to week 8
what is the fetal period?
from week 9 until birth
what or organogenesis
process of organ formation
what happens in week 2?
little embryonic growth, structures that support the embryo form, beginning of PLACENTA forms
what happens in week 3?
embryo is a 3-layered oval shaped disk and organ formation begins. Nervous system begins to form, FOLIC ACID CRITICAL
What happens in week 4?
morphogenesis which is change in shape occurs in two ways:
-transverse folding when embryo folds laterally and again at either end. creates the future torso
-cephalocaudal folding which is forming a c-shape with head and tail ends that are destinct. head region grows faster than tail region,
-tissues contributing to each organ system exist in their earliest form
-limb formation
what happens in week 1?
fertalization, rapid increase in number of cells
what happens in week 5-8?
-head enlargement
-all major organ systems formed (primordial form)
What counts as preterm birth?
Infants born before 37 weeks
-negative effect likelihood increases the younger they are
what are two of the most serious abnormalities?
lung and brain abnormalities
What are the two types of fractures in youth?
1. Salter-harris fracture of growth plate. This will lead to bone being shorter than intended
2. Midshaft fracture. This will lead to bone being longer than intended because it can cause osteoblasts to go into overdrive
What is the critical period for bone growth?
Before puberty
What is a critical period/problem in the lungs?
-alveoli dont reach peak amount until around age 20
-in people who begin smoking as teenagers, their lungs never fully develop and additional alveoli never form. Increases cancer risk
What were the results of the football brain injury study?
Onset of CTE symptoms were 12 years earlier in those who began playing football before age 12
Does the endocrine system really change with aging?
Not really