Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Compound (definition)
A substance that is made up of two or more different elements combined together chemically.
What is the octet rule?
When bonding occurs, atoms tend to reach an electron arrangement with eight electrons in the outermost energy level
Exceptions to the octet rule
Transition Metals. First four elements tend to get two electrons in the outermost energy level. Group 3 elements tend to be satisfied with 6 electrons
Ion (definition)
A charged atom or group of atoms
What is a cation?
Positive ion
What is a anion?
Negative ion
Ionic Bond (definition)
The force of attraction between oppositely charged ions in a compound. Ionic bonds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another
What happens to the charges when two atoms join together in an ionic bond?
Charges cancel each other out
How do you know which element goes first when writing the chemical formulas of ionic compounds?
Positive ion goes first.
What is a complex ion?
An ion made up of two or more different atoms
Formula for Hydroxide ion
OH-
Formula for Nitrate ion
NO3 -
Formula for Hydrogencarbonate ion
HCO3 -
Formula for Permanganate ion
MnO4 -
Formula for Carbonate ion
CO3 2-
Formula for Chromate ion
CrO4 2-
Formula for Sulphate ion
SO4 2-
Formula for Sulphite ion
SO3 2-
Formula for Thiosulphate ion
S2O3 2-
Formula for Phosphate ion
PO4 3-
Formula for Ammonium ion
NH4 +
What are Transition Metals used as?
Catalysts
Why are Transition Metals special (charge)?
They make different ions with different charges. Charge is shown using a Roman Numeral e.g. Mn+7 is Manganese (VII).
Why are Transition Metals special (colour)?
Produce compounds of different colours depending on its charge.
What does covalent bonding involve?
Electrons shared between atoms
Molecule (definition)
A group of atoms joined together. It is the smallest particle of an element or compound that can exist independently.
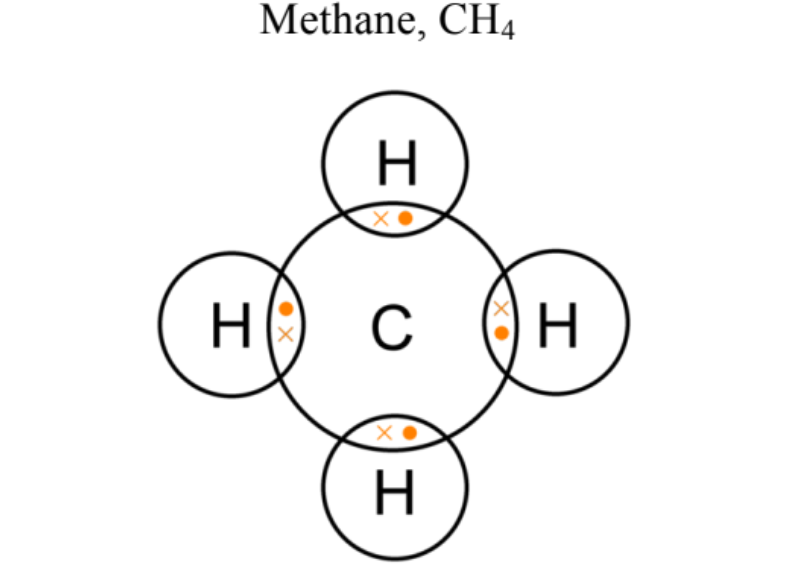
Draw a dot and cross diagram for Methane (CH4)
…
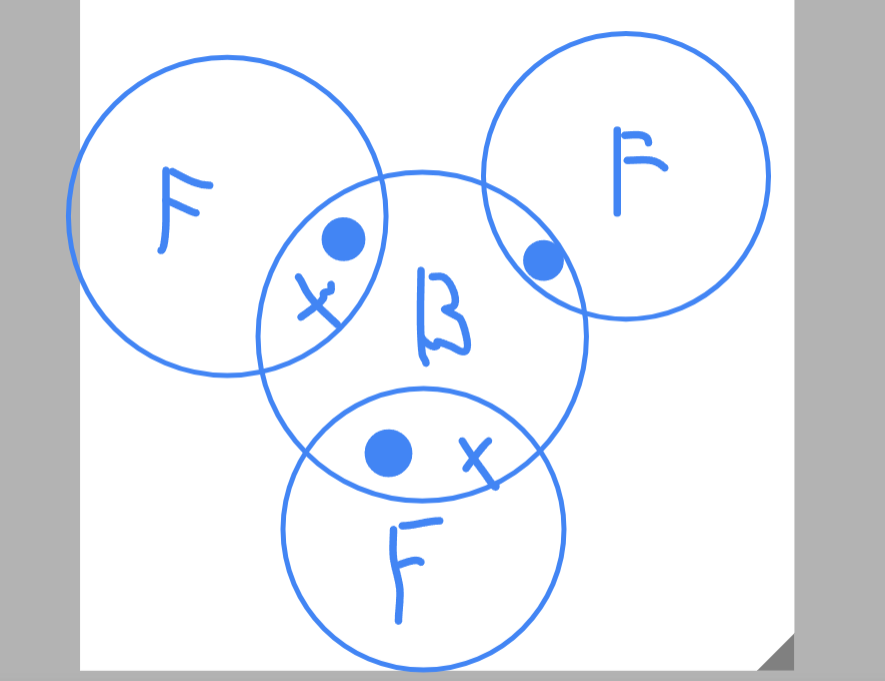
Draw a dot and cross diagram for BF3
…
Valency (definition)
The number of atoms of hydrogen which the element will combine with
Does sigma and pi bonding occur in covalent bonds, ionic bonds, or both?
Only covalent bonds
What does sigma and pi bonding entail?
The overlapping of atomic orbitals
Sigma bond (definition)
Formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals
Features of sigma bonds
Involves all types of orbitals (s, p, d). Forms first, then pi bonds (relevant for double and triple bonds)
Pi bond (definition)
Formed by the sideways overlap of orbitals
Features of pi bonds
Involves p, d orbitals but not s. Only forms after a sigma bond is formed
What does a single bond always consist of?
A sigma bond
What does a double bond always consist of?
One sigma bond + one pi bond
What does a triple bond always consist of?
One sigma bond + two pi bonds
Properties of ionic compounds (5)
Hard + brittle. High melting + boiling points. Solid at room temp. Network of ions in crystals. Conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water
Properties of covalent compounds (5)
Soft. Low melting + boiling points. Liquids/gases/soft solids at room temp. Contain individual molecules. Don’t conduct electricity (insulators)
Why do lone pairs affect the shape of the molecule?
Lone pairs are negative and repel other electrons, affecting the shape
What are the possible shapes if you have three atoms?
Linear. V-shaped
What are the possible shapes if you have four atoms?
Triangular planar. Pyramidal. Tetrahedral
What shape do you have with 2 bond pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Linear
What shape do you have with 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs?
V-shaped
What shape do you have with 3 bond pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Triangular planar
What shape do you have with 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pairs?
Pyramidal
What shape do you have with 4 bond pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Tetrahedral
At what angle are Linear molecules?
180 degrees
At what angle are V-shaped molecules?
104.5 degrees
At what angle are Triangular planar molecules?
120 degrees
At what angle are Pyramidal molecules?
107 degrees
At what angle are Tetrahedral molecules?
109.5 degrees
Electronegativity (definition)
the relative attraction that an atom in a molecule has for the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond.
Why are there two main types of bonds in a covalent bond?
One atom has a greater pull on the electrons in the bond than the other and is the more electronegative atom. Electrons not always shared
What is a non-polar covalent bond?
The atoms in the molecule all share electrons equally
What is a polar covalent bond?
The atoms in the molecule do not share electrons equally. Causes one end to be slightly positive (δ+), the other slightly negative (δ-)
Charges of atoms in a non-polar bond
No charges on atoms in a non-polar bond
Charges of atoms in a polar bond
Partial charges on atoms
If a molecule has polar bonds, does that mean the molecule itself is polar?
No
How to find out if a molecule is polar (centres)?
Find centre of positive charge. Find centre of negative charge.
How to find out if a molecule is polar (conclusions)?
If centres are in the same place, the molecule is non-polar (even if the bonds are polar). If they’re not in the exact same place then it’s polar
How can you prove that water is polar?
By placing a charged plastic rod near a thin stream of water
How can you prove that water is polar (explanation)?
Charge on rod attracts opposite charge on polar water molecules
How to see what type of bonding is occurring in a molecule (Log tables)?
Find electronegativity values in log tables. Subtract two values (ignore the minus if you get a minus number). Compare answer with numbers
Electronegativity bonding type (non-polar covalent)
0 - 0.4
Electronegativity bonding type (polar covalent)
0.4 - 1.7
Electronegativity bonding type (ionic)
Over 1.7
Intramolecular Bonding (definition)
Bonding that takes place within a molecule. It holds the atoms in a molecule together e.g. covalent bonding
Intermolecular Forces (definition)
The forces of attraction that exist between molecules. E.g. Van der Waals forces, dipole dipole forces, hydrogen bonding
Van der Waals forces (definition)
Weak attractive forces between molecules resulting from the formation of temporary dipoles. They are the only forces of attraction between non-polar molecules. Usually gases
What is the weakest intermolecular force?
Van der Waals Forces
Van Der Waals Forces (explanation)
Electrons constantly move around. May be on one side of the molecule, giving it a negative charge on one side and a positive one on the other. This is temporary. May be attracted to the opposite side of another molecule also undergoing this
Does the size of a molecule effect Van der Waals forces? If so how?
Yes, the bigger the molecule the stronger it is due to bigger molecules having more electrons (more likely for this to occur)
Does the Van der Waals forces on a molecule effect its boiling and melting points?
Yes, stronger the Van der Waals forces, the higher the boiling + melting point.
Dipole-Dipole forces (definition)
Forces of attraction between the negative pole of one polar molecule and the positive pole of another polar molecule
What molecules do Dipole-Dipole forces occur between?
Polar covalent molecules (permanent dipole)
Are Dipole-Dipole forces stronger than Van der Waals forces and how does this effect the boiling + melting point?
Stronger than Van der Waals forces. Polar molecules have higher boiling + melting points
Hydrogen bonds (definition)
Particular types of dipole-dipole attractions between molecules in which Hydrogen atoms are bonded to Nitrogen, Fluorine or Oxygen. The Hydrogen atom carries a partial positive charge and is attracted to the electronegative atom (N, O or F) in another molecule
Is Hydrogen bonding weaker, or stronger than the other two?
Strongest form of intermolecular force
How does hydrogen bonding effect boiling point?
Highest boiling points e.g. boiling point of water is 100 degrees
Are the forces of intramolecular bonding weaker or stronger than covalent bonds?
Much much weaker
Rule for trying to make up solutions + explanation
LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE (polar solvent dissolves a polar solute)
The more polar the substance, the more … it will dissolve in water
easily
Which force of intermolecular bonding dissolves in water the easiest?
Hydrogen bonding
Do non-polar compounds dissolve in water?
No
What solvent do non-polar solutes dissolve in and what is it?
Cyclohexane (non-polar solvent)