Comprehensive Human Sensory and Skin Anatomy: Receptors, Layers, and Functions
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
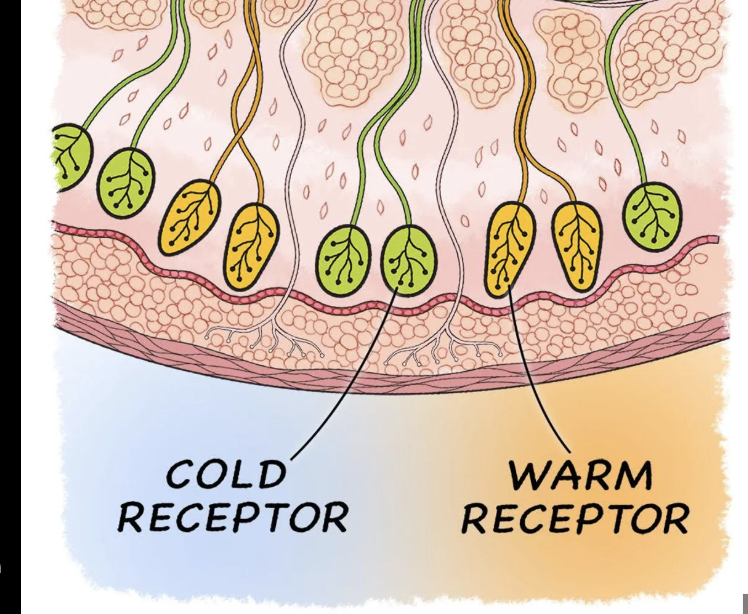
Thermoreceptors
Change in temp-
Heat- 45 degrees c
Cold-27 Celsius
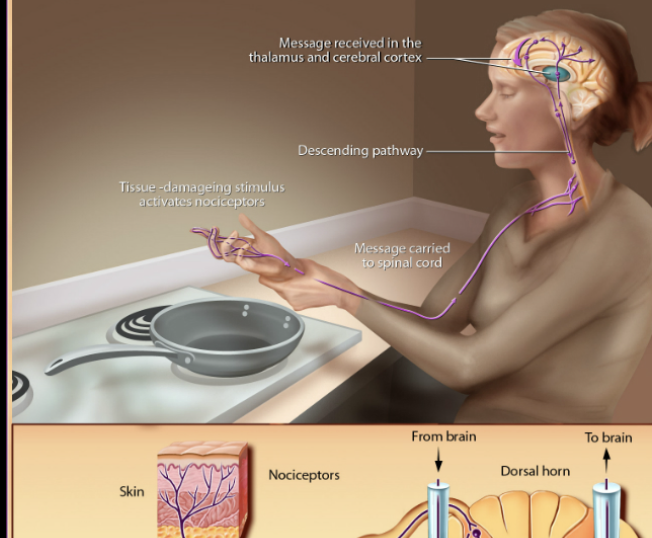
Nociceptors
Detect pain, temp, pressure and chemicals /can vary
Spinal reflex
Allows rapid withdrawal before conscious perception.
Sensation
Detecting the stimulus.
Perception
Interpreting the stimulus. happens when the sensory stimulus is processed and organized into a meaningful pattern. To consciously interpret the stimuli, they have to reach their ultimate destination in the brain (central level).
Transduction
Converts stimulus energy into a nerve signal.
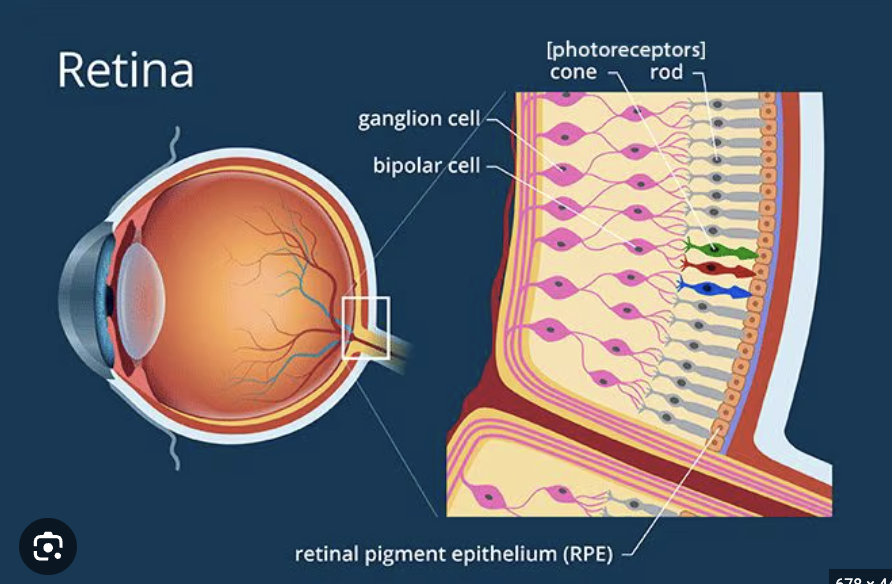
Photoreceptors
Light
Rods and cones in the retina that perform transduction in vision.
Phasic receptors
Adapt rapidly, so sensory input diminishes over time.
does not provide information on the duration of the stimulus
some convey information on rapid changes in stimulus intensity and rate
Ex: smell
Tonic receptors
Maintain activity as long as the stimulus is present.
adapts slowly to a stimulus and continues to produce action potentials over the duration of the stimulus.
it conveys information about the duration of the stimulus.
some are permanently active and indicate a background level
Ex: pain receptors, tactile discs, muscle spindles, joint capsules, and Ruffini corpuscles.
Receptive fields
Small fields with high receptor density
allow for better discrimination of stimuli.
Pacinian corpuscles
Detect deep pressure and vibration.
Meissner corpuscles
Detect light touch.
Muscle spindle
Proprioceptor.
Free nerve ending
Exteroceptor.
Taste bud
Special sense (exteroceptor).
Rods
Photoreceptors.
Mechanoreceptors
Touch/pressure receptors.
Chemoreceptors
Chemical detection receptors.
General senses
Touch, pressure, pain, temperature.
Special senses
Vision, hearing, smell, taste, equilibrium.
Olfactory receptors
Phasic receptors that adapt quickly.
Merkel discs
Detect continuous pressure.
Ruffini corpuscles
Detect skin stretch.
Epidermis
stratified squamous epithelium
Dermis
connective tissue (papillary: areolar, reticular: dense irregular)
Hypodermis
adipose + areolar tissue
Components of the integumentary system
Skin, hair, nails, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, sensory receptors.
Stratum Corneum
The most superficial layer of the epidermis; provides protection and a waterproof surface.
Stratum Lucidum
Found only in thick skin (palms and soles); provides protection and a waterproof surface.
Stratum Granulosum
A protective, water-sealant layer that helps prevent fluid loss.
Stratum Spinosum
A protective, water-sealant layer that contains dendritic cells (macrophages) for immune defense.
Stratum Basale
The deepest layer; forms new keratinocytes, contains Merkel discs (touch receptors), and melanocytes, which produce melanin and transfer it to keratinocytes for UV protection.
Functions lost after epidermis burn
Barrier protection, water retention, pigmentation (melanocytes), tactile discrimination (Merkel cells).
Thin vs Thick skin differences
Thick skin: palms/soles, 5 layers, no hair, more keratin → protection and friction. Thin skin: most of body, 4 layers, hair, sebaceous glands.
Keratinocytes
mechanical barrier
Melanocytes
UV protection
Langerhans
immune defense
Merkel
touch
Extracellular lipids
water barrier
Pale skin after sun exposure
Melanin production low or uneven; hemoglobin level may also influence color.
Dermis functions
Support, flexibility, houses blood vessels, sensory receptors, glands.
Hypodermis functions
Cushioning, insulation, fat storage, thermoregulation.
Structure/function of hair
Hair follicle produces hair shaft, protects, senses light touch, reduces heat loss.
Scalp vs Forearm hair sensitivity
Scalp has more hair follicles with active hair root plexuses; forearm has fewer.
Structure/function of nails
Protect fingertips, enhance sensation, growth from nail matrix.
Sebaceous and sweat glands
Sebaceous → sebum, lubricates hair/skin, absent in thick skin. Eccrine sweat → thermoregulation; Apocrine sweat → scent.
Palms dry but sensitive to touch
Thick skin lacks sebaceous glands but contains many Meissner corpuscles for fine touch.
Patient cannot sweat after exercise
Eccrine sweat glands, affecting thermoregulation.
Hair growth cycle
Anagen (growth), Catagen (regression), Telogen (resting/falling).
Cold pool response
Cold thermoreceptors detect decrease, hypothalamus triggers vasoconstriction & shivering → negative feedback to maintain temperature.
Sweating after running
Warm thermoreceptors detect heat, hypothalamus triggers eccrine sweat glands and vasodilation → cooling.
Older adults feeling colder
Fewer/sensitive thermoreceptors, thinner hypodermis fat layer, slower vasomotor response.
Below the head
carried from the periphery of the body by 31 pairs of mixed nerves, then through tracts within the spinal cord and finally reaching the postcentral gyrus of the brain
From the head
carried by 12 pairs of cranial nerves: some are sensory, some are motor, some are mixed. Special senses reach different parts of the brain.
Any sensory neuron detects stimuli within an area called
Receptive field
Modality
the type of stimulus or the sensation it produces. Vision, hearing, and taste are examples of sensory ___