3.2 Drugs of Abuse Med Chem
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Su (he only has three questions on the exam)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
leo hollisters criteria for hallucinogens
changes thoughts, mood, and perception
little memory impairment
little stupor (unconsciousness), narcosis (drowsiness), or excessive stimulation
minimal autonomic side effects (dizziness, light leaded, HR issues, GI issues)
non-addicting
classical hallucinogens (meet or do not meet) Hollisters criteria?
meet
classical hallucinogens act on the ____ and produce psychological effects that influence behavior
CNS
classical hallucinogens bind to _____ receptors in the CNS
5HT2
5HT2 receptors regulate
mood, cognition, and perception
what are the two classical hallucinogens structural classes
indole-alkylamine and phenyl-alkylamines
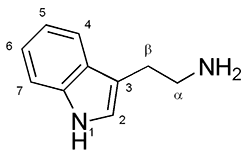
what classical hallucinogen class is this structure?
a. indole -alkylamine
b. phenyl-alkylamine
a
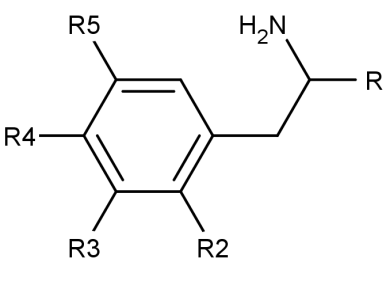
what classical hallucinogen class is this structure?
a. indole -alkylamine
b. phenyl-alkylamine
b
psychomimetic are behaviorally heterogenous, what does that mean?
while they all mimic symptoms of psychosis, they all do so in varying, different, and unpredictable mechanisms
many psychedelics have chemical structures that are very similar to…
neurotransmitters
LSD and LSD like agents share…
common stimulus properties (which means that they produce the same sensations in animals and humans)
almost all Hallucinogens contain a ____ in their structure
N (nitrogen)
what is the purpose of the Nitrogen in hallucinogen structures?
allows for mimicking of 5HT so they can bind to the 5HT2 receptors
all hallucinogens that contain a N are considered to be…
alkaloids
psychedelic compounds have high affinity for _____ receptors
5HT
T/F:
psychedelic compounds only have affinity for 5HT receptors
F (false)
nonclassical hallucinogens are CNS _____
stimulants
nonclassical hallucinogens are _____ stimulants
CNS
PCP is a…
a. classical hallucinogen
b. nonclassical hallucinogen
b
ketamine is a…
a. classical hallucinogen
b. nonclassical hallucinogen
b
behavioral stimulants tend to affect…
motor activity, alertness, and energy
amphetamines are…
a. classical hallucinogens
b. nonclassical hallucinogens
c. behavioral stimulants
d. analeptics
e. not hallucinogens
e
cocaine is a/an…
a. classical hallucinogen
b. nonclassical hallucinogen
c. behavioral stimulant
d. analeptic
e. not an hallucinogen
e
why are amphetamines, THC, and cocaine not hallucinogens?
because they only cause hallucinogenic effects after multiple doses
____% of 5HT is distributed in the CNS and the other ___% is distributed in the GIT
a. 20;80
b. 25;75
d. 10;90
d. 50;50
d
T/F:
Genes can play a roll in abusive/addictive tendencies
T (true)
classical hallucinogen general structure
Ar-C-C-N
classical hallucinogen general structure:
Ar meaning
aromatic ring that is a substituted phenyl, 3-indolyl, or substituted 3-indolyl moiety
classical hallucinogen general structure:
C-C
ethyl or branched ethyl chain
classical hallucinogen general structure:
N
primary, secondary, or tertiary amine
N-alkyl tryptamines have ___ onset of action and ____ duration of action
rapid; short
DMT administration methods
inhalation, smoking, injection
DMT is not active by ____ admin
oral
DMT is a…
indole alkylamine/ N-alkyl tryptamine
what changes to N-alkyl tryptamines confer oral activity?
N-alkyl or N,N-dialkyl substituents are bulky and lipophilic enough
what changes to N-alkyl tryptamines can lead to changes in the potency?
substitution on the benzenoid ring

what two N-alkyltryptamines are found on the skin of frogs
bufotenine and 5-OMe DMT
psilocin is a _____ DMT
4-OH (4 hydroxy)
psilocin has a polar hydroxyl group yet it can cross the BBB, how??
the 4-OH group forms a hydrogen bond with the terminal amine to decrease polarity enough to cross

where can psilocin and psilocybin be found?
mushrooms
what is the phosphate ester of psilocin?
psilocybin
once psilocybin is ingested ,it is rapidly metabolized to…
psilocin
ayahuasca is a _____ hallucinogen
B-carboline and classical
Bcarbolines are indole alkaloids and consist of…
a pyridine ring that is fused to an indole skeleton
examples of B-carbolins
harmine, harmaline, and tetrehydro-harmine
which is more potent, mescaline or LSD?
LSD
LSD induces which three changes in a person?
perceptual, psychic, and somatic
LSD induced perceptual changes
changes in shapes, colors, and heightened sense of hearing
LSD induced psychic changes
changes in mood, depersonalization, visual hallucinations, and altered sense of time
LSD induced somatic changes
nausea, blurred vision and dizziness
phenyl propylamines are made by…
structural modification of mescaline
what structural modification of mescaline leads to the formation of phenyl-propylamines?
adding an alpha-methyl group and deleting or rearranging the position of the methoxy groups
what are the three possible mono-methoxy-phenyl-propyl-amines?
OMA, MMA, and PMA
what does OMA mean?
ortho methoxy analog
what does MMA mean?
meta-methoxy-analog
what does PMA mean?
para methoxy analog
introduction of alpha methyl into mescaline leads to ____ potency
doubled
which of the following is a hallucinogen?
a. OMA of mescaline
b. MMA of mescaline
c. PMA of mescaline
d. none of the above
d
PMA is a _____ CNS stimulant
weak
di-methoxy-amphetamines (DMAs) are substituted derivatives of…
phenylpropylamine amphetamine
Tri-methoxy-amphetamines (TMAs) are substituted derivatives of…
phenylpropylamine amphetamine
which is more potent, TMA or DMA
TMA
where is the potential metabolic site on DMA and TMAs?
para position
how can you block potential metabolism of TMAs and DMAs?
substituting a methyl group at the para group
substituting the para position with a methyl group on TMA and DMA makes…
DOM
DOM has ____ stability than TMA and DMA
higher
DOM is _____ lasting than TMA and DMAs
longer
DOM is more or less potent than mescaline
more
Amphetamine like action:
main effect
central stimulation, increased energy and attention
Amphetamine like action:
neuromechanism
increases release of DA and NE
Amphetamine like action:
behavioral effects
excitement, enhanced locomotion, addictive potential
Amphetamine like action:
examples
amphetamine and metamphetamine
DOM like action:
main effects
hallucinations, perceptual distorsions
DOM like action:
neuromechanism
activates 5HT2A receptors
DOM like action:
behavioral effects
hallucinations, sensory distorsions
DOM like action:
examples
mescaline, DOM, LSD
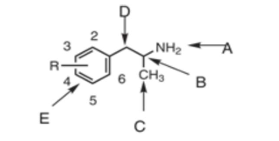
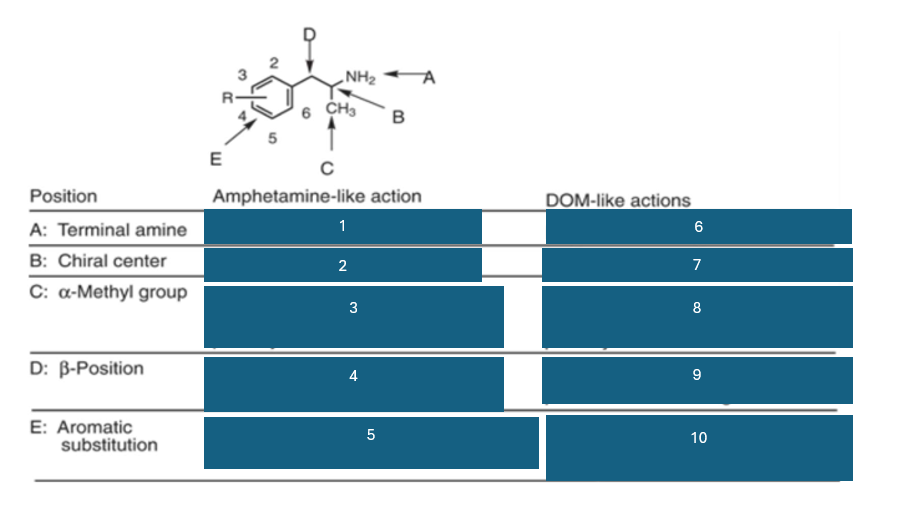
position A is the…
terminal amine
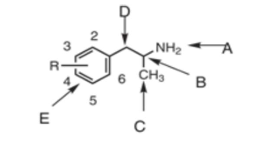
position B is the…
chiral center
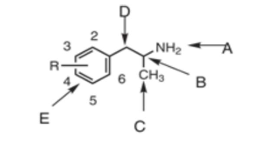
position C is…
the alpha-methyl group
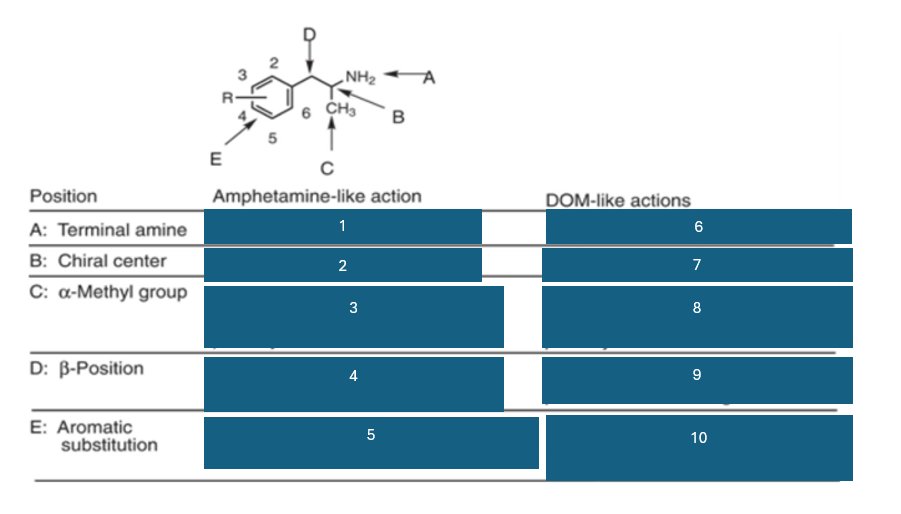
fill in the blank #1
N methyl > NH2 > NHR > NR2
fill in the blank #2
S (+) > (+) > R (-)
fill in the blank #3
homologation decreases potency; replacement by H decreases potency
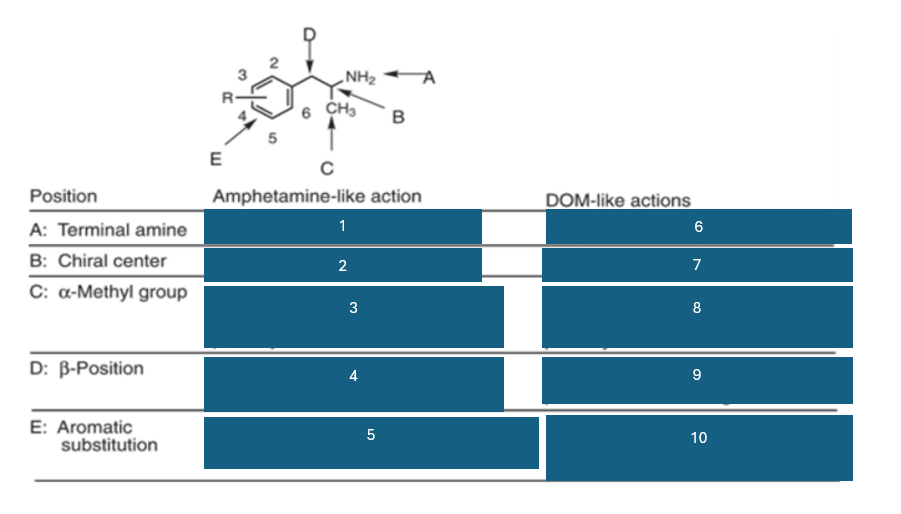
fill in the blank #4
B-OH reduces potency
B=O retains activity and potency
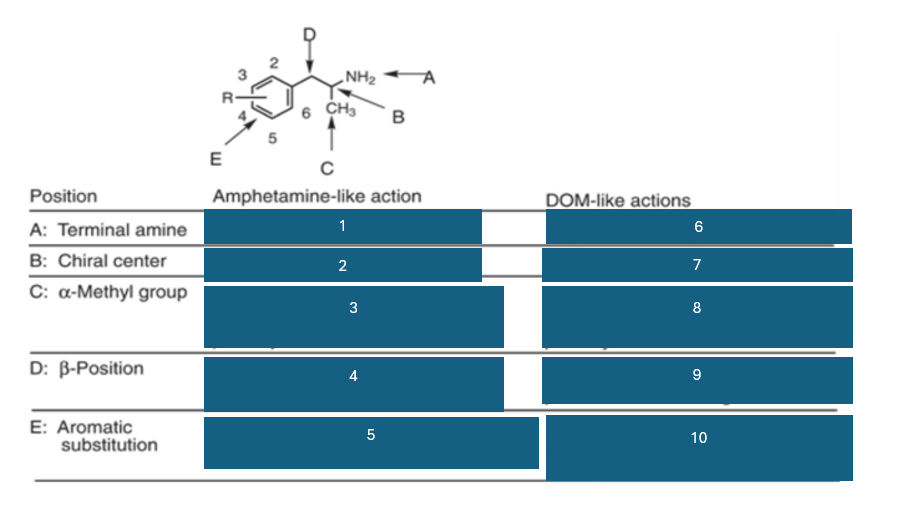
fill in the blank #5
unsubstituted aromatic ring preferred
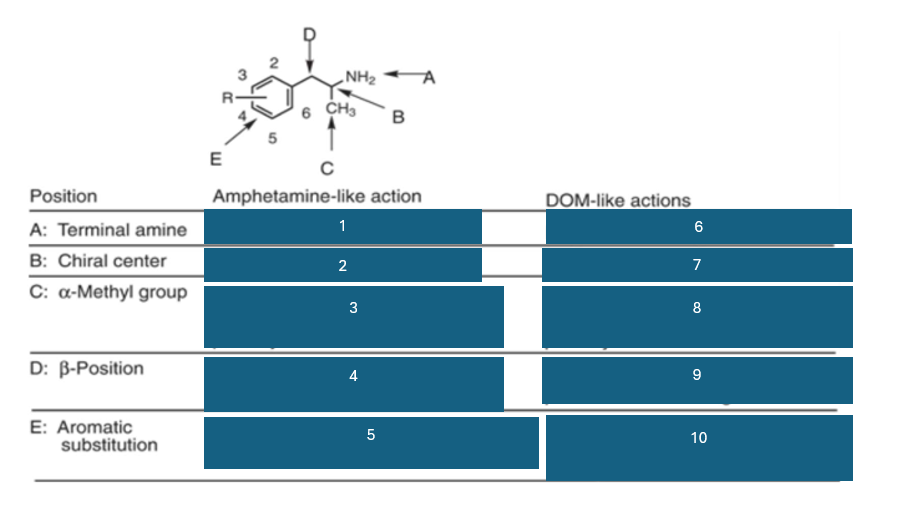
fill in the blank #6
NH2 > NHR > N2
fill in the blank #7
R(-) > (+) > S (+)
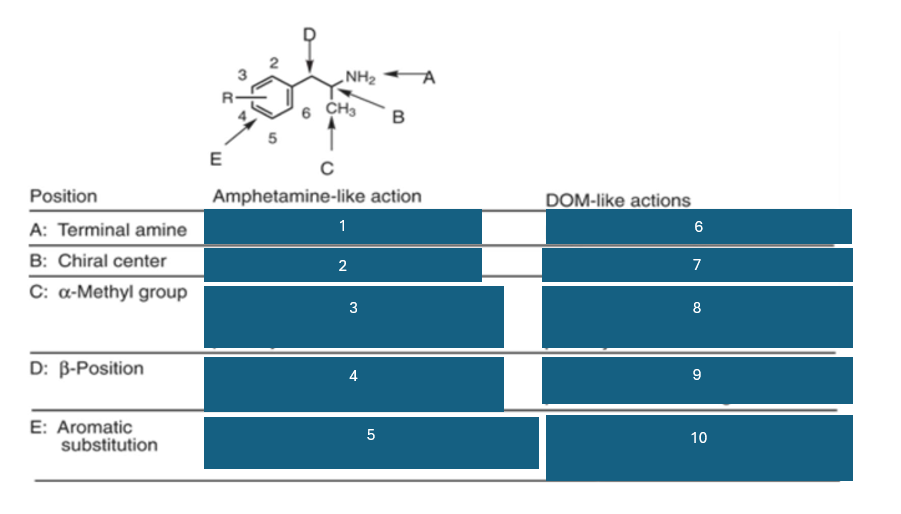
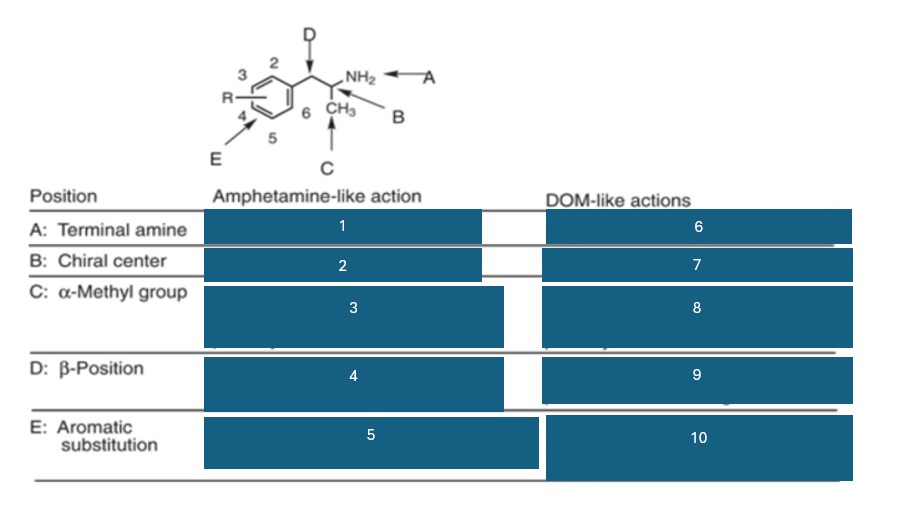
fill in the blank #8
homologation decreases potency, and replacement by H decreases potency
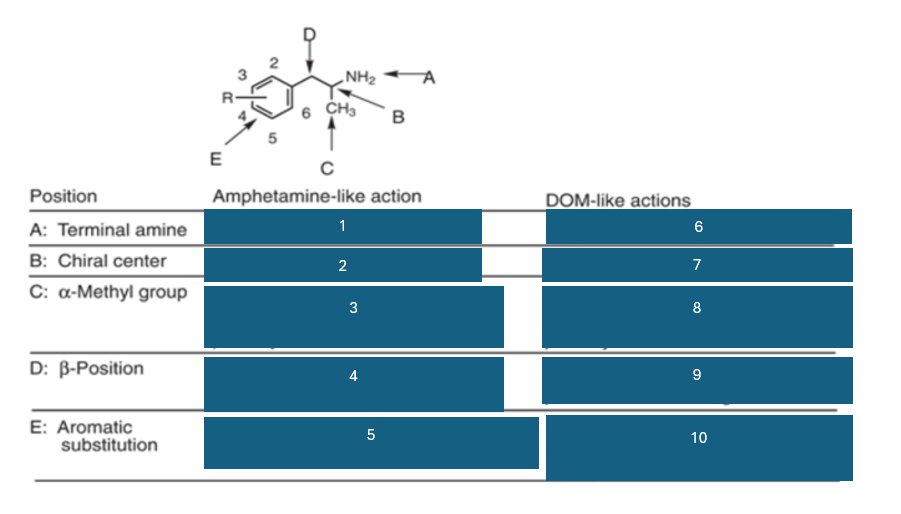
fill in the blank #9
BOH and B=O are not well investigated
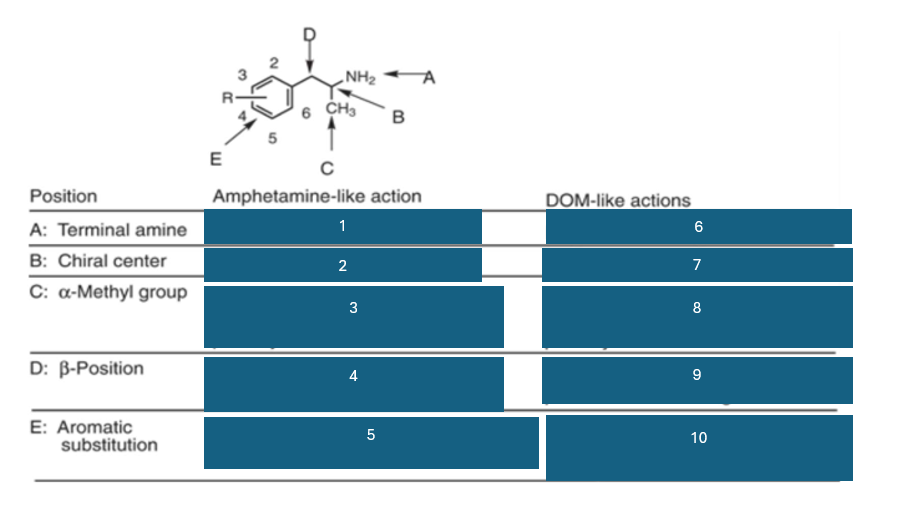
fill in the blank #10
2,5 dimethyl-substitution preferred
4-substitutino further modulates activity
classical hallucinogens bind to 5HT receptors and the affinity to these is correlated with…
DOM stimulus generalization potencies and human hallucinogenic potencies
TMA substitution of C-4 with ____ leads to enhanced activity
halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, SCH3)
TMA substitution of _____ with halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, SCH3) leads to enhanced activity
C-4
TMA substitution of C-4 with halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, SCH3) leads to ____ activity
enhanced
TMA activity increases by insertion of ____ at C-4
ME, ethyl, isopropyl
TMA activity is decreased if ____ is inserted on the C-4
bulky or butyl groups
TMAs lose their activity if ____ groups are used at C-4
COOH and OH
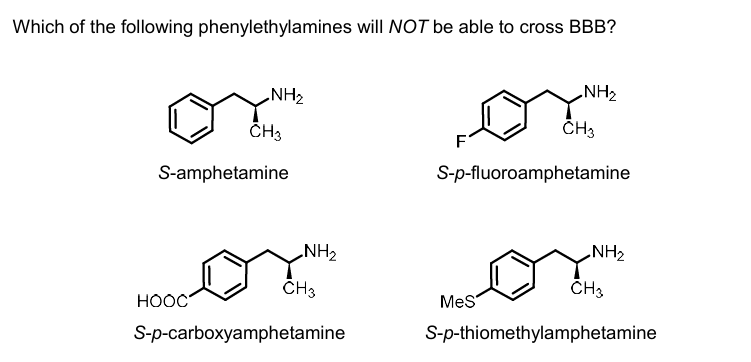
c
incorporation of substituents into the aromatic ring of amphetamines leads to…
reduced or loss of psychostimulant activity
4-OH-amphetamine lacks _____ action and is unlikely to ____
central stimulant; cross the BBB
why is 4-OH- amphetamine unlikely to cross the BBB and lack central stimulant action
presence of polar aromatic hydroxyl group